Fluoro Part 1: UGI/Esophagus
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Accessory Glands
Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder and pancreas; secrete digestive enzymes into alimentary canal
Alimentary Canal
Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon) and anus
Uvula
Center of soft palate
Mastication
Chewing
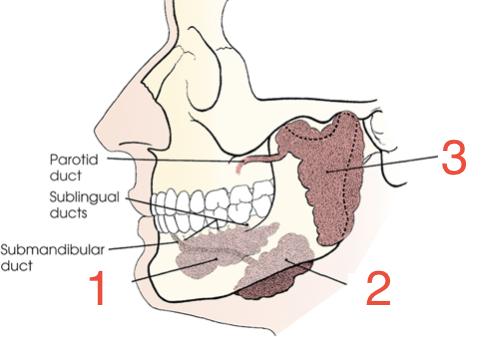
1?
Sublingual gland
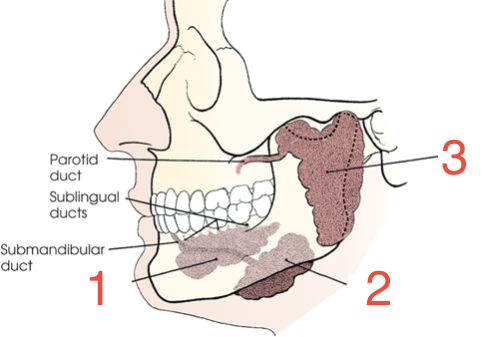
2?
Submandibular gland
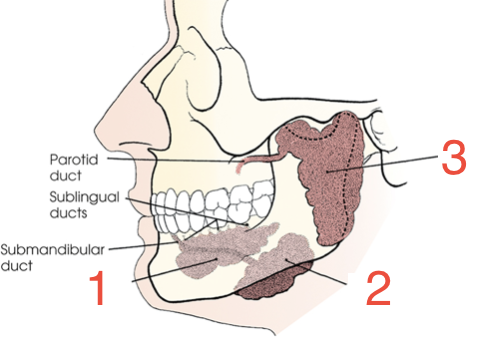
3?
Parotid gland
Pharynx
Passageway for air and food; extends from portions of sphenoid/occipital bones to C6-C7
Nasopharynx
Above hard/soft palates
Oropharynx
Extends from soft palate to hyoid bone
Laryngeal Pharynx
Posterior to larynx; extends inferior to esophagus
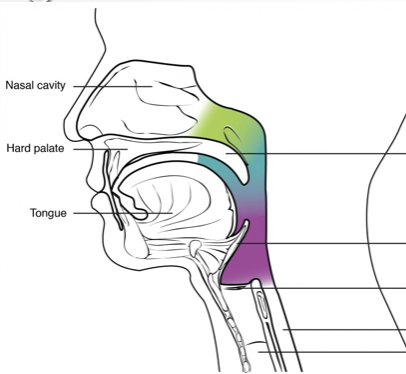
Green?
Nasopharynx
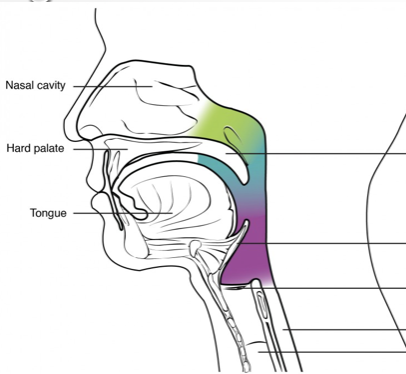
Blue?
Oropharynx
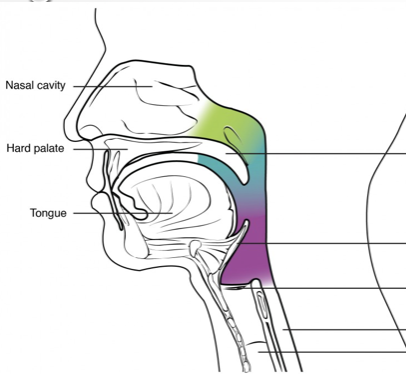
Purple?
