Cellular Respiration
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Glucose
A simple sugar that is an important source of energy.
Glucose and oxygen
reactants of cellular respiration
Glycolysis
first step in releasing the energy of glucose, in which a molecule of glucose is broken into two molecules of pyruvate + 2 ATP (does not use oxygen)
Krebs cycle
second stage of cellular respiration, in which pyruvate is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of hydrogen-extracting reactions; takes place in the mitochondria
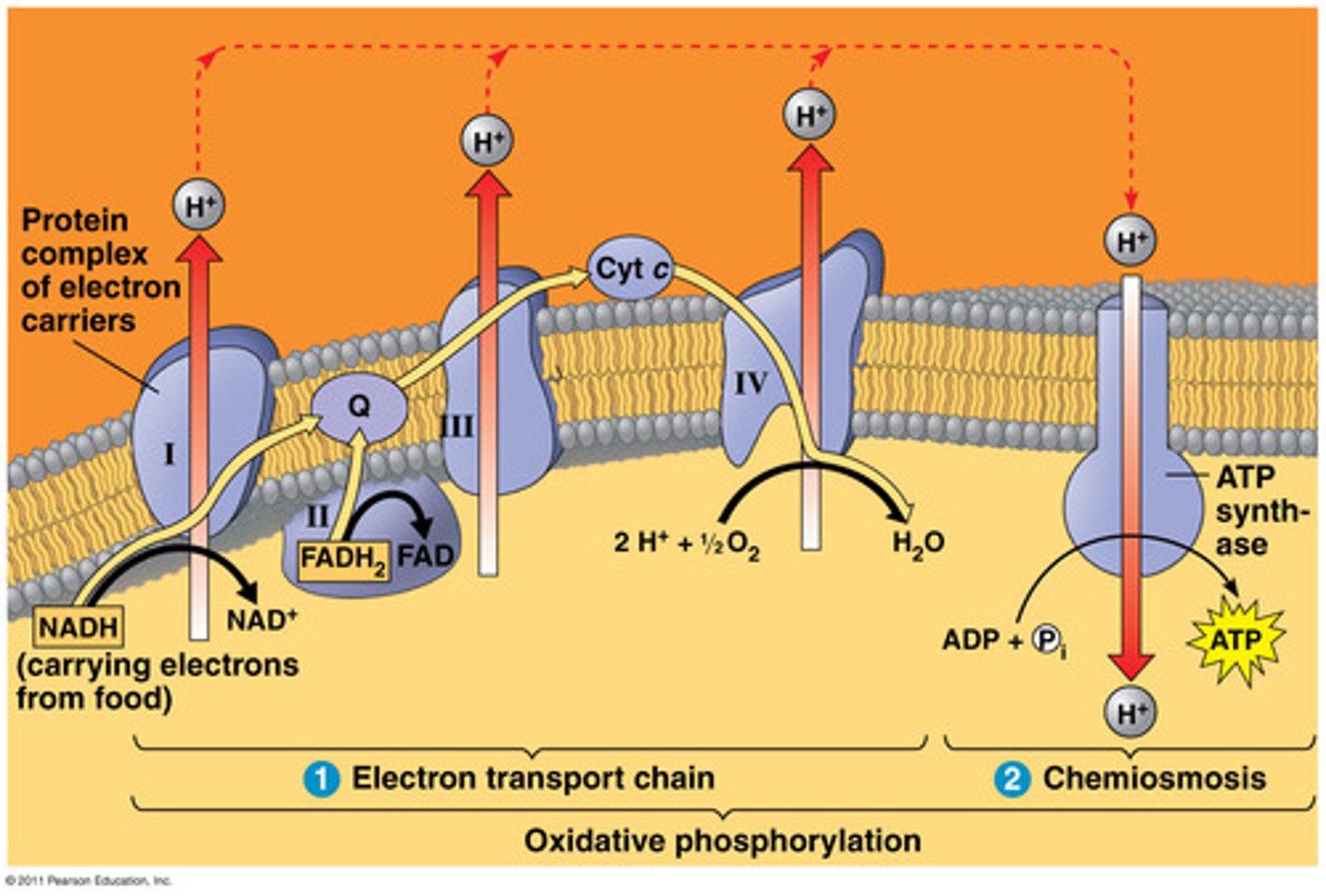
Electron transport chain
The third stage of cellular respiration hydrogens that were harvested during the Krebs/Citric acid cycle are moved through proteins creating the energy used to convert ADP into ATP.

ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
The main energy source that cells use for most of their work
Cellular respiration
The process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen forming ATP
Breathing out
Removes the Carbon Dioxide produced through cellular respiration
Cellular respiration equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 + ADP + P---> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
Carbon dioxide and water
products of cellular respiration
Mitochondria
site of aerobic cellular respiration
Aerobic
requires oxygen
Anaerobic
Process that does not require oxygen
Fermentation
A process that makes a limited amount of ATP from glucose without oxygen.
alcohol fermentation
The conversion of pyruvate to carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol by yeast cells
lactic acid fermentation
The conversion of pyruvate to lactate with no release of carbon dioxide by muscle cells.
why oxygen is needed in aerobic respiration
accepts electrons to form water to keep the electron transport system going.