Resting and Active Membrane Potentials
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
How does potassium play a role in creating the resting membrane potential?
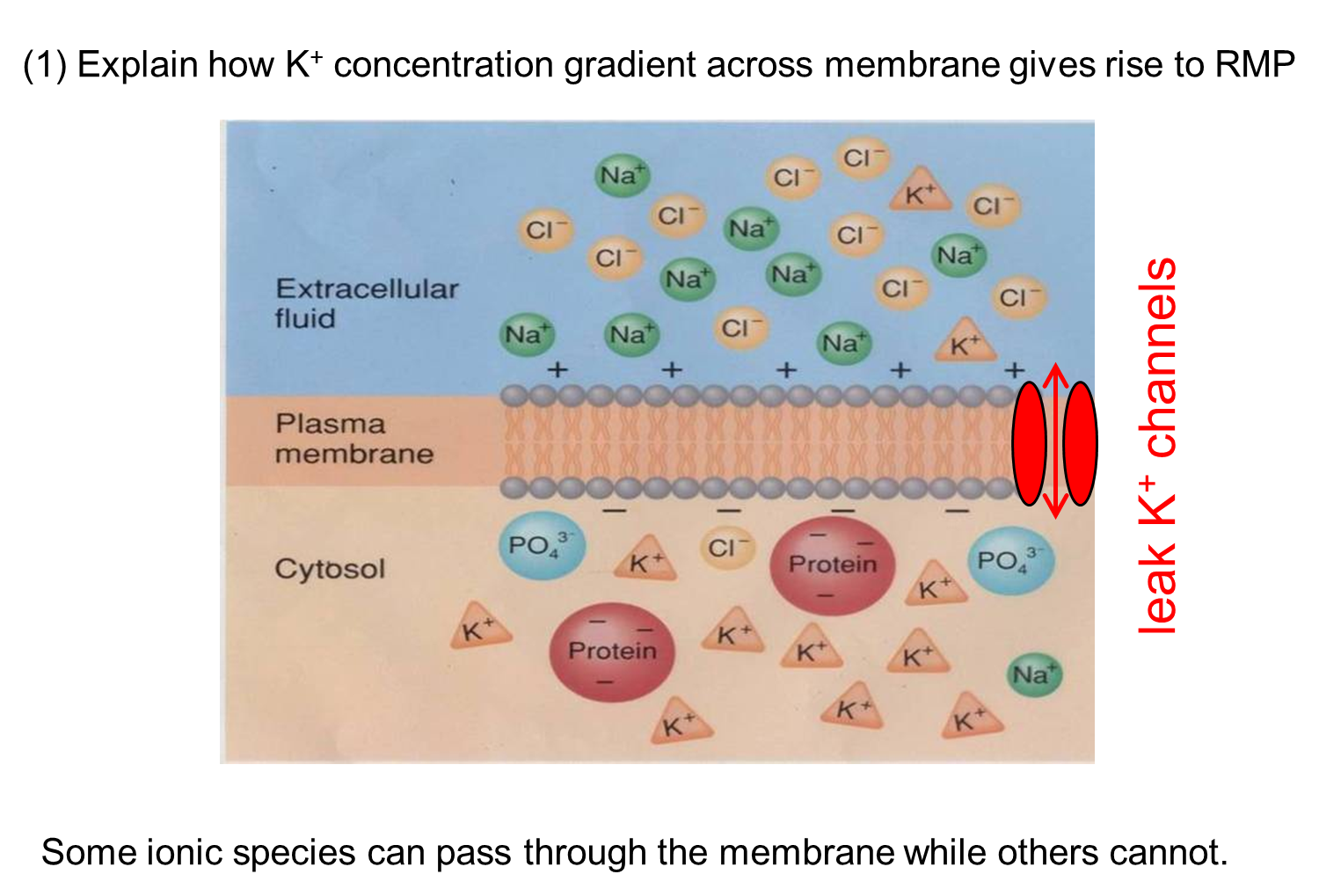
The membrane contains potassium leak channels that create a gradient of potassium
1) There is more potassium on the inside of the cell than the outside, generating a potential difference of around 60 mV
2) This resting membrane potential is calculated based on the Nernst Equation assuming there is no net movement of ions
How is the Resting Membrane Potential calculated? What ion determines this?
