Geography - Extreme weather hazards in the UK + climate change
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
define extreme weather
weather that is unusual, severe, or not normal for a place. it can cause threats to life and cause damage to properties
what are the 6 types of extreme weather in the UK
heavy rainfall → floods
droughts → agriculture yields can ⬇ so £ ⬆, and water rationing
strong winds → dmg to infrustructure + properties, trees fall
thunderstorms → lightning can spark fire
snow and ice → injuries due to slipping, transport disruptions (1st most deadly)
heatwaves → heatstrokes (2nd most deadly)
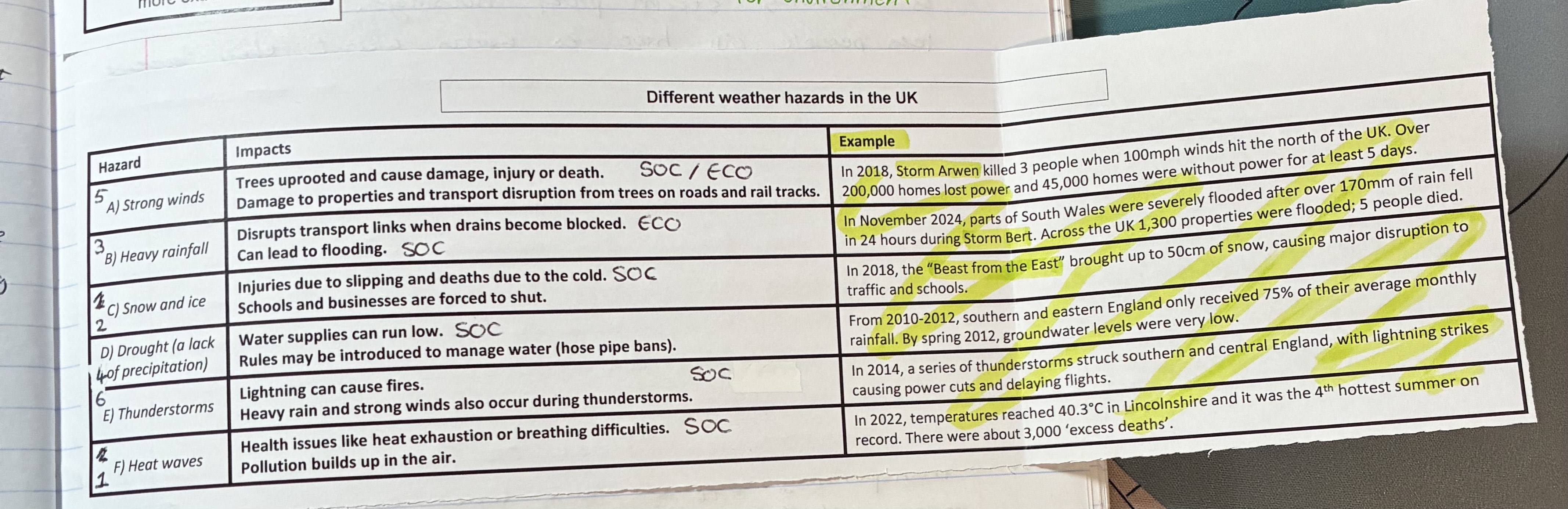
what are the impacts of strong winds, give examples
Impacts (SOC/ECO)
trees uprooted cause dmg, injury, or death
dmg to properties and transport disruption from trees on roads and rail tracks
example
storm arwen
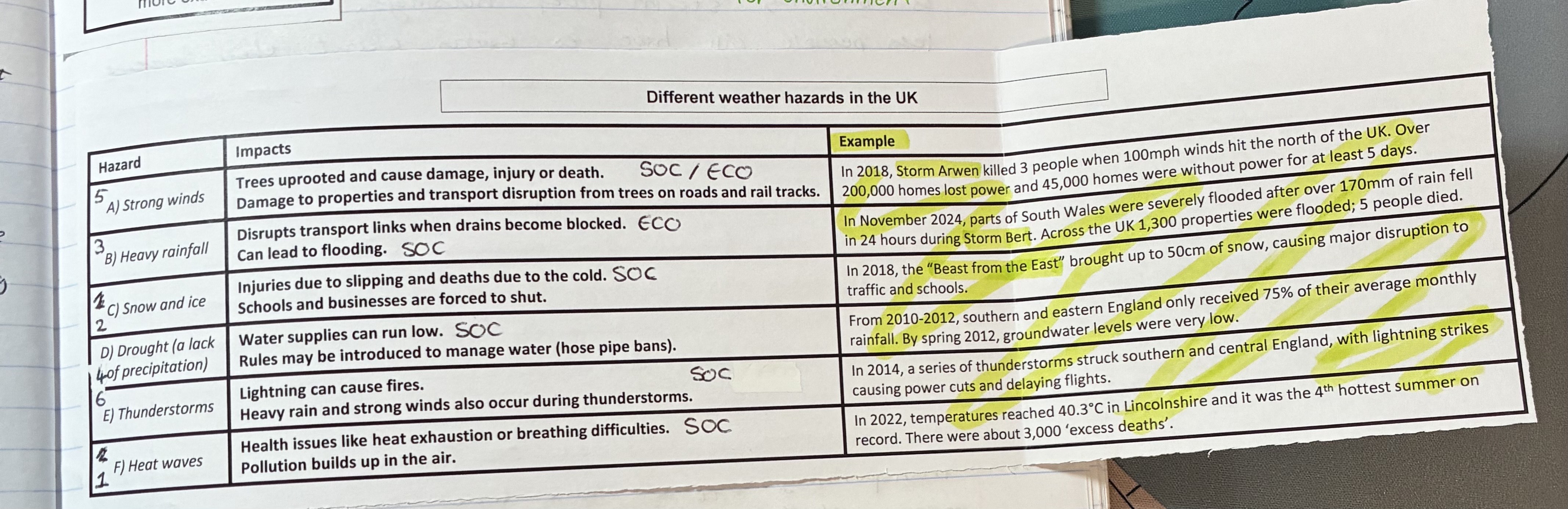
what are the impacts of heavy rainfall, give examples
impacts (ECO/SOC)
disrupts transport links when drains become blocked
can lead to flooding
example
storm Bert in south wales
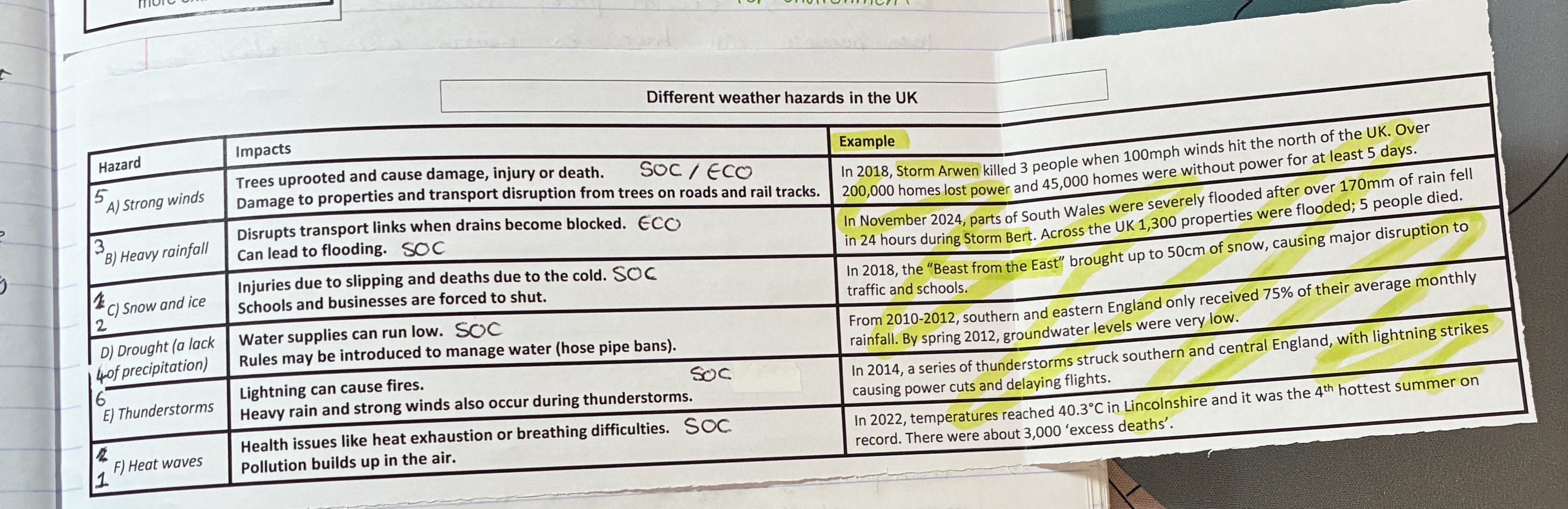
what are the impacts of snow and ice, give examples
impact (SOC)
injuries due to slipping and deaths due to cold
schools and businesses are forces to shut
example
Beast from the East in 2018
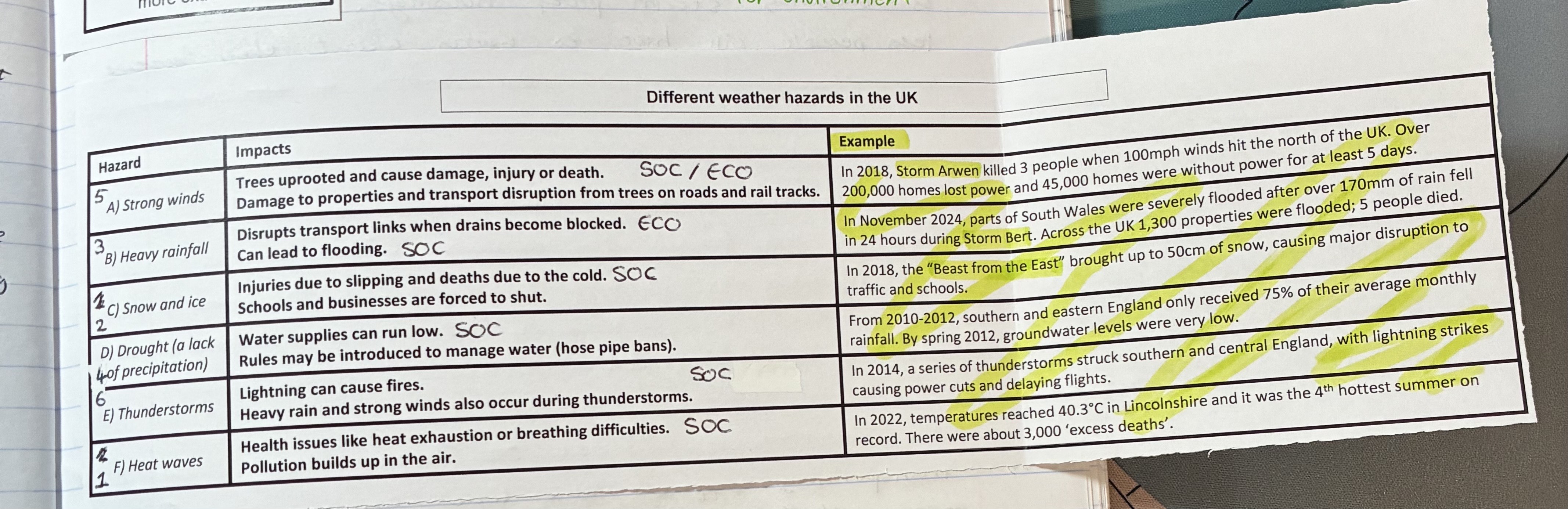
what are the impacts of droughts, give examples (
impacts (SOC)
