Comparative Advantage
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Adam Smith’s Theory of Absolute Advantage
A country is expected to export those goods in which it has an absolute cost advantage and import goods in which it has an absolute disadvantage (compare different countries)
A nation should produce and export goods for which it has a lower production cost compared to other nations, while importing goods that other nations produce more efficiently.
David Ricardo’s Theory of Comparative Advantage
(compare within country)
Mutually beneficial trade can occur when one nation is absolutely better at producing all goods
Although the rest of the world is absolute better, the key is relative prices (or costs) and not absolute prices (costs) of products
=> It is the opportunity cost of producing each product in each country that will determine the basis for trade among nations
Ricardo’s Theory of Trade
LOW opportunity cost
EXPORT
Ricardo’s Theory of Trade
HIGH opportunity cost
IMPORT
Ricardo’s Constant Costs and The Production - Possibility Curve (PPC)
PPC shows all the combinations of amounts of different products that an economy can produce with full employment of its resources and maximum feasible prodcutivity of these resources
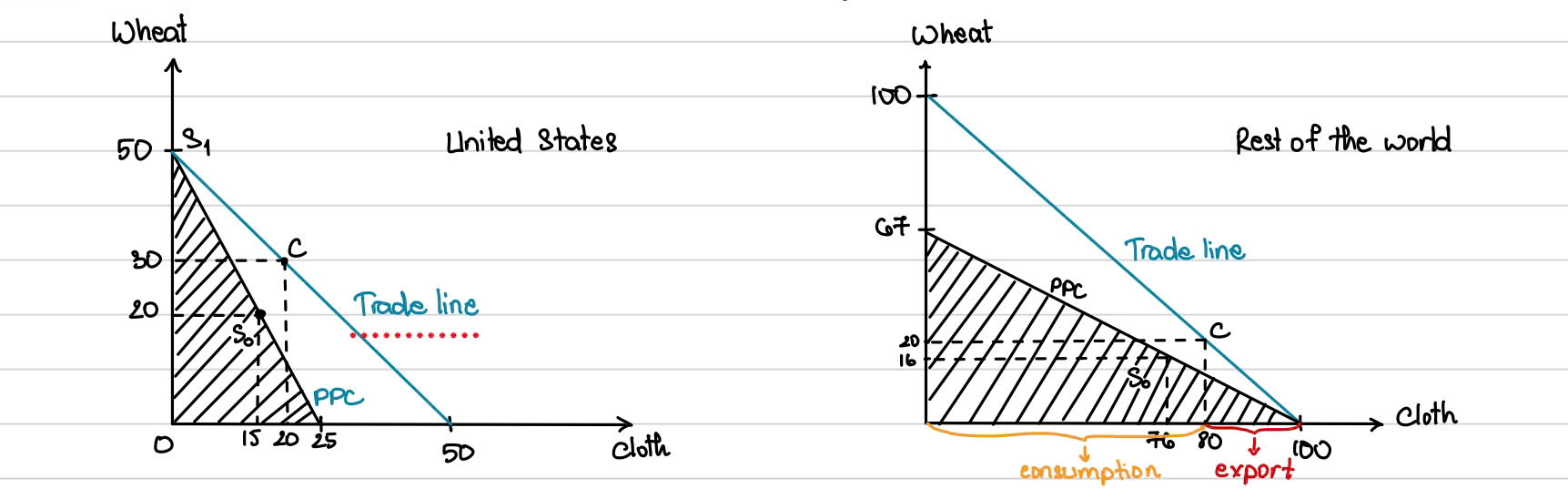
With no trade, each nation’s choices for the ______ of wheat and cloth is ____ to a point along its PPC
consumption, limited
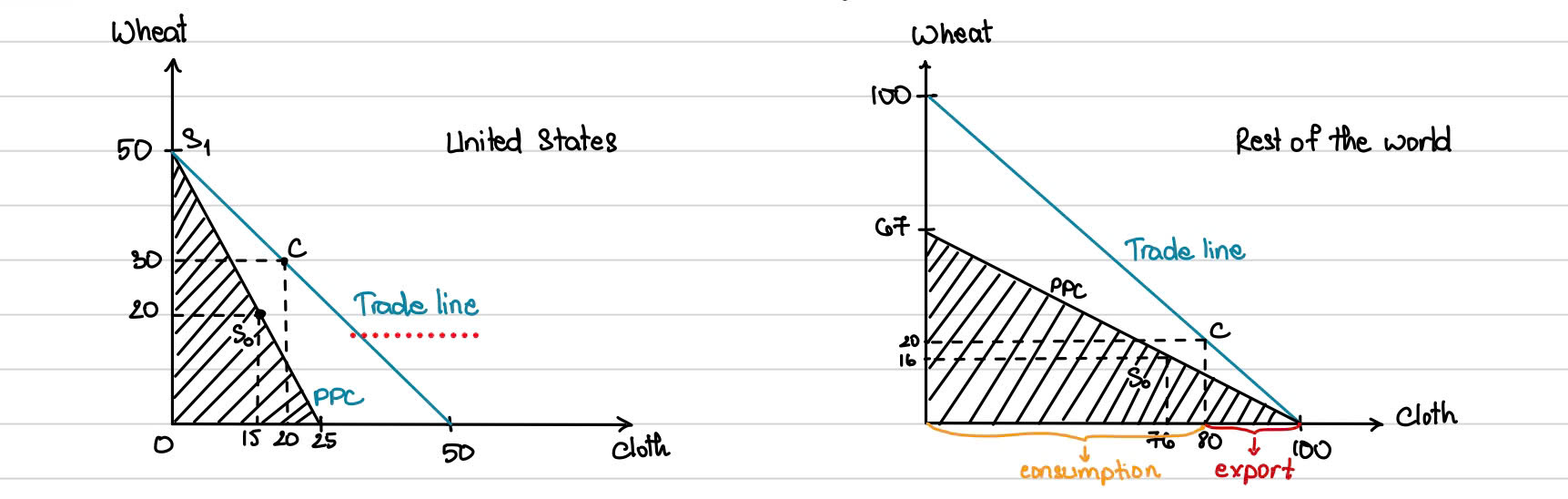
With free trade between two countries, rach country _____ (at point S1) in producing its __________ product
specializes; comparative advantage
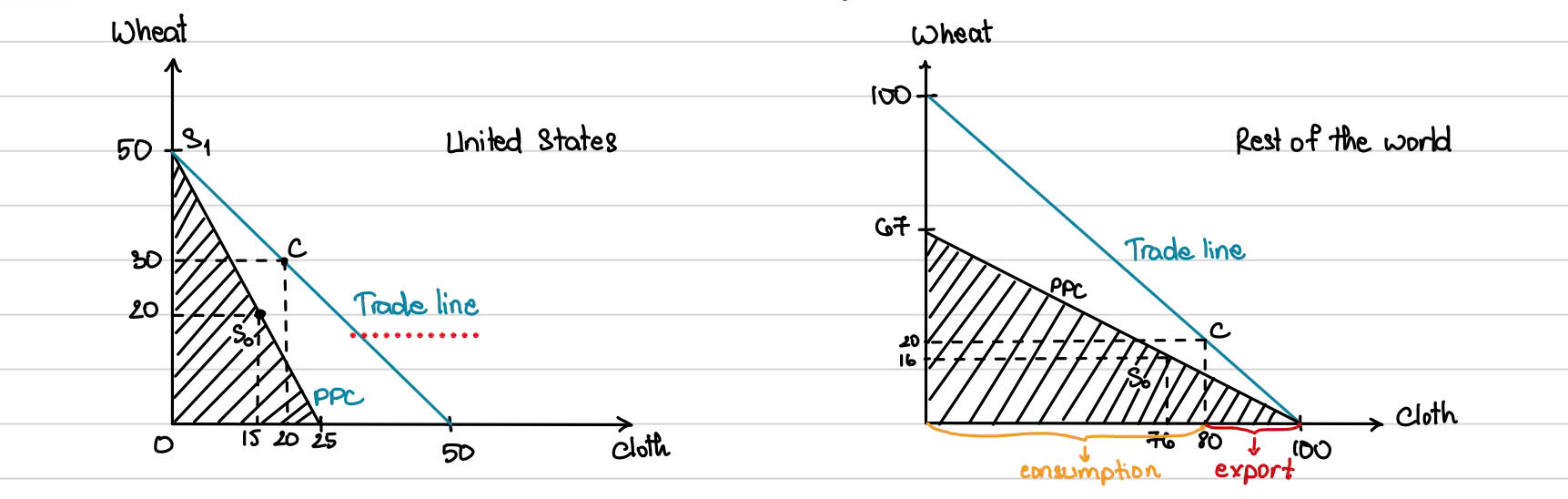
With free trade, consumers in each country can _____ at any point along the new _________ (for example, at point C) and enjoy a ______ standard of living
consume; trade line; higher
Implications of the Theory of Comparative Advantage
=> According the Ricardian model, relative prices ______ arise from the _____ ______ that are in turn due to exogenous differences in technology among nations
differences; productivity differences
Does absolute advantage matter?
=> It is matter not for determining ________ but rather for determining ___________ and national _________
the trade pettern; national wage levels; living satndards
Does absolute advantage matter?
=> Workers can recieve __________ and enjoy ___________ if they are highly productive. Workers with ____ productivity are paid low wages.
higher wages; better living standards; low