LZHS H Bio I Topic 8 Inheritance of Traits
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

22 Terms
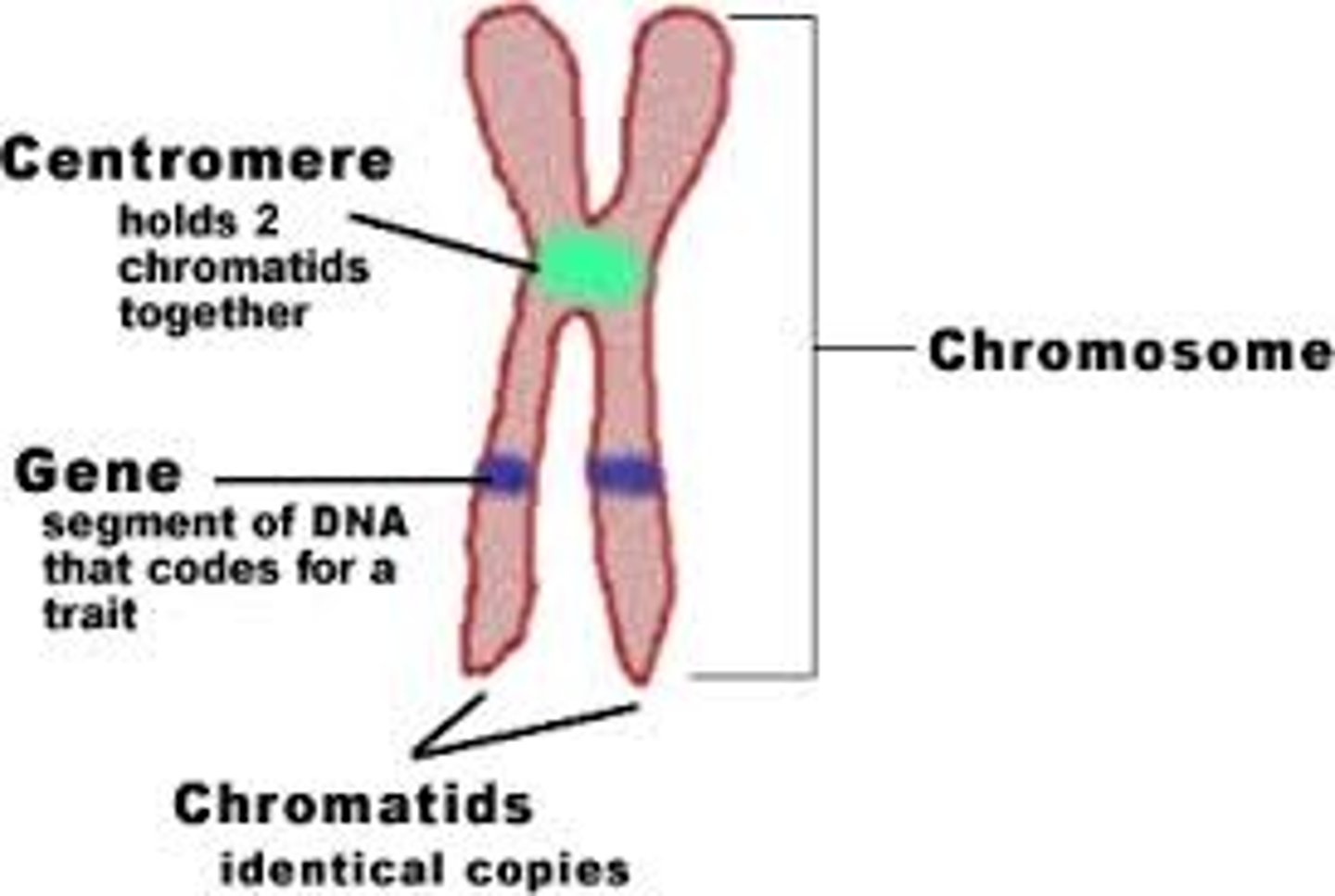
Chromosome
A threadlike, gene-carrying structure found in the nucleus. Each chromosome consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins.
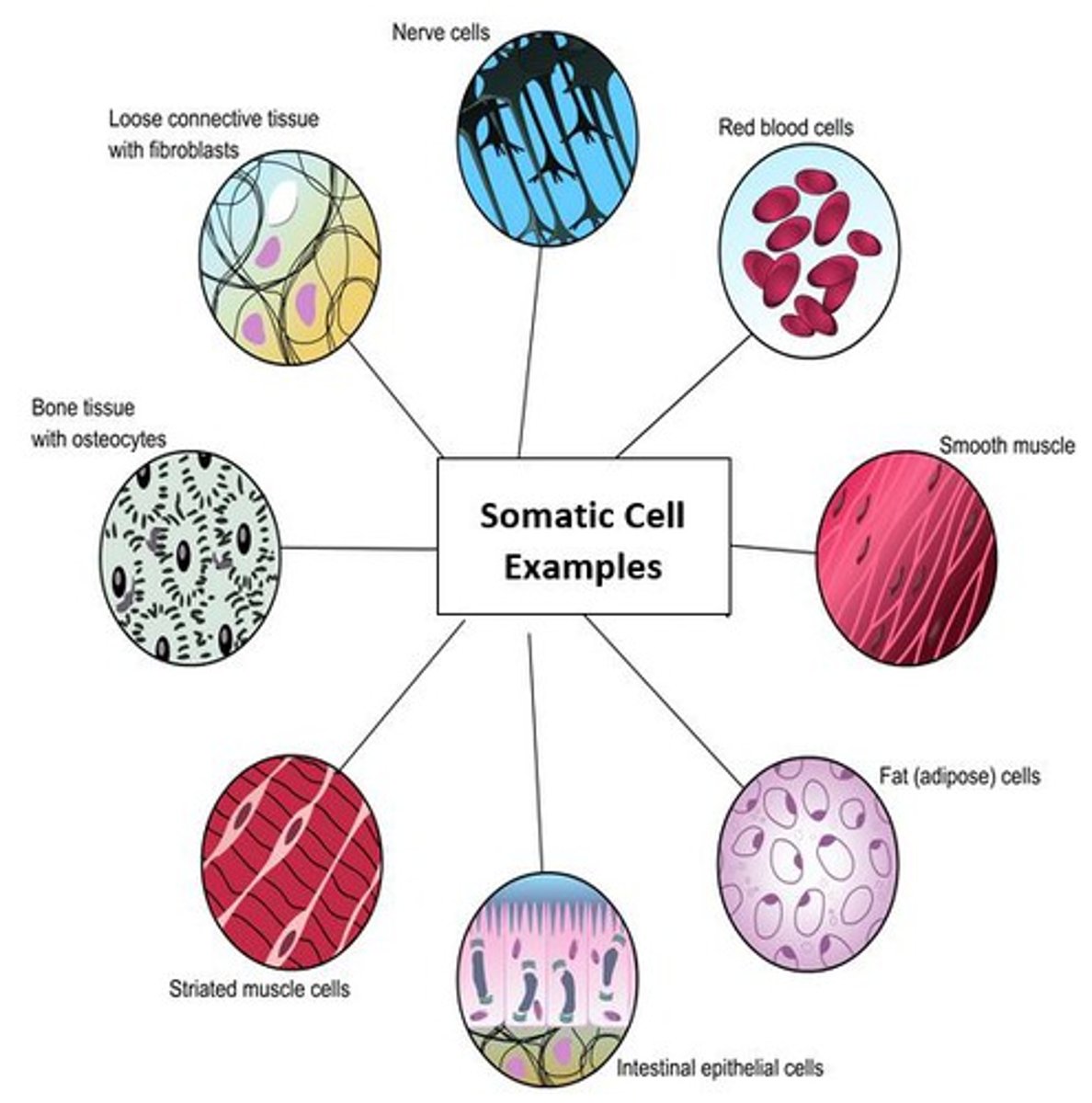
Somatic Cells