water supplies run low
rules may be introduced to manage water
example
from 2010-2012 S + E England only received 75% of their average monthly rainfall
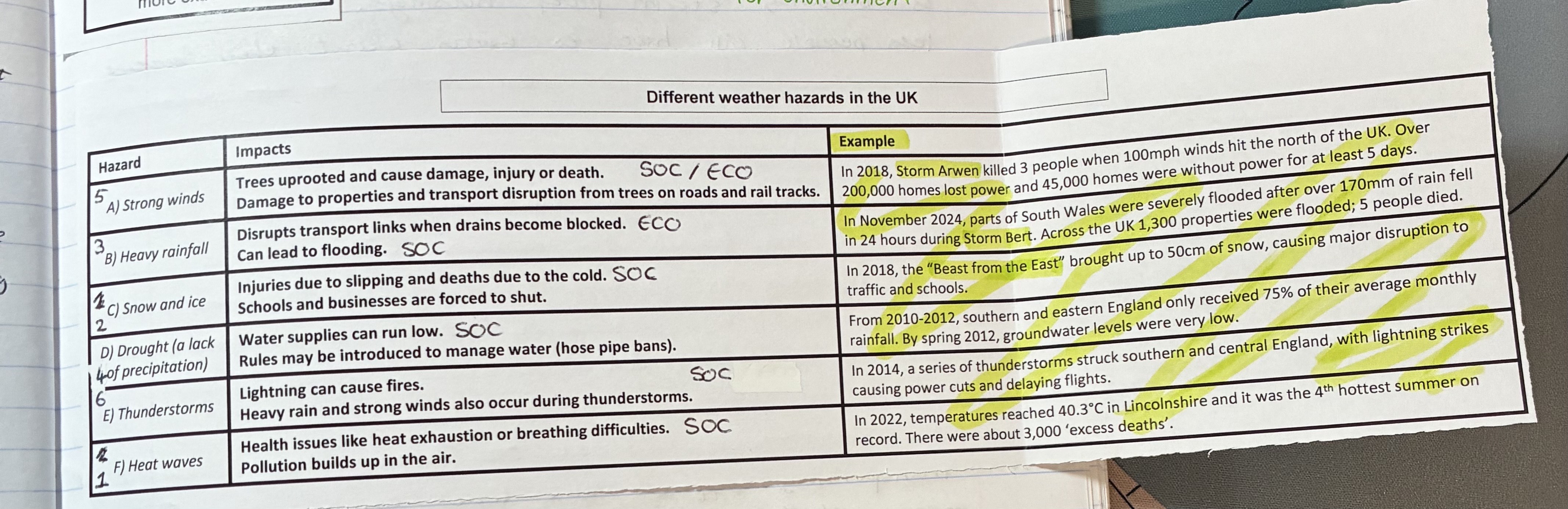
what are the impacts of thunderstorms, give examples
impacts (SOC)
Lightning can cause fires
heavy rain and strong winds also occur
example
in 2014 lightning strikes causes power cuts + delays in flights
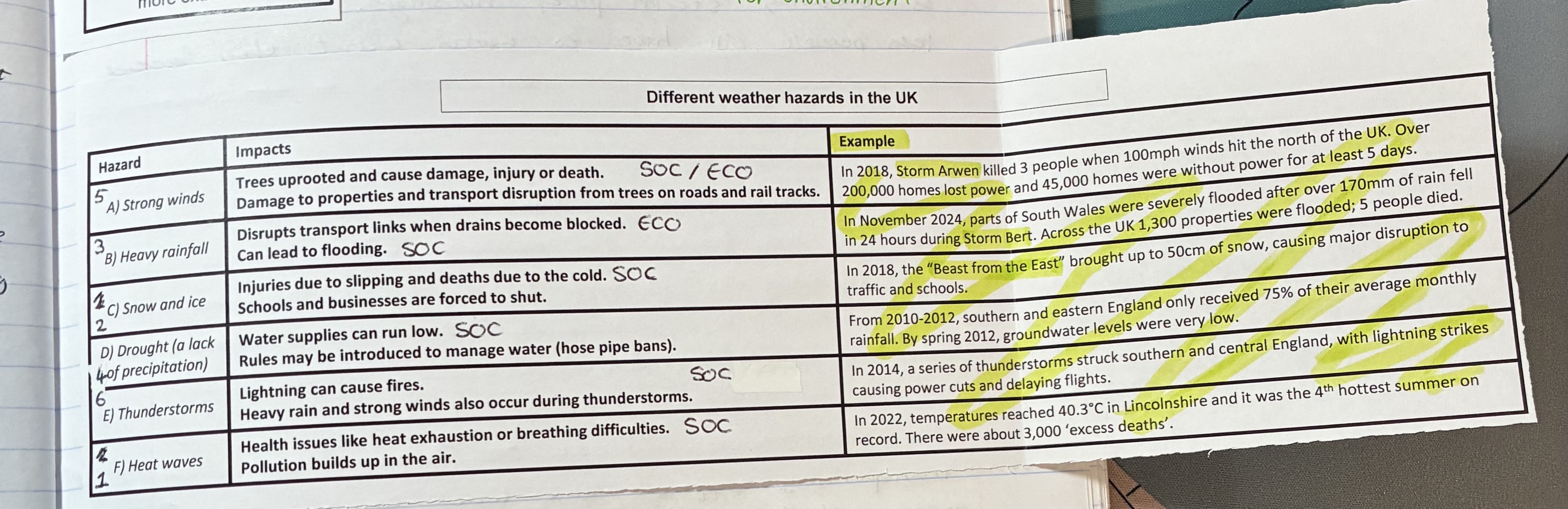
what are the impacts of heat waves, give examples
impacts (SOC)
health issues like heat exhaustion or breathing difficulties
pollution build sup in the air
example
in 2022 temps reaches up to 40.3oC in Lincolnshire
how is extreme weather in the UK changing
getting more common
floods + droughts + heatwaves + storms are more intense (except snow n ice)
rainfall in the UK in inc by 15% → flooding more frequent
what are our case study for extreme weather hazards
UK 2022 heatwave
what are the facts about the UK 2022 heatwave
UK got to 40.3oC in Lincolnshire
in Cambridge >3 days + >28oC = heatwave
with climate change UK will have more extreme hot weather
what was the cause of the 2022 UK heatwave
there was a high pressure heat dome
what were the social impacts of the 2022 UK heatwave
wildfires ( in Wennington houses got burned down)
deaths from heatwaves e.g heatstrokes
tracks get buckled in the heat → ppl late for work
what were the economic impacts of the 2022 UK heatwave
