Childhood Neurological Disorders
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
5 questions for each disorder:
Frequency - How common is the disease?
Cause
Part of CNS affected
Functions affected
Treatments or cures
Incidence
Rate at which new cases occur during a specified period (# of new diagnoses)
Prevalance
How many people have the disease at a given time
Possible causes:
Genetic/developmental
Injury
Infectious Disease
Toxicity/environmental
Unknown/combination
Structure of neuron
Cell body (soma) has multiple dendrites (fibrous projections) and one axon covered in myelin
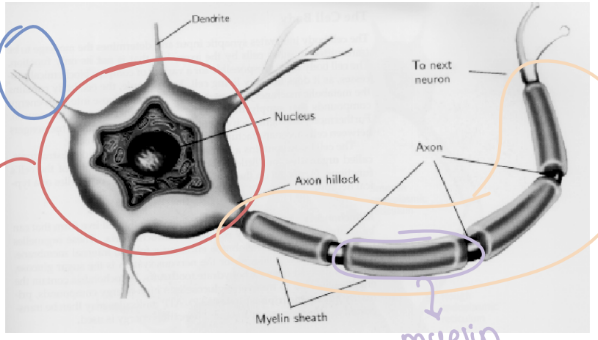
Gray matter
Cells arranged in structures called nuclei (located at the soma)
White matter
Axons (white because of myelin sheath)
Function of dendrites
Receive signals from other neurons
Myelin function
Speeds up signal transduction down the axon (makes signals faster)
Axon function
Sends signals to the soma of the next neuron
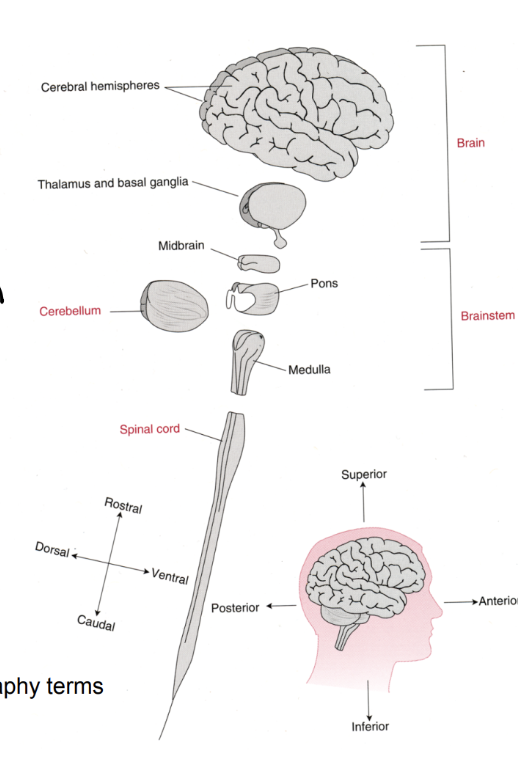
Major Divisions of the CNS (Rostral → Caudal)
Cerebral Hemispheres (cortex)
Thalamus and basal ganglia (subcortical)
Brainstem (midbrain, pons, and medulla)
Cerebellum
Spinal Cord
Brain Functions
Sensory
Balance, vision, hearing, etc.
Motor
Muscle tone, coordination, etc.
Cognitive and affect
IQ, language, memory, emotion
Types of Treatments
Medication
Surgery
Support (OT/PT, in-home care)
3 main childhood disorders
Down Syndrome (DS)
Krabbe Disease
Seizure Disorder (epilepsy before)
History of DS
People with DS used to be institutionalized, but now much more accepted
Frequency of DS
Not that common, 1 in 800 births
Cause of DS
Trisomy 12 (extra copy of chromosome 21)
Genetic cause
Trisomy Mosaic
Some cells have normal chromosome number, some have trisomy which results in less severe symptoms
Majority (75%) of DS cases result in…
Spontaneous miscarriage
DS Detection
Genetic testing, especially in older moms (higher risk) although most DS are born to young women
Symptoms of DS
Developmental: facial structure
Cognitive: Low IQ (variable), intellectual disability if IQ is less than 70
High functioning vs. Low functioning
Motor: Delayed ‘motor milestones’
DS affect on CNS
Smaller cerebral cortex and cerebellum
Subcortical structures not affected as much as cortical
DS-associated Medical Problems
Heart surgery due to structural problems
Strabismus, myopia, spontaneous nystagmus (vision)
Short stature, obesity
Tongue thrust impairs speech
Seizure and autism spectrum disorders
C-spine instability
Early onset Alzheimer’s
Behavioral/Stereotypes
Strabismus
2 eyes don’t work together, requiring ocular muscle surgery
Myopia
Nearsightedness
Spontaneous nystagmus
Abnormal eye movements without stimulus
DS C-Spine Instability
Atlanto-axial subluxation not common in DS; too much movement between skull and spine is dangerous to spinal cord
Why are people with DS at risk for early onset Alzheimer’s?