any cell of a living organism other than the reproductive cells, diploid (2n)
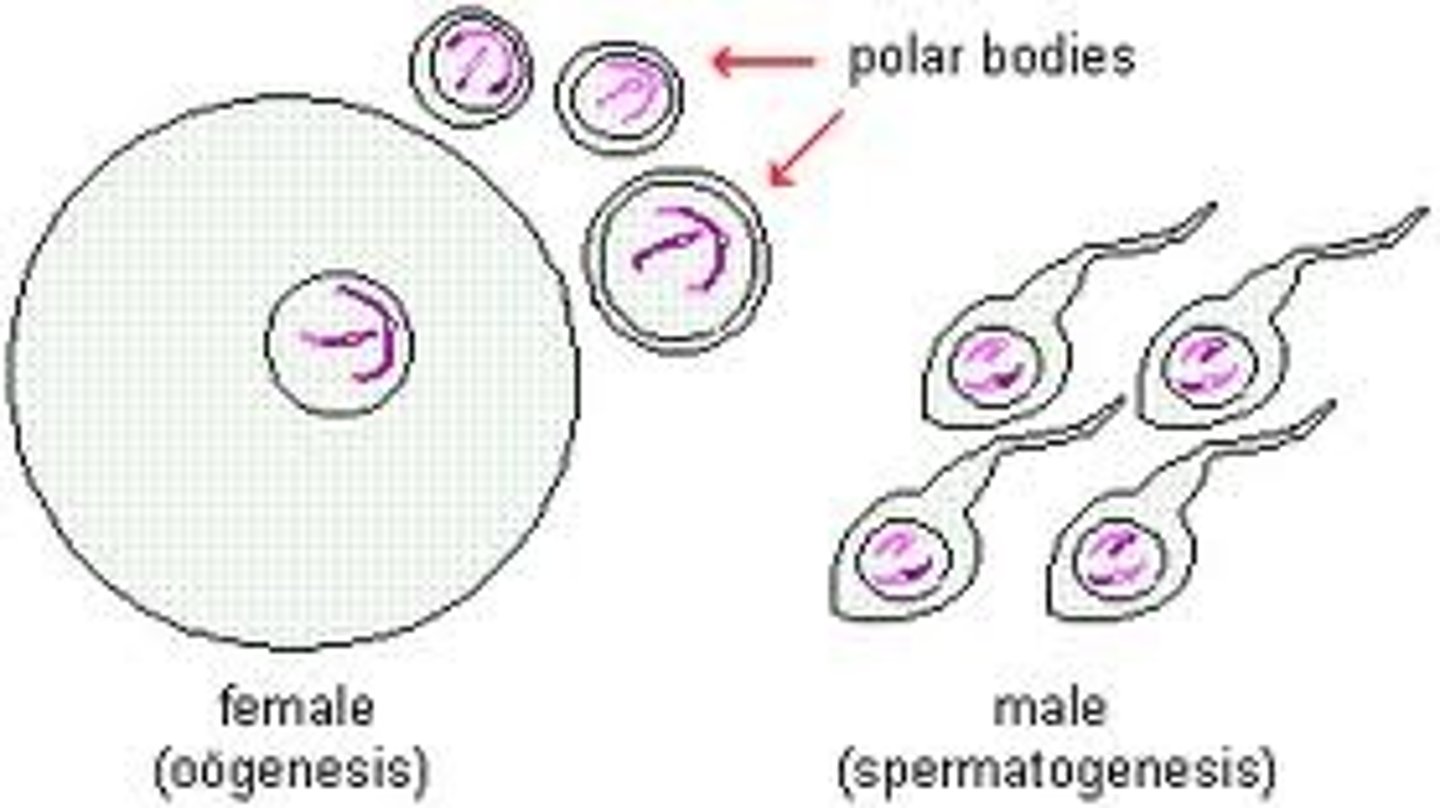
Gametes
a mature haploid (n) male or female germ cell that is able to unite with another of the opposite sex in sexual reproduction to form a zygote.
Independent Assortment
the random distribution of the pairs of genes on different chromosomes to the gametes