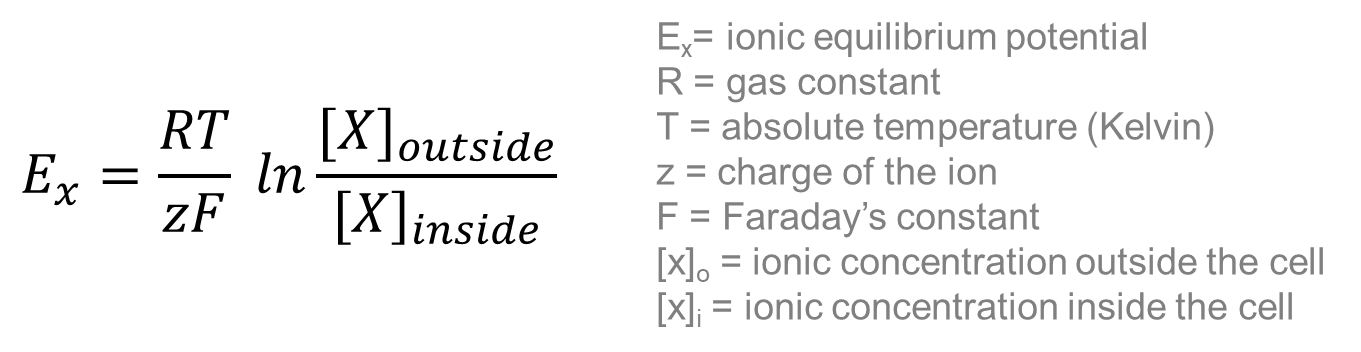
The above equation is the Nernst Equation which uses the potassium concentration inside and outside the cell in order to estimate the resting membrane potential
1) The more potassium on the outside, the more positive the resting membrane potential
→ when there is less potassium on the outside, there is a more negative resting membrane potential
2) Basically as the ions start to balance across the membrane, the RMP will become less negative
What is the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation?

GHK Equation is a modified version of the Nernst Equation that takes into account the permeability of other ions aside from potassium such as sodium and chloride
1) importantly, the concentration of chloride inside is on the same side as the outside due to the fact that it has a negative valence
What controls the slow leakage of sodium and potassium?
Sodium slowly leaks into the cell while potassium slowly leaks out of the cell
→ this is compensated for by the Na/K+ ATPase (3 Sodium Out, 2 Potassium in)
What are the phases of an action potential?
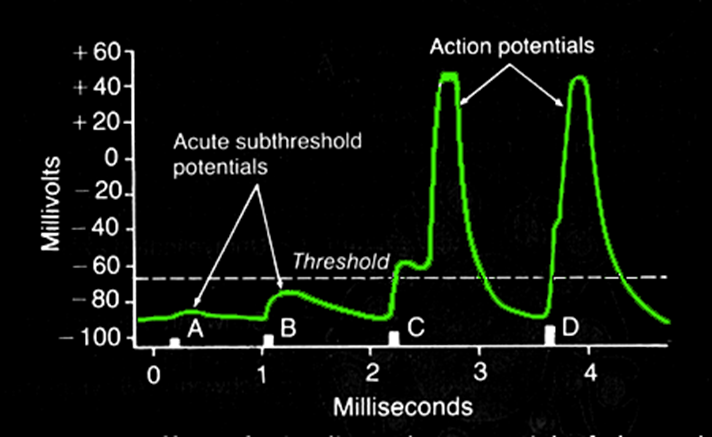
1) Resting Membrane Potential
→ set around -60
→ when a threshold is reached triggers depolarization of the membrane
2) Depolarization
→ membrane becomes more permeable to sodium, causing membrane potential to become more positive
→ controlled by voltage-gated sodium channels which open fast and temporarily inactivate
3) Repolarization
→ Membrane becomes more permeable to potassium than sodium, making the membrane more negative
→ controlled by voltage-gated potassium channels which open slowly
4) Refractory Period
→ immediately during repolarization, no other depolarization can occur absolute refractory period
→ during hyperpolarization, there is a relative refractory period where you need a larger than normal stimulus
What does it mean that a membrane is a capacitor?
