Understanding the U.S. Legislative and Executive Branches
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
Articles of Confederation
Early US governing document with weak central authority.
The Great Compromise
Established a bicameral legislature combining Virginia and New Jersey Plans.
Connecticut Compromise
Another name for The Great Compromise.
Bicameral Legislature
Legislative body with two chambers: House and Senate.
Upper House
Senate with equal representation: 2 members per state.
Lower House
House of Representatives with population-based representation.
3/5 Compromise
Counted enslaved individuals as 3/5 for representation.
14th Amendment
Grants citizenship and equal protection under the law.
Congressional Prerogatives
Specific powers granted to Congress by the Constitution.
Authority to Tax
Power of Congress to levy taxes on citizens.
Borrow and Coin Money
Congress's power to manage national currency.
Operate Postal Service
Congress manages postal operations across the nation.
Declare War
Congress's exclusive power to initiate military conflict.
Raise and Support Armies
Congress can create and fund military forces.
Suppress Insurrections
Authority to quell rebellions and maintain order.
Build a Capital City
Congress responsible for establishing the nation's capital.
Making Laws
Congress's role in creating and approving legislation.
Veto Override
Requires 2/3 majority to override a presidential veto.
Treaty Approval
Requires 2/3 majority in Senate for treaty ratification.
Single-Member Districts
Each district elects one representative to Congress.
Plurality Rule
Candidate with most votes wins, not necessarily majority.
Proportional Representation
Seats allocated based on percentage of votes received.
Primary elections
Elections to select party candidates for general elections.
District boundaries
Geographical lines defining electoral districts.
Gerrymandering
Manipulating district boundaries for political advantage.
Trustee
Legislator making decisions based on personal views.
Delegate
Legislator voting based on constituents' feedback.
Constituency service
Assistance provided to constituents by Congress members.
Incumbency advantage
Benefits current officeholders have over challengers.
Pork-barrel bills
Spending benefiting a narrow constituency for political support.
Party discipline
Pressure on members to support party leadership's bills.
Speaker of the House
Constitutionally designated leader of the House of Representatives.
Reed's rules
Guidelines for committee assignments and legislative order.
Majority leader
Head of the party with the most congressional seats.
Whip
Party member coordinating votes and enforcing discipline.
Standing committees
Permanent committees handling specific policy areas.
Special committees
Temporary committees for specific investigations or issues.
Conference committees
Joint committees resolving differences between House and Senate bills.
Committee membership
Assignment of Congress members based on interests and expertise.
Electoral factors
Various influences affecting election outcomes.
Internal institutions
Structures within Congress managing legislative processes.
Legislative Branch
Branch of government responsible for making laws.
Committee System
Divides congressional work among multiple groups.
Caucuses
Legislators unite to promote specific agendas.
Congressional Staff
Personnel assisting legislators in various functions.
Research Services
Provide information and analysis for legislative decisions.
Proposals
Initial suggestions for new laws by Congress members.
Referrals
Assigning bills to specific committees based on topic.
Committee Action