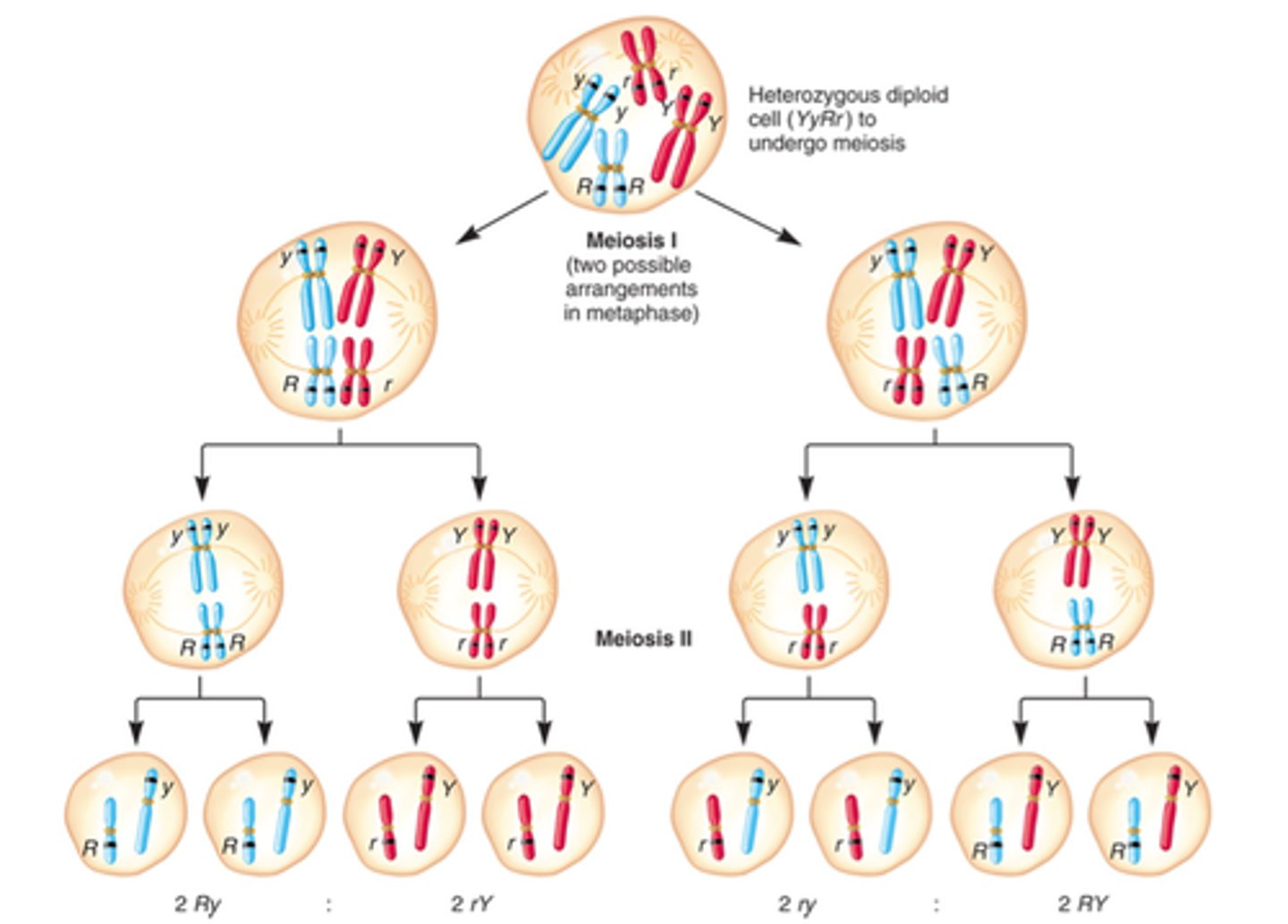
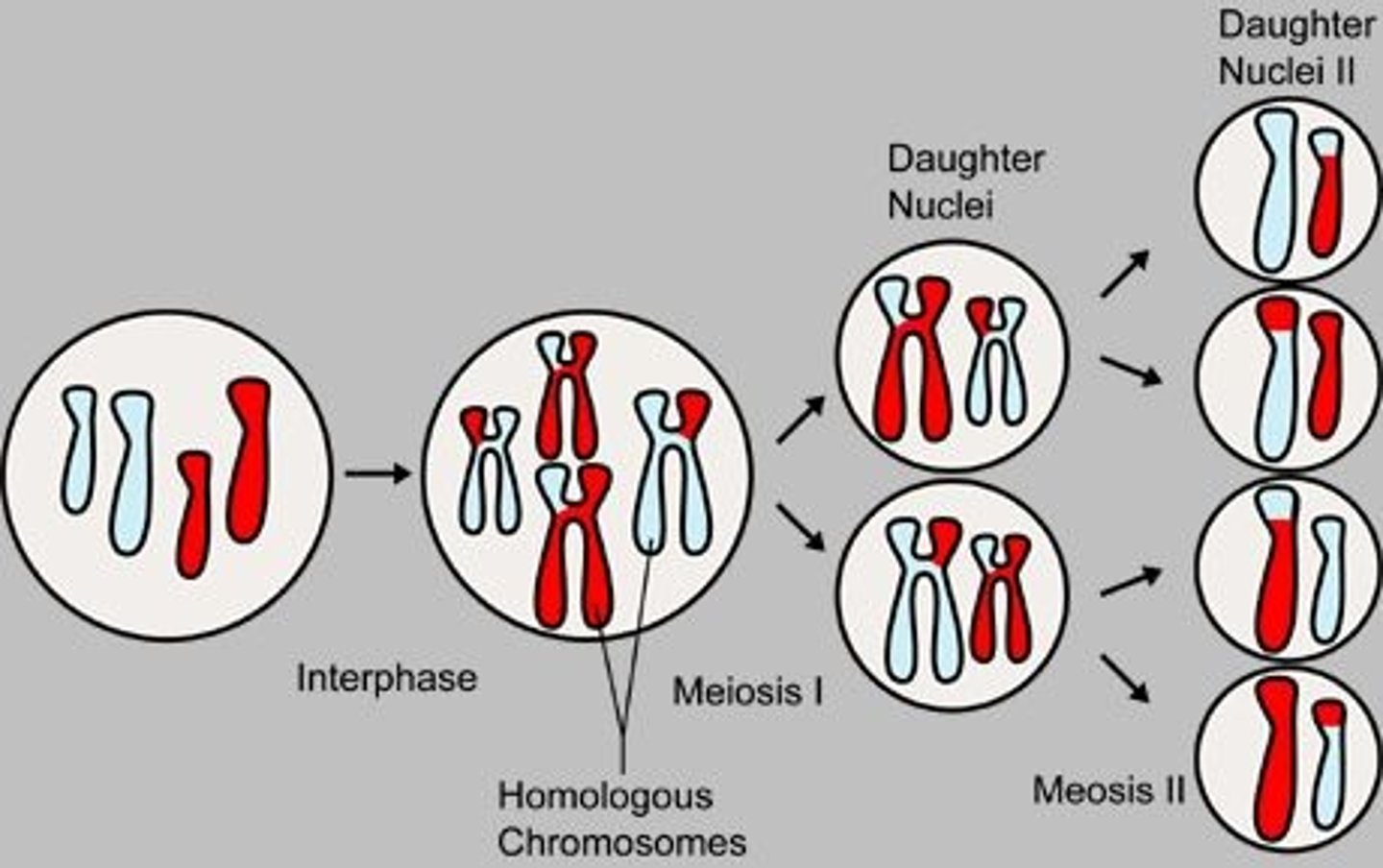
Meiosis
a type of cell division that results in four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell, as in the production of gametes.
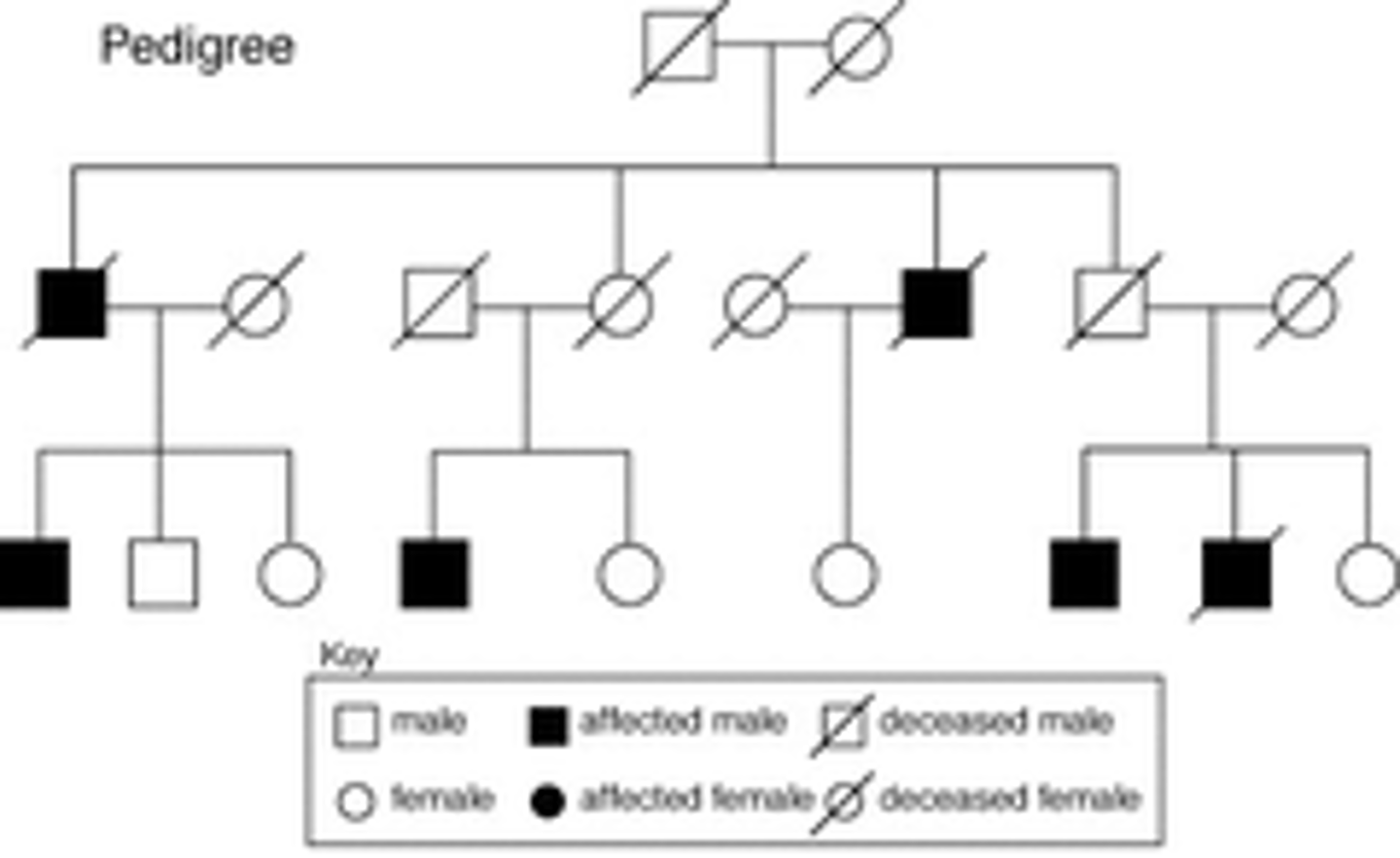
Pedigree
A diagram that shows the occurrence of a genetic trait in several generations of a family.