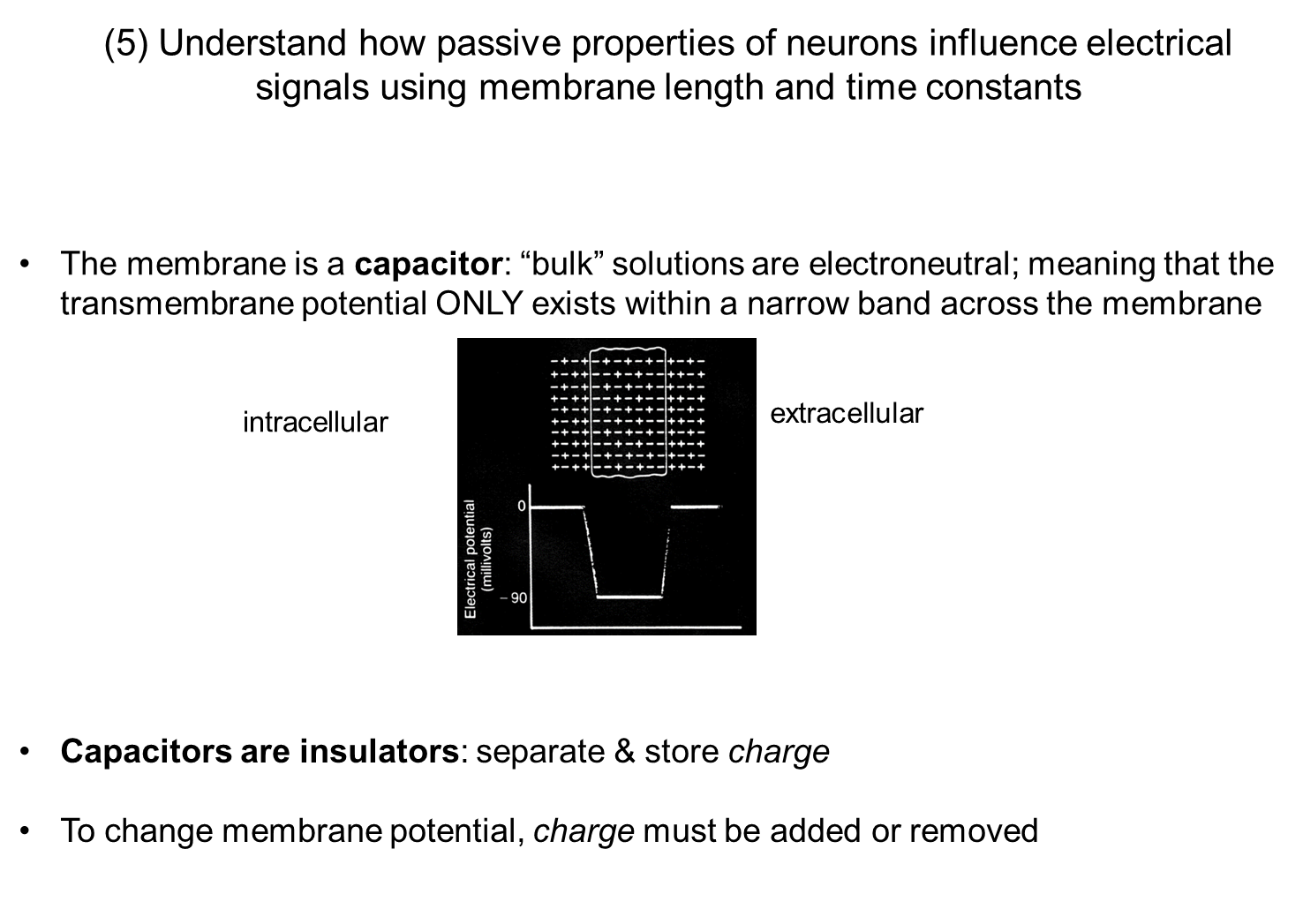
Capacitors are devices that store electrical energy by accumulating charges on either side of a surface
→ membranes act similarly by separating and storing charge
What is the membrane length constant?