Laryngeal pharynx
Larynx
Organ of voice; air passage between pharynx and trachea
Epiglottis
Serves as trap to prevent leakage into larynx between acts of swallowing
Piriformis Recess
Each side of larynx; visualized on AP projections of esophagus study when puffing cheeks with air
Esophagus
Runs C6-T11 (cardiac opening of stomach); 4 layers, anterior to spine, posterior to trachea and lies in midsagittal plane
Esophageal Hiatus
Passes through diaphragm around T10
Esophagogastric Junction
Joins the stomach around T11; opening is called the cardiac orifice
Cardiac Antrum
Wide, distal end of esophagus; lies in abdomen
Upper Esophageal Sphincter (UES)
Junction with pharynx; prevents air from entering esophagus during respiration
Lower Esophageal Spincter (LES)
Relaxes to allow food to pass into the stomach; closes to prevent stomach acid and digestive juices from flowing back into the esophagus
Stomach
Storage area for food until digested; acids, enzymes and chemicals are secreted to break down food chemically, mechanically broken down by churning (peristalsis)
Chyme
Mechanically and chemically broken down food in stomach to duodenum
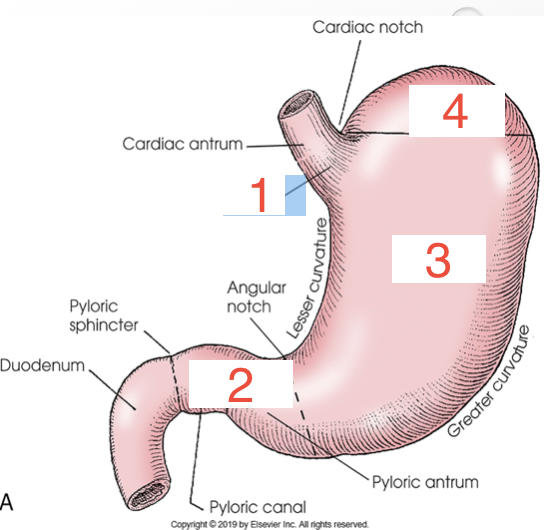
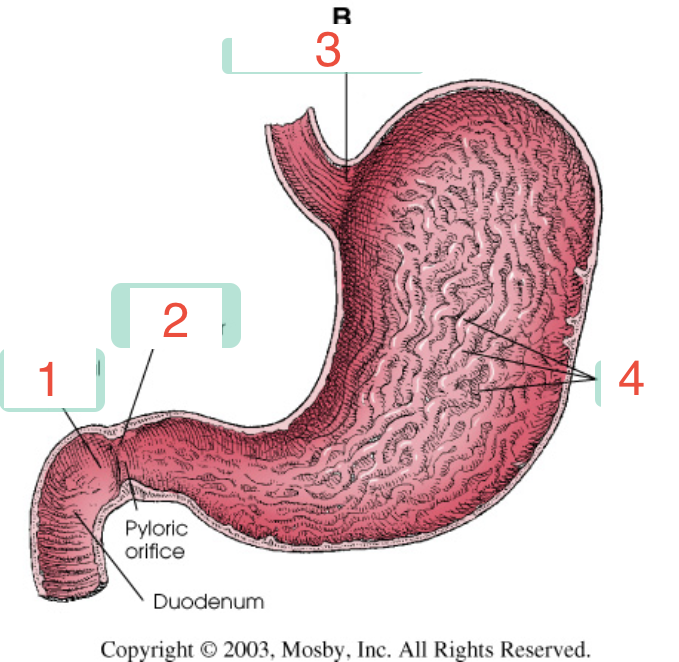
1?
Cardia
2?
Pylorus
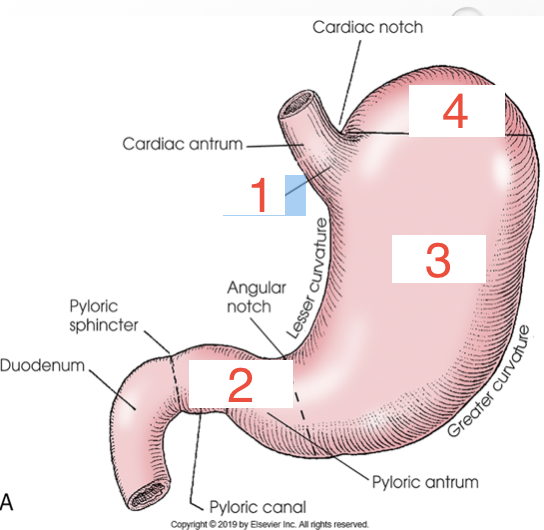
3?