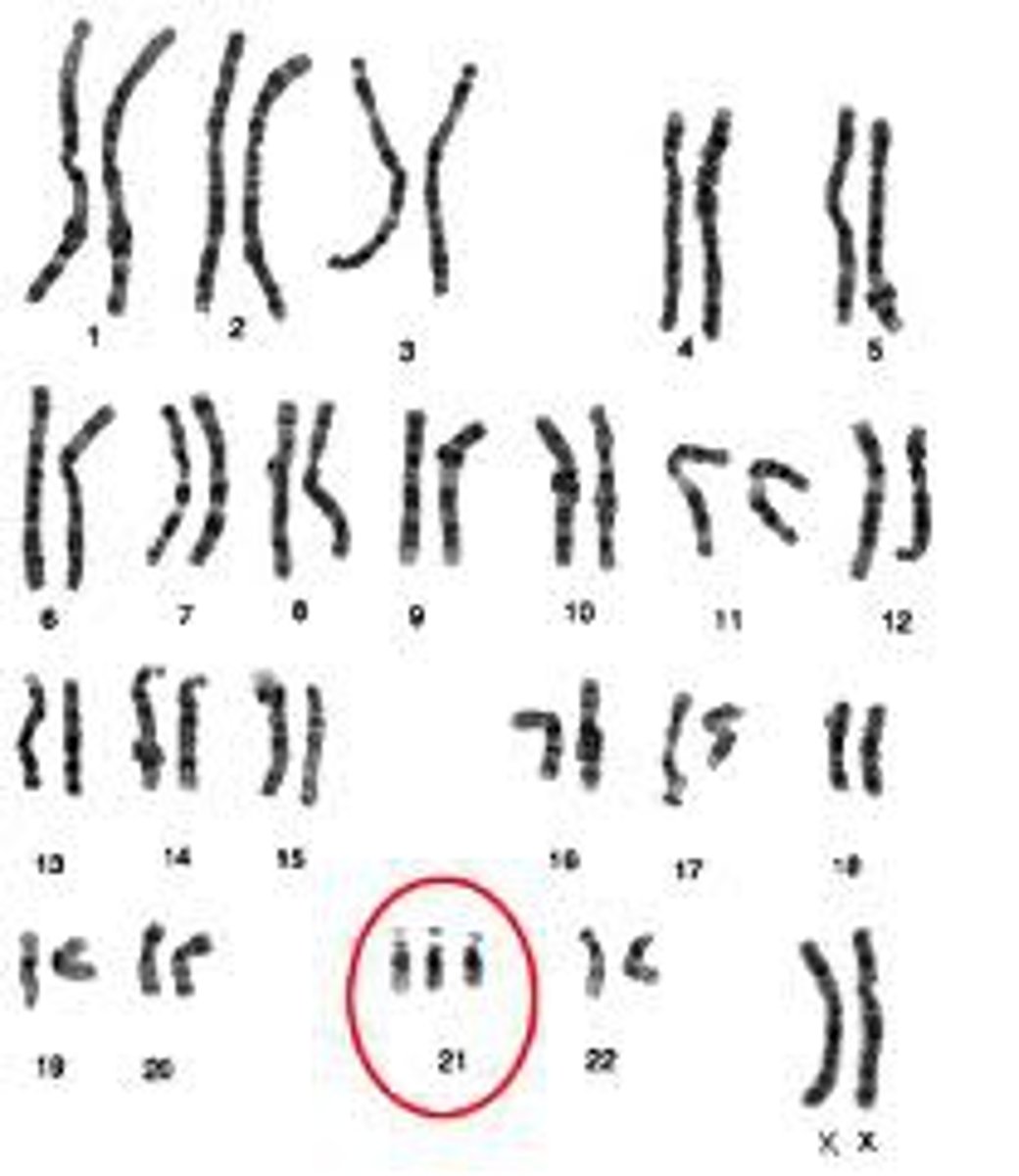
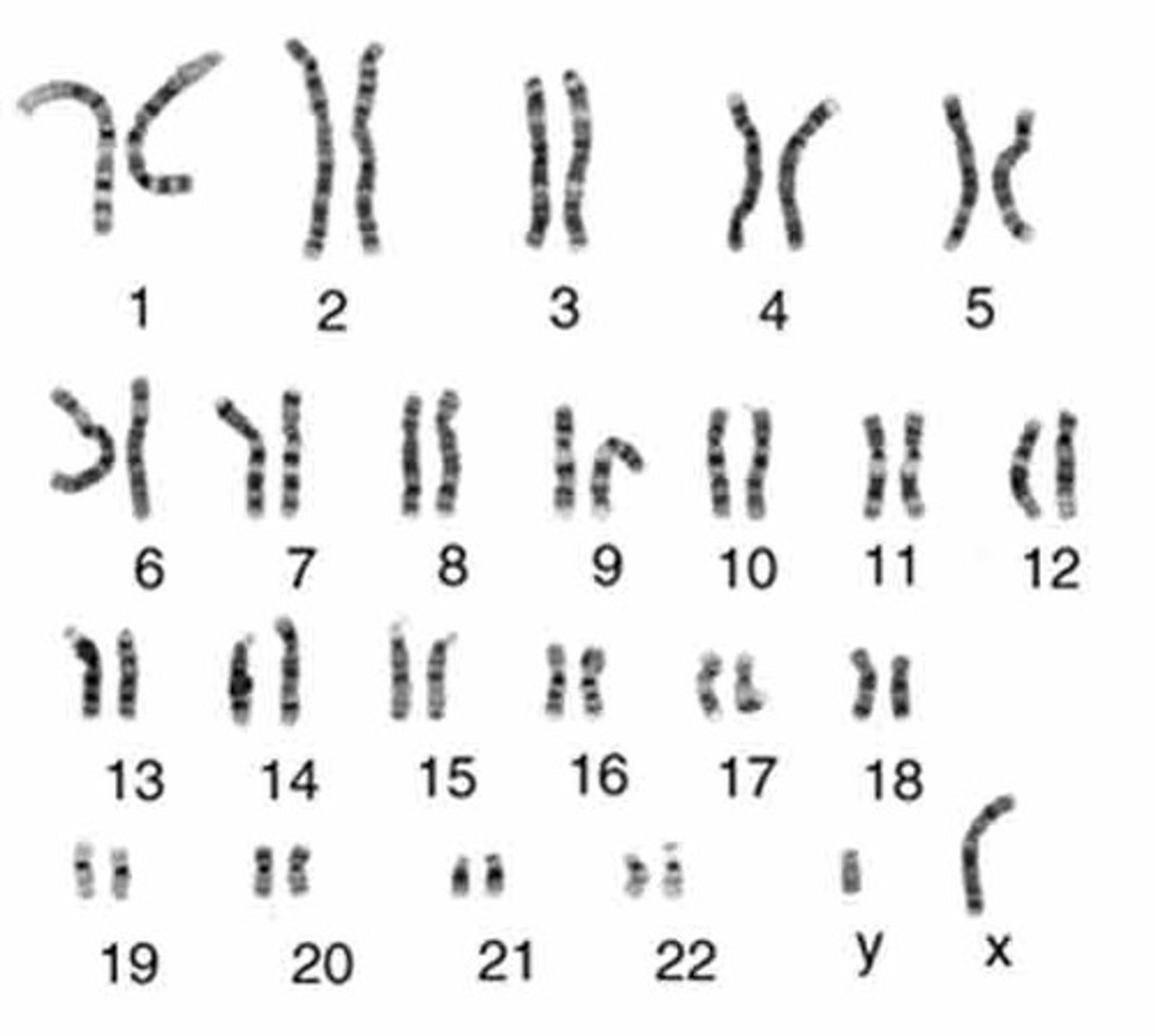
Karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape.