Committees review, amend, and recommend bills.
Moving Bills to the Floor
Process of bringing bills for full legislative debate.
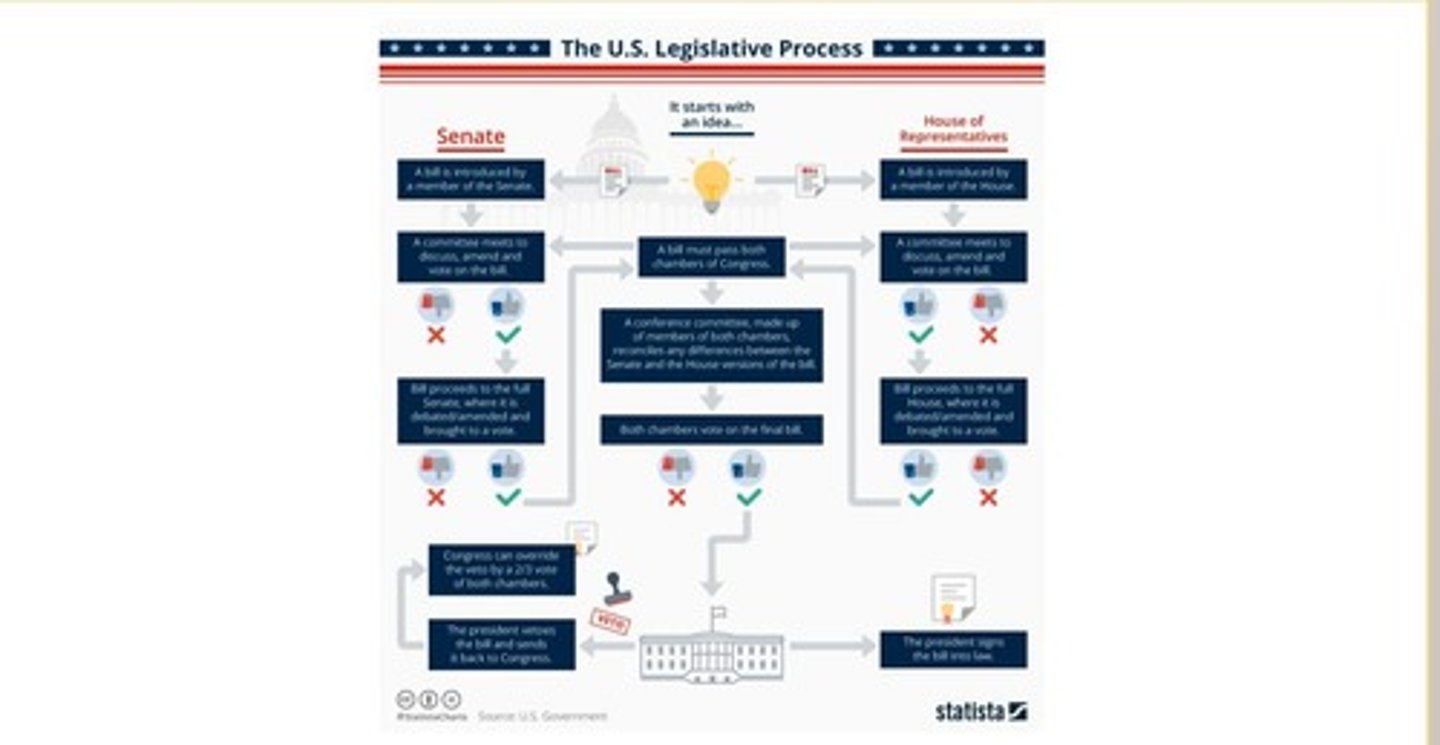
Senate Distinctiveness
Unique procedural rules governing Senate operations.
Floor Action
Debate and voting on bills by the full chamber.
Presidential Signature
Final approval needed for a bill to become law.
Tax Bills
Must originate in the House of Representatives.
Bill Proposals
Over 9000 introduced annually in Congress.
Split Referral
Allows dividing a bill into sections for committees.
Mark-up
Editing and amending process for bills in committees.
Open Rule
Allows any amendments to be proposed on bills.
Closed Rule
No amendments permitted during bill consideration.
Restricted Rule
Limits types of amendments that can be proposed.
Unanimous Consent Agreements
Senate rules requiring all members' agreement to proceed.
Filibuster
Extended speech to delay Senate voting on a bill.
Cloture
Limits debate to a set number of hours.
Veto
President rejects a bill passed by Congress.
Pocket Veto
Bill not signed within 10 days, Congress adjourned.
Executive Branch
Carries out laws enacted by the legislature.
Judicial Branch
Evaluates laws and interprets the Constitution.
Parliamentary System
Government system where executive authority rests with prime minister.
Ceremonial Head of State
President's role in India, advised by prime minister.
Lok Sabha
Directly elected lower house of India's parliament.
Rajya Sabha
Upper house of India's parliament, limited power.
Independent Judiciary
Supreme Court interprets the Constitution in India.
Federal Structure
Union of states with defined governmental responsibilities.
First-Past-The-Post System
Electoral method for Lok Sabha elections in India.
Checks and Balances
System ensuring branches of government monitor each other.
Presidential Power
Authority derived from constitutional and informal sources.
Spoils System
Rewarding political supporters with government positions.
Divided Government
President from different party than Congress majority.
Unified Government
President from same party as Congress majority.
Bully Pulpit
President's platform to advocate for policies.
New Deal
FDR's program expanding executive power in governance.
Power to Persuade
Neustadt's view on presidential influence over command.
Informal Powers
Unwritten powers exercised through tradition or necessity.
George Washington's Inauguration
First president sworn in on April 30, 1789.
Presidential Style
Personal approach influencing effectiveness in governance.
Enumerated powers
Clearly written powers in the Constitution.
Administrative law
Law created by executive agencies refining legislation.
Veto threats
Public statement indicating intent to veto a bill.
Executive orders
Presidential instructions on executing laws.
Executive agreements
International agreements not requiring Senate approval.
Signing statements
President's interpretation attached to a bill.
White House staff
Organizes schedules and political strategies for the President.
Executive Office of the President
Permanent staff supporting the President's administration.
Impeachment
House charges official with serious misconduct.
Special prosecutors
Independent counsel investigating government officials.
Electoral pressures
Influence on officials to maintain popularity for re-election.
Parliamentary democracy
Executive elected by legislature, responsible to it.
Presidential system
Executive elected independently, not responsible to legislature.
Mixed presidential system
Executive shares responsibility with legislature.
Line-item veto
Partial veto allowing specific bill passages to be struck.