Body
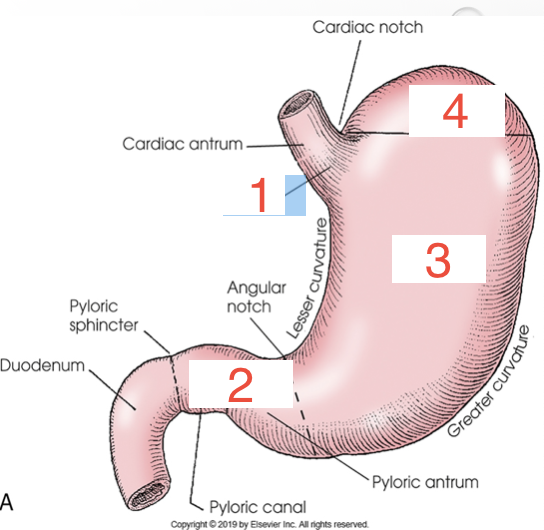
4?
Fundus
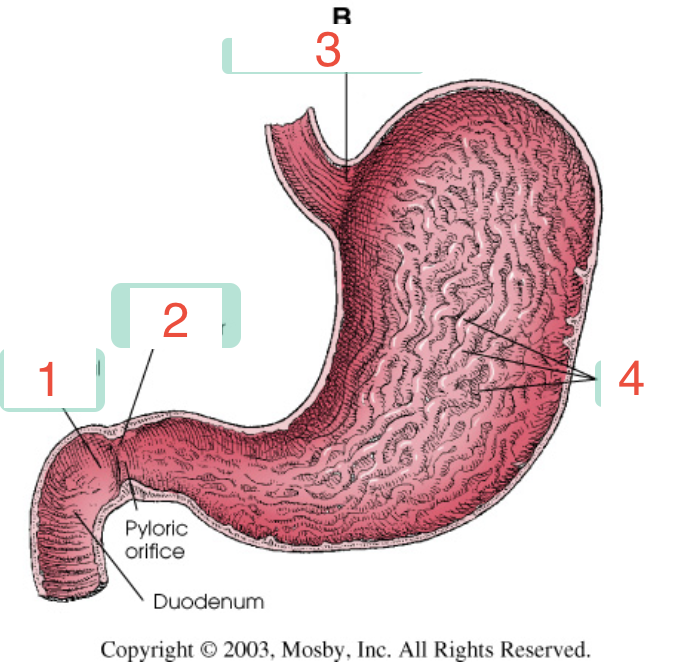
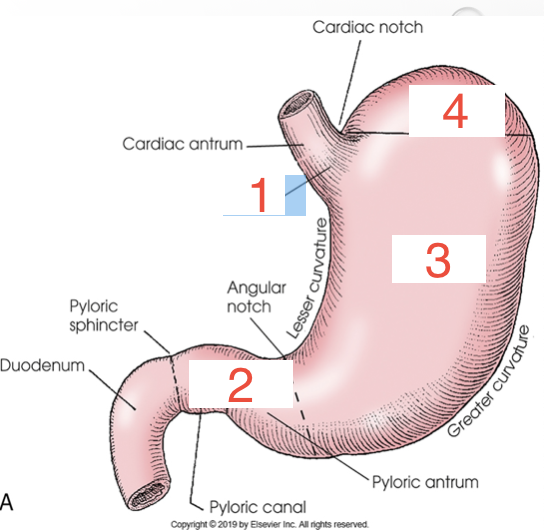
1?