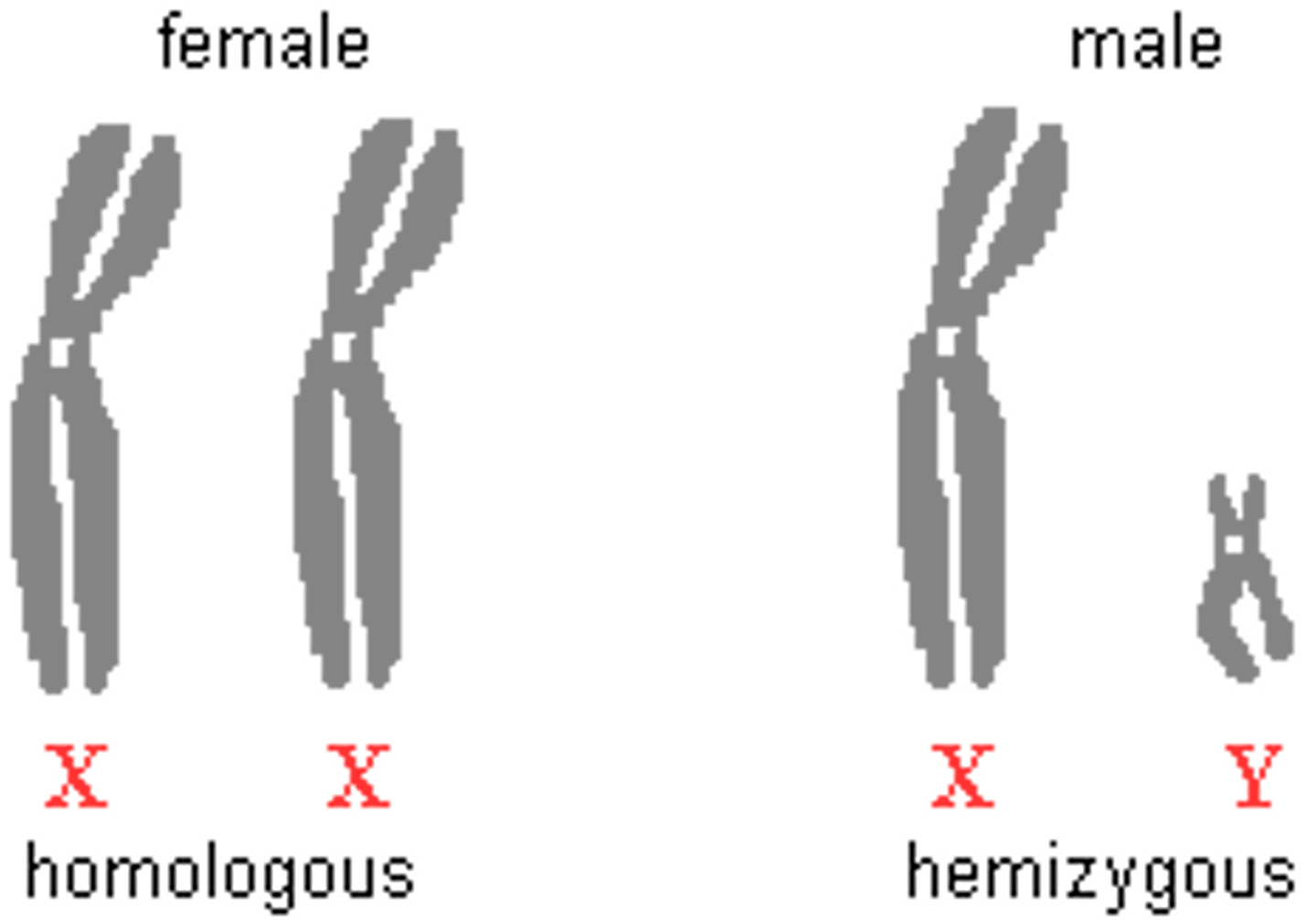
XX Chromosomes
female sex chromosomes
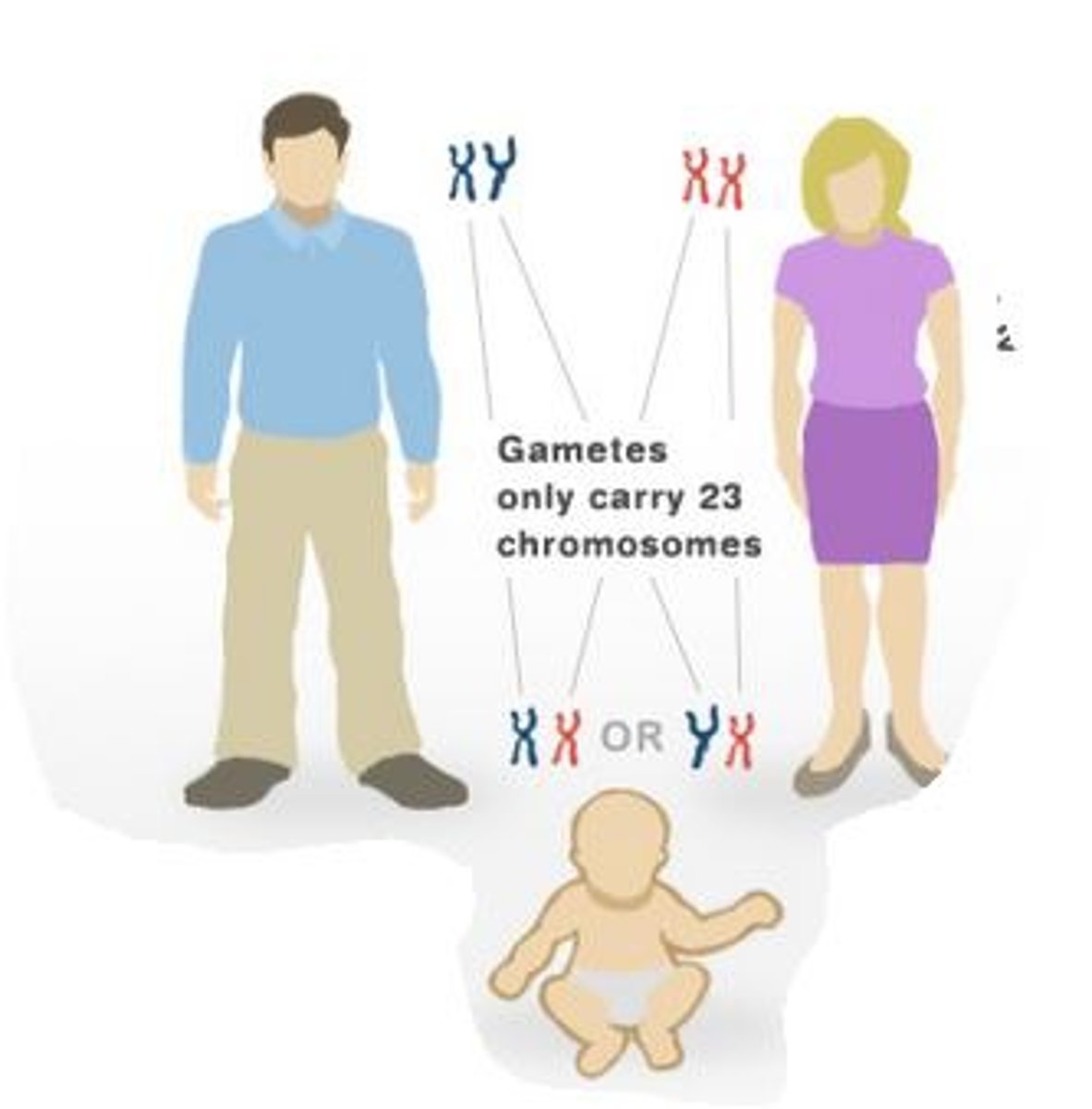
XY Chromosomes
male sex chromosomes
Mutation
A change in a gene or chromosome.
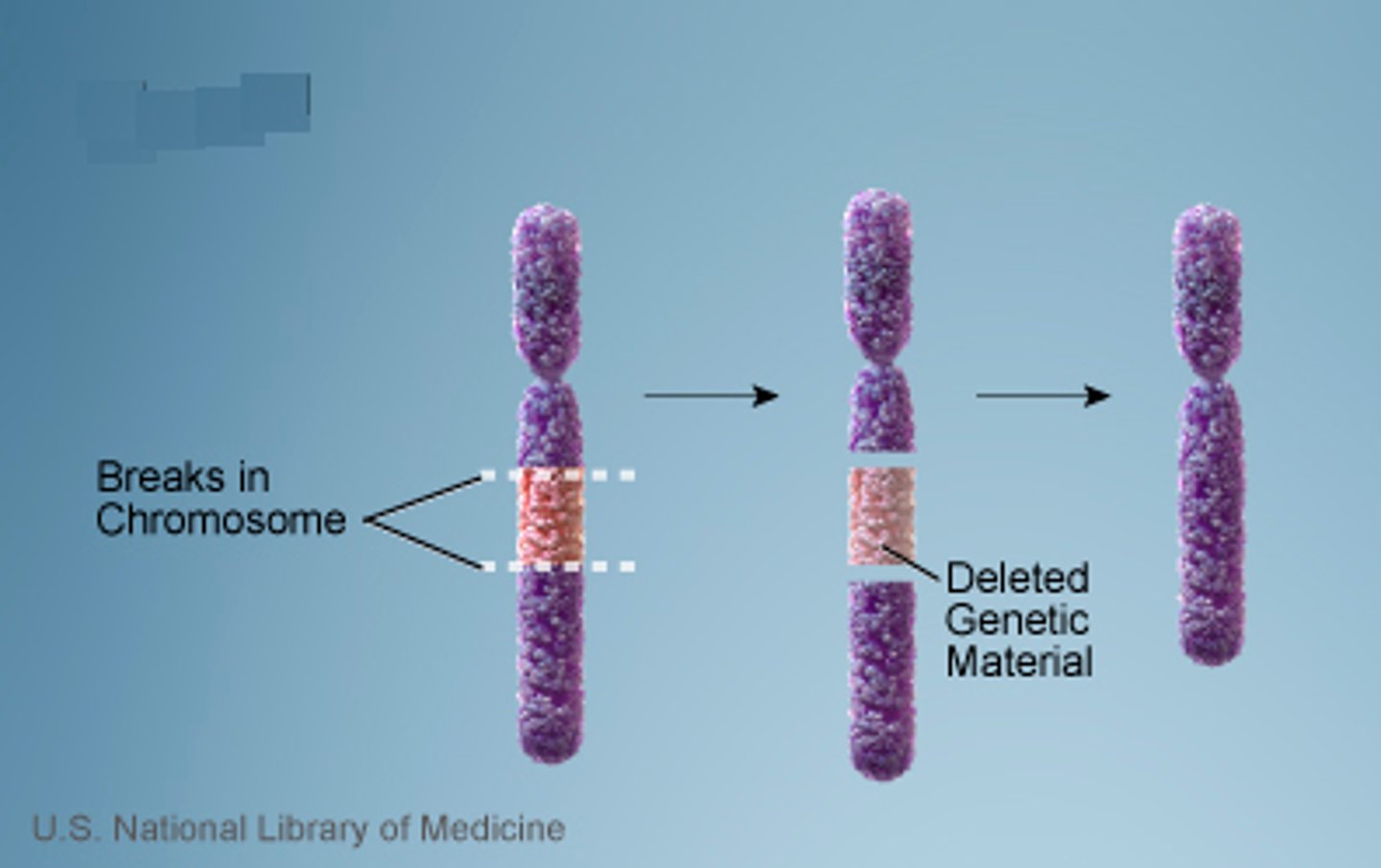
Deletion
removes a chromosomal segment
Insertion
A mutation involving the addition of one or more nucleotide pairs to a gene.