wildfires (farmers losing crops ⬇ yield)
some businesses e.g ice cream will earn more money/ hotels bc ppl go to the beach (positive)
tracks buckled in the heat → costs money to replace
what were the environmental impacts of the 2022 UK heatwave
wildfires (fire burning releases CO2)
rivers dried up → fish in the rivers die, biodiversity ⬇ / birds can die bc can’t find water
what were the short term responses to the 2022 UK heatwave
met office issues “red warning” on the 15th July
what were the long term responses to the 2022 UK heatwave
building heatproof buildings e.g planting plants on buildings + shutters on windows
fountains (sprays water vapour) in cities e.g London
painting roofs + roads white (absorbs less heat, reflects light)
what are the facts about the excess deaths in the 2022 UK heatwave
there was 1134 excess deaths
temp at night barely exceeds below 27oC
the 3 potential causes of death are: dehydration, heatstroke, overheating
3 groups at risk are” infants, old people, homeless
What impact does droughts have during the 2022 UK heatwave
Drought orders are made to allow water companies to take actions such as banning the use of hosepipes (SOC impact)
what does quaternary mean
the last 2.6 million years
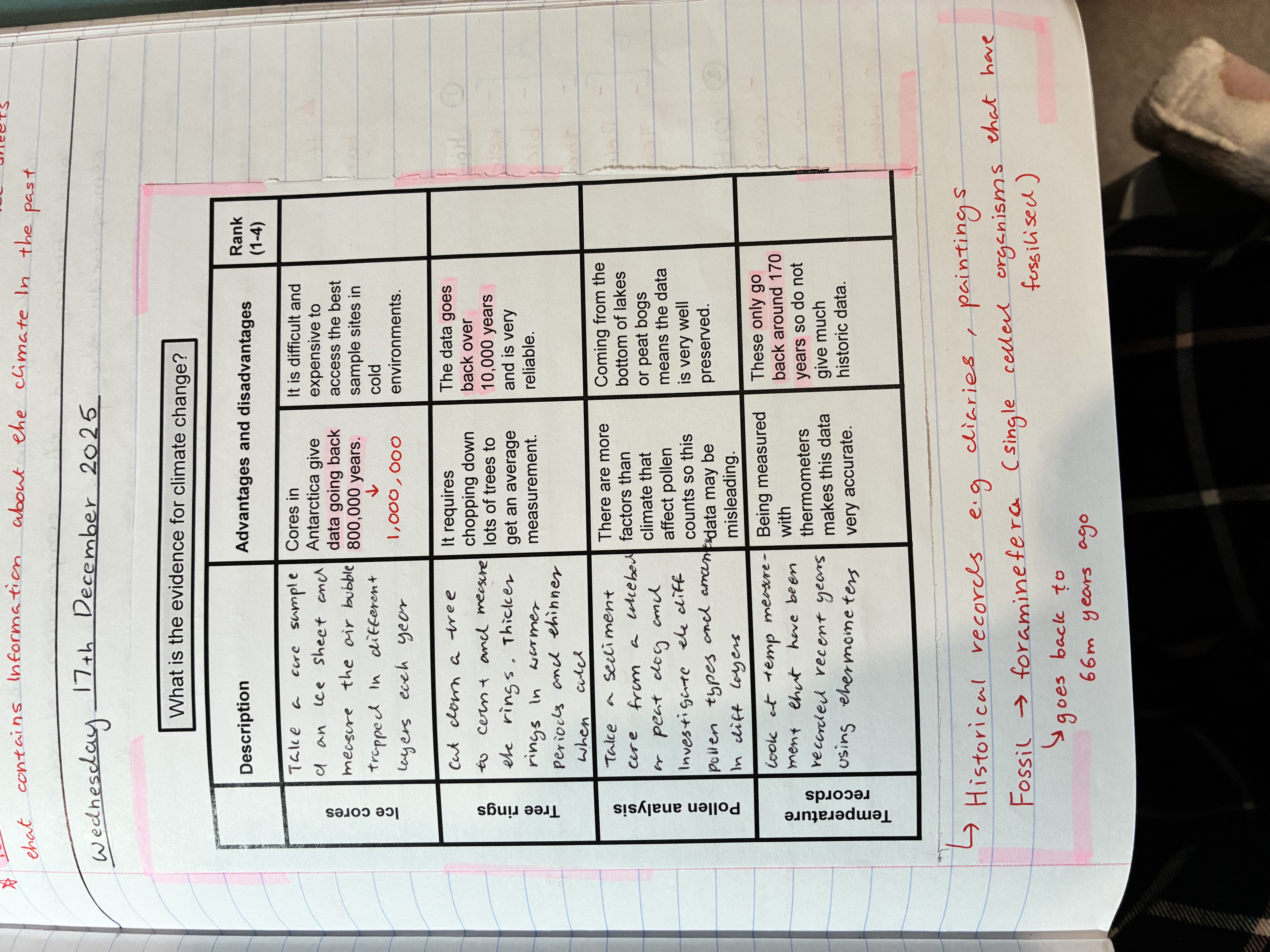
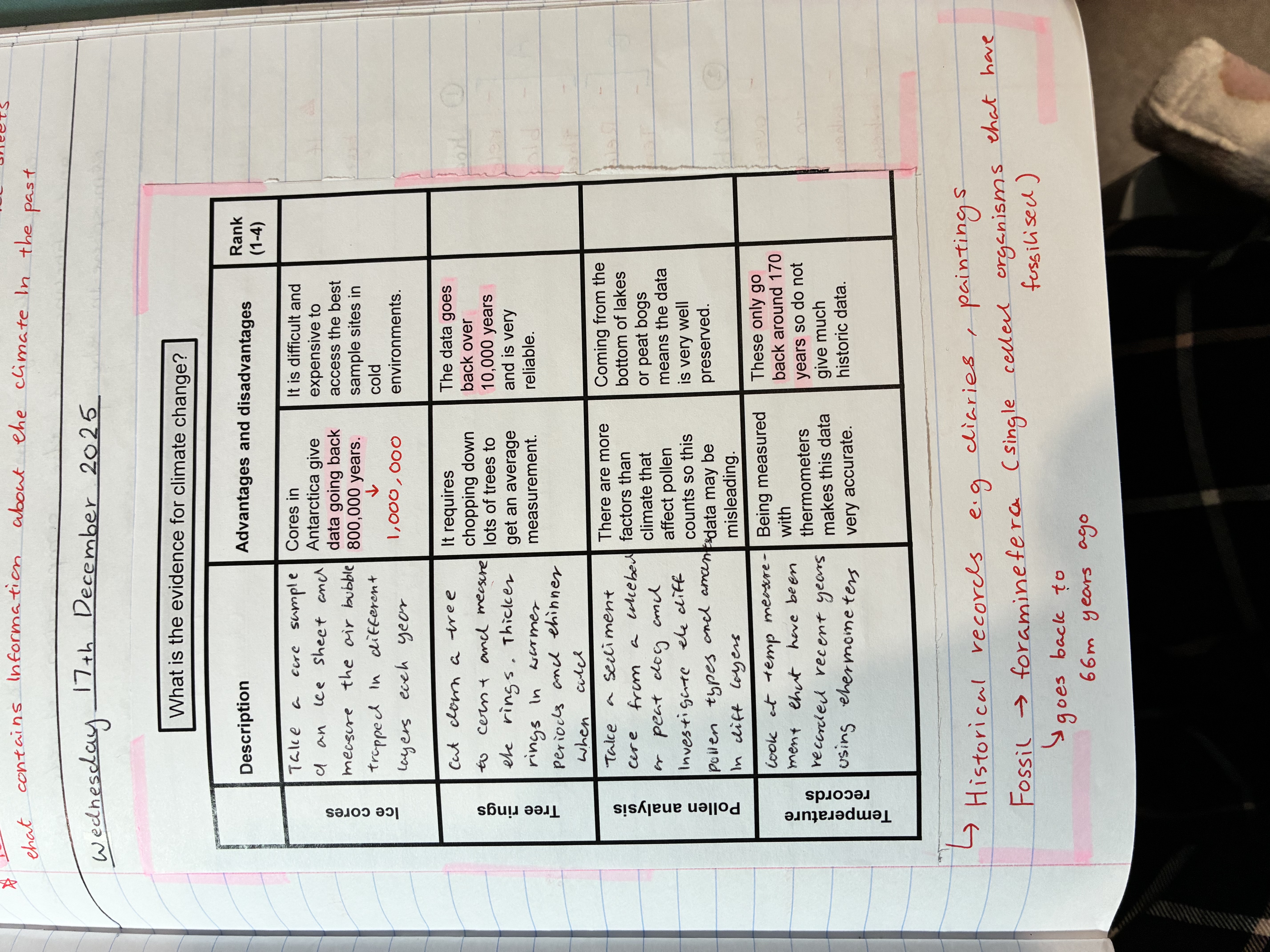
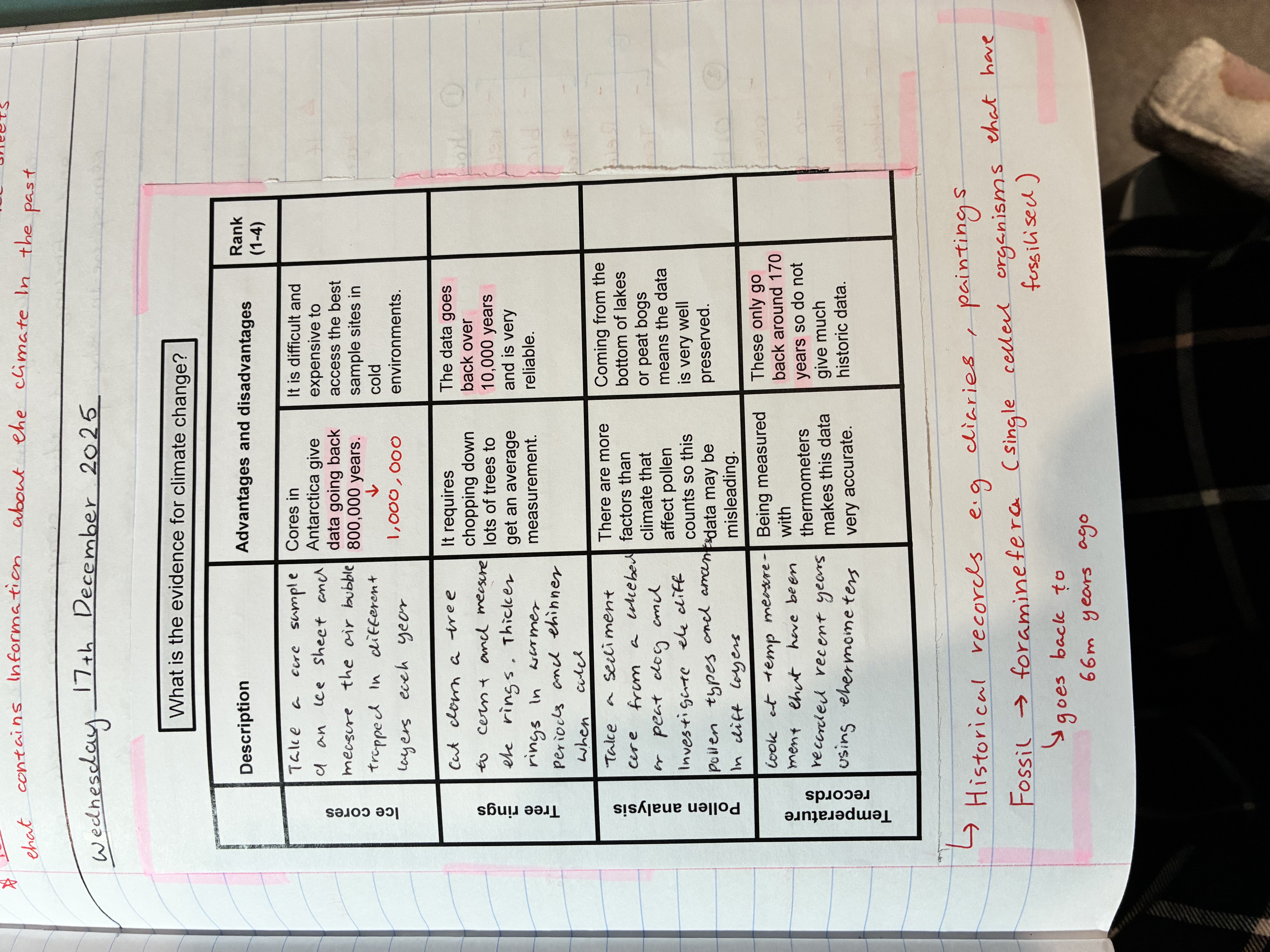
what are the different ways to gather evidence about climate change
ice cores
tree rings