Duodenal bulb
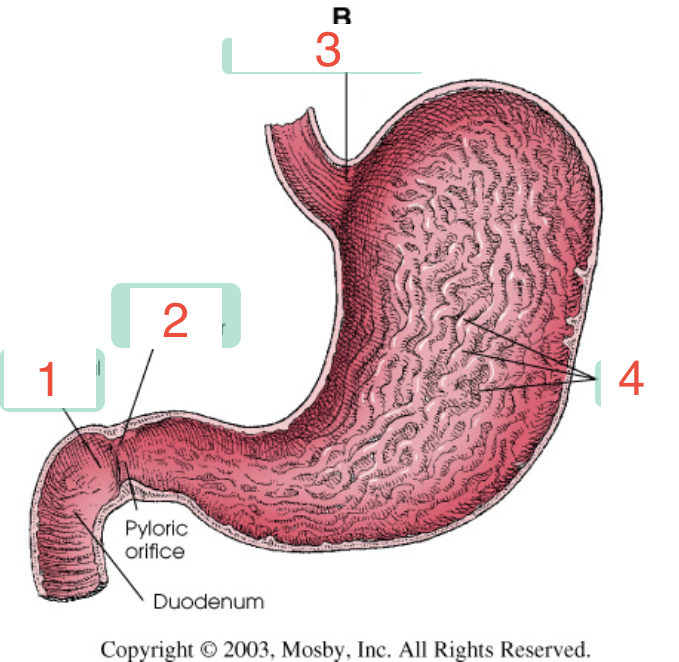
2?
Pyloric sphincter
3?
Cardiac sphincter
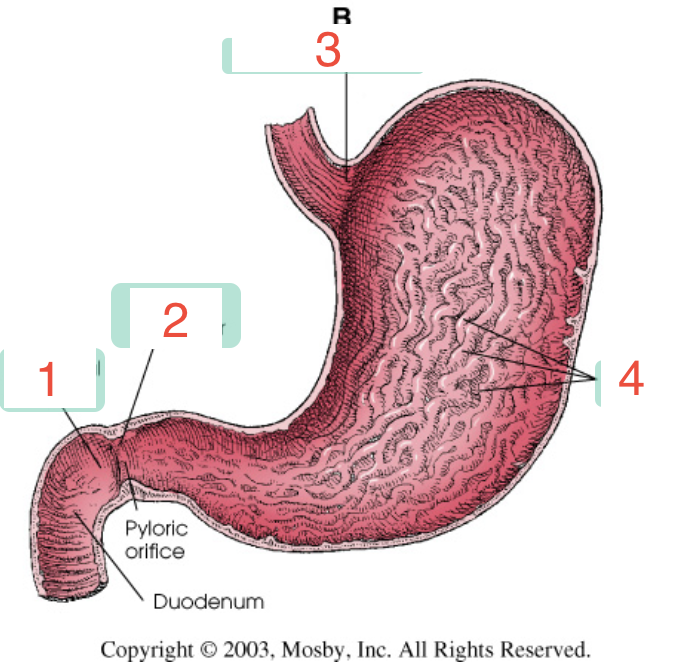
4?
Rugae
Hypersthenic
Sthenic
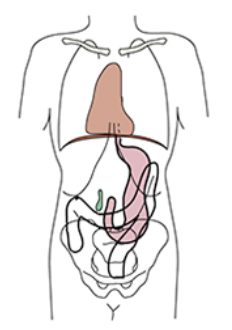
Hyposthenic
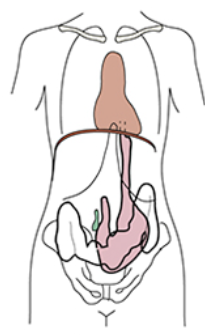
Asthenic
Around what level does the pylorus and duodenal bulb lie on a hypersthenic patient?
T11-12
Around what level does the pylorus and duodenal bulb lie on a sthenic patient?
L2
Around what level does the pylorus and duodenal bulb lie on a hyposthenic/asthenic patient?
L3-4
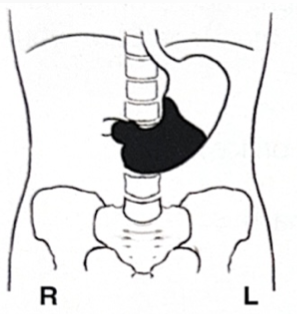
White is barium: what position is the patient in?
Supine
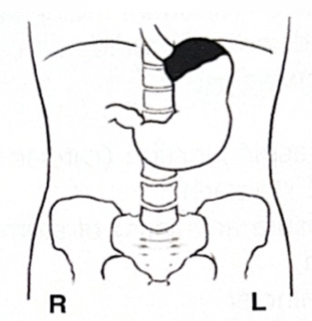
White is barium: what position is the patient in?