Substitution
A mutation in which a nucleotide or a codon in DNA is replaced with a different nucleotide

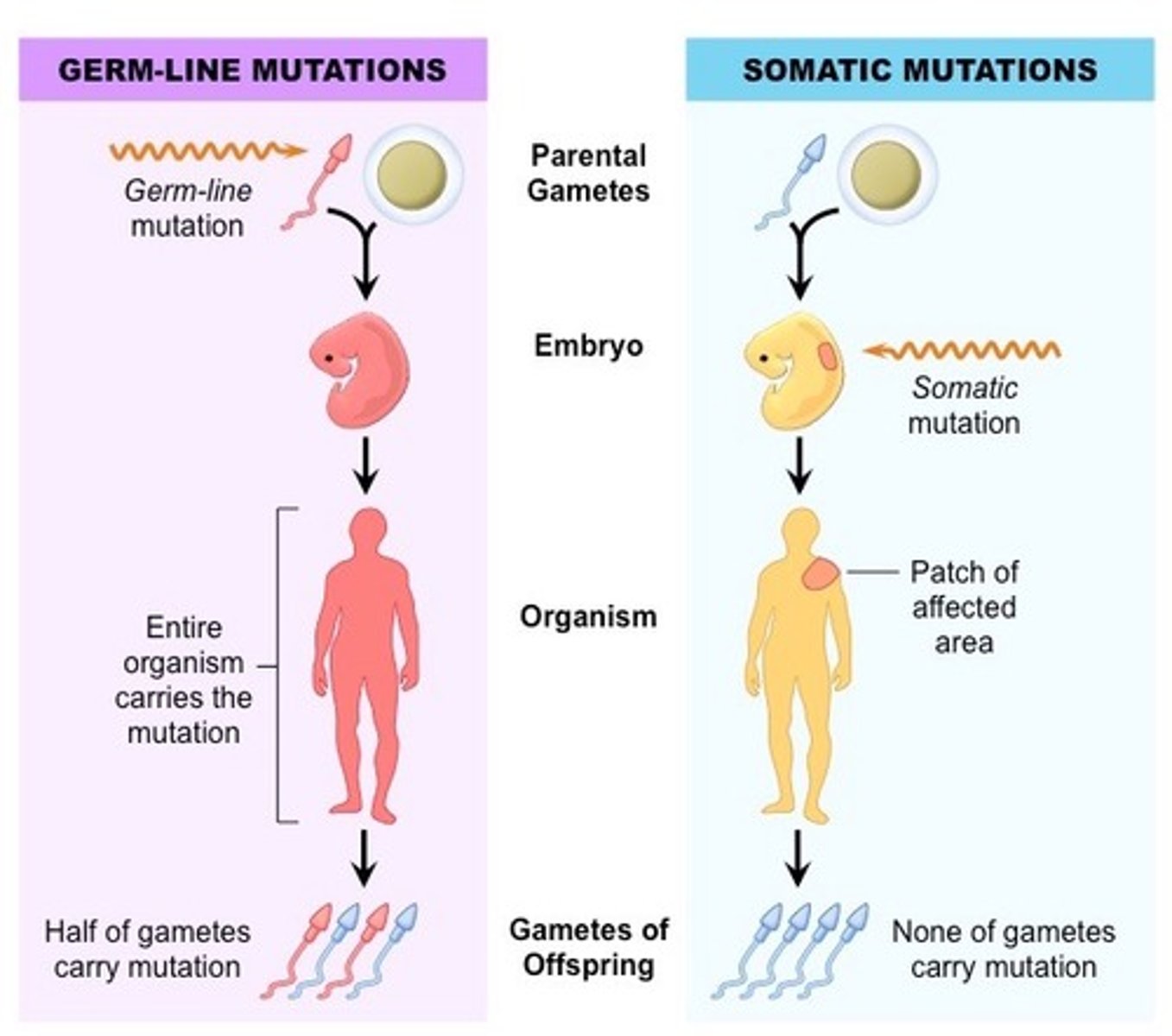
Germ Mutation
mutation or mistake in a germ or reproductive cell, can be passed to offspring
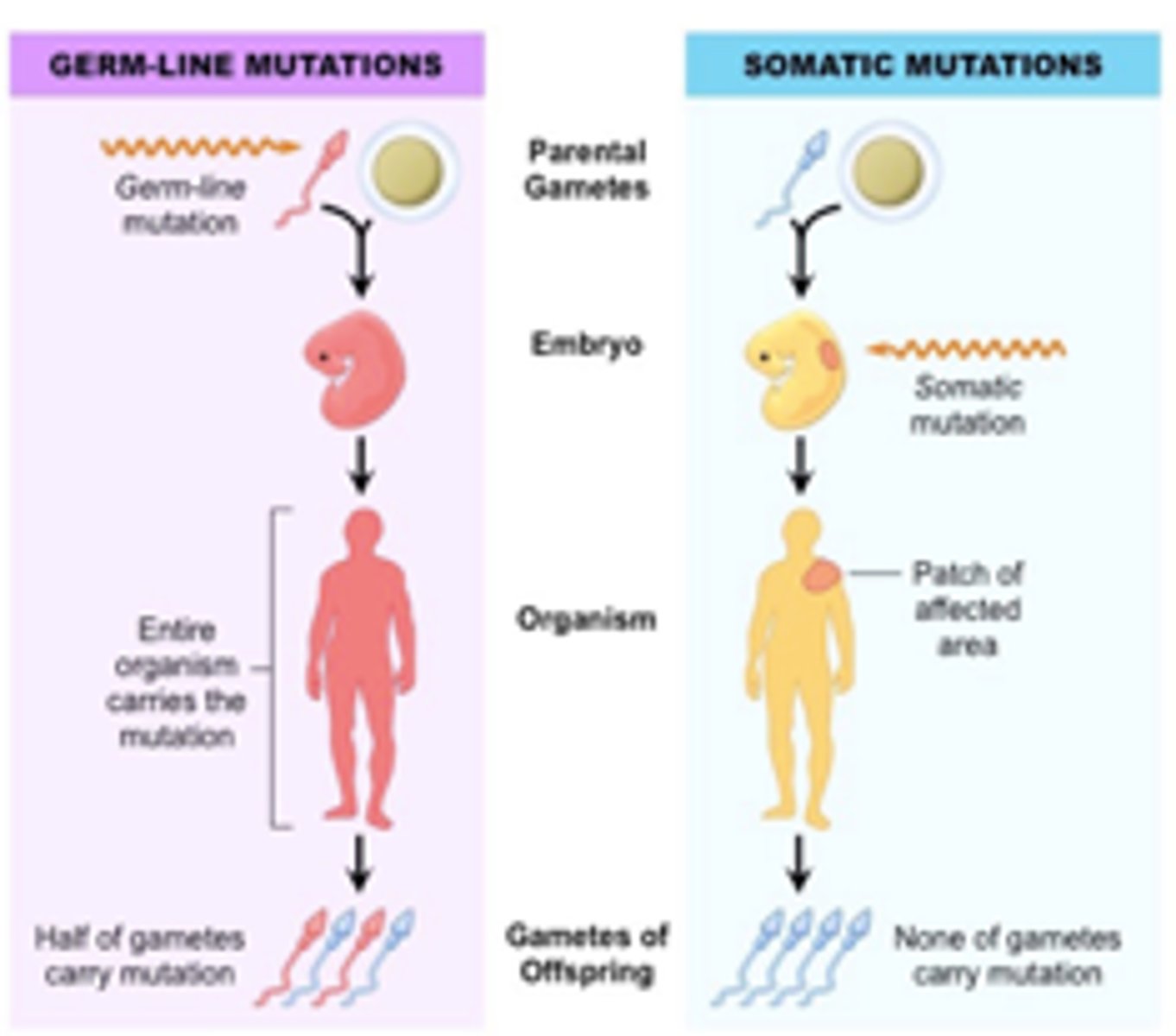
Somatic Cell Mutation
change within cells of the body, cannot be transmitted
Environmental Mutations
damage to DNA and chromosomes caused by environmental factors
