LECTURE 17 - SPECIAL SENSES: THE EYE
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
what are the 2 classes of functional receptors? what type of stimuli does each detect?
-general senses
temperature, pain, touch, stretch, and pressure
distributed throughout the skin and organs
-special senses
taste, smell, sound, equilibrium, and vision
housed within specialty organs of the head
where are exteroceptors found? interoceptors? proprioceptors?
exteroceptors: detect stimuli from the external environment
interoceptors: detect stimuli in the viscera
stretch receptors found within the smooth muscle of different organs (stomach, small and large intestines)
proprioceptors: detect stimuli within the muscles, tendons, and joints
what are 5 types of exteroceptors? what type of stimuli does each detect?
-mechanoreceptors: detect touch and pressure
-thermoreceptors: detect temperature
-nociceptors: detect pain
-photoreceptors: detect light
-chemoreceptors: detect taste and smell
what is the function and composition of lacrimal fluid? what structure produces the lacrimal fluid? where does it flow to?
lacrimal gland produces lacrimal fluid
-excretes lacrimal fluid (tears)
composition: water, salts, and bacterial fighting enzymes
function: moistens, cleans, and lubricates the eye
exits via the lacrimal duct
where is the conjunctiva found? what is its funciton? histology?
-composition: stratified squamous epithelium and stratified columnar epithelium
-covers the inner surface of the eyelids and the anterior of the eye
forms conjunctival sac
function: lubricates and moistens the eye; detection of foreign objects
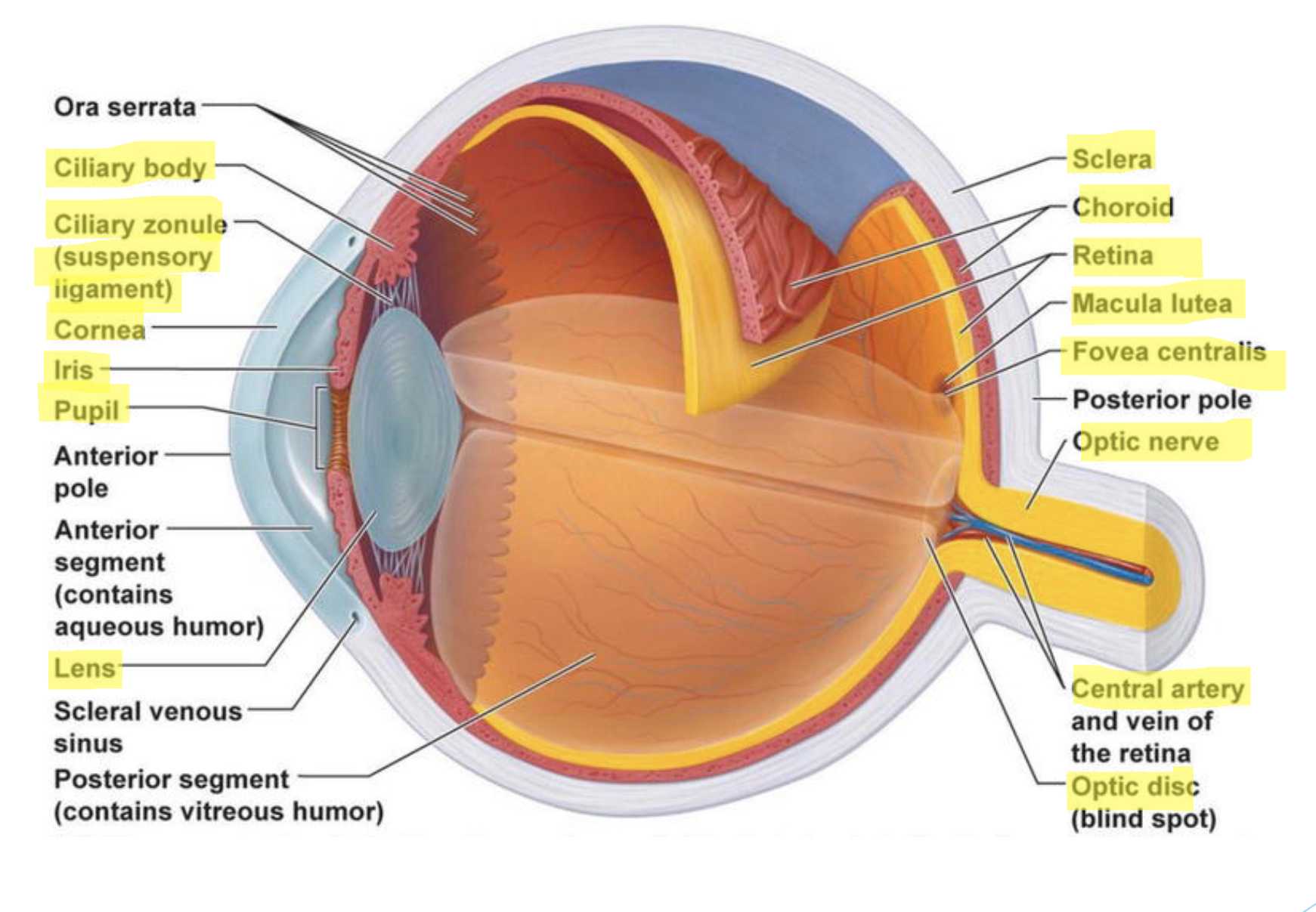
what are the 3 tunics of the eye? what structures comprise each tunic?
