Introduction & Physical Examination
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Purpose of Medical Record
Basis for patient care
Referrals
Legal evidence of care of the patient
Major categories of disease
Degenerative
Anomaly
Metabolic
Neoplastic & Nutritional
Inflammatory, Infectious, and Immune-mediated
Trauma and Toxicity
Vascular
POMR means
Problem-Oriented Medical Record
POMR provides?
Clear problem identification
Basic components of POMR / Weed System
Data base
Problem identification
Plan formulation
Progress notes
Data base includes
Chief complaint
Patient profile
History
Review of old records
Physical examination
Laboratory data
Plan formulation includes
Diagnostic section
Therapeutic section
Client education
Progress notes include
Subjective data
Objective data
Assesment of problem
Plans
The first component of database
History
Second and most important component of database
Physical examination
Second step in clinical problem solving
Problem identification
Problems are numbered consecutively and dated chronologically on separate form called:
MPL or Master Problem List
Master Problem List includes:
Symptoms
Sign
Physiologic Abnormality
Physical Finding
Abnormal Laboratory Test
Diagnosis
After the problems are identified and listed on the MPL, the next step is:
Plan Formulation
Plan Formulation purpose:
Dictates the medical action for the first 24-48 hours
3 components of plan formulation
Diagnostic section
Therapeutic section
Client education section
It is intended to resolve or help. This provides a method to audit the logic of treatment.
Therapeutic section
Describes the information given to clients about their animal’s problems , diagnostic tests, cost, and prognosis
Client education section
4 types of DDB
Minimum
Maximum
Comprehensive
Problem-specific
These are free nerve endings especially abundant in the skin, cornea, anus, periosteum, joint capsule, muscles, tendons and meninges
Nociceptors
3 types of nociceptors characterized by responsiveness
Extreme heat
Excessive mechanical stress
Chemicals
Serotonin
Bradykinin
Histamine
Prostaglandins
Leukotrienes
Proteolytic enzymes
Classification of Pain
Acute of Physiologic Pain
Chronic or Clinical Pain
Musculoskeletal Pain
Visceral Pain
Neurologic Pain
Ischemic Pain
Referred Pain
Results stem from minimal tissue damage that triggers high-threshold sensory nerve fibers. Pain is typically well-localized, short-lived and stimulates reflexive responses
Acute or Physiologic pain
Results from intense or prolonged stimuli from tissue damage, extended discomfort, and abnormal sensitivity. It induces physiologic, metabolic, and immunologic alterations that promote illness and death.
Chronic or Clinical Pain
Joint surfaces and periosteum contain abundant nociceptors, and focal stimulation may cause intense pain or a waxing and waning pain.
Musculoskeletal Pain
Primary consequence of Musculoskeletal Pain
Lameness
This contains a lower density of nociceptors and more widespread tissue involvement is necessary to elicit pain.
Stimuli include ischemia, distention of hollow viscus, chemical damage to visceral surfaces, spasm of smooth muscle, and stretching of ligaments.
Visceral pain
The only nervous structure that has abundant nociceptors
Meninges
Pain that is manifested in a site considerable distance from the primary lesion is called referred pain.
Referred pain
Common cause of pain in spinal column (cervical and back pain)
Intervertebral disk disease
Diskospondylitis
Fractures /luxations
Meningitis
Caudal cervical spondylomyelopathy
Lumbosacral stenosis
Common cause of muscle pain
Polymyositis
Ischemic myoneuropathy
Exertional rhabdomyolysis
Common cause of Joint/long bones pain
Arthritis
Fractures
Osteomyelitis
Neoplasia
Common cause of pain in abdominal cavity
Acute Pancreatitis
Pyelonephritis
Renal and ureteral calculi
Gallbladder disease
Peritonitis
Torsion/volvulus (spleen, stomach, and intestine)
Common cause of pain in thoracic cavity
Pleuritis
Pericarditis
Common cause of referred pain to the abdomen
Disk disease
Meningitis
Diskospondylitis
Common cause of referred pain to the back
Abdominal cavity diseases
Common cause of perianal pain
Fractured tail
Perianal fistulas
Rectal strictures/foreign bodies
Anal sac abscess/impaction
Rectal trauma
Two essential components of practicing medicine
History
Physical examination
It is frequently key in determining the cause of an illness, its significance, treatmen options and even prognosis.
History
It is the second and most important component of the database.