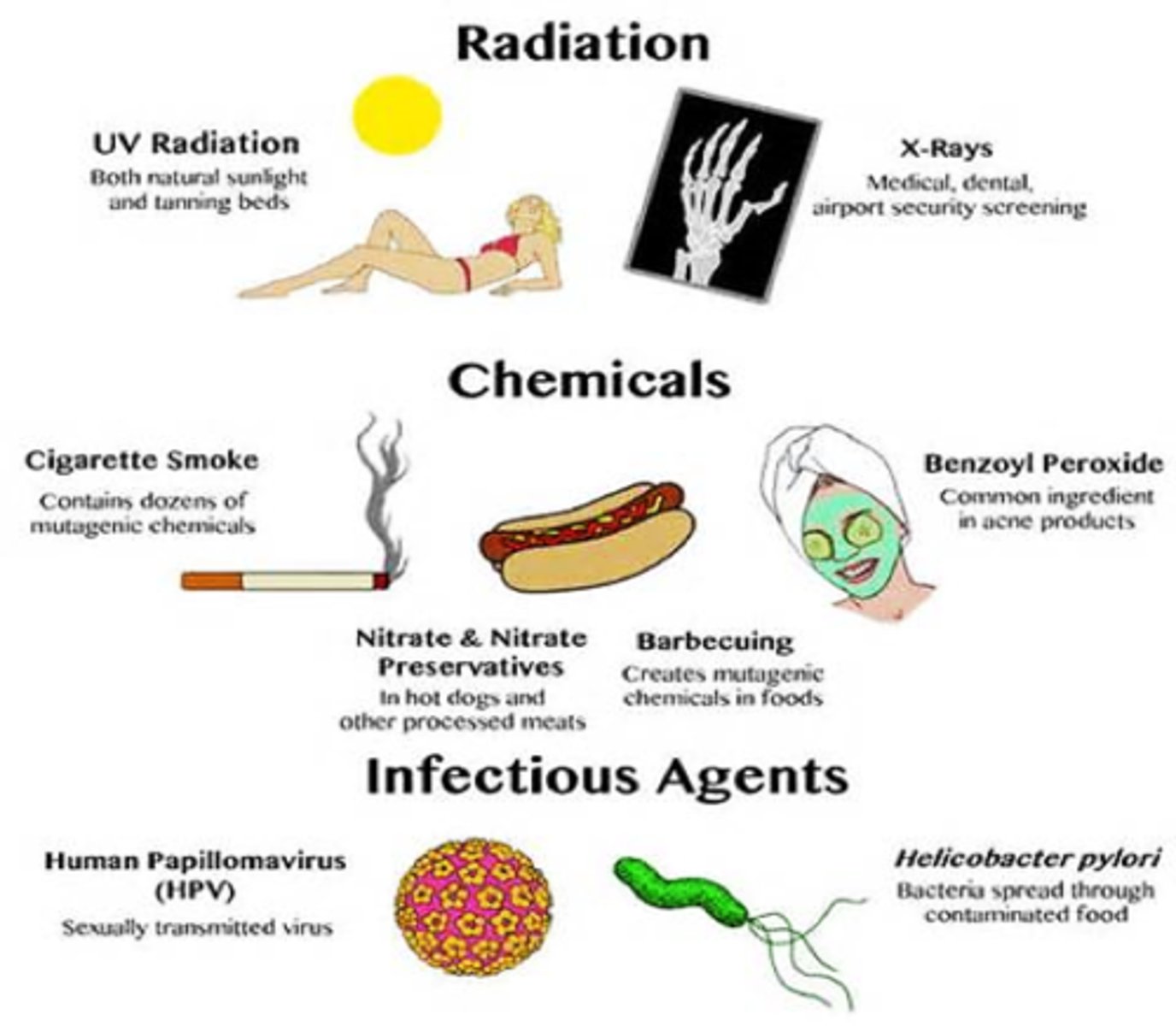
Environmental Factors
Those "nonbiological" factors that are involved in a person's surroundings such as the nature of the person's parents, the person's friends, and the person's behavioral choices.

Pollutant
A material found in air, water, or soil that is harmful to humans or other organisms, can cause an environmental mutation
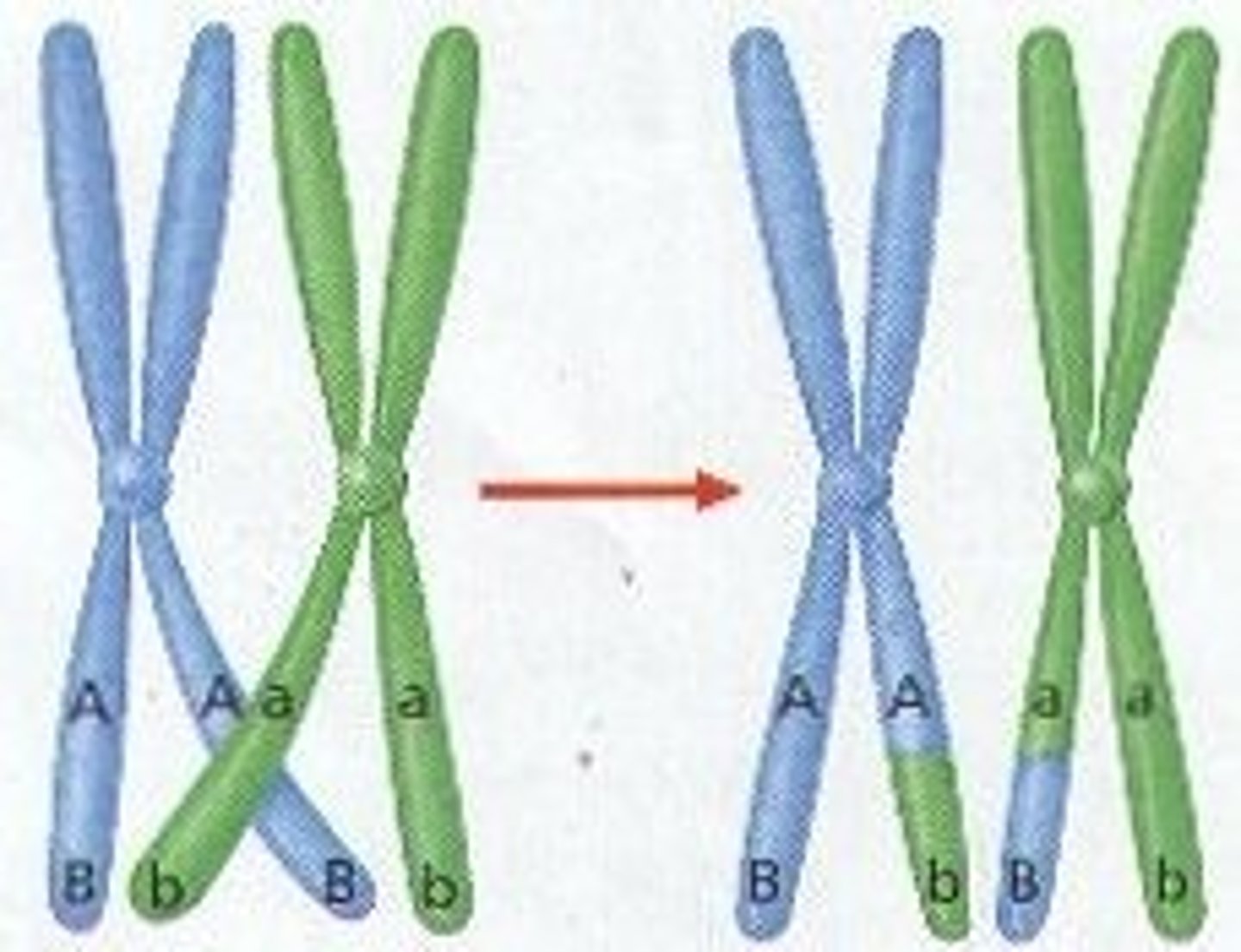
Crossing Over
exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during prophase I of meiosis