Gene on chromosome 21 has a key protein in AD (more of chromosome 21 = higher risk)
Life expectancy for DS
Shorter than average, but has been improving with conditions
Treatment for DS
No cure; often requires therapy, special ed., support groups for families, change in society’s attitude
Krabbe Disease (GCL)
Abnormal structure of white matter and presence of globoid cells in the brain (AKA globoid cell leukodystrophy)
Frequency of Krabbe Disease
Very rare (1 in 100,000 live births)
Cause of Krabbe Disease
Autosome recessive gene mutation (hereditary - autosomal recessive)
Myelin in Krabbe Disease
Mutatation affects galactocerebrosidase which forms myelin, leading to wrong structure of myelin
Areas affected by Krabbe Disease
Since myelination is not able to finish at birth:
The brain and spinal cord are all affected
Functions affected by Krabbe Disease
Affect: babies are unusually irritable
Motor: loss of control, increase muscle tone (stiffness)
Symptoms of Krabbe Disease
Irritability
Stiffness and no motor control
Seizures, blindness, deafness
Death by 2 years old
Life Expectancy for Krabbe Disease
2 years old; very short
Treatment for Krabbe Disease
Cord blood transplants (HSCT - stem cell) must be done early to replace the defective gene
NOT cure, but increases life expectancy and QoL
Newborn screening
Irreversible
Seizure Disorder
Recurrent, unprovoked seizures (one seizure cannot be classified as SD)
Frequency of Seizure Disorder
Much more common than other childhood NDs; a good portion are pharmaco-resistant/intractable
What is a seizure?
Spontaneous, simultaneous discharges of neurons that generate many action potentials in the brain
Symptoms of a seizure
Variable, and depends on part of brain affects (seizure focus in where it starts)
Cause of Seizure Disorder
Many different causes:
Brain structure (developmental or mutations)
Head injury (scar tissue → electrical abnormality)
Tumors
Multiple sclerosis (due to scar tissue)
Critical Parameters for Seizures:
Where did it start?
Is it motor or nonmotor (absence)?
Is consciousness affected?
Focal Onset Seizures
Aware vs. impaired
Aware maintains consciousness
Abnormal electrical activity is limited to a specific part of the brain
Determines symptoms
Seizure Classification Flowchart
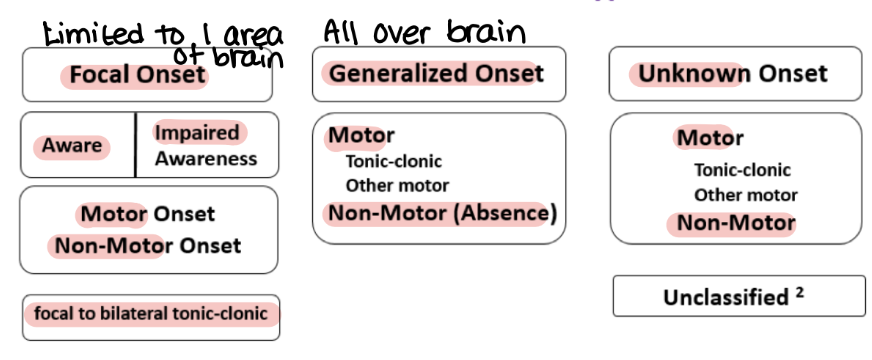
Focal Impaired
Temporal lobe origin
Temporal - complicated movements
No loss of postural control (stay standing)
Not fully conscious, no memory
Often preceded by an aura
Generalized Onset
The entire brain is involved, falls into motor or non-motor:
Motor: tonic-clonic (two phases of seizure)
Lasts seconds to minutes
Tonic Phase
Increased muscle tone; rigidity
Clonic Phase
Back and forth movement of body (contracting opposite muscles)
Seizure Triggers
Often no trigger but some are due to lights, sounds, etc.
Dangers of Seizures
Generalized motor are not dangerous, but falling/drowning/car accidents are concerns
STATUS EPILEPTICUS
Status Epilepticus
Prolonged, repeated seizures with no recovery between (5-10 minutes without consciousness)
Requires immediate medical treatment (IV, life support)
Seizure First Aid
Move objects
Pay attention to TIME (status)
Don’t hold person down, nothing in their mouth
Call 911 if longer than 5 minutes
Post-Ictal Period
Period immediately after seizure, causing confusion or deep sleep
Non-Motor (Absence) Seizure
Staring spells, no loss of postural tone
Most common in children, often outgrown
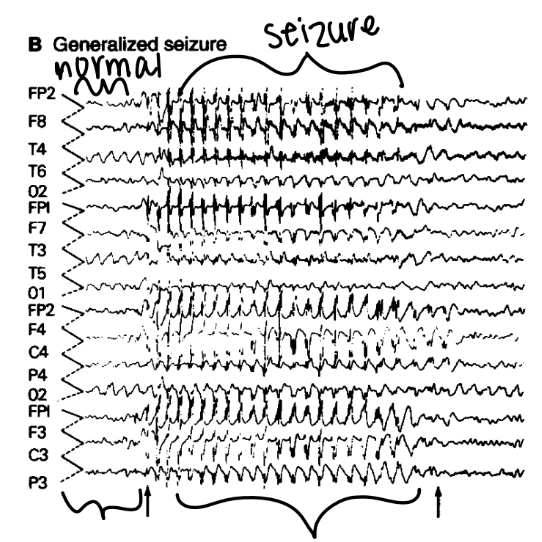
EEG
Diagnostic tool to record brain waves and find the seizure focus
Useful for determining type of seizure
Treatments for Seizure Disorder
Goal is to prevent/control seizures and risk of SUDEP:
Drugs
Ketogenic Diet
VNS
Brain surgery
Drugs for Seizure Disorder
Anti-epileptic Drugs (AEDs), don’t always work though
Ketogenic Diet
Very controlled diet high in fat, changing metabolism (Atkins or low glycemic index diets)
VNS (Vagal Nerve Stimulation)
Implanted pacemaker-like device delivering stimulation to brain via Vagus nerve
Surgeries for Seizure Disorder
Remove focus (small site to entire hemisphere)
Cut corpus callosum to prevent spread from 1 hemisphere to the other
Seizure Precautions
Driving, swimming, alcohol should be limited
Helmets - protective reflex doesn’t work