IB Biology HL - Unit A2.1: Origins of Cells
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Early Earth Conditions
Extreme conditions existed around 4 billion years ago.
Atmosphere Composition
Lacked oxygen, mainly methane and carbon dioxide.
Cause of High Temperatures in Early Earth
Volcanic activity and greenhouse gases.
UV Radiation
Intense UV radiation reached Earth's surface.
Volcanic Activity
Frequent eruptions contributed to chemical reactions.
Asteroid Bombardment
Impacts delivered materials and released energy.
Organic Molecule Formation
Carbon compounds formed under reducing conditions.
Energy Sources
Lightning, UV radiation, and volcanic heat drove reactions.
Cells
Smallest unit of self-sustaining life.
Characteristics of Life
Metabolism, reproduction, growth, and homeostasis.
Viruses
Non-living entities lacking metabolism and independent structures.
Catalysis
Simple organic molecules formed with energy input.
Self-Replication
RNA likely first molecule capable of self-replication.
Self-Assembly
Amphipathic molecules form vesicles in water.
Compartmentalization
Vesicles may have enclosed RNA and proteins.
Protocells
Primitive cells that could grow, divide, and evolve.
LUCA
Last Universal Common Ancestor of all life.
Spontaneous Origin Challenge
Difficult to observe cell origin directly today.
Reducing Conditions
Absence of oxygen favored organic molecule formation.
Chemical Reactions
Driven by environmental factors like heat and radiation.
First Living Cells
Evolved from self-assembled vesicles trapping biological molecules.
Miller-Urey Experiment
Simulated early Earth conditions to test organic molecule formation.

Amino Acids
Organic compounds formed in the Miller-Urey Experiment.
Vesicles
Membrane-bound structures formed from fatty acids.
Hydrophobic Barrier
Separates internal vesicle chemistry from external environment.
RNA
Presumed first genetic material capable of self-replication.
Ribozymes
RNA molecules that catalyze their own reactions.
Hydrothermal Vents
Proposed environment for LUCA's evolution.
Spontaneous Formation
Natural occurrence of structures from simple organic molecules.
Fatty Acids
Non-polar molecules that form micelles in water.
Micelles
Aggregates of fatty acids avoiding contact with water.
Spherical Bilayer
Structure formed by polar organic monomers and fatty acids.
Prebiotic Chemistry
Study of chemical processes leading to life formation.
Organic Molecules
Compounds essential for life, formed under early Earth conditions.
Peptide Bonds
Links formed between amino acids during protein synthesis.
Experimental Support
Evidence backing theories of life's origins.
Complex Molecules
Advanced structures arising from simpler organic precursors.
Atmospheric Composition
Uncertain makeup of early Earth's atmosphere affecting experiments.
Evolutionary Evidence
Data supporting the development of life from LUCA.
Domains of Life
Three branches: archaea, bacteria, and eukarya.
DNA
Molecule used for genetic information storage.
Enzymes
Proteins that catalyze metabolic reactions.
Lipid-based cell membrane
Structure surrounding LUCA's cells for protection.
Horizontal gene transfer
Gene exchange between organisms, not through reproduction.
Earth's age
Approximately 4.6 billion years old.
Date of First cells' evolution
Estimated between 3.5-4 billion years ago.
LUCA's estimated age
Approximately 3.5 billion years old.
Chemical evidence
Fossil-like structures indicating ancient life.
Biomarkers
Molecular fossils indicating past biological activity.