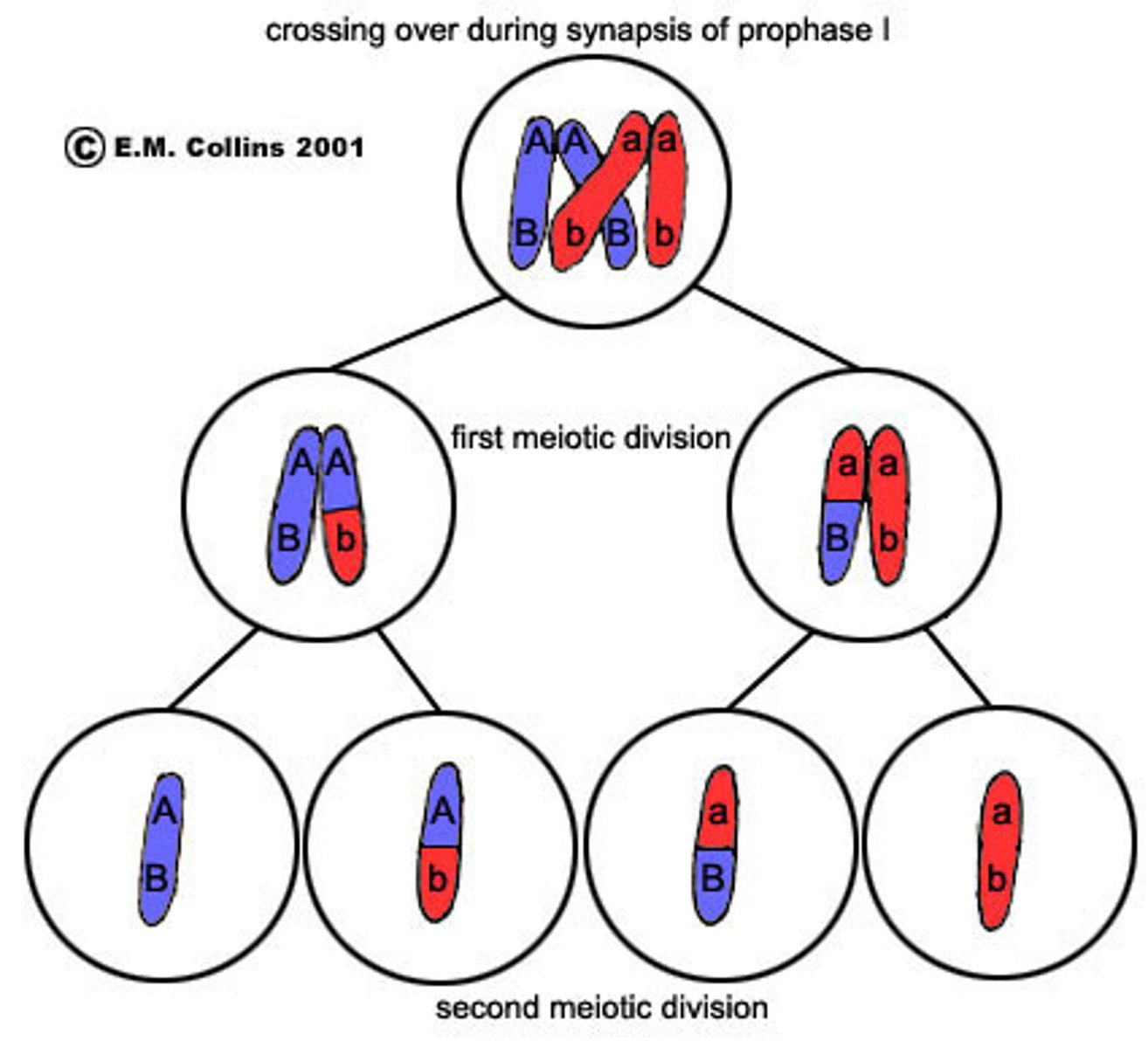
Genetic Variation in Meiosis
Results in cells that are genetically different as the result of crossing over and independent assortment
Nondisjunction in Meiosis I
Homologous chromosomes do not separate properly (all cells abnormal); usually occurs during Anaphase 1
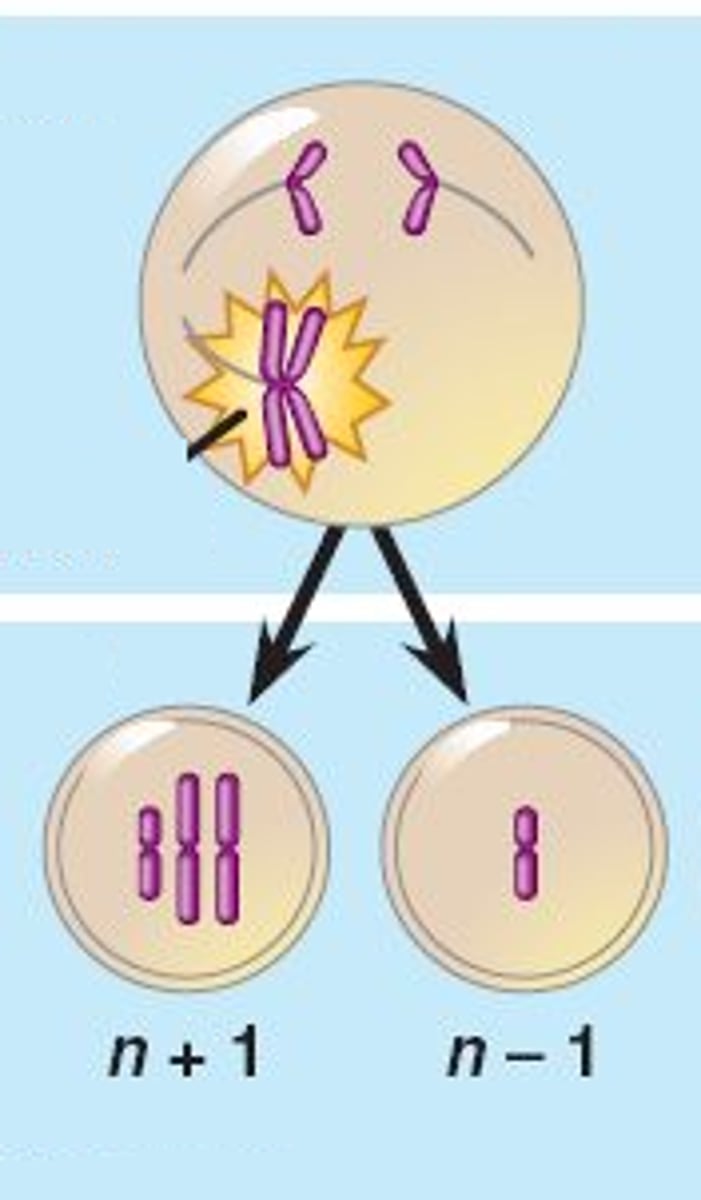
Trisomy
3 copies of a chromosome; occurs when chromosomes fail to separate properly