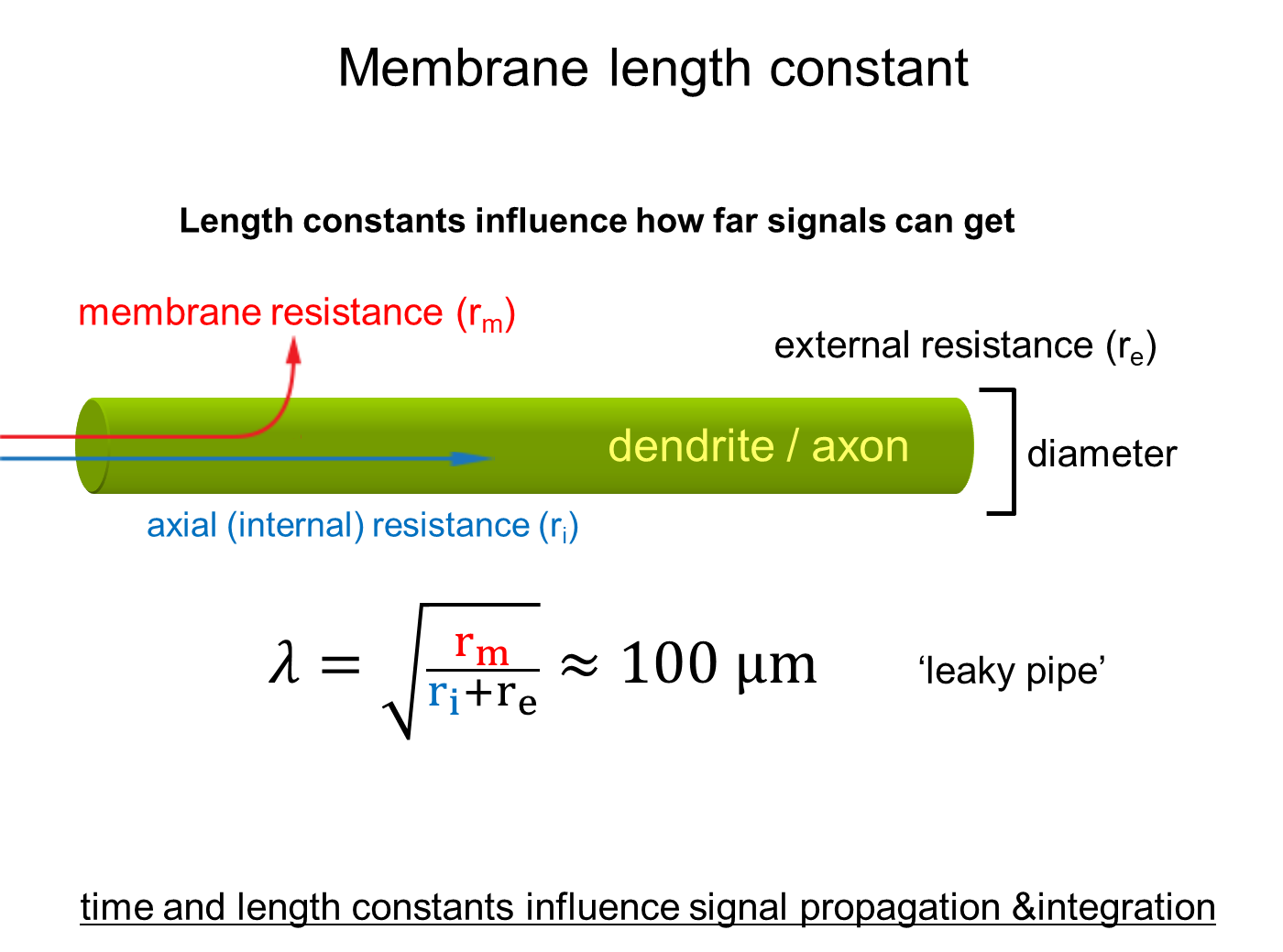
The membrane length constant is the distance along an axon where a voltage signal decays to 37 percent of its original value
1) Determined by three factors, membrane resistance, axial resistance, and external resistance
→ the leakier the axon, the shorter the distance the signal can go
What is the membrane time constant
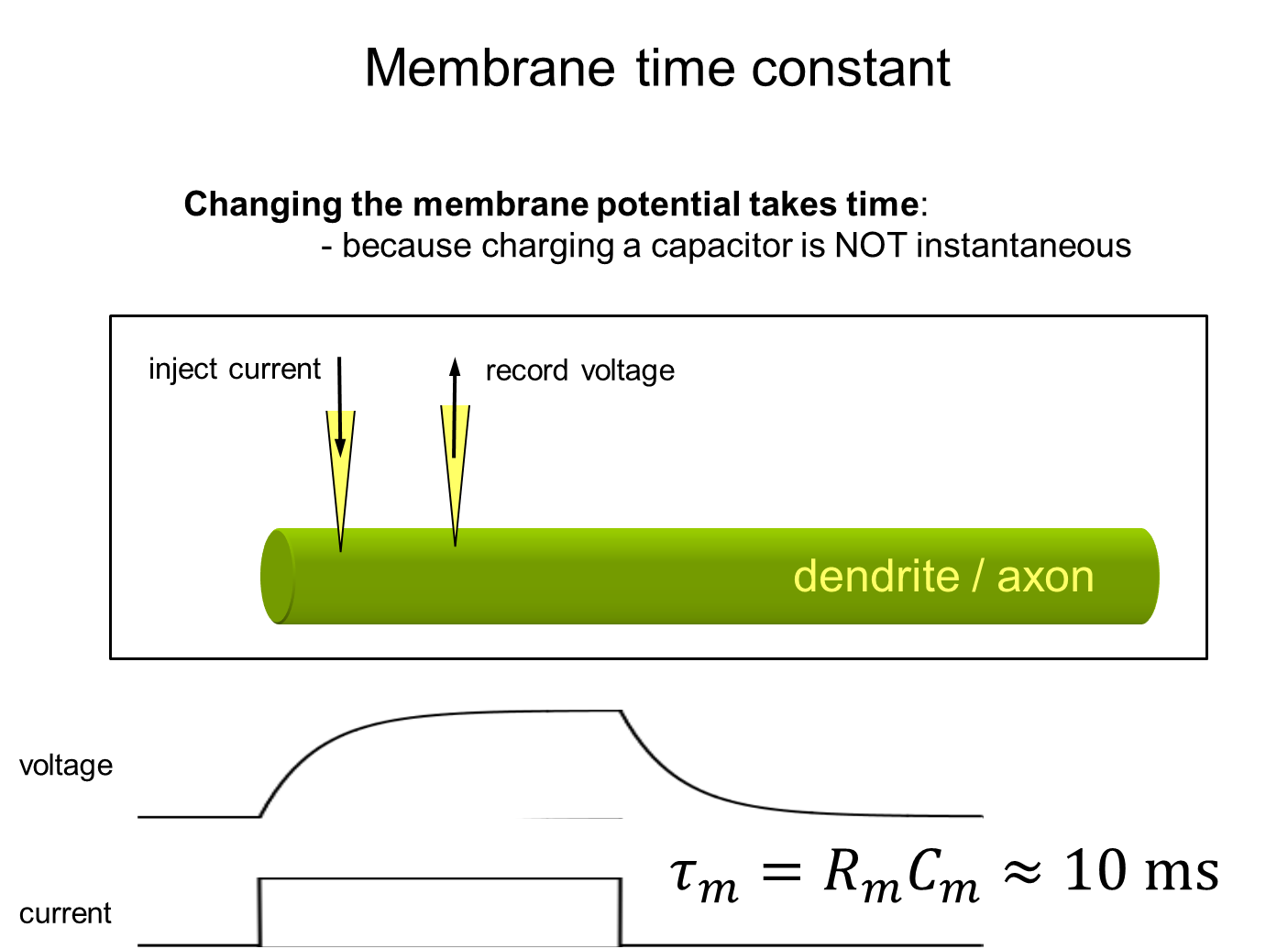
Constant that describes how quickly membrane potential responds to changes in input
→ time it takes for membrane potential to change from its starting value in response to an input
1) Based on membrane resistance times membrane capacitance
→ so, if either capacitance or resistance is higher, the longer the time it will take for a signal to reach point A to point B
What is the purpose of myelination and Nodes of Ranvier?