pollen analysis
temperature records
historical records e.g paintings, diaries
fossils e.g foraminefera (goes back to 66m years ago)
what are the advantages and disadvantages of ice cores
advantages
cores in Antarctica give data going back 1,000,000 years
disadvantages
it is difficult and expensive to access the best sample sites in cold environments
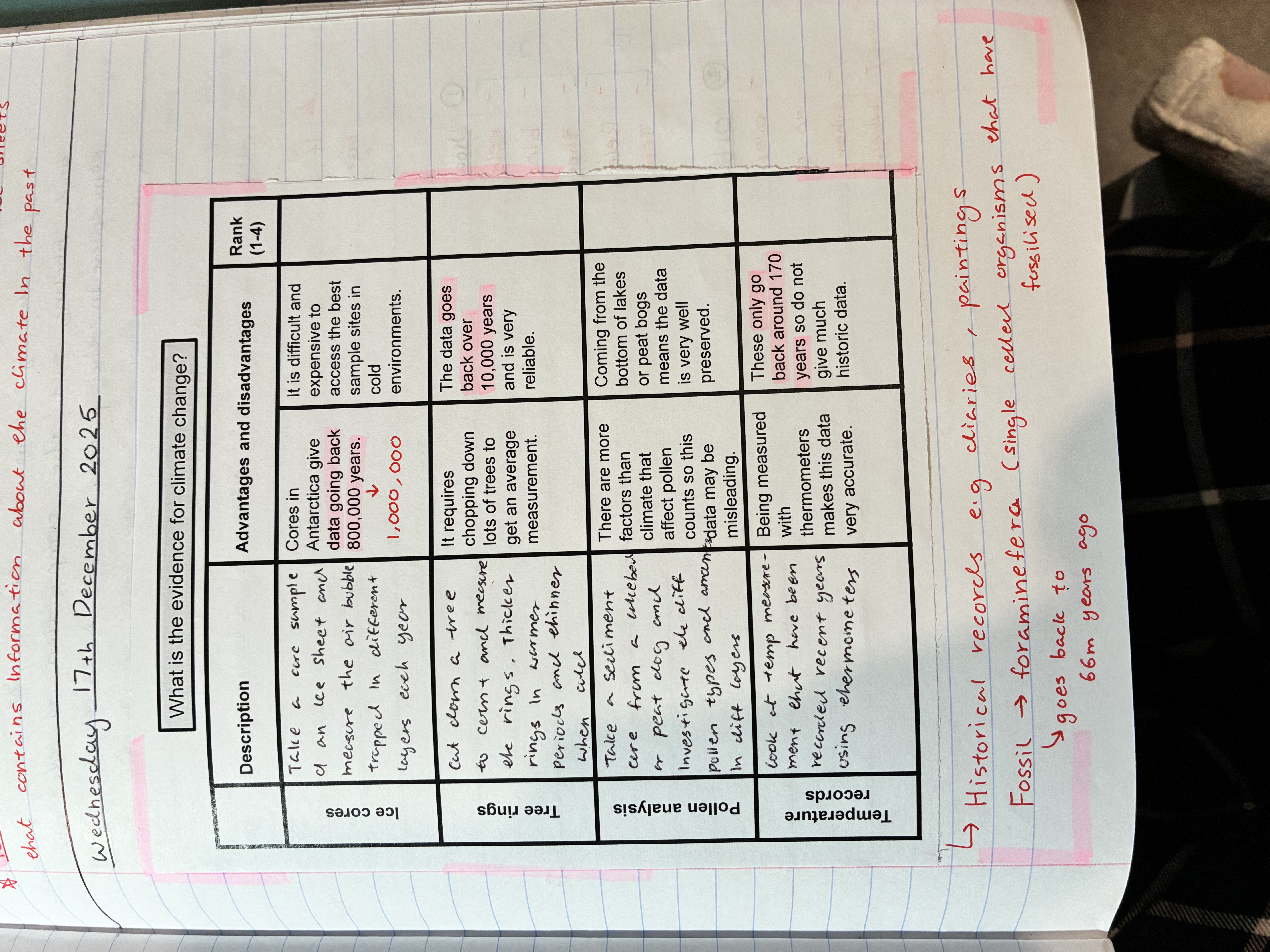
what are the advantages and disadvantages of tree rings
advantages
data goes back over 10,000 years and is very reliable
disadvantages
requires chopping down lots of tres to get an average measurement
what are the advantages and disadvantages of pollen analysis
advantages
comes from the bottom os lakes or peat dogs meaning the data is well preserved
disadvantages
there are more factors than climate that affect pollen counts so this data may be misleading
what are the advantages and disadvantages of temperature records
advantages
being measured with thermometers makes this data more accurate
disadvantages
these only go back around 170 years ago so do not give much data
what are the theories about the natural cause of climate change
volcanic eruptions
orbital changes
solar output
how can volcanic eruptions potentially contribute to climate change
releases ash
blocks the sun
therefore temp ⬇ e.g Mt. Pinatubo 1991 → temp ⬇ 0.5oC
releases GHG e.g CO2 + sulfure dioxide
temp ⬆
how can orbital changes potentially contribute to climate change
