chp 12 - perfect competition and the supply curve
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
price taking producer
producers actions cannot affect market price of good/service
price taking consumer
consumer actions cannot affect market price of good/service
perfectly competitive market
market in which all market participants (consumers + producers) are price takers
perfectly competitive industry + 2 conditions necessary (+1 feature)
industry in which producers are price takers
must be many producers NONE OF WHOM HAVE large market share (fraction of total industry output owned)
products of producers must be regarded as equivalent (good substitutes) → standardized products/commodity
free entry + exit → not strictly necessary
marginal revenue
change in TOTAL REVENUE (P x q) generated by an additional unit of output → MR of last unit produced ≥ MC of last unit produced (anymore reduces Profit (TR-TC) )
MR = ΔTR/Δq
optimal output rule
price taking firm optimal output rule
why different?
profit maximized for outputs when MR=MC → anymore will reduce profit
P maximized when market price = MC
BC for price taking firms, MR = market price as market price/MR is perfectly elastic demand curve!!!
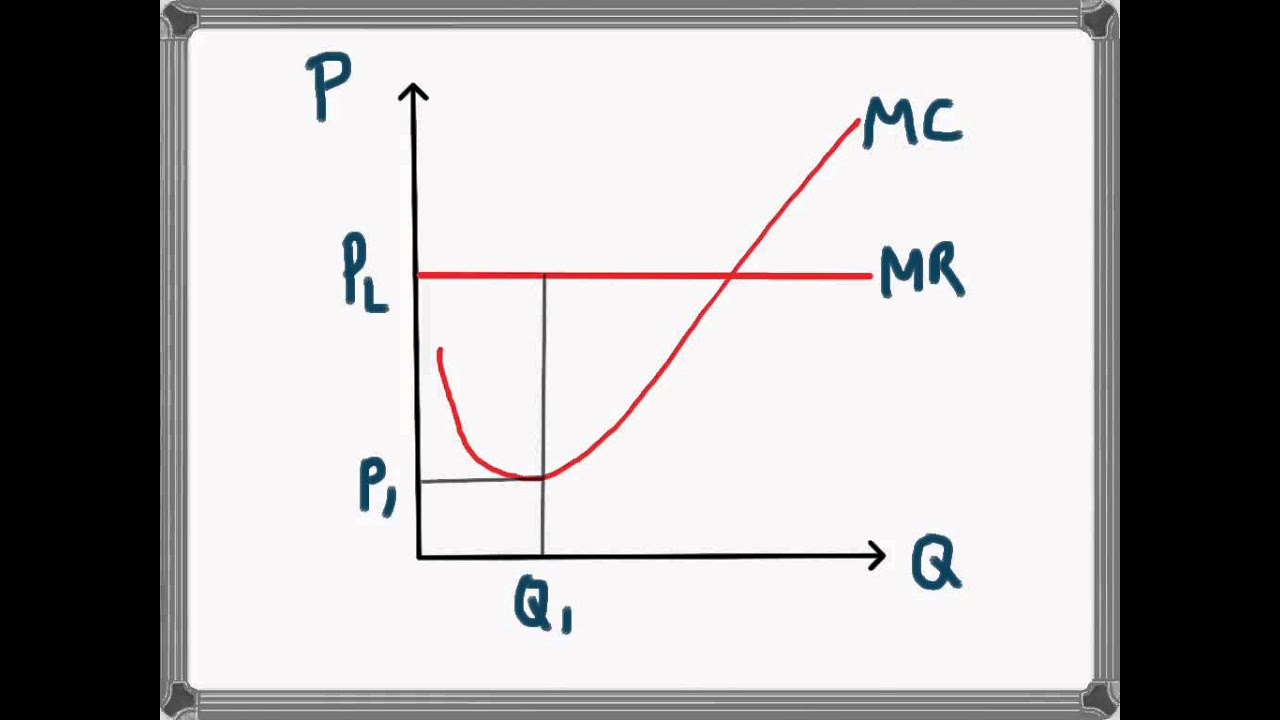
average total revenue (ATR)
average total cost (ATC)
TR/q or ALSO IS MARKET PRICE
TC/q
Market price VS ATC in terms of firm profit
P>ATC = profitable → enter into industry in the long run
P=ATC = breaks even → neither
P<ATC = incurs loss → exit industry in the long run
how does a producer know if it will be profitable (LONG RUN????)? (2)
for profit, market Price must exceed min ATC
for highest possible profit, MP=MC
how does a producer know if it will be profitable/optimal production decision (in short run)? (2)
MP > min AVC
min ATC
min AVC
break-even price
shut down price
Market price VS AVC in terms of firm profit
P>AVC = firm produces in short run → covers all VC and may cover some FC
P=AVC = only carries VC → firms indifferent
P<AVC = firm shuts down in short run → does not cover VC
Emkt
short run market equilibrium : Qs=Qd of a short run industry supply curve
profit maximization condition
MC=MR(=market P)
SR shut down condition
LR exit condition
SR : AVC>P
LR : ATC>P