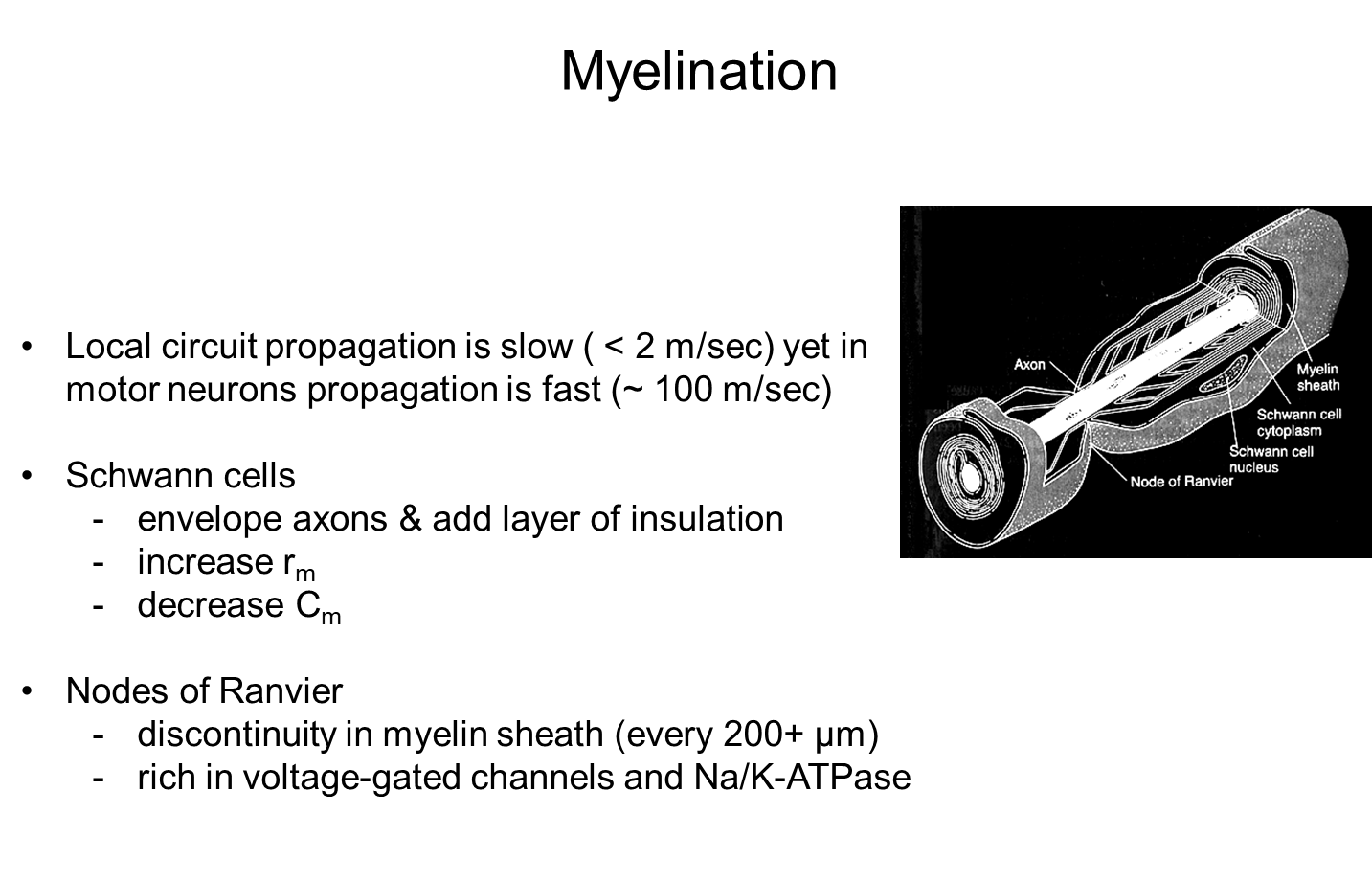

Schwann cell envelope the axons and add layers of insulation known as myelination increasing membrane resistance while decreasing membrane capacitance
1) By changing these properties, the membrane length constant increases and the membrane time constant decreases creating faster propagation
→ the thicker the myelin the faster the axon
2) there are gaps in the myelination known as Nodes of Ranvier which are rice in voltage gated Na/K ATPases
→ These spots are where the action potentials are generated
3) this system creates a axon where action potentials are generated at the Nodes and flow rapidly in between
→ known as saltatory conduction
What property of channels leads to one way conduction of action potentials
During the refractory period in areas of the membrane behind propagation, sodium channels are inactivated
→ this allows for one way conduction