over 96,000 years the path it takes changes from circular to oval
when earth is closer to the sun, temp was higher
when earth is further away, temp was lower
How can solar output e.g sun spots potentially contribute to climate change
Cooler areas on the sun’s surface are called sun spots
they are black spots that cause solar flares
solar flares are sudden explosives of energy
more solar flares = higher temp
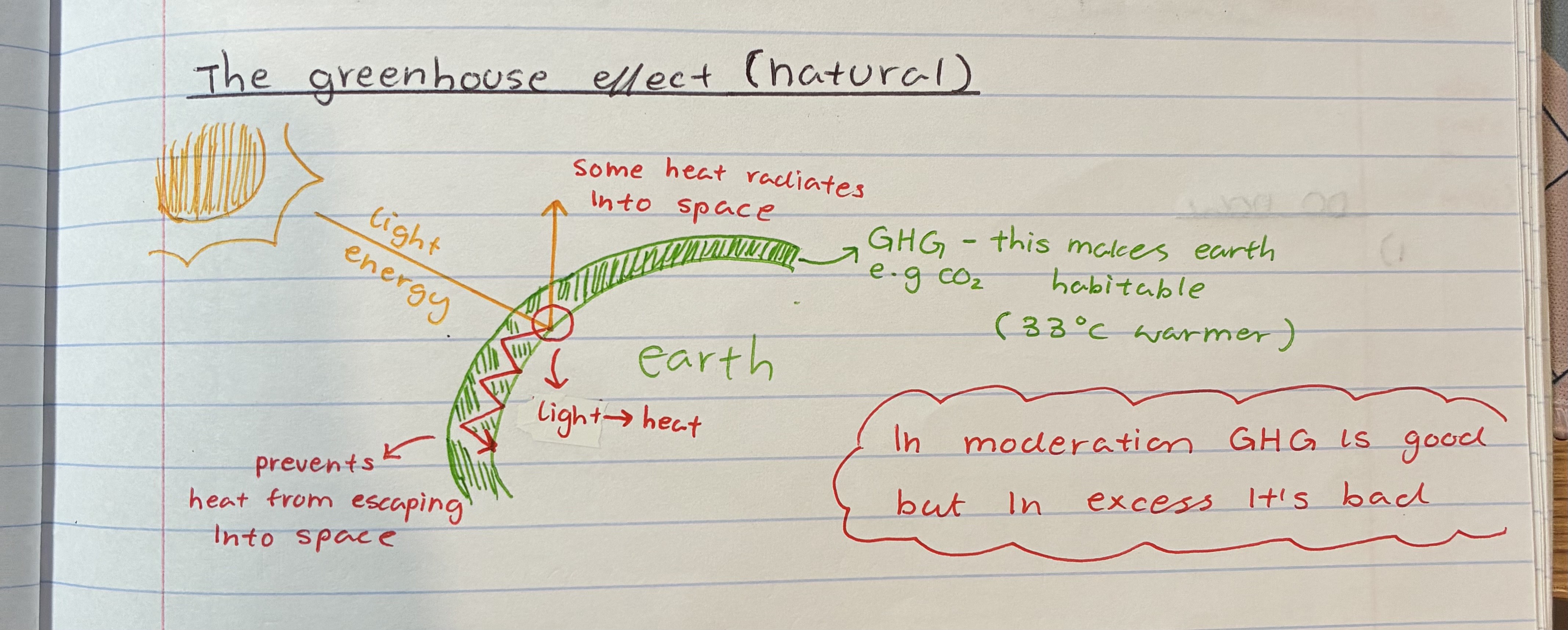
explain the greenhouse effect
when the sun’s light rays hit the earth and turn into heat energy
some light and heat are reflected into space
some are trapped in the earth’s atmosphere due to GHG e.g CO2
therefore temp ⬆
explain the enhanced greenhouse effect
Human release more GHG into the atmosphere
less heat escapes into space
more heat in our atmosphere
therefore global warming occurs
what are the human causes of climate change
deforestation
agriculture
burning FF
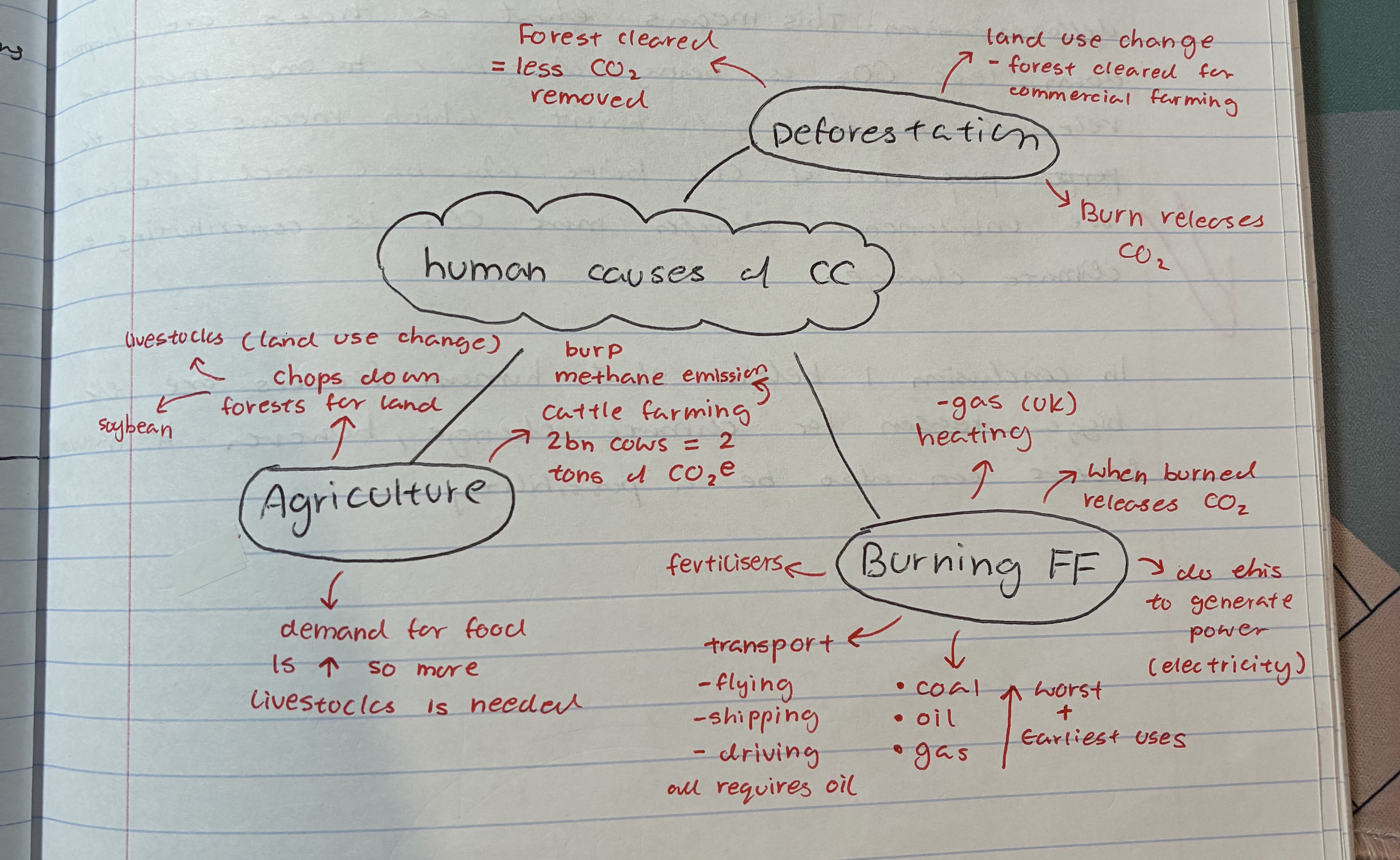
explain how deforestation contributes to climate change
forest cleared = less CO2 removed
burn releases CO2
land use change → forest cleared for commercial farming
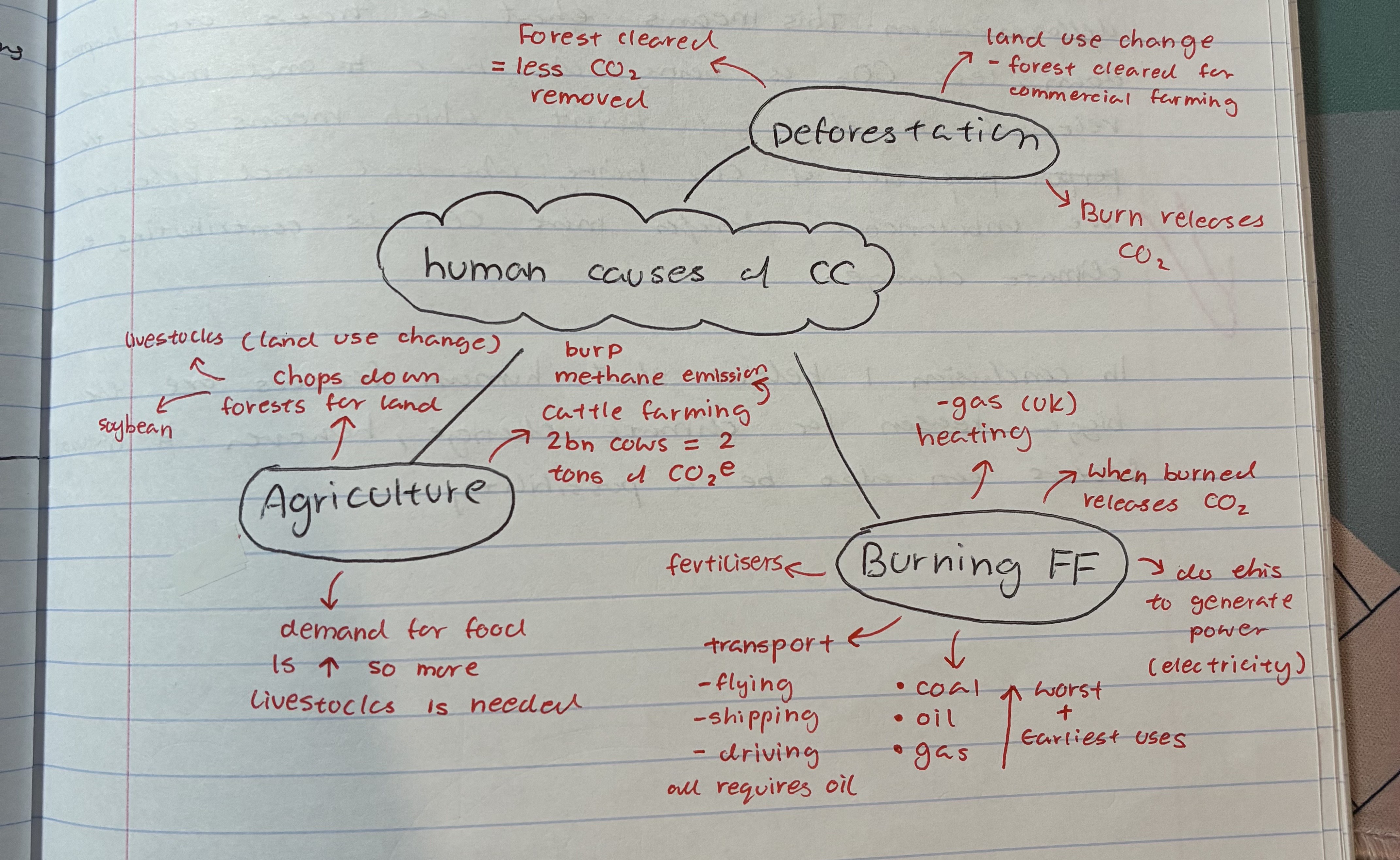
explain how agriculture contributes to climate change
cattle farming 2bn cows = 2 tons of CO2e + methane
demand for food ⬆ so more livestocks needed
chops down forests for land → livestocks + soybeans
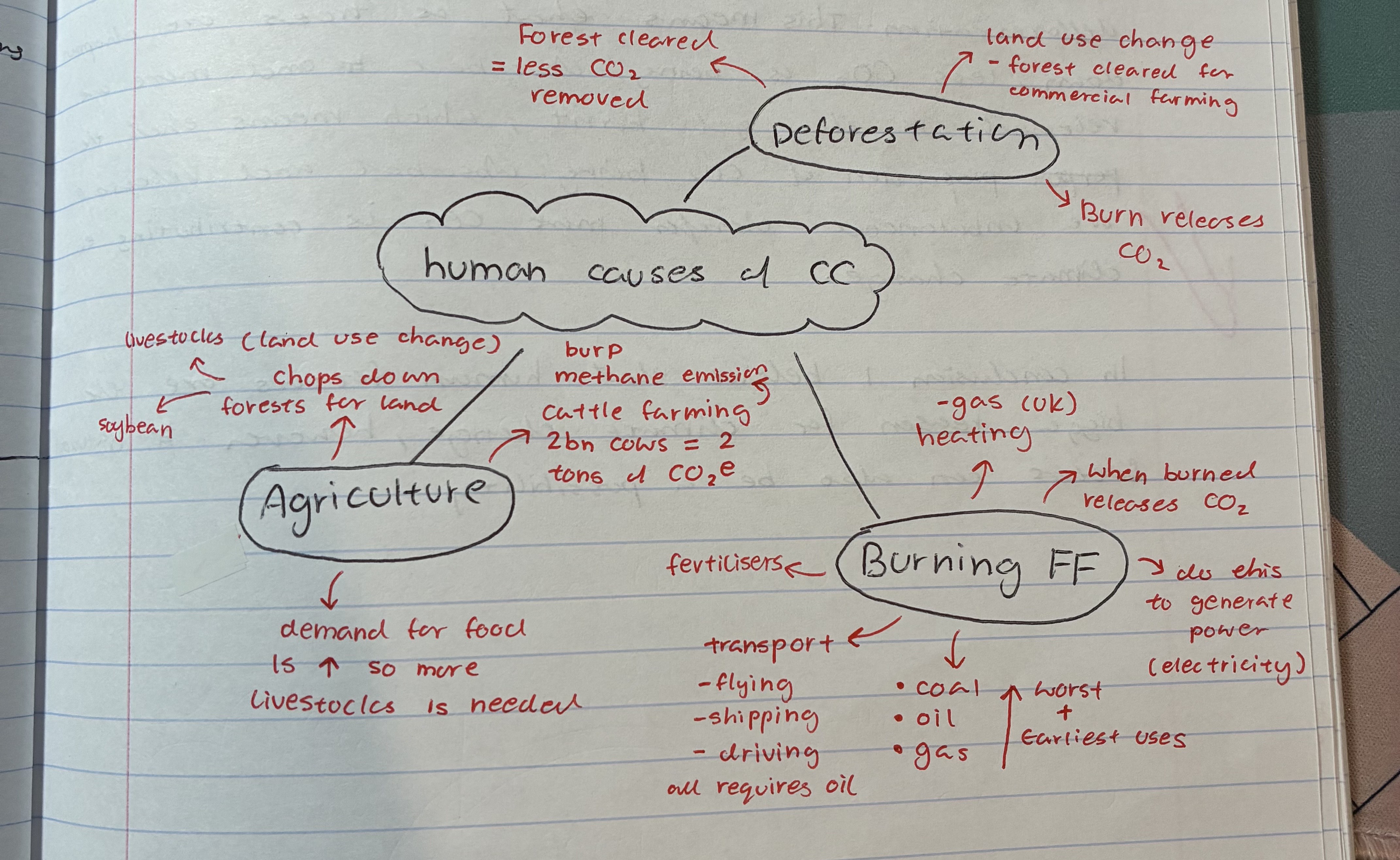
