blood pressure regulation
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
likely incomplete
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
parasympathetic innervation of the heart
SA node and AV node
Releases acetylcholine which binds to muscarinic receptors (M2)
Slows the heart rate and rhythm
mechanism:
inhibits cyclic AMP (cAMP) (by inhibiting adenylyl cyclase, the enzyme responsible for its production)
intracellular Ca2+ levels decreases (calcium channels close) (slows AV node conduction)
K+ conductance increased leading to hyperpolarisation of membrane (slows heart rate)
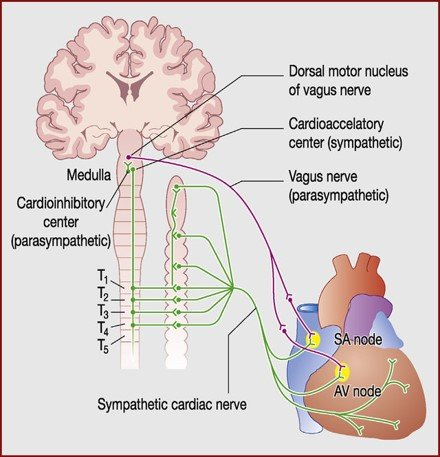
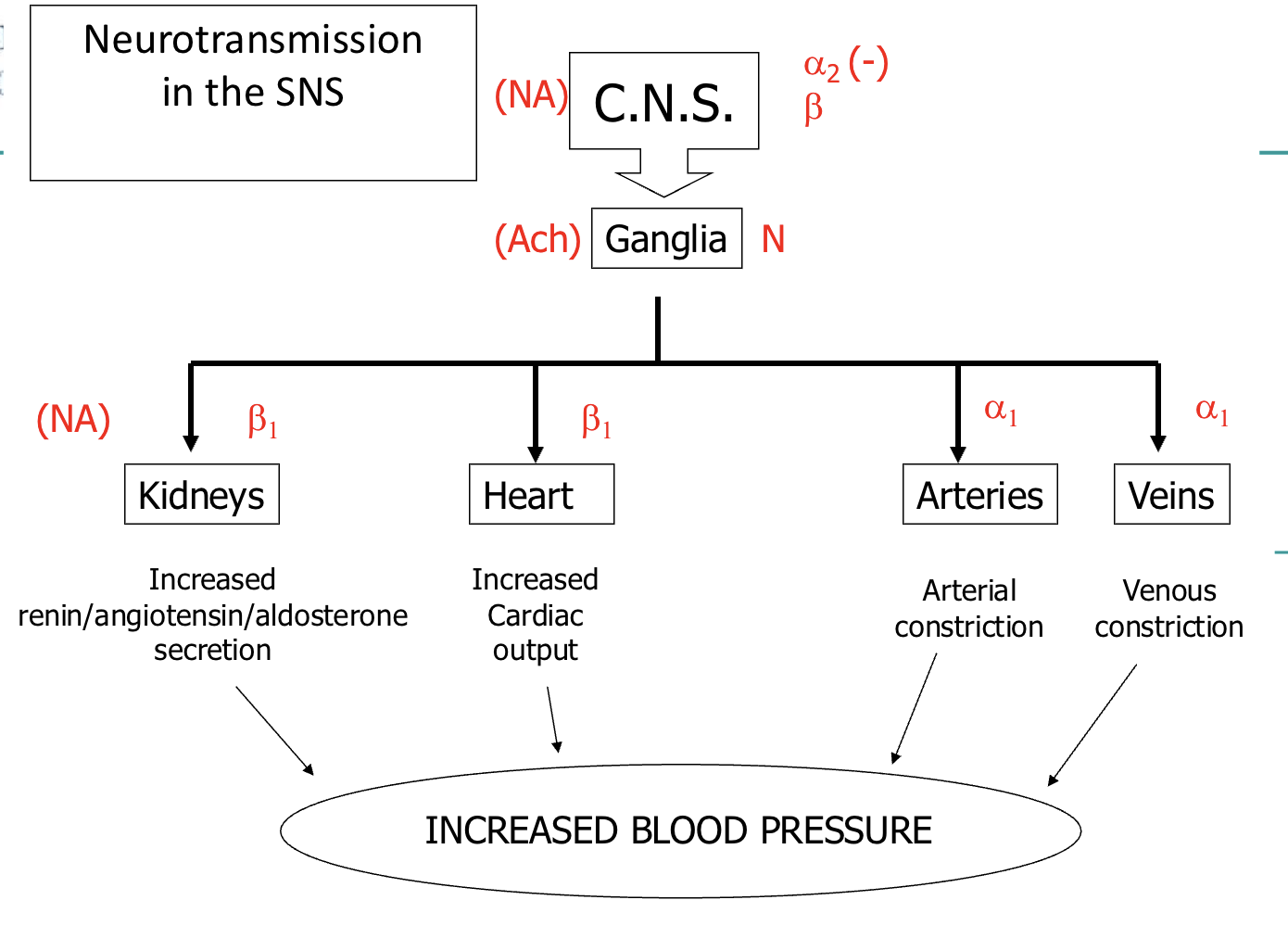
sympathetic regulation of blood pressure
Responsible for immediately increasing blood pressure
e.g. Exercise, standing, etc.Releases noradrenaline →
Heart:
NA acts on β1-receptors in heart to increase heart rate and contractility
Blood vessels:
α1-receptors vasoconstriction (TPR) → increased cardiac output
parasympathetic: β2-receptors vasodilation (rarely)
Kidneys:
α1-receptors → renin/angiotensin/aldosterone
secretion
blood volume
controlled by kidneys
high blood volume = high bp
hypotension risks
Circulatory collapse (vessels collapse)
Tissue ischemia/hypoxia
No filtration in the kidney
MAP below 60mmHg can cause syncope (fainting)
hypertension risks
Retinal, renal damage
Oedema
MAP above 160mmHg can result in cerebral oedema
Aneurysm/haemorrhage
Heart hypertrophy/failure
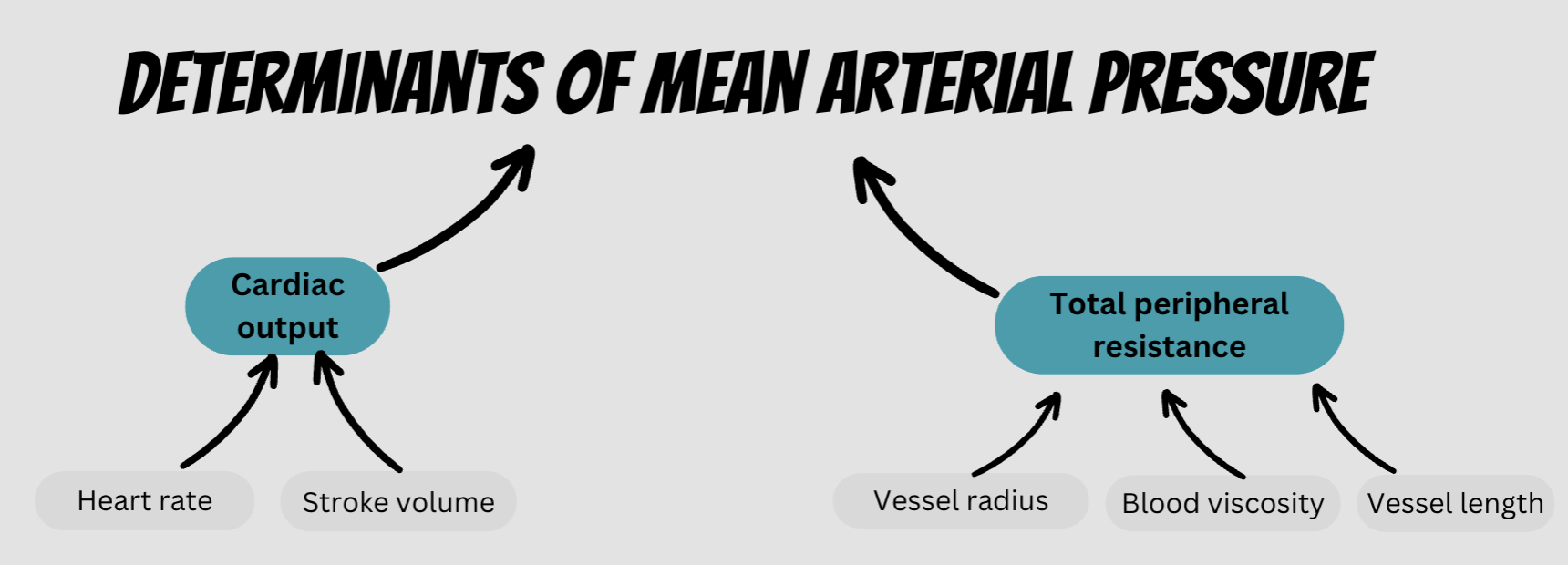
main factors influencing blood pressure
Blood volume (kidneys)
Total peripheral resistance (TPR) (SNS + blood vessels)
Cardiac output (SNS + blood vessels)
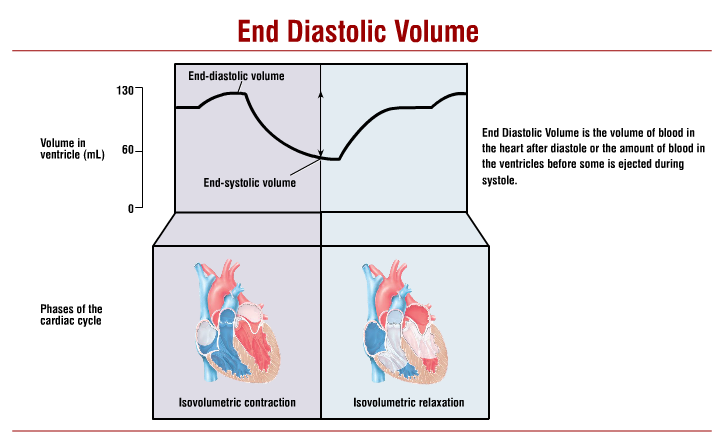
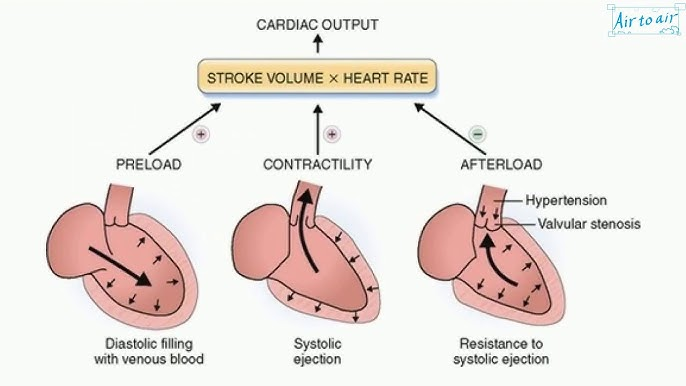
stroke volume
volume of blood ejected per beat (mL)
usually approx. 70mL/beat
EDV (end diastolic volume) - ESV (end systolic volume)