Physical examination
Two types of physical examination
Routine physical exam
Emergency physical exam
Elements of history
Obtaining facts
Diet and appetite
Drinking, urination, and defecation patterns
Geographic history
Describe home environment
Chronology of the sequence of events
Initial abnormal signs and their progression
Changes in body weight
Vaccinations and medications
Animals present condition
A good physical examinations can:
Detect minor abnormalities before they become serious problems
Identify major organ dysfunction without extensive and expensive medical tests
How to do physical examinations
Gain trust
Restraints
Away from the animal or back off
Thorough and consistent
Experiences help
Record
Physical examination process
Inspection
Palpation
Percussion
Auscultation
Inspection of the animal should involve observation of the following:
General appearance
Body condition / state of nutrition
Mentation / level of consciousness
Posture and gait
Hydration status
In inspecting general appearance, it is important to note:
Symmetry, note any asymmetry and difference in size or shape or extremities
What to observe in inspecting posture and gait
Limping, incoordination or unsteadiness and abnormal limb placement
How is hydration status reported
Adequate, marginal, or inadequate
First sign of dehydration
Loss of skin elasticity (skin turgor)
Skin may tent more in certain breeds, what are these?
Sharpei and Basset Hounds
It is the application of the fingers with light pressure to the surface of the body for the purpose of determining the condition of the parts beneath.
Palpation
Locations of Lymph Nodes
Submandibular
Prescapular
Axillary
Inguinal
Popliteal
Abdominal palpation is divided into three, what are these:
Cranial abdomen
Mid abdomen
Caudal abdomen
Organs present upon cranial abdominal palpation
Stomach
Liver
Spleen
Area of pancreas
Small intestines
Organs present upon mid abdominal palpation
Spleen
Kidneys
Small intestines
Kidneys is usually not palpable in what animal?
K9
Upon palpation, what shape is the bladder on dogs?
Pear-shaped
Upon palpation, what shape is the bladder on cats?
Spherical
What is the purpose of tapping fingers or hands quickly and sharply against parts of the animal’s body?
Locate organ borders
Identify organ shape and position
Determine if an organ is solid or filled with fluid or gas
Two types of percussion
Direct or immediate percussion
Indirect or mediate percussion
It is the striking of the part under examination directly with the finger or a plexor, without the intervention of another finger or pleximeter.
Direct percussion
It is a percussion performed by using the fingers of one hand as a plexor and those of the opposite hand as a pleximeter
Indirect percussion
Drum-like sounds heard over air filled structures during the abdominal examination
Tympanitic
It is said to sound similar to percussion of puffed up cheeks
Hyperresonant (pneumothorax)
The sound produced by percussing a normal chest
Normal resonance / resonant
Lower than normal percussion sounds
Impaired resonance
Similar to percussion of a mass such as a liver
Dull
Involves listening for various lung, heart, and bowel sounds with a stethoscope
Auscultation
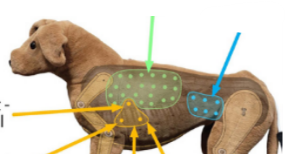
What is usually heard in the yellow triangle (left side)
Mitral
Atrial
Pulmonic
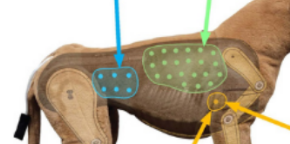
What is usually heard in the yellow circle (right side)
Tricuspid
In respiratory auscultation, listen for noisy breathing at mouth and nares without stethoscope, then auscultate at least four different areas of the chest, including?
Right and left ventral, right and left dorsal lung fields
musical sounds-low or high pitched
Rhonchi
Continuous high pitched hissing heard more often on expiration occur with small airway diseases such as asthma
Wheezes
This may indicate pleural space disease (pleural effusion) or space - occupying lesions
Absence of breathe sounds
This lung sound may indicate pneumonia, or consolidation
Dull lung sound
May be heard when fluid in the lungs
Rales / crackles
Where do you auscultate when you want to listen to the mitral valve
Left 4th-6th (PMI) intercostal space just above the sternal border
Where do you auscultate when you want to listen to the pulmonic valve
Left 2nd-4th intercostal space above sternal border
Where do you auscultate when you want to listen to the aortic valve
Left 3rd-5th intercostal space at mid thorax
Where do you auscultate when you want to listen to the tricuspid valve
Right 3rd-5th intercostal space at mid thorax
S1 should be:
Loud, long, low pitch
S1 indicates
Closure of the atrioventricular valves
S2 indicates
Closure of the semilunar valves
Three or four sounds instead of two
Arrhythmia
Slight increase in heart rate during inspiration and decrease with expiration. More common in the dog than in the car
Sinus arrhythmia
Prolonged series of audible vibrations during normally silent part of cardiac cycle. Often heard as a soft, swooshing sound.
Murmur
This heart sound may be a result of fluid in the chest – if having difficulty hearing the heartbeat do not assume it is just you – it never hurts to get a second opinion
Muffled heart sounds
Examples of arrhythmia
Sinus arrhythmia
Atrial fibrillation
Heart block
Premature ventricular contractions
Gallop rhythm
Part of stethoscope that is best for higher pitched sounds, like- breath sounds and normal heart sounds
Diaphragm
Part of stethoscope that is best for detecting lower pitch sounds, like some heart murmurs, and some bowel sounds. used for the detection of bruits, and for heart sounds
Bell