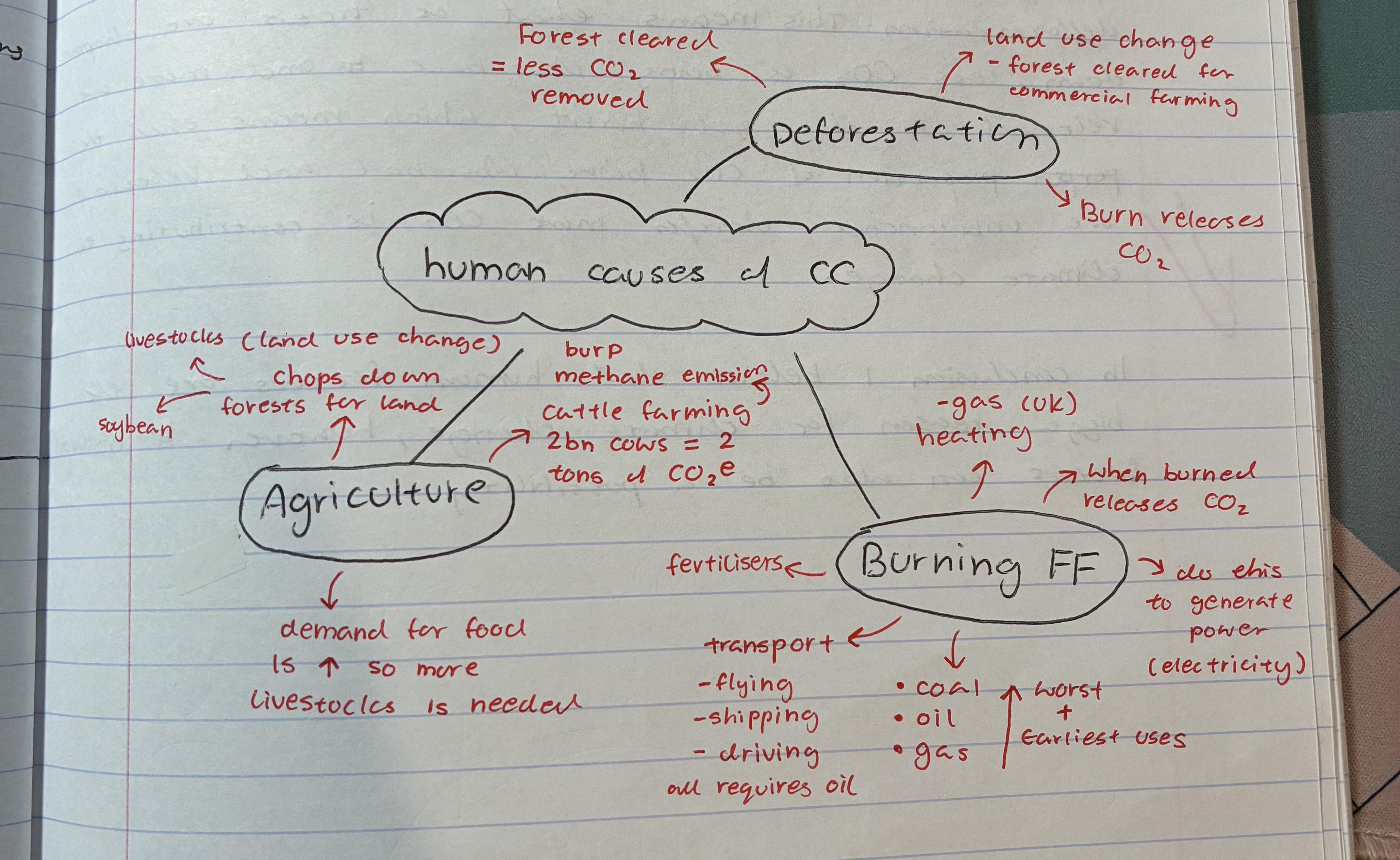
explain how burning FF contributes to climate change
when burned releases CO2
coal, oil, gas
done to generate power (electricity)
Transpo
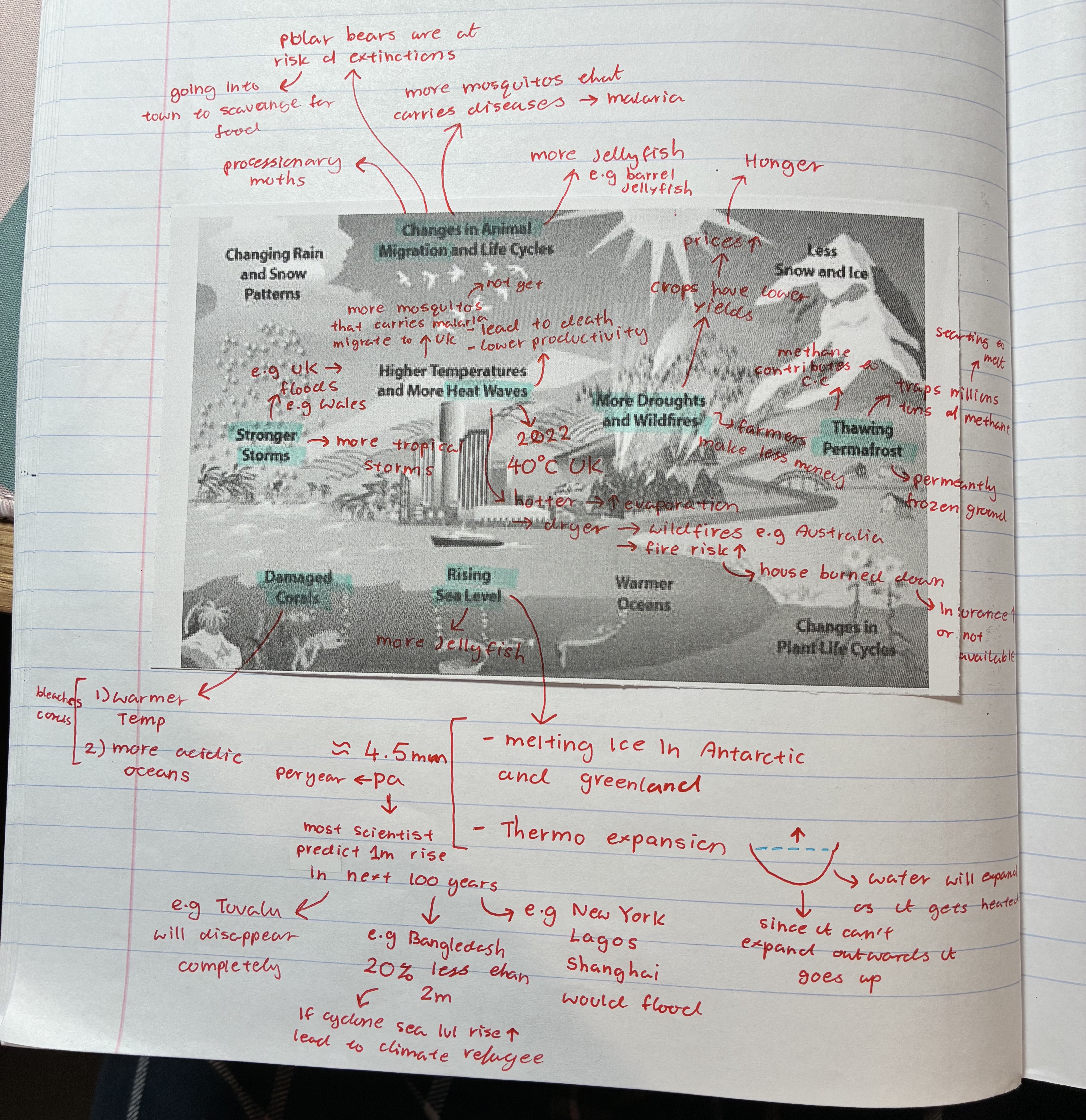
how does climate change affect animal migrations
more mosquitoes that carry diseases e,g malaria moving to e.g UK
polar bears are at risk of extinctions → going into town to scavange for food
more jellyfish e.g barrel jellyfish
processionary moths
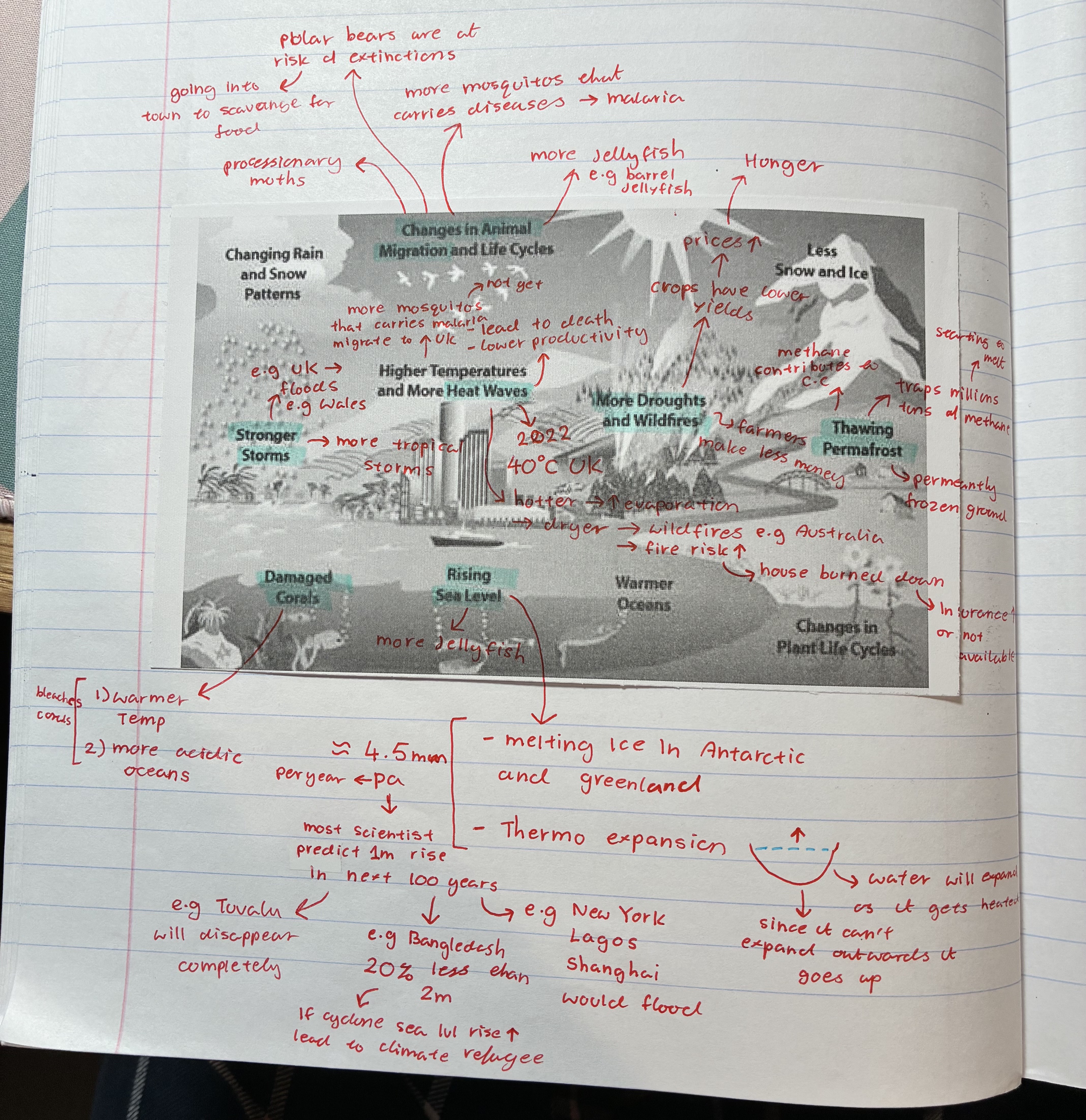
what are the different ways climate change can affect the people and environment
changes in animal migrations
heatwaves
stronger storms
thawing permafrost
rising sea levels
damaged corals
more droughts + wildfires
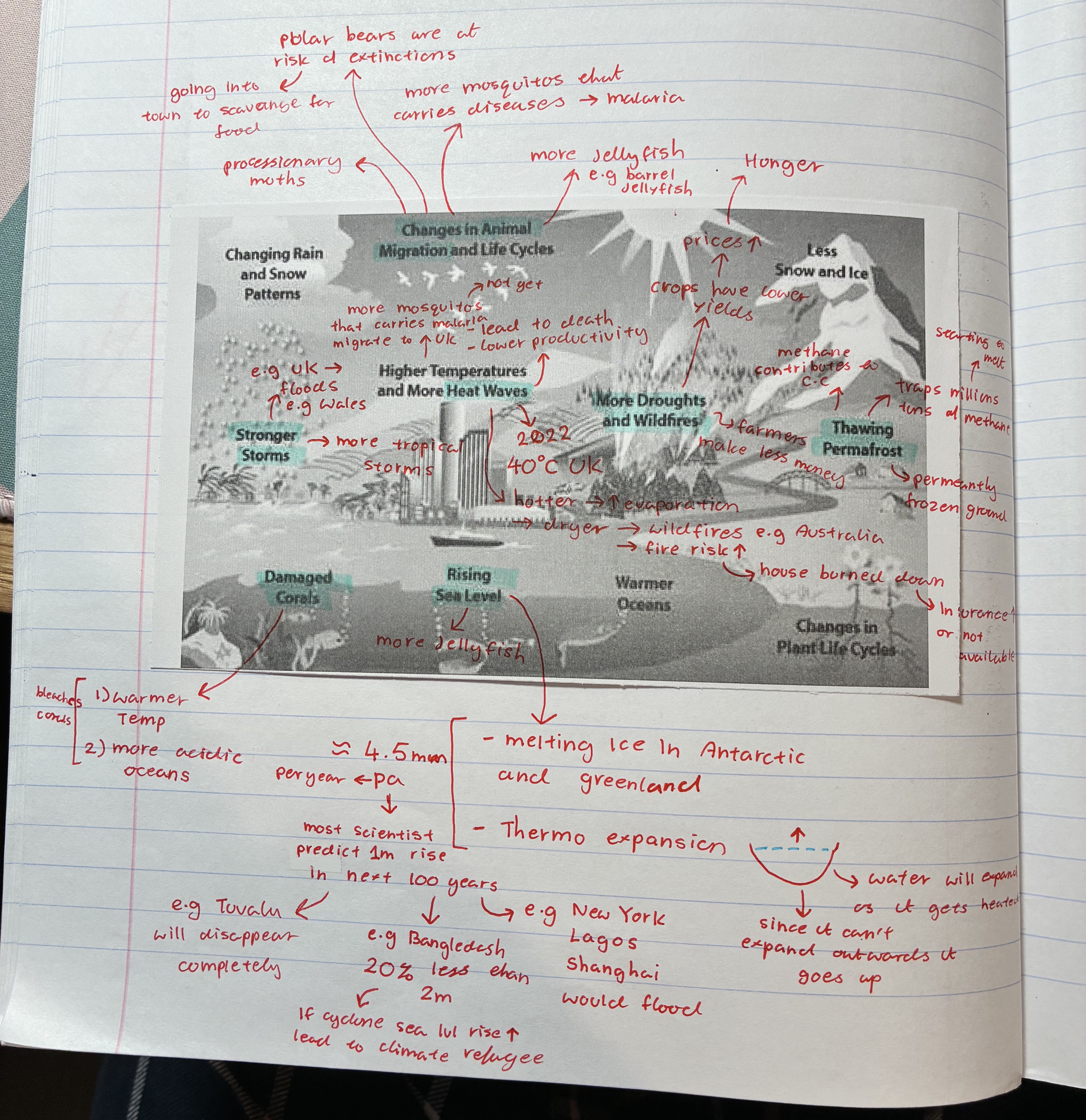
how does climate change affect heatwaves
2022 UK 40oC
hotter → evaporation ⬆ → dryer → wild fire e.g Australia + fire risk ⬆ e.g house burned down leading to insurance ⬆ or not available
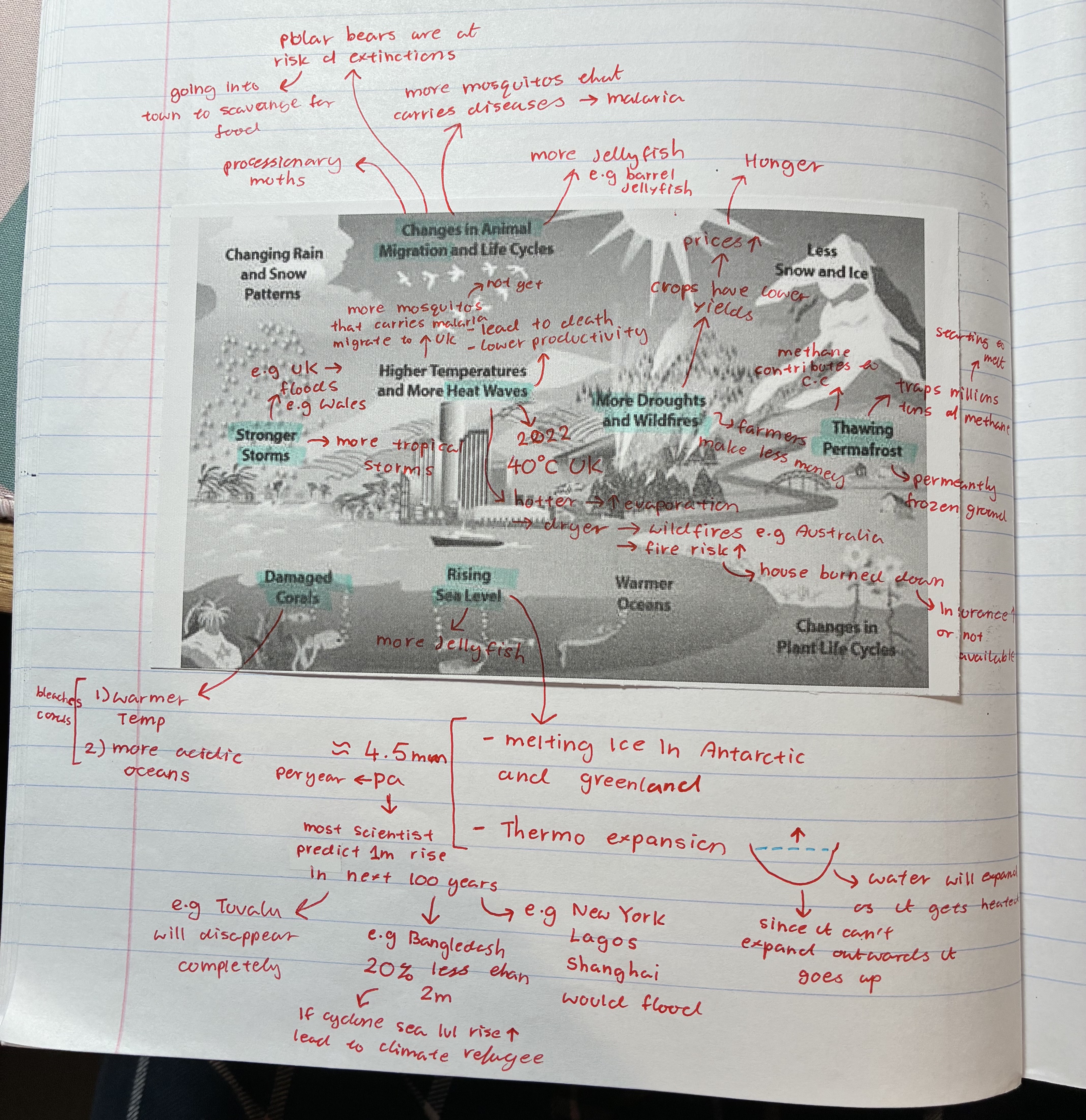
how does climate change affect stronger storms
UK floods e.g Wales
more tropical storms
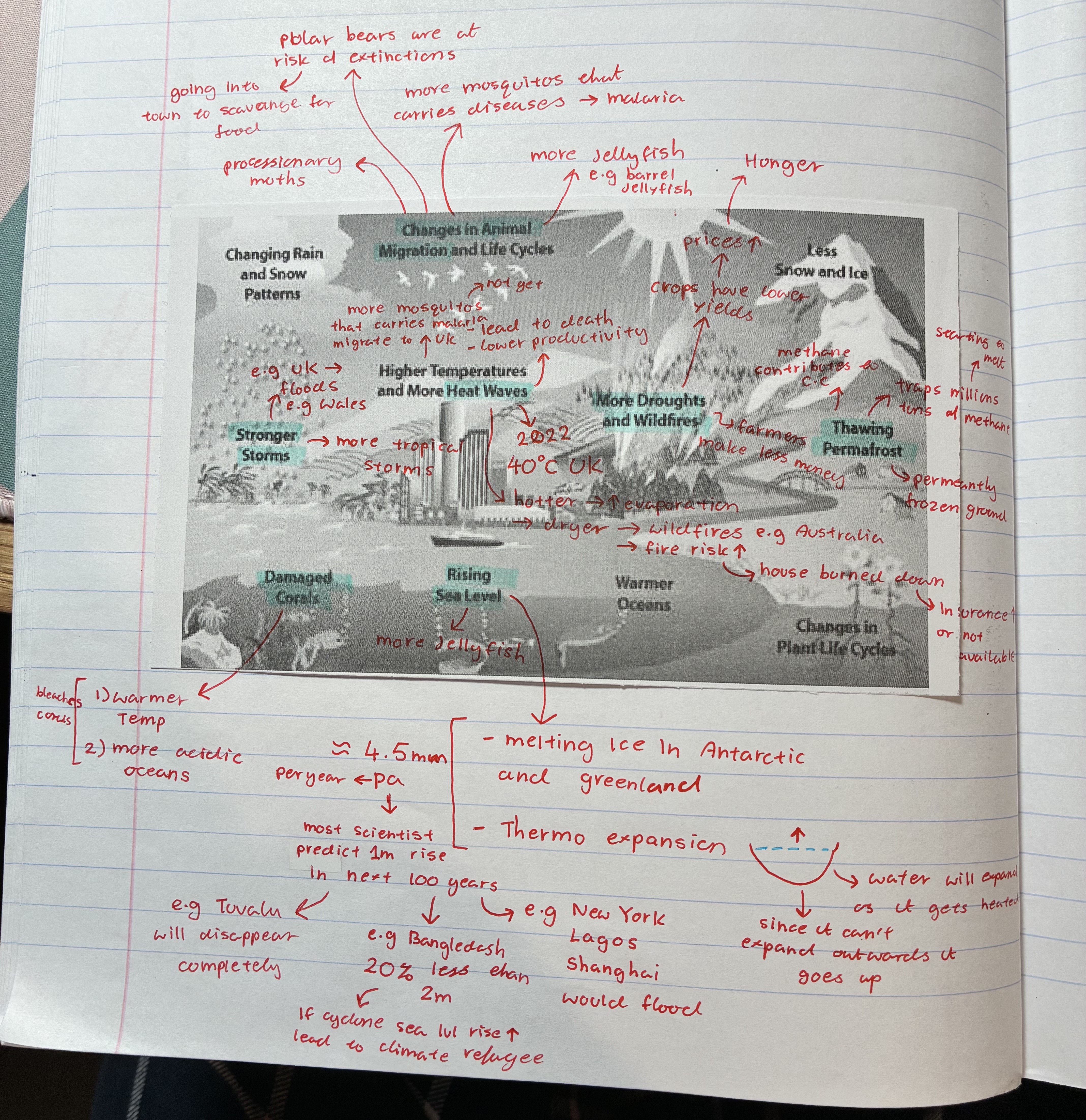
how does climate change affect damaged corals
warmer temp + more acidic oceans → coral bleaching
corals die therefore fishes that depends on them for shelter dies
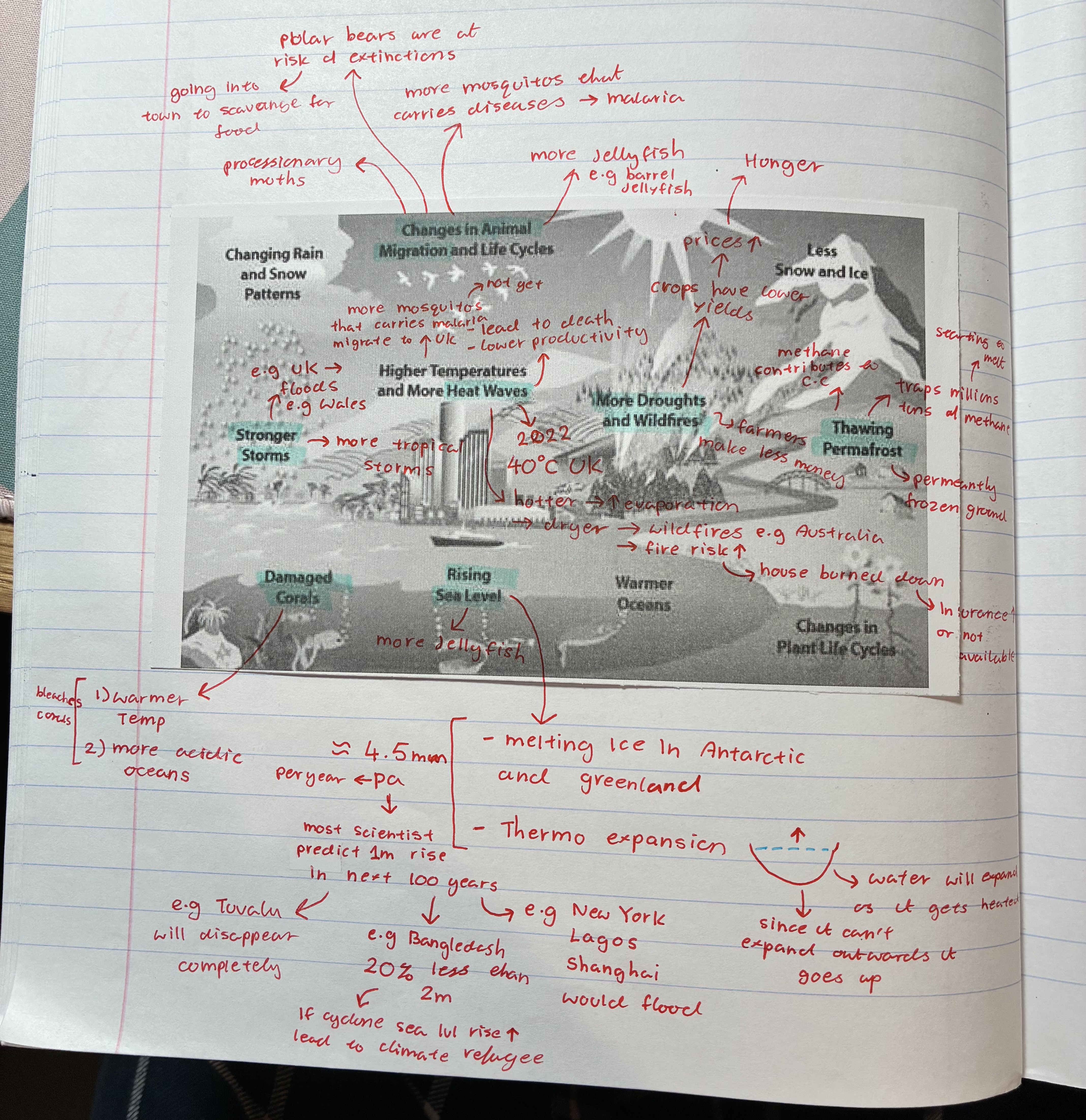
how does climate change affect rising sea levels
melting ice in Antarctica + Greenland → thermo expansion