NA acts on β1-receptors in the heart to increase SV
heart rate
number of beats per minute
NA acts on β1-receptors in the heart to increase HR
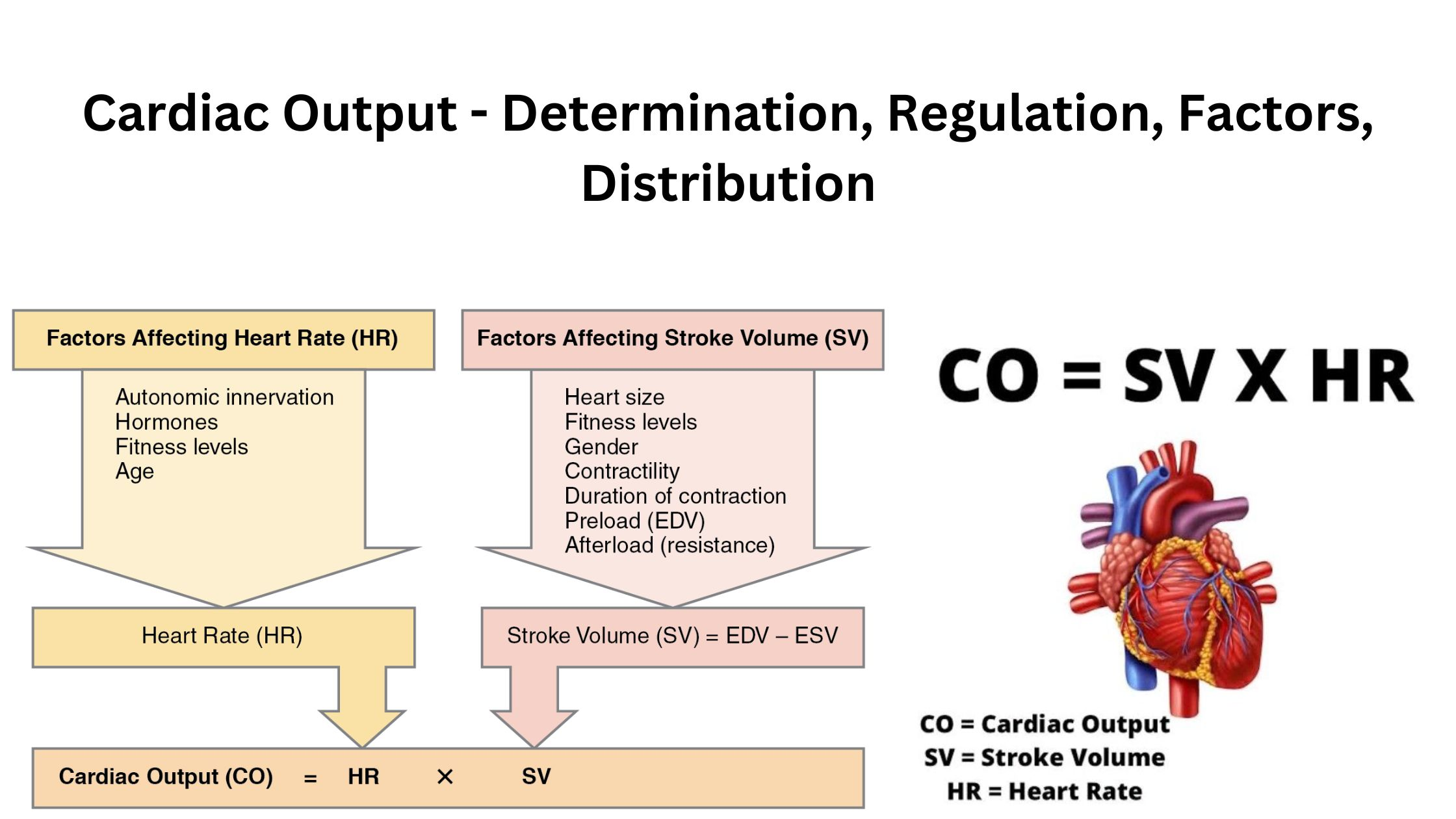
cardiac output
heart rate X stroke volume
the volume of blood flowing through the circulation in one minute (L/min)
determined by blood vessels (due to venous return) and SNS
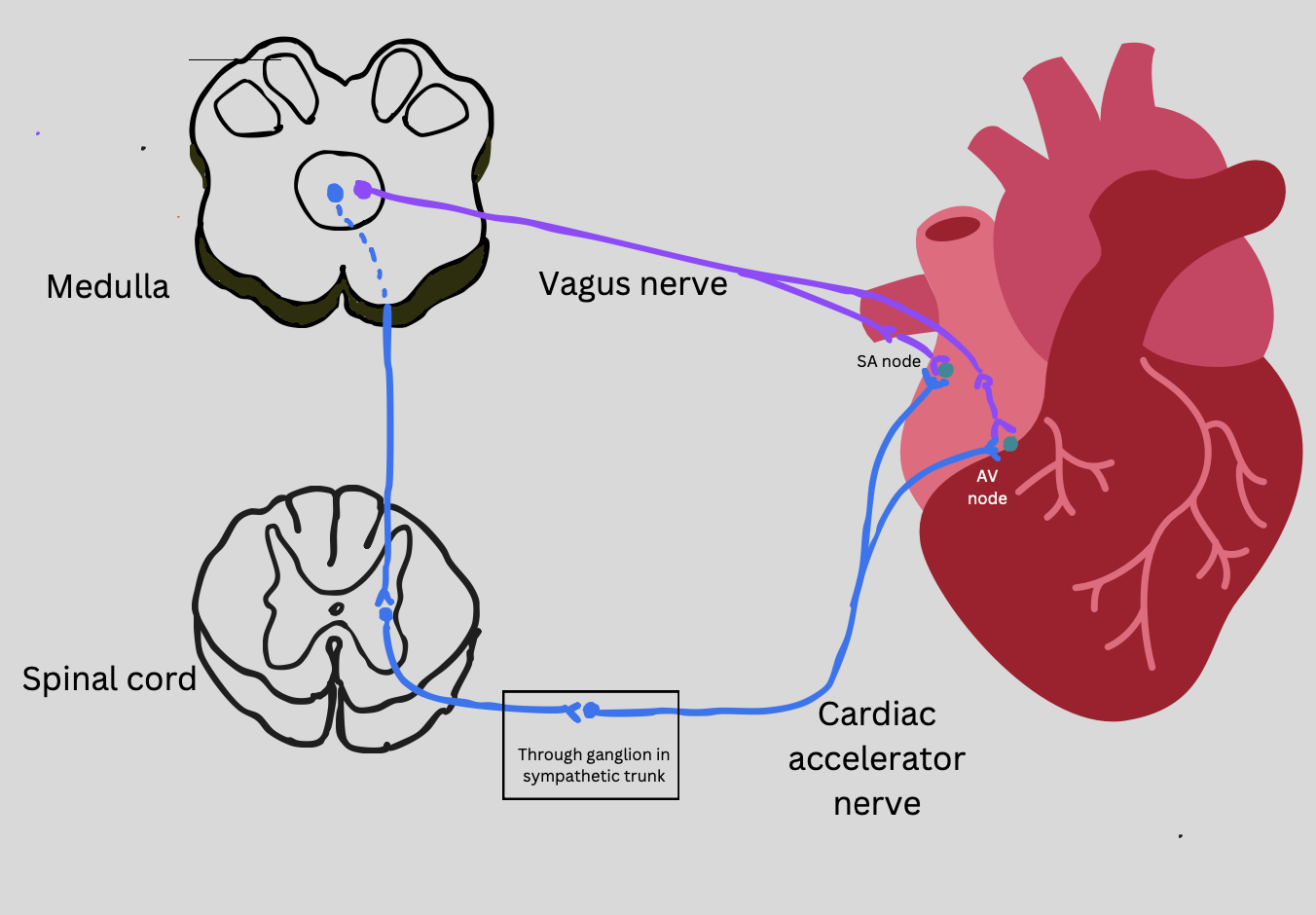
nerve regulation of heart rate
SA node innervated by the parasympathetic nervous system via the vagus nerve
cranial nerve
direct innervation
decrease HR
SA and AV nodes innervated by the sympathetic nervous system via the cardiac accelerator nerve
through spinal cord
Increase HR
factors affecting stroke volume
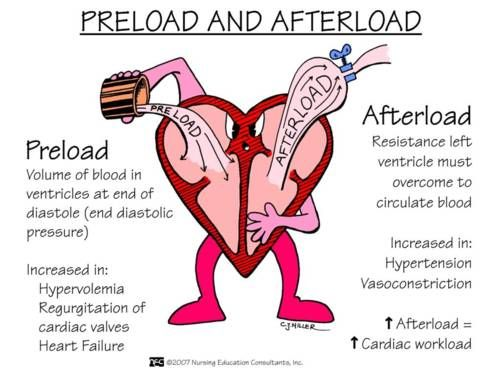
preload
amount of ventricular stretch after diastole (Frank-Starling mech)
contractility
controlled by SNS
afterload
amount of resistance heart must overcome to open aortic valve (inverse to stroke volume)
