In vivo gene cloning
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is in vivo cloning?
transferring the fragments to a host cell using a vector
How are restriction endonuclease used to combine DNA?
restriction endonuclease cut the DNA at recognition site in a staggered fashion - cut ends are left with a single strand that is a few nucleotides long
the SAME restriction endonuclease is used to cut plasmid - will have complementary stick ends
complementary bases of sticky ends align and DNA ligase joins sticky ends
What is the promoter region?
DNA sequence needed for transcription factors and RNA polymerase to bind to
What is the terminator region?
DNA sequence that releases RNA polymerase to stop transcription at the appropriate place
The promoter and terminator region must be what?
added to the DNA fragment before insertion
How do you insert a gene into a plasmid vector?
same restriction endonuclease sued to CUT OUT gene and cut plasmid
leaves sticks ends
DNA fragment and open plasmid are mixed together with DNA ligase
DNA ligase joins the DNA and plasmid
How is the recombinant plasmid transferred into the host bacterial cell (transformation)?
plasmids and bacterial cells are mixed in a medium containing calcium ions
calcium ions and temperature change make the bacterial membrane permeable - plasmids pass through the cell-surface membrane into cytoplasm
Why will not all the bacterial cells possess the DNA fragments with the desired gene?
only a few bacterial cells (1%) take up the plasmids
some plasmids will close up without incorporating the DNA fragment
sometimes the DNA fragments ends join together
How do you figure out which bacterial cells have taken yp the plasmids?
all bacterial cells are grown on a medium that contains ampicillin
bacterial cells that have taken up the plasmids have the gene for ampicillin resitsance
these will survive and those that didn’t take up the plasmids will die
How do the plasmids have antibiotic resistance?
plasmids with antibiotic resistance for 2 different antibiotics are selected and then combine with the DNA fragments
1 of these genes is then cut to insert DNA fragment (tetracycline)
What does a diagram look like that summarises the use of antibiotic resistance?
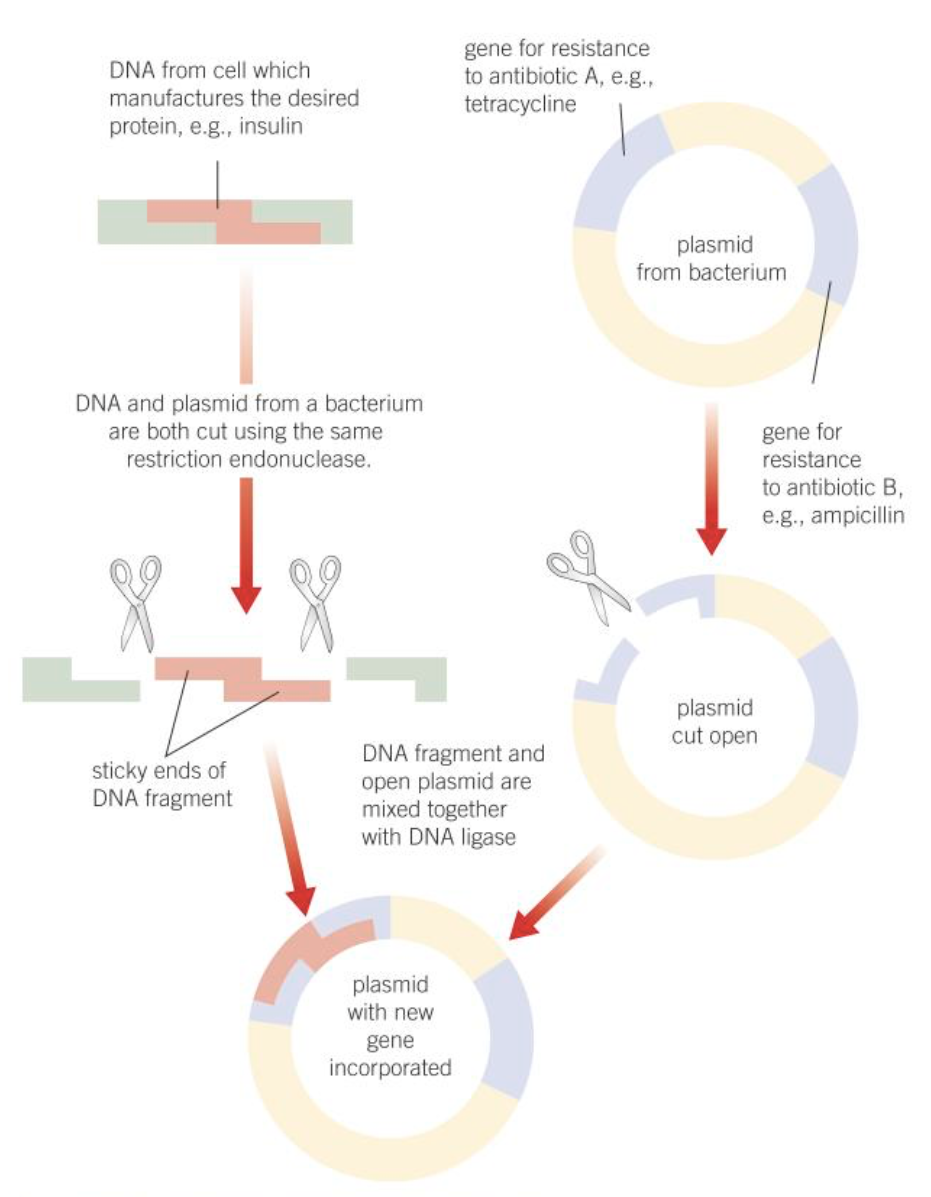
What are the 3 types of marker genes commonly used?
antibiotic resistance
fluorescence
enzyme
How do you identify those will plasmids that have taken up the new gene using antibiotic resistance?
use replica plating
uses the antibiotic of the antibiotic resistance gene that was cut in order to incorporate the right gene (tetracycline)
when tetracycline is added, the plasmids containing the desired gene will not be resistant and so the bacteria will die
compare plate to identify the corresponding bacteria
How are fluorescent markers used to identify if the desired gene is present?
a gene that produces a green fluorescent protein (GFP) is transferred into the plasmid
desired gene is inserted into GFP
any bacterial cell that has taken up the plasmid with the gene will not because to produce GFP and won’t fluoresce
How are enzyme markers used to determine if the desired gene has been taken up?
desired gene is inserted into the gene that makes lactase
lactase turns a particular colourless substrate blue
if the plasmid with the required gene is present, the colonies will not produce lactase - colour doesn’t change