aprox 4.5mm per year → scientists predict 1m rise in the next 100 years
→ e.g Tuvalu will disappear completely
→ e.g Bangledash 20% less than 2m → if cyclone sea lvl ⬆ leading to climate refugee
→ e.g new York, Lagos, Shanghai will flood
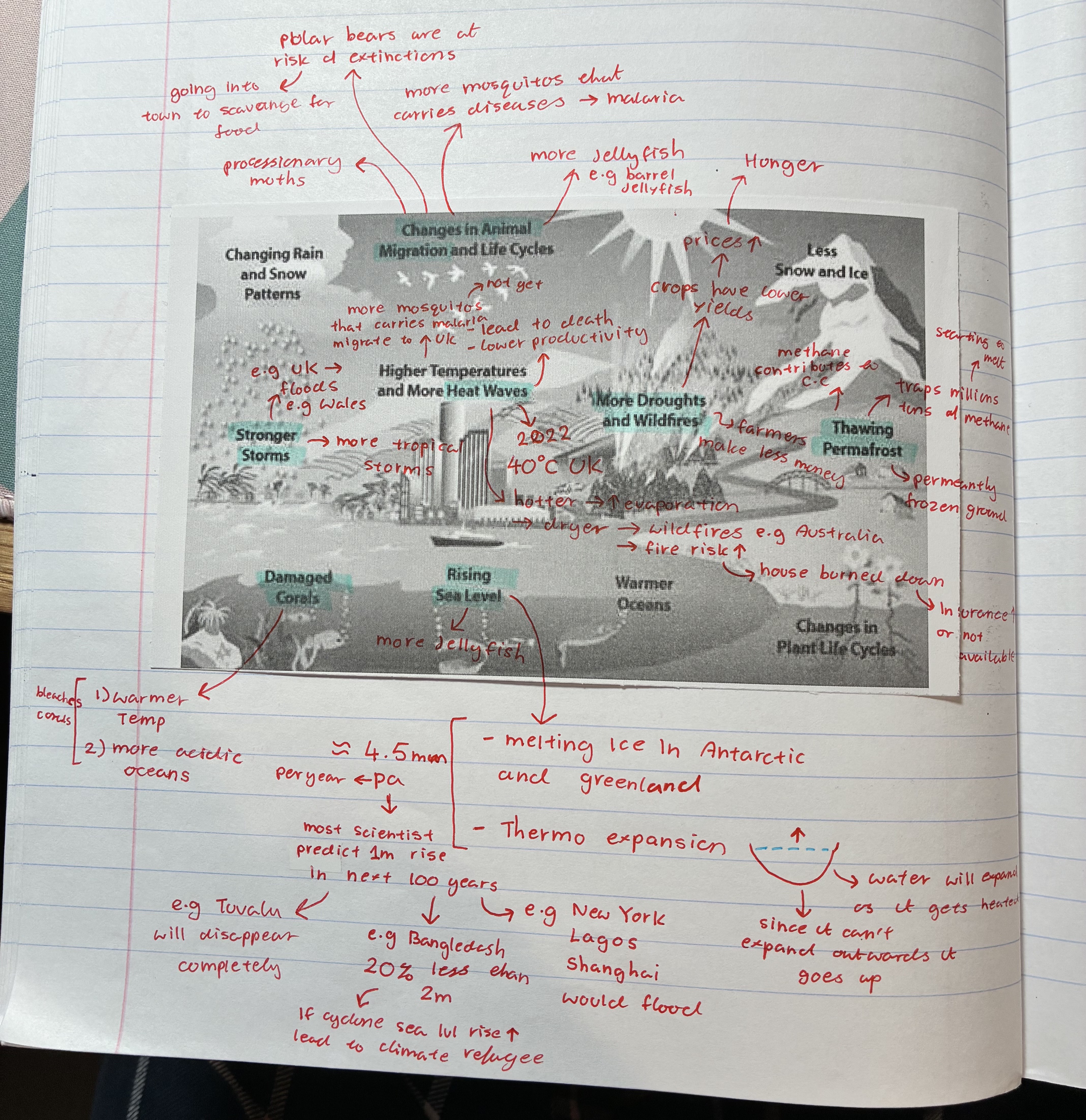
how does climate change affect thawing permafrost
permafrost = permanently frozen ground
traps millions of methane → starting to melt therefore all those methane are being released
contributes to C.C
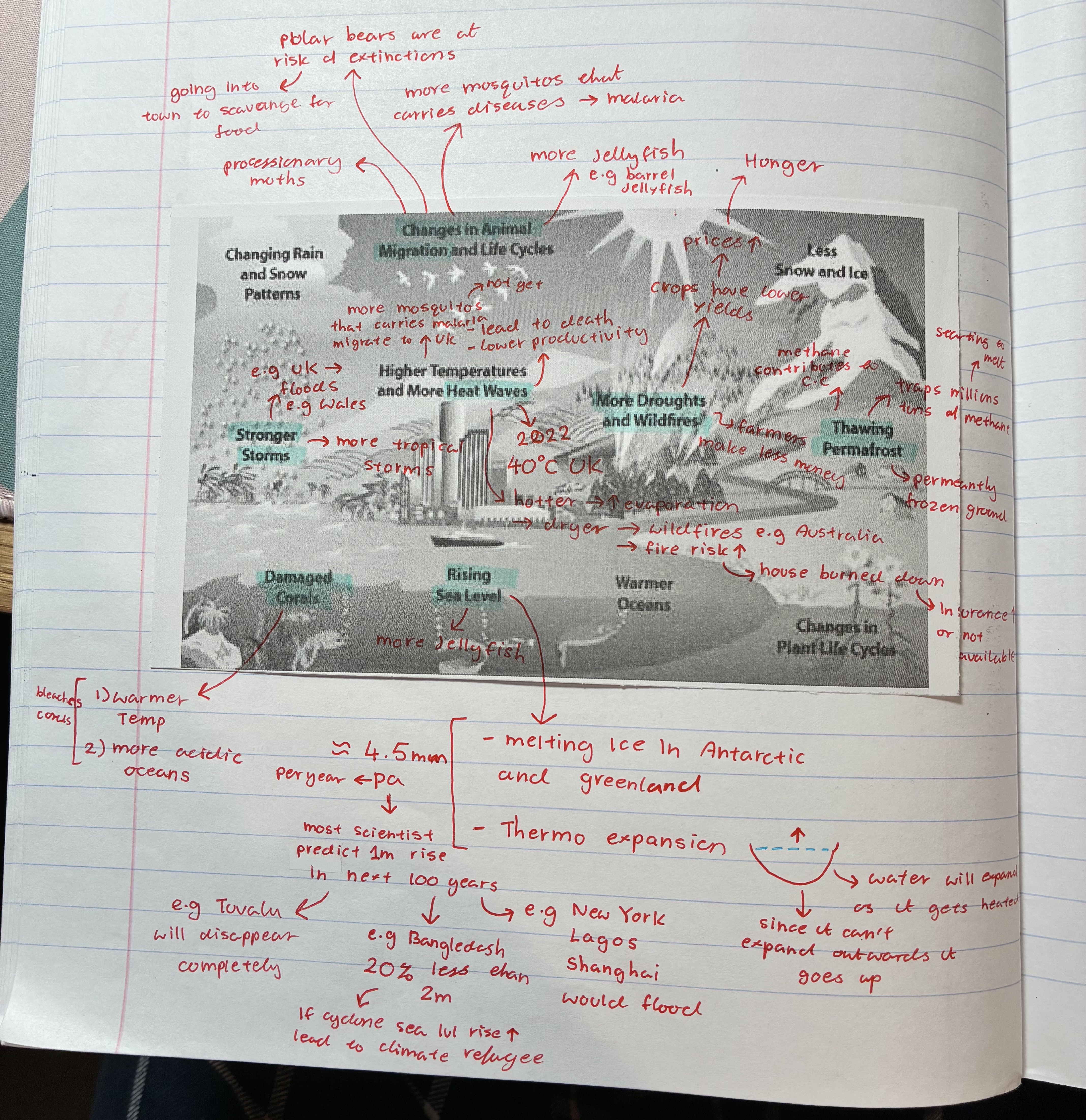
how does climate change affect droughts
farmers make less money
crops have lower yields → prices ⬆ → leads to hunger (ppl not being able to afford)
what are the 2 strategies for C.C
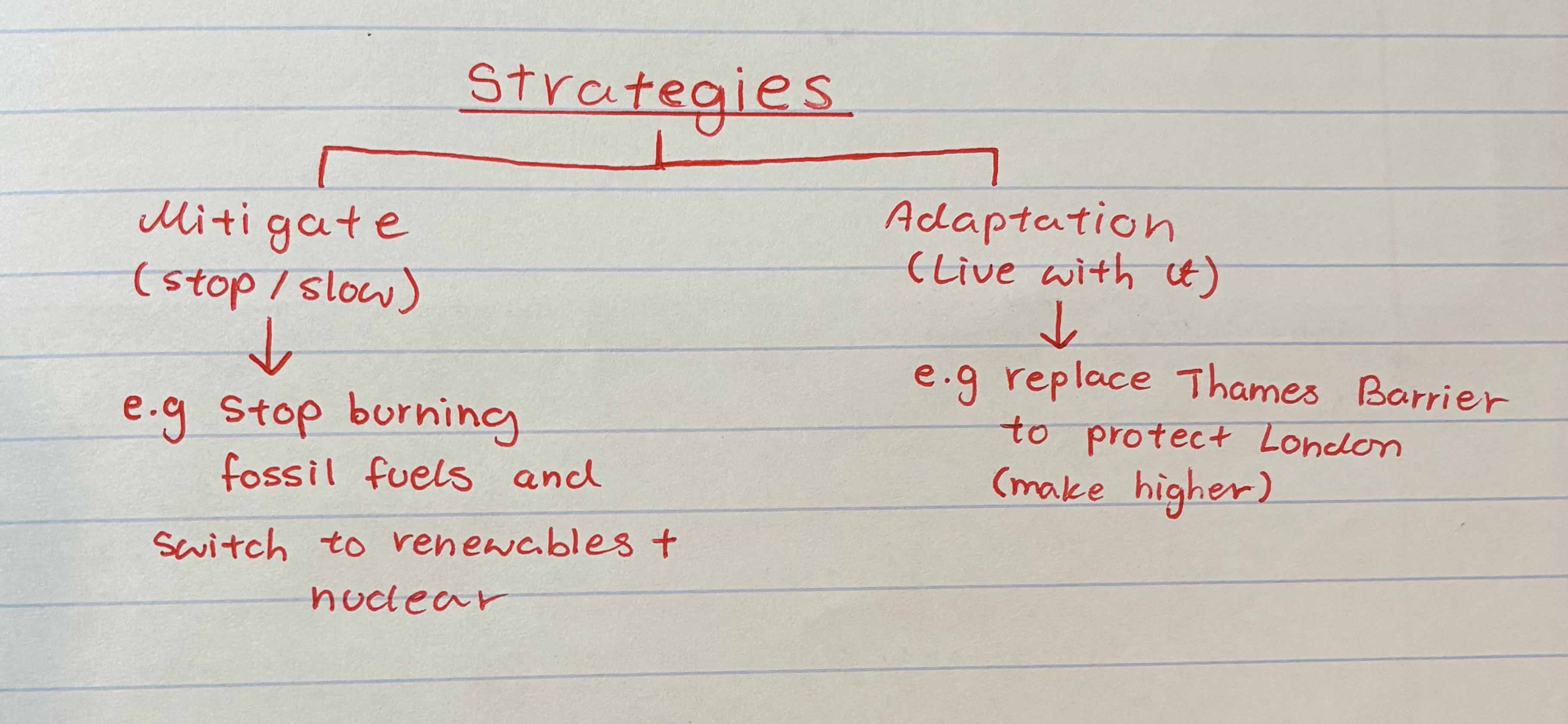
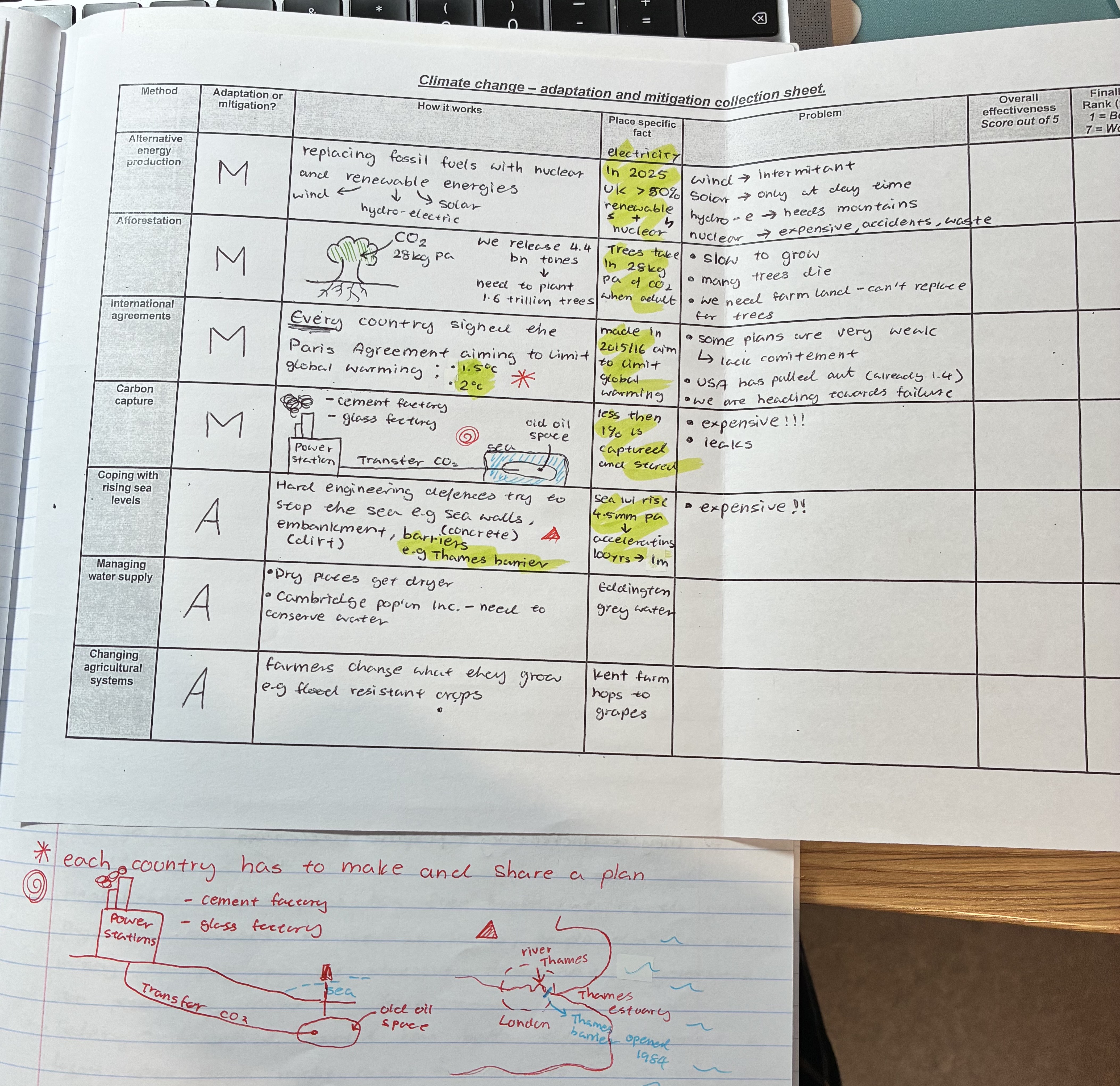
what are the different mitigation methods for C.C
alternative energy production
afforestation
international agrrem
what are the different adaptations for C.C
coping with rising sea levels
managing water supply
changing agricultural systems
explain how alternative energy production works + problems
How to works
replaces FF with nuclear + renewable (solar, wind, hydro-electric) energies
In 2025 UK >50% renewable + nuclear for electricity
problem
wind → intermitant
solar → only at day time
hydro-e → needs mountains
nuclear → expensive, accidents, waste
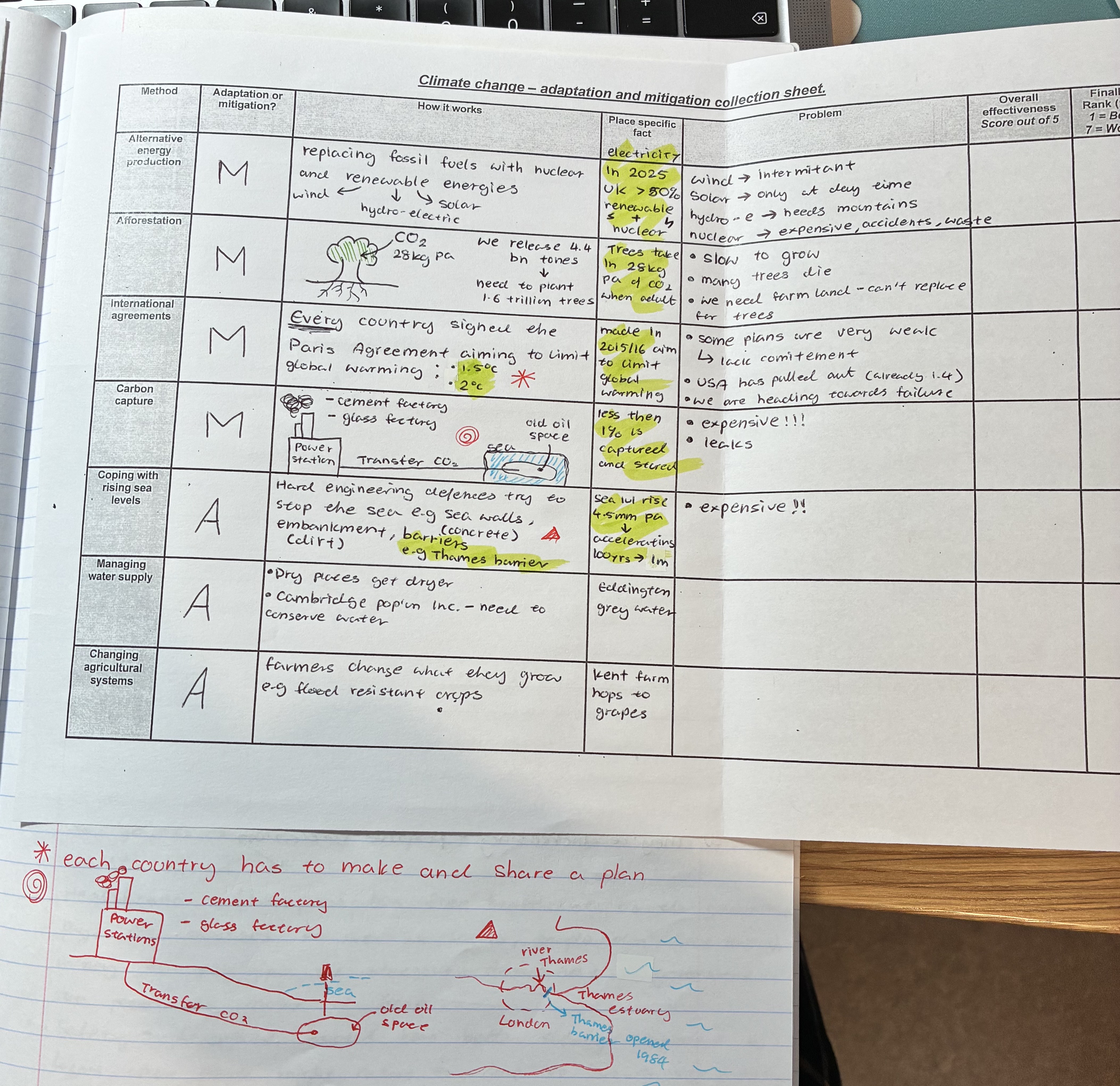
explain how afforestation works + problems
how it works