fibrous layer (outer)
vascular layer (middle)
nervous layer (inner)
fibrous layer (outer)
sclera
white layer of dense irregular connective tissue
supports, protects, and shapes the eye
cornea
transparent, convex collagen fibers
serves for preliminary focus—→bends entering light (refraction)
what are the 3 tunics of the eye? what structures comprise each tunic?
fibrous layer (outer)
vascular layer (middle)
nervous layer (inner)
vascular layer (middle)
choroid
vascular, darkly pigmented layer with melanin
contains ciliary vessels supplying O2
absorbs light, preventing scatter and reflection
ciliary body
anterior portion is continuous with choroid
serrated ring of ciliary muscles covered by ciliary processes
focuses the lens via suspensory ligaments
lens
avascular, thick, transparent, biconvex, “disc” of compact epithelial cells
changes shape via constriction/relaxation of the ciliary muscles
allows light to be refracted onto the retina
iris
anterior most portion of middle layer
attaches to the ciliary muscles: found between the cornea and lens
forms the opening called the pupil that allows for the passage of light
contains circular and radial smooth muscles
allows for constriction and dilation of pupil
may be pigmented with melanin
what are the 3 tunics of the eye? what structures comprise each tunic?
fibrous layer (outer)
vascular layer (middle)
nervous layer (inner)
nervous layer (inner)
retina
photoreceptive layer
contains rods and cones
maintained by branches of the central artery
includes: macula lutea, central fovea, and optic disc
rods
detect low levels of light
“black/white” vision
cones
detect “higher” wavelengths of light
color vision
optic nerve
protected by the meninges
exits the eye carrying sensory information toward the brain
know the location, function, and histology (when relevant) of each eye structure listed in class.
sclera
cornea
ciliary body
lens
iris
choroid
retina
optic nerve
sclera
location: outer white layer of eyeball
function: supports, protects, and shapes the eye
histology: white layer of dense irregular connective tissue
cornea
location: clear curved front part of eye
function: serves for preliminary focus —→bends entering light (refraction)
histology: convex collagen fibers
ciliary body
location: ring shaped structure behind the iris, around the lens
function: focuses the lens via suspensory ligaments
lens
location: behind iris and pupil
function: focuses light onto retina by changing shape
iris
location: colored part of the eye in front of lens
function: controls size of the pupil to regulate how much light enters
histology: smooth muscle tissue, avascular, thick, transparent, biconvex “disc” of compact epithelial cells
choroid
location: layer between sclera and retina
function: absorbs light, preventing scatter and reflection
retina
location: inner layer lining the back of the eye
function: contains photoreceptors (rods and cones) that detect light and send signals to the brain.