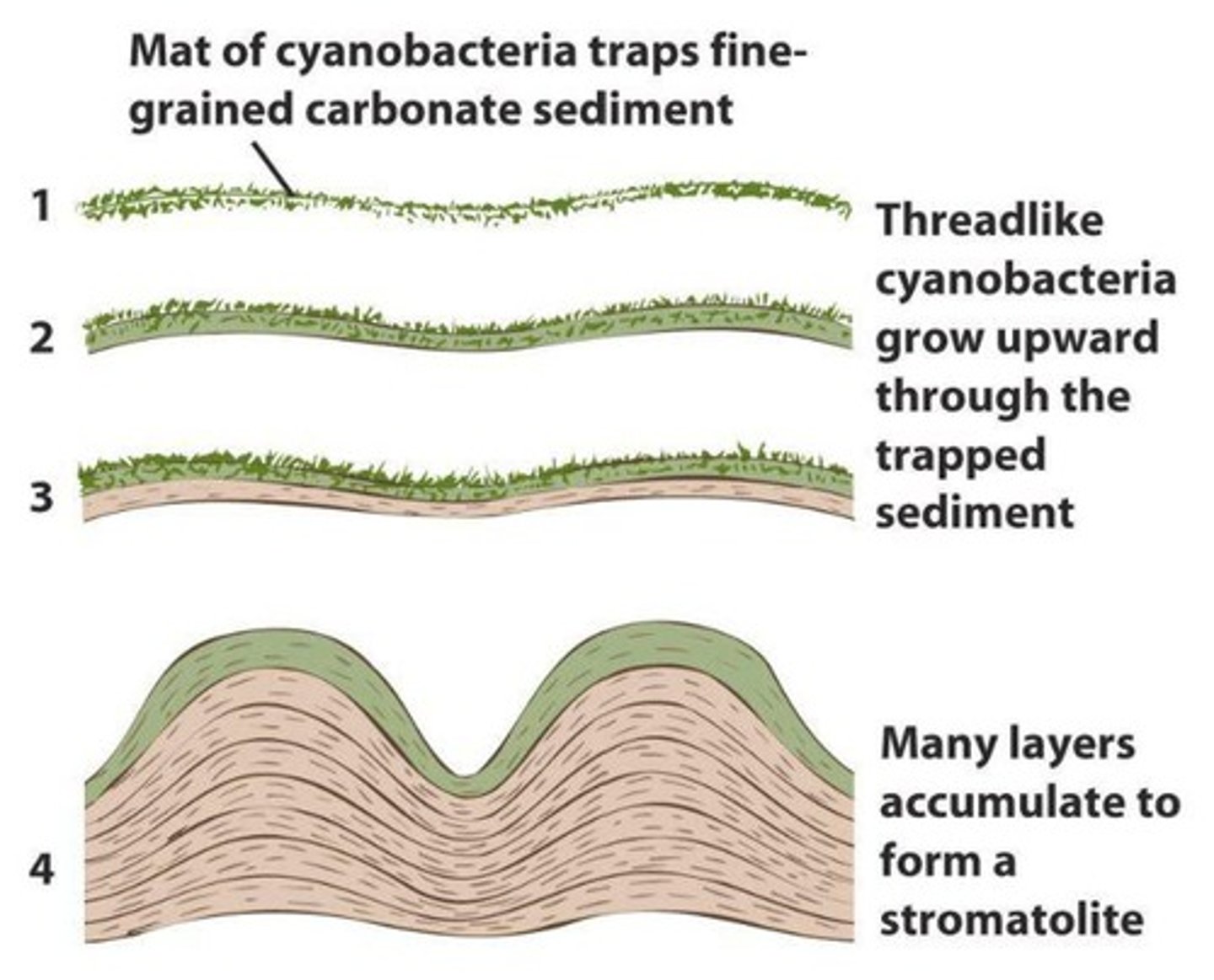
Stromatolites
Layered structures formed by photosynthetic bacteria.
Hydrothermal vents
Locations proposed for LUCA's evolution, rich in minerals.