plants trees
Trees take in 28kg pa of CO2 when adult
Problems
slow to grow
many trees die before adulthood
we need farm land - can’t replace for trees
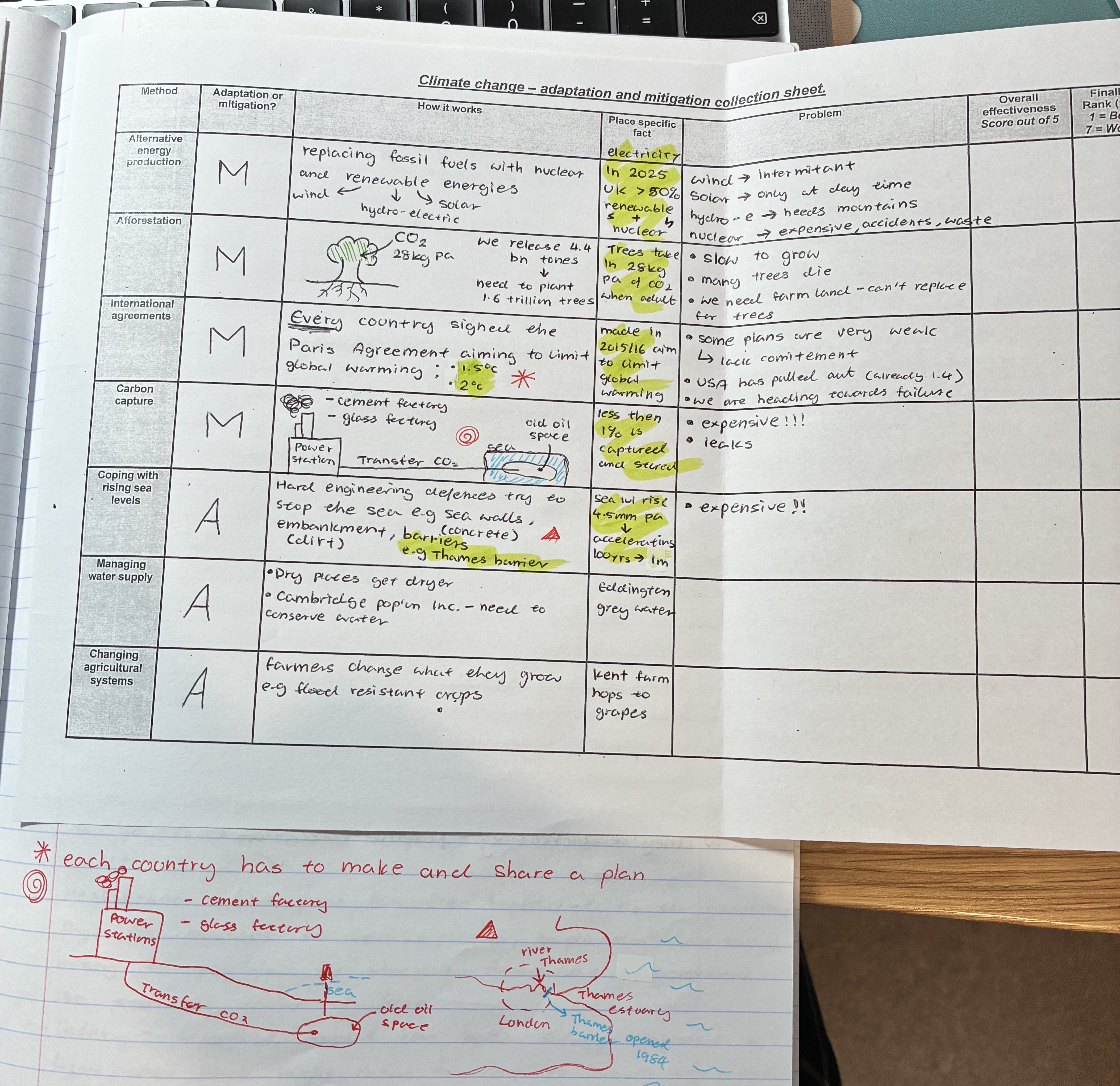
explain how international agreement works + problems
how it works
EVERY country signed the Paris Agreement aiming to limit global warming
trying to prevent temp to rise above 1.5oC or 2oC, each country has to make and share plans
made in 2015/16 aim to limit global warming
problems
some plans are very weak → lack commitment
USA has pulled out
we are already heading towards failure (1.4oC)
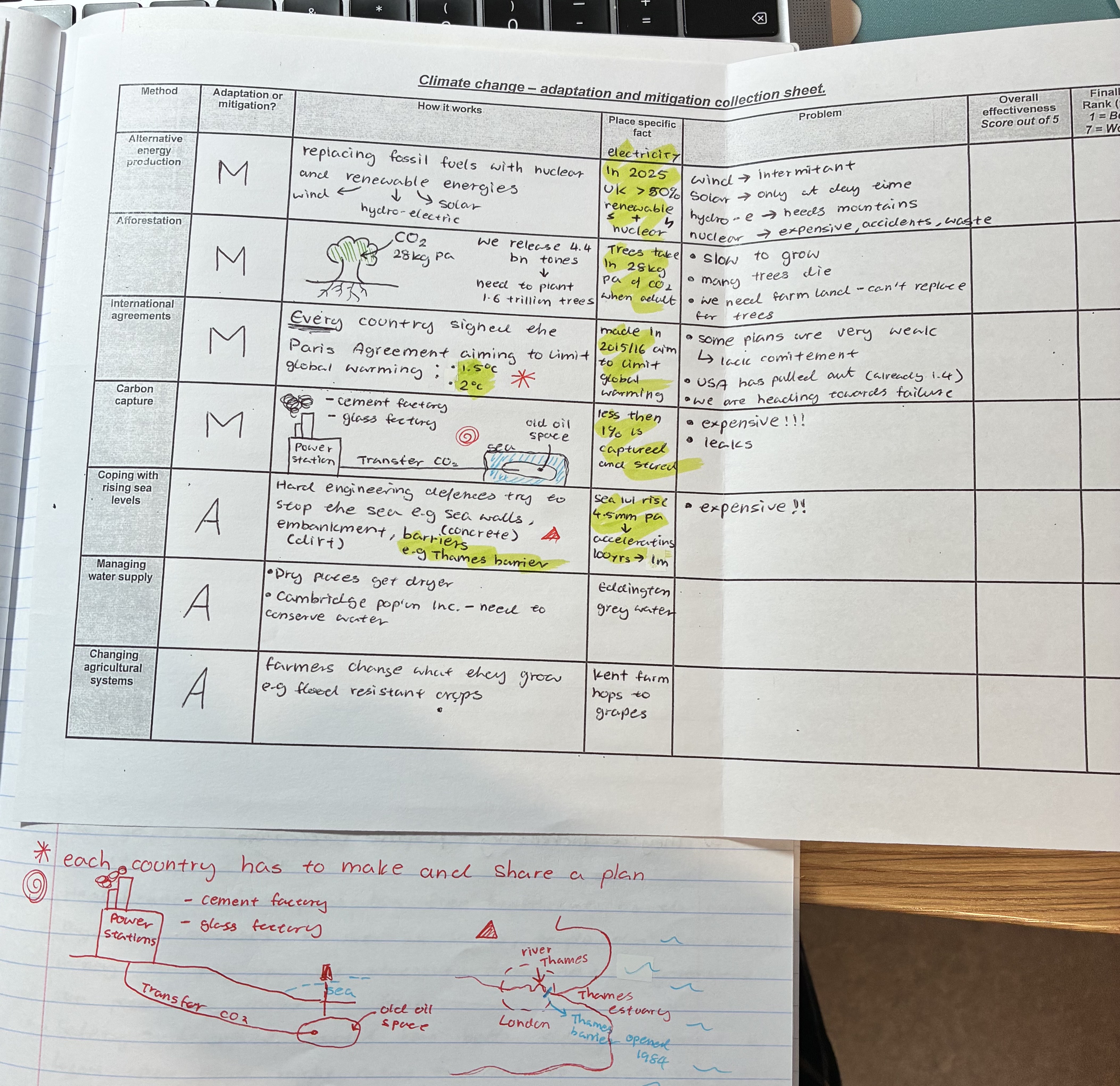
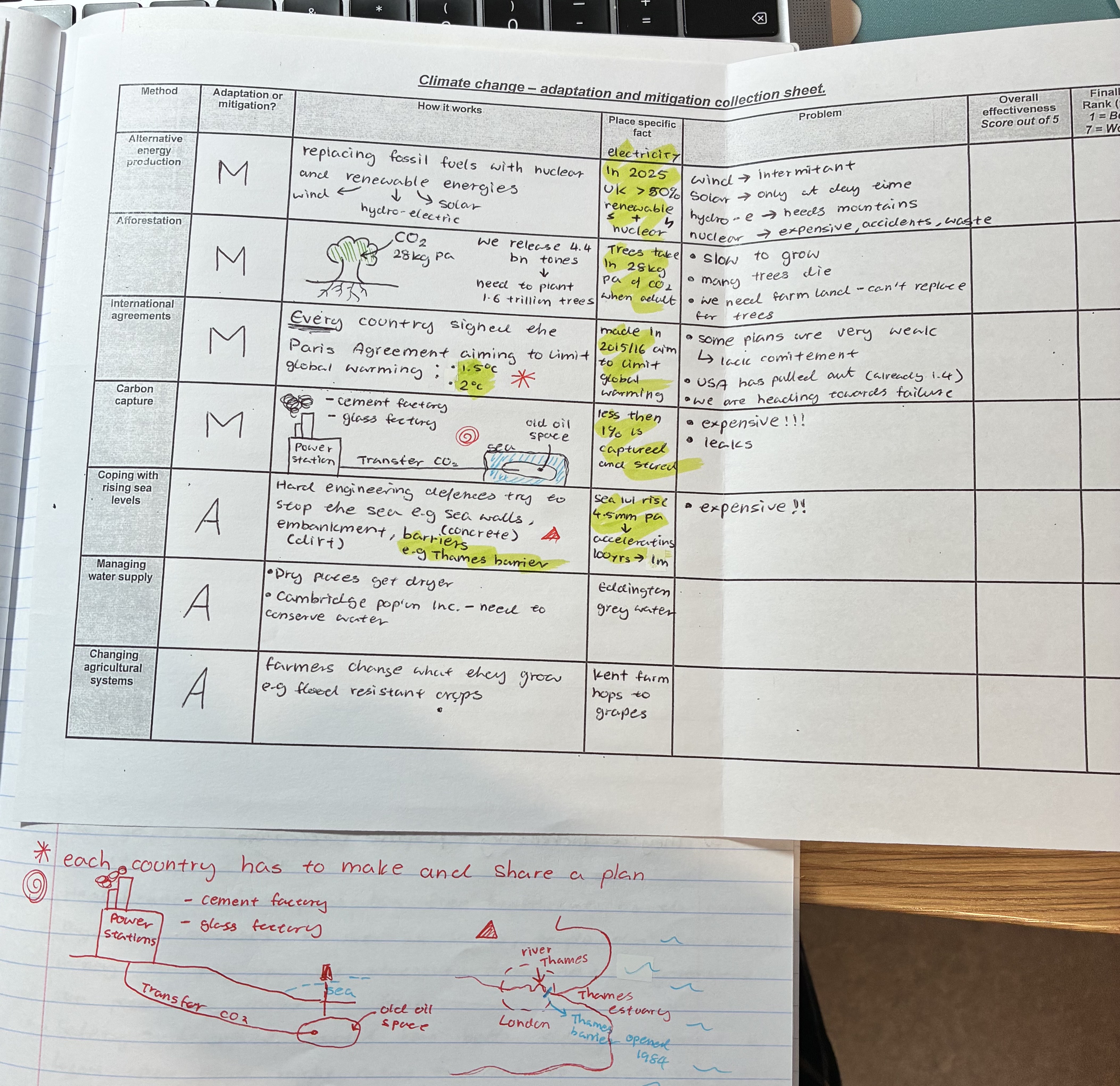
explain how carbon capture works + problems
how it works
(see pic)
less then 1% is captured and stored
problems
expensive!!
leaks
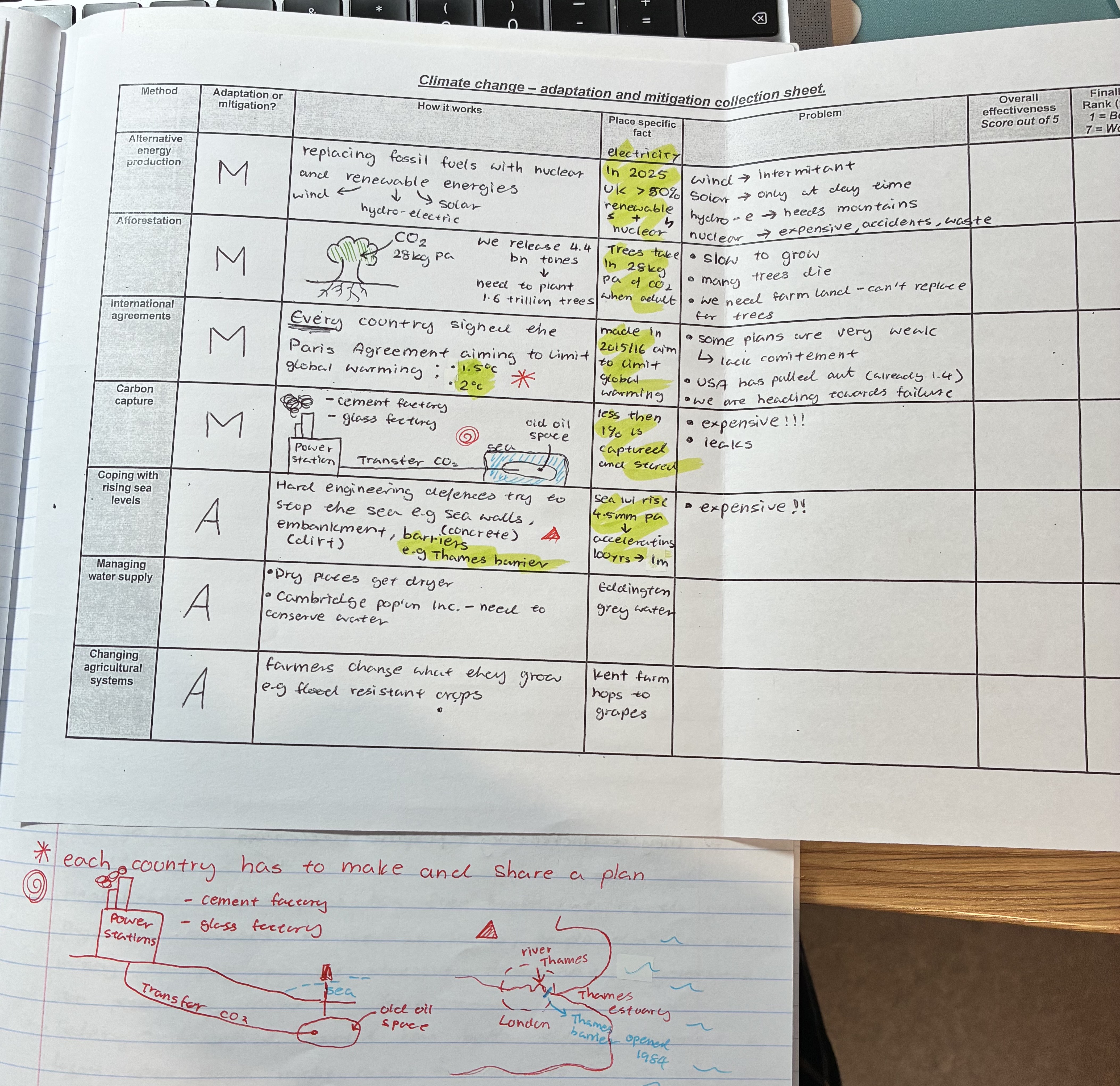
explain how coping with rising sea levels works + problems
how it works
hard engineering defences try to stop the sea e.g sea walls (concrete), embankments (dirt) , barriers (thames barrier)
sea lvl rising by 4.5mm per year → accelerating, 100yrs → 1m
problems
EXPENSIVE
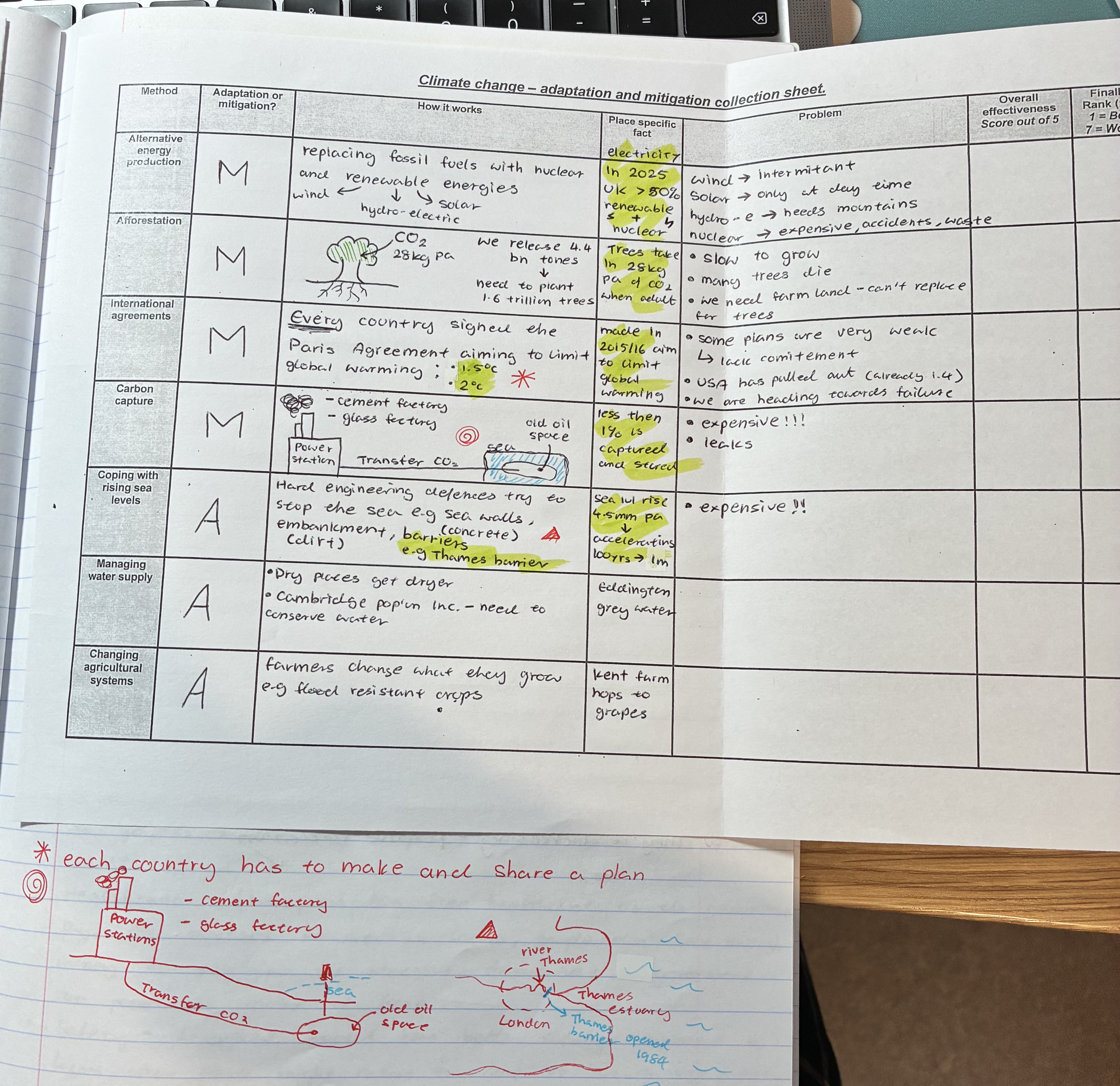
explain how managing water supplies works
how it works
as dry places get dryer, places like Cambridge need to conserve water
Eddington grey water
explain how changing agricultural systems works
how it works
farmers change what they grow e.g flood resistant crops
Kent farm hops to grapes