optic nerve
location: back of the eye, connecting retina to brain
function: exits the eye carrying sensory information toward the brain
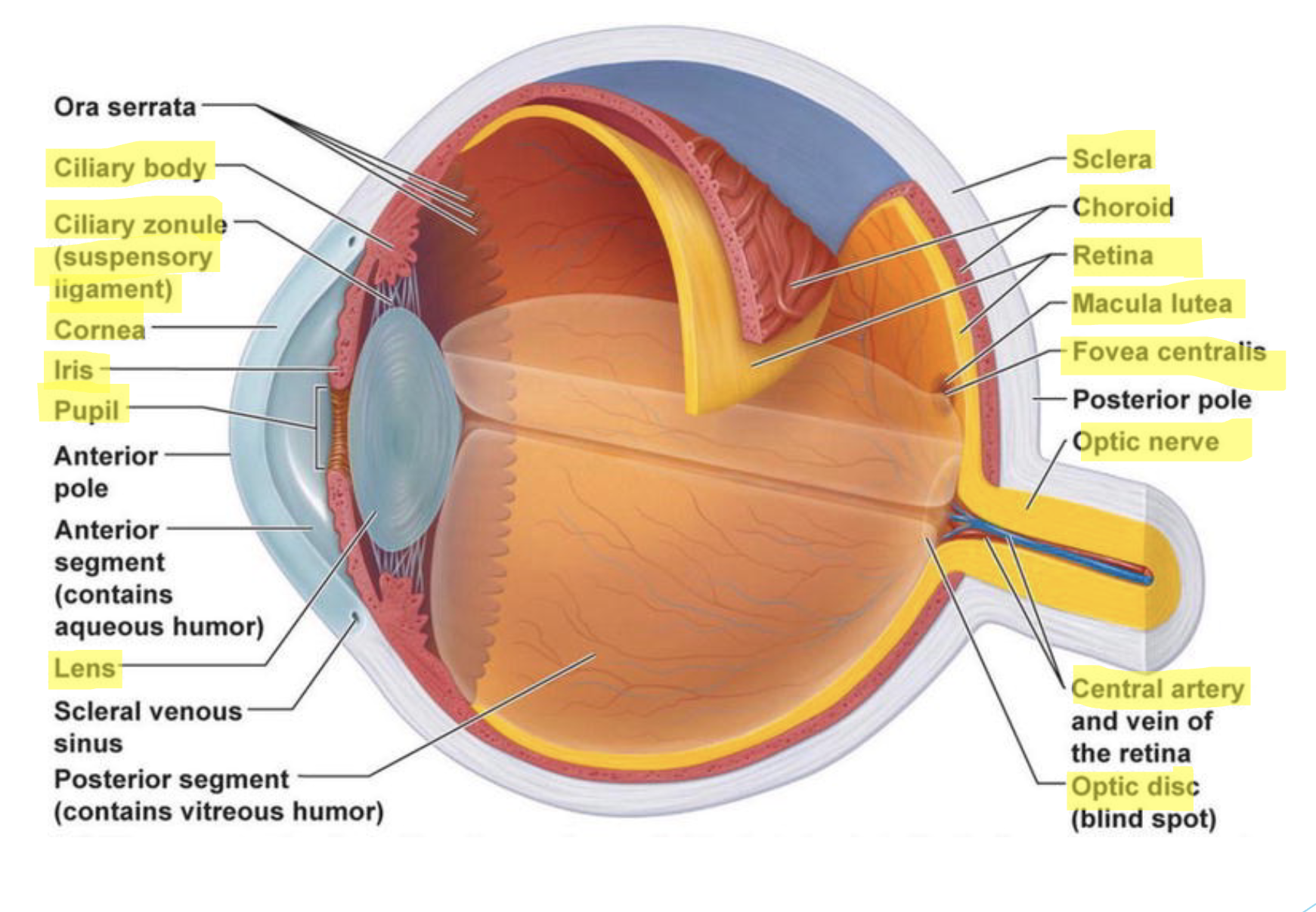
what is the optic disc?
blind spot that occurs at the optic nerve (area lacks rods and cones)
what is the macula lutea? where is the central fovea found?
-macula lutea is the center of the retina
-central fovea is found inside the macula; highest cone cell density
what do rods detect? cones?
rods: detect low levels of light
“black/white” vision
cones: detect “higher” wavelengths of light
color vision
what are the 2 cavities/segments of the eye? what fluid fills each?
the internal space within the eye is subdivided by the lens into two cavities/segments:
anterior segments
filled with aqueous humor
posterior segments
filled with vitreous humor
what are the two chambers of the eye? where is each found?
in the anterior segment it is subdivided into two chambers via the iris:
anterior chamber: between the cornea and iris
posterior chamber: between the iris and the lens
what is the flow of aqueous humor through the anterior segment?
FLOW OF AQUEOUS HUMOR
secreted by the ciliary body into the posterior chambers —→
flows through the posterior chamber across the anterior surface of the lens —→
through the pupil —→
into the anterior chamber —→
exits via the scleral venous sinus (canal of schlemm) —→
blood stream
be able to identify the following structures on a diagram of the eye:
sclera
cornea
conjunctiva
iris
ciliary body
suspensory ligaments
choroid
retina
optic disc
macula lutea
optic nerve
anterior segment
posterior segment
anterior chamber
posterior chamber