Prone
White is barium: what position is the patient in?
Erect
Federal regulations tabletop exposure rates should not exceed ________ mGy per minute
88
SSD Fixed Fluoro
15 in (38 cm)
SSD Mobile Fluoro
12 in (30 cm)
Purpose of Contrast
Better anatomic definition and to assess function
Positive Contrast Agents
Barium sulfate and iodinated contrast (omnipaque or gastrografin)
Negative Contrast Agents
Air; EZ Gas, CO2, O2
What age do you use thick barium?
12+
Single Contrast Study
One type of contrast used; typically barium, shows overall function/motility of body part
Double Contrast Study
Two types of contrast used; typically barium (+) and air (-), shows both function/motility and more detail of the organ
What study requires no patient prep?
Esophagus
How long must a patient be NPO before studies?
Typically 8 hours
When is a scout image done?
When a patient had to prep their body prior to the exam
RAO Esophagus Obliquity
35-40 degrees
RAO Esophagus Collimation
12×17
RAO Esophagus: If esophagus is over the spine what positioning error occured?
Under obliqued
RAO Esophagus: If esophagus is over the heart what positioning error occured?
Over obliqued
What does a PA UGI best visualize?
Body of stomach, medial and lateral margains
PA UGI collimation
14×17
What does a right lateral UGI best visualize?
Retrogastric area and duodenal loop in profile, anterior and posterior margains
Right lateral UGI collimation
11×14
PA oblique UGI obliquity
RAO 40-70 degrees
What does a PA oblique stomach UGI best visualize?
Duodenal bulb filled with barium
Reflux
Stomach contents leak backwards from the stomach into the esophagus
Esophagitis
Inflammation of the esophagus
Reflux esophagitis
Most common type; Occurs when acids and digestive agents escape your stomach and reflux into your esophagus irritating and eroding the mucous lining
Drug-induced esophagitis
Also called “pill esophagitis”; Occurs when medications lodge into the esophagus, dissolve there and cause ulcers, inflammation and other damage to the esophageal line
Infectious esophagitis
Occurs due to fungal and viral infections most common in esophagus, yet rare
Eosinophilic esophagitis
Types of overreactions of the immune system (too many WBCs)
Barrett’s Esophagus
Cell lining of the lower esophagus is replaced by columnar epithelium due to repeated exposure to stomach acid, occurs after a lot of reflux, associated with cancer and will typically have a hiatal hernia; appears as a “ringed” esophagus
Achalasia
Inability of the lower esophageal sphincter to open and let food pass into the stomach; Rat tail or beak-like appearance
Diverticula
Outpouching of the lining in weakened spots of the GI tract
Killian-Jamieson
Diverticula located on anterolateral wall of upper esophagus below cricopharyngeal muscle
Zenker's
Diverticula located in posterior wall of upper esophagus above the cricopharyngeal muscle
Esophageal Varices
Dilated veins in the wall of the esophagus; normal blood flow to the liver is blocked, one of the most common causes of GI bleeds; Appears as a wavy border with thickened folds
Perforation
Hole or punctured area
Mallory-Weiss tear
Split in the inner layer of your esophagus caused by forceful vomiting or straining
Gastritis
Inflammation of the mucous lining of stomach; thickened gastric folds
Gastric Ulcer
Also called peptic ulcer; localized area of erosion in the stomach lining from acid eating through protective lining of stomach
Hiatal Hernia
Portion of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm and up into the chest
Pyloric Stenosis
Infant's pylorus muscles thicken and narrows; food unable to pass through
Diabetic Neuropathy
A type of nerve damage that can happen with diabetes; most often damages nerves in the legs and feet, slow emptying stomach on UGI
Esophagus RAO technique
120 kVp, center cell (6 mAs)
UGI single contrast images
Scout, PA, RAO, Right lateral
UGI double contrast images
Scout, PA, Right lateral
Scout image technique
90 kVp, all cells (10 mAs)
UGI PA and right lateral single contrast technique
120 kVp, center cell (5 mAs)
UGI PA and right lateral double contrast technique
90 kVp, center cell (5 mAs)
UGI RAO single contrast technique
120 kVp, center cell (7.5 mAs)