(not affected by heart rate)
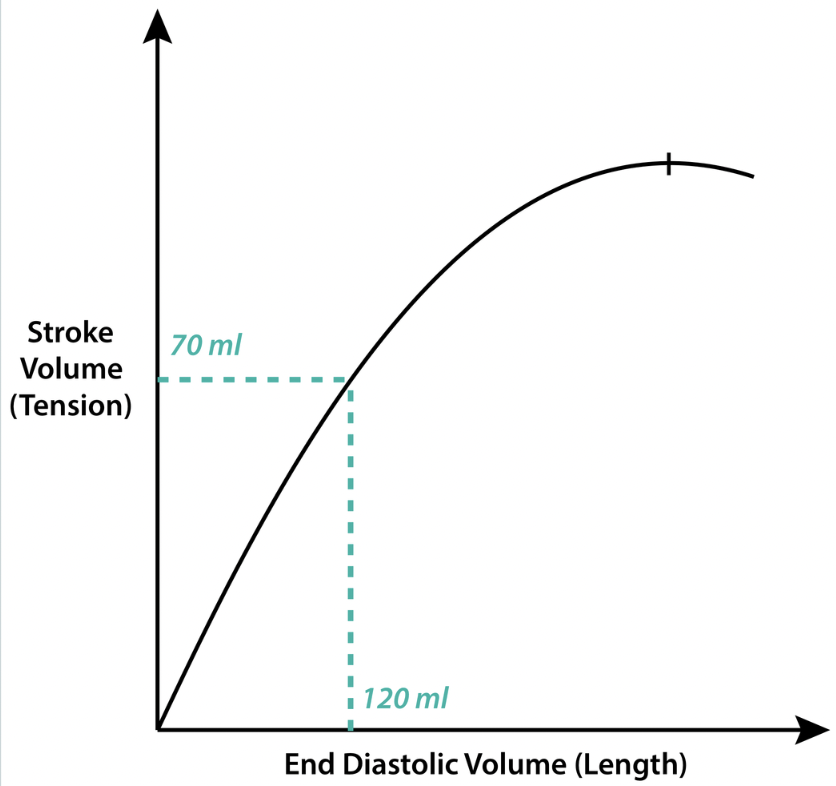
preload
the amount of sarcomere stretch experienced by cardiomyocytes, at the end of ventricular filling during diastole
i.e. the stretch that the blood places on the walls of the ventricles when it’s maximally filled (EDV)
Frank-Starling law: the more you stretch the heart, the greater the reflexive contraction of the heart will be, and the more blood that will be ejected (until plateau)
directly related to venous return
contractility
the relative ability of the heart to eject a stroke volume (SV) at a given prevailing afterload and preload (end-diastolic volume)
impacted by sympathetic activation - contractile strength increasing
afterload
the resistance the blood experiences as it leaves the ventricle
increased afterload = decreased stroke volume
atherosclerosis effect on stroke volume
plaques in the walls of arteries
→ narrowed diameter of the arteries
→ increased afterload
→ decreased stroke volume
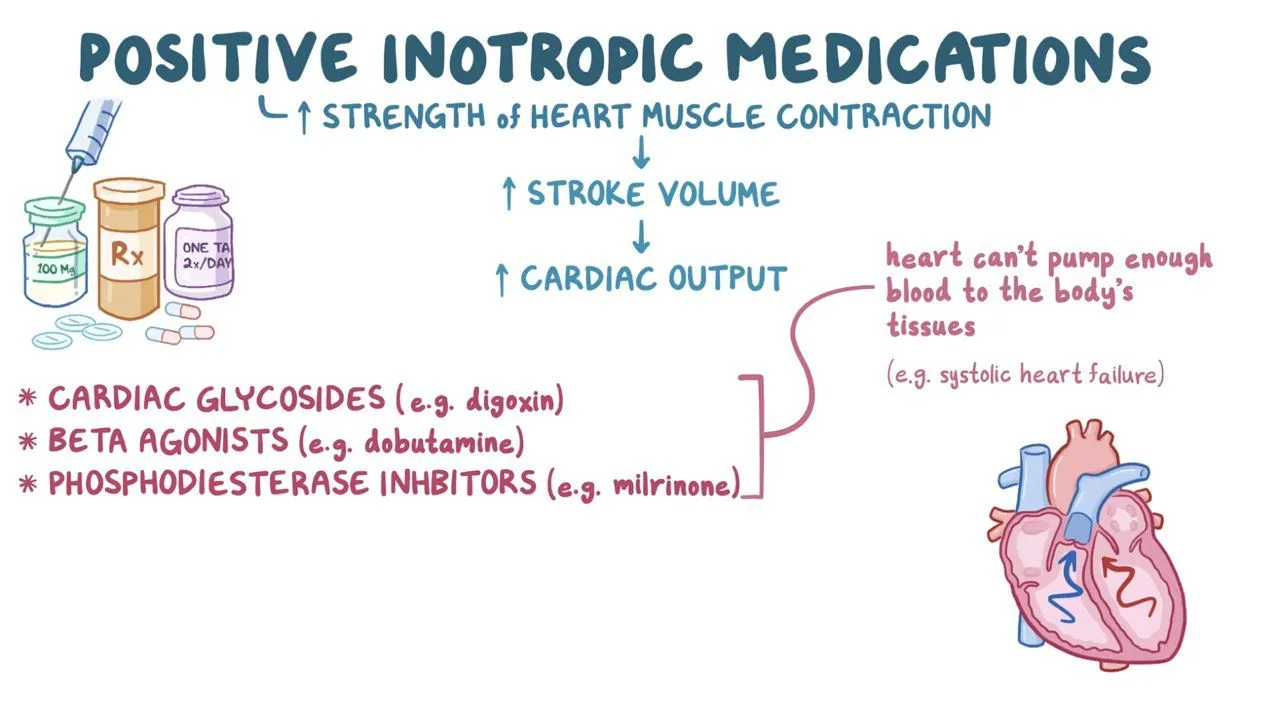
inotropic agents
influence contractile force
positive inotropic agents: factors increasing the availability of Ca2+
noradrenaline
thyroid hormone
negative inotropic agents: factors decreasing the availability of Ca2+
calcium blockers
electrolyte imbalances
chronotropic effects
influence heart rate
positive chronotropic effect:
sympathetic stimulation
anticholinergics (block acetylcholine)
negative chronotropic effect:
parasympathetic stimulation
beta-blockers
total peripheral resistance (TPR)
The sum of the resistance encountered throughout the circulation
For the blood to overcome the resistance and keep flowing forwards, a pressure gradient is required
Controlled by blood vessels and SNS
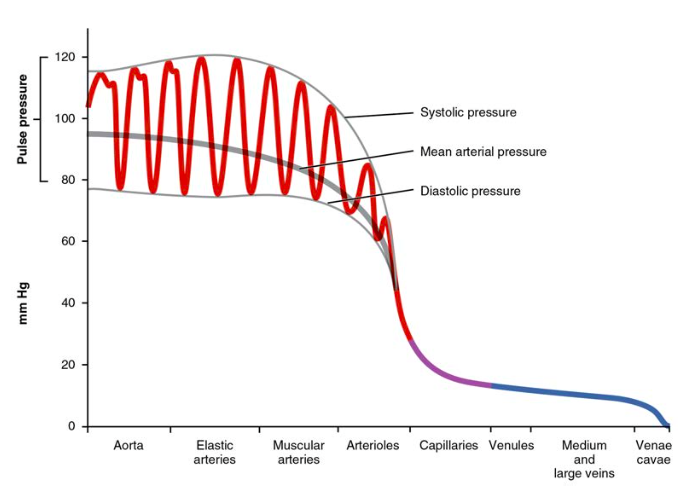
mean arterial pressure (MAP)
the average pressure exerted by the blood
against the vessels
MAP = diastolic pressure + 1/3 pulse pressure
determined by: cardiac output & total peripheral resistance
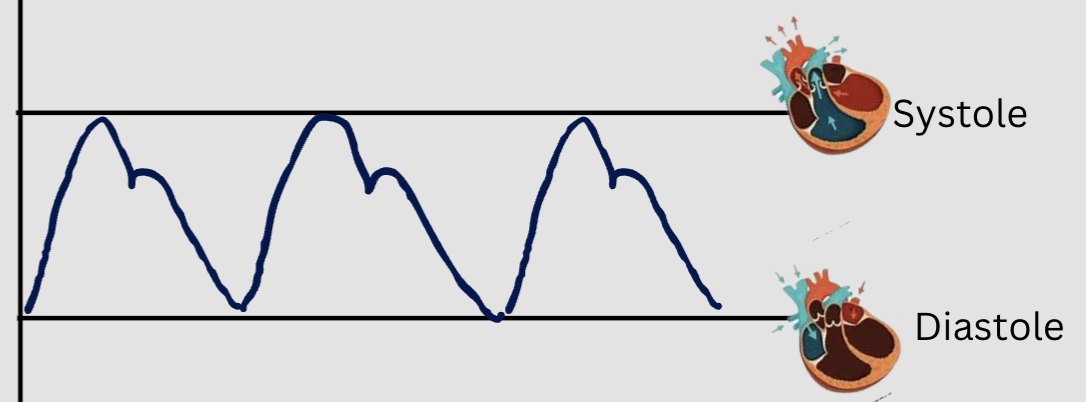
systolic blood pressure
pressure exerted against the walls of the arteries during systole
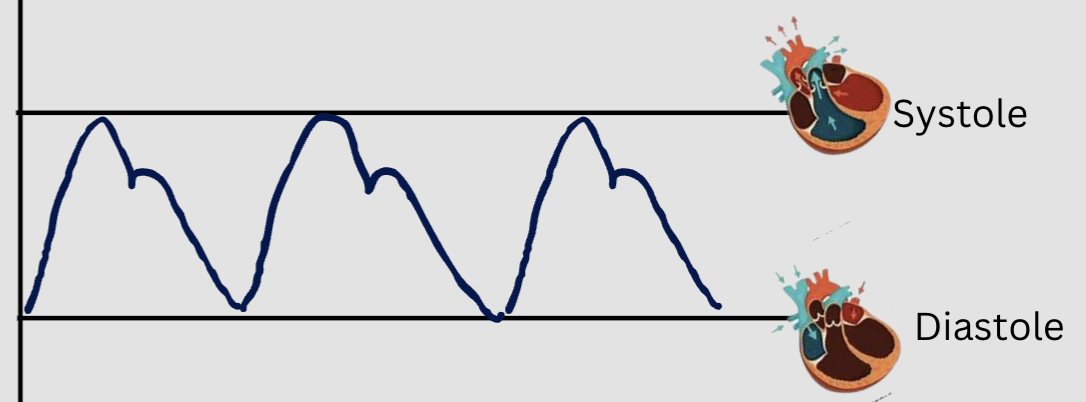
diastolic blood pressure
pressure exerted against the walls of the arteries during diastole
elastic arteries purpose (maybe only Y1)
maintain constant pressure gradient despite pumping action
experience high pressure - Windkessel effect
distension accommodates increased volume with only moderate increase in pressure
recoil maintains relatively high pressure as blood flows away and volume is reduced
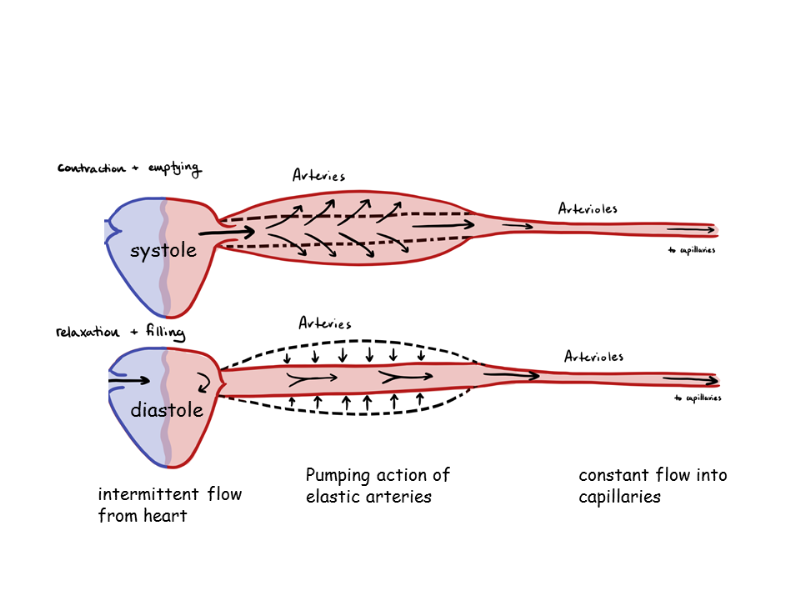
muscular arteries purpose (maybe only Y1)
distribute blood flow to muscles/organs
dampen pulsatility
(don’t have to withstand as much pressure as elastic arteries)
arterioles
regulate blood flow to capillaries
innervated by sympathetic system (only)
a1 → vasoconstriction (SNS)
vasodilates in response to hormones, metabolic controls but NO ß2 for vasodilation (PNS)
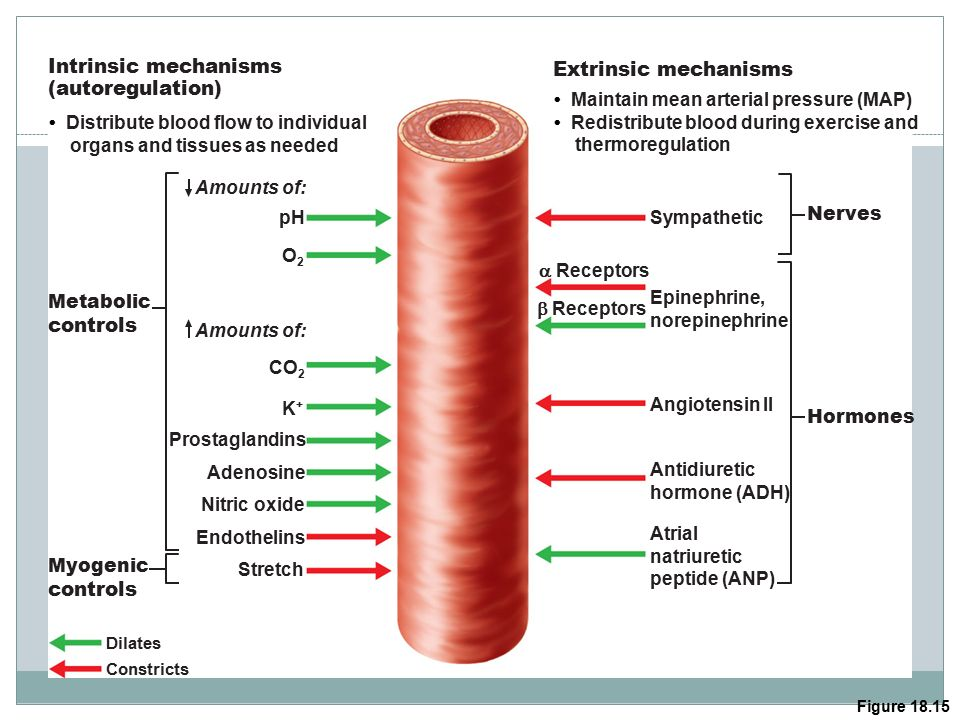
short-term blood pressure regulation
regulate blood flow + TPR
ensure effective capillary exchange
(think kidneys afferent and efferent arterioles)
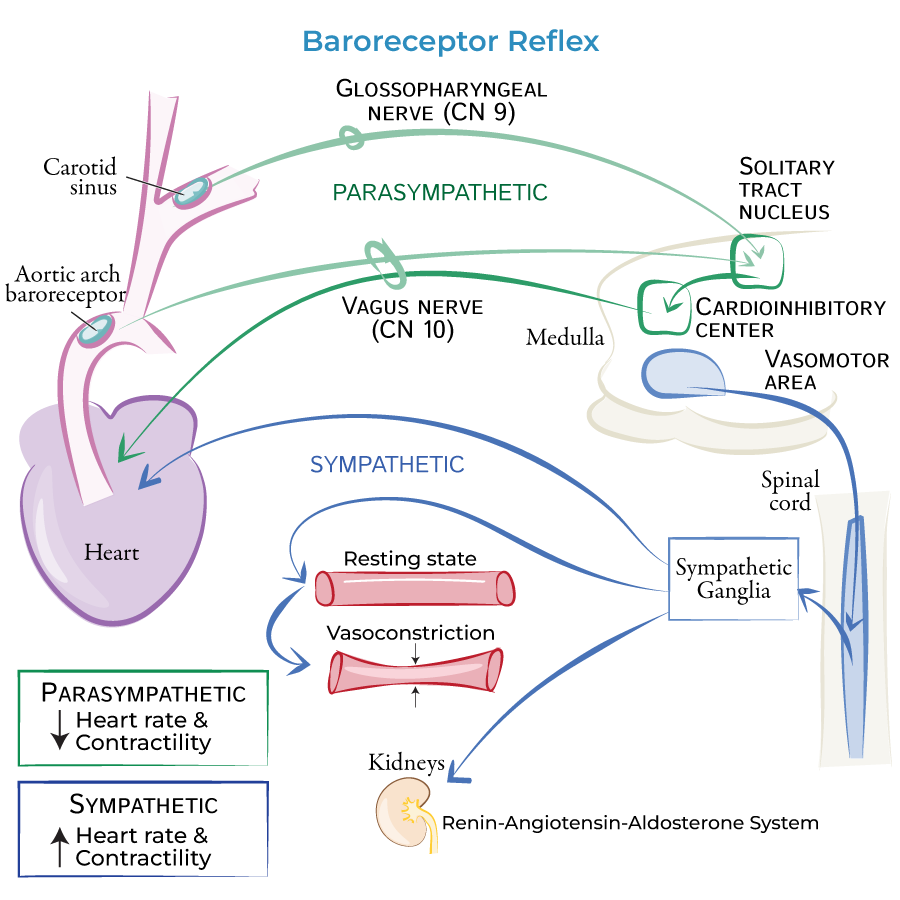
baroreceptors
detect blood pressure
high pressure baroreceptors:
located in arteries (carry blood away from the heart under high pressure):
aortic arch (CNX sensory fibres)
carotid sinus (CNIX sensory fibres)
high pressure baroreceptors send information → cardiovascular centre in the medulla
→ adjusts sympathetic and parasympathetic activity appropriately
low pressure baroreceptors:
located in veins and atria (blood returning to the heart at much lower pressure)
venous system
right atrium
→ pituitary gland releases ADH when blood volume is low
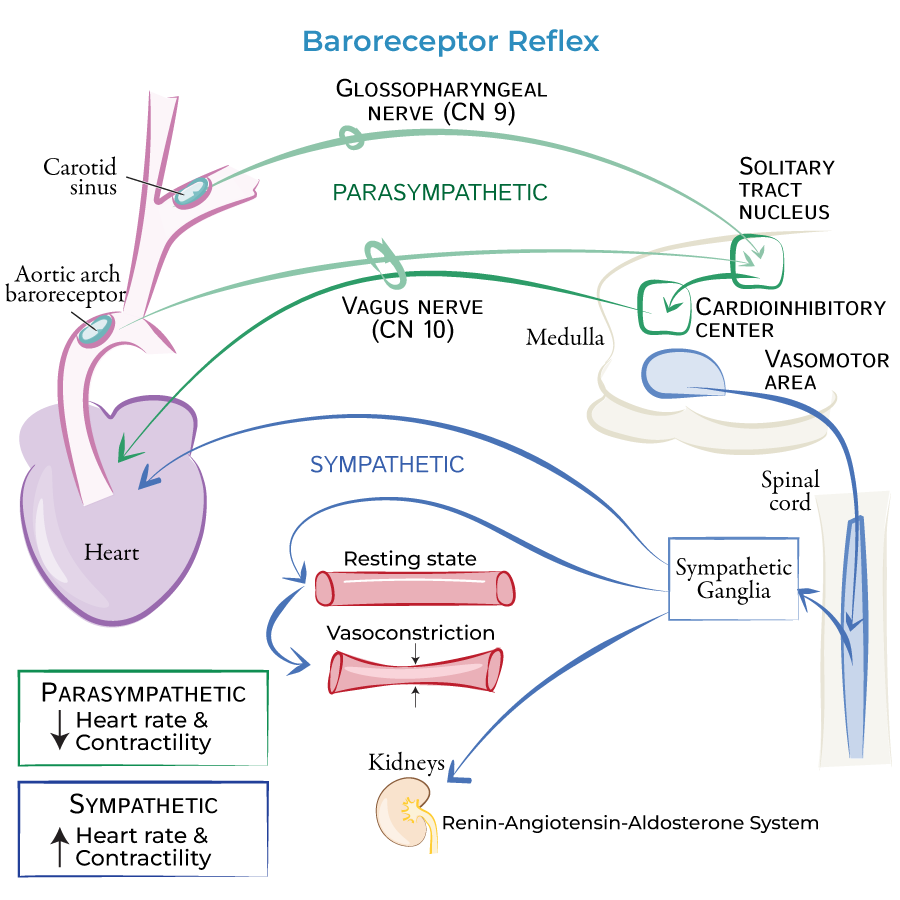
autonomic innervation of the circulatory system
SNS and PNS:
SA and AV nodes
SNS only:
ventricles
blood vessels
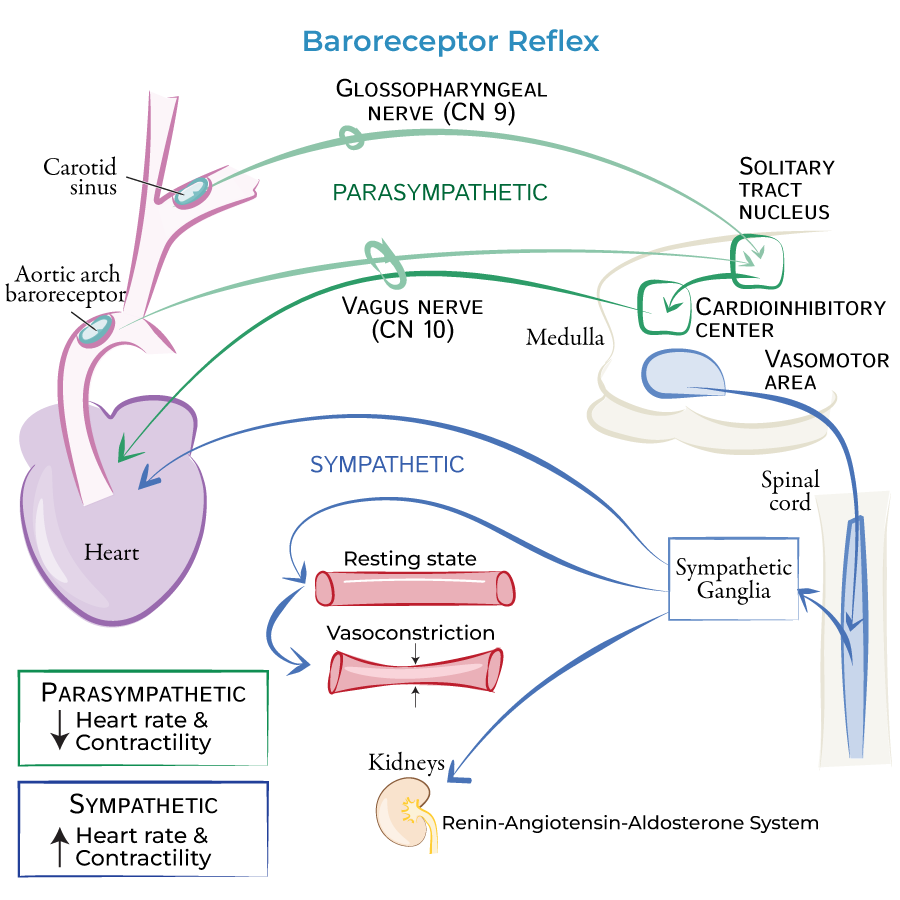
baroreceptor reflex - low BP
Reduced MAP
→ decreased baroreceptor firing rate
→ medulla cardioacceleratory center
sympathetic impulses to heart increasing:
heart rate
contractility
resulting in increased cardiac output
+ vasomotor center activates
increased: total peripheral resistance (vasoconstriction)
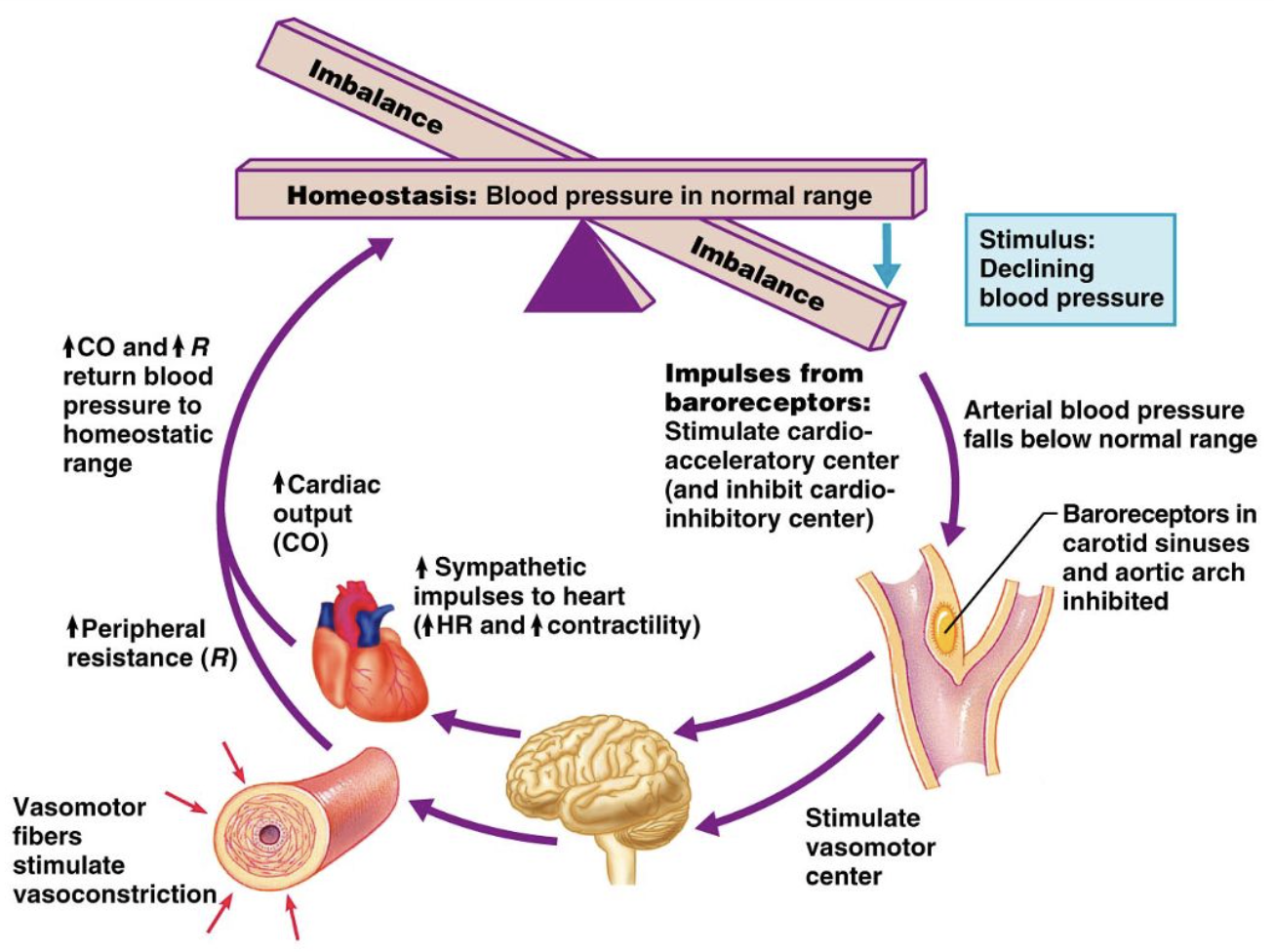
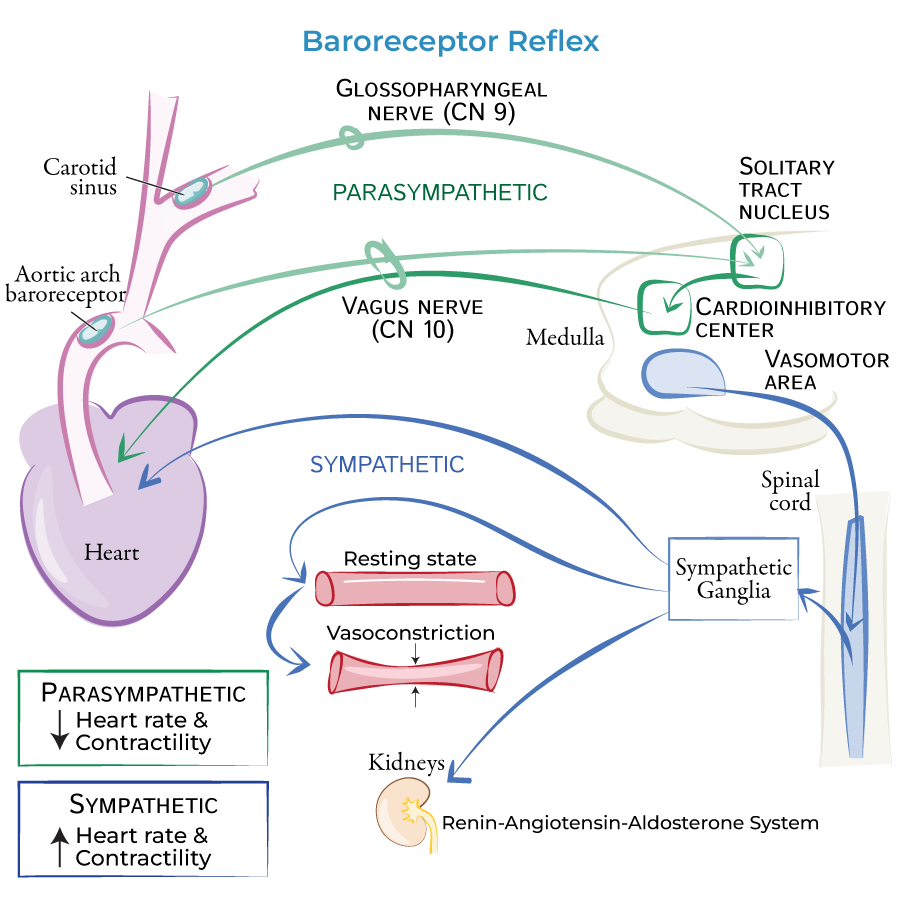
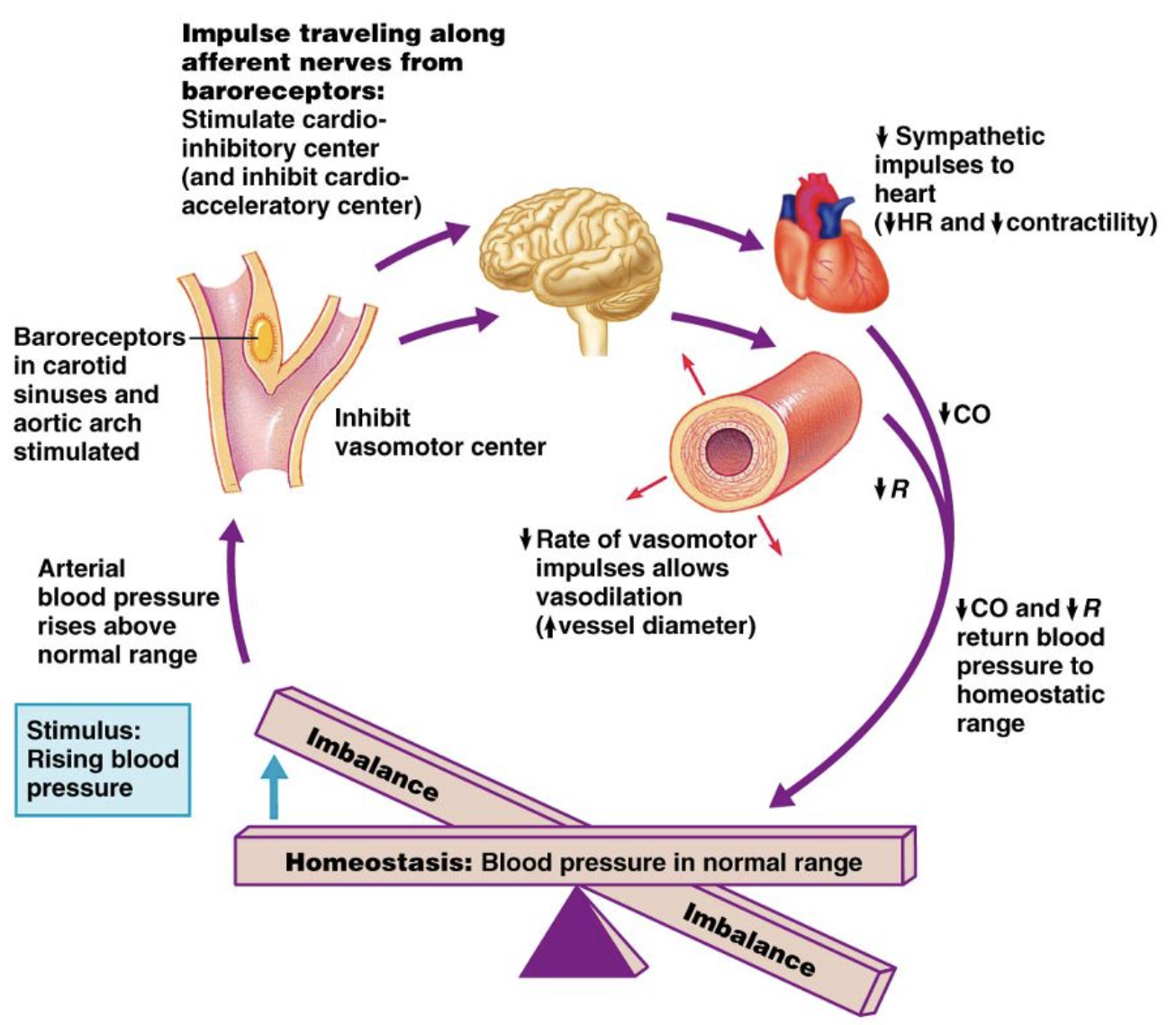
baroreceptor reflex - high BP
Increases in MAP
→ increased firing rate of baroreceptors
→ activate the medulla cardioinhibitory centre (parasympathetic),
decreasing
heart rate
cardiac contractility
therefore decreasing cardiac output
+ vasomotor centre inhibited
decrease total peripheral resistance (vasodilation)