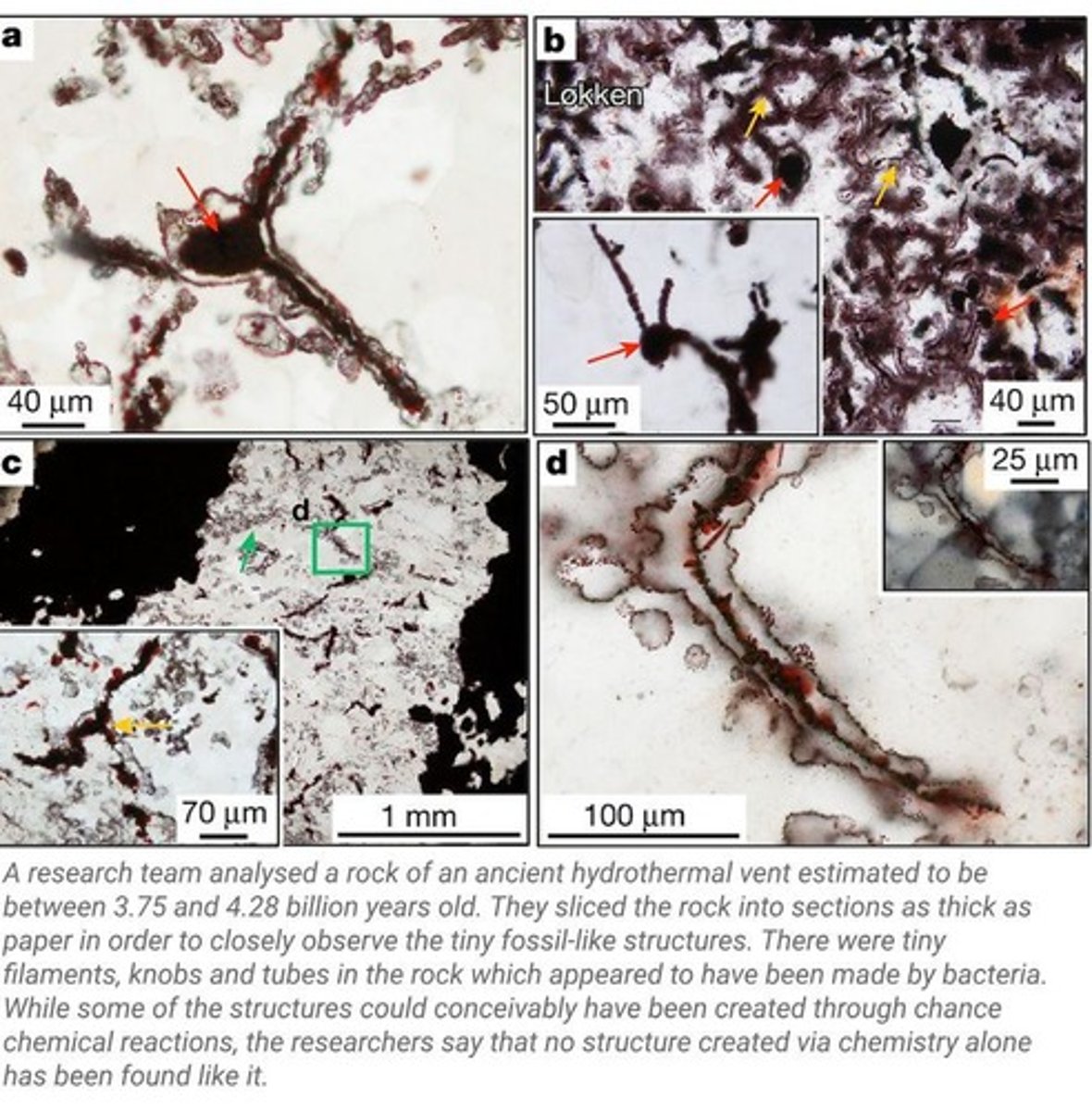
Fossil evidence
Physical remains indicating past life forms.
Genetic evidence
Comparison of genes across organisms to infer LUCA.
Obligate anaerobe
Organism that does not require oxygen for survival.
Chemoautotroph
Organism that derives energy from inorganic compounds.
Thermophile
Organism that thrives in extreme heat environments.
Effect of Recognizing 355 shared genes across all life
ancient common ancestry between bacteria and archaea.
Carbon isotopes
Chemical signatures indicating biological processes in rocks.
Sedimentary rocks
Rocks containing preserved organic compounds and biomarkers.
Fossilized stromatolites
Ancient structures formed by microbial activity.
Deep sea vents
Proposed early habitats for life on Earth.
Molecular fossils
Organic compounds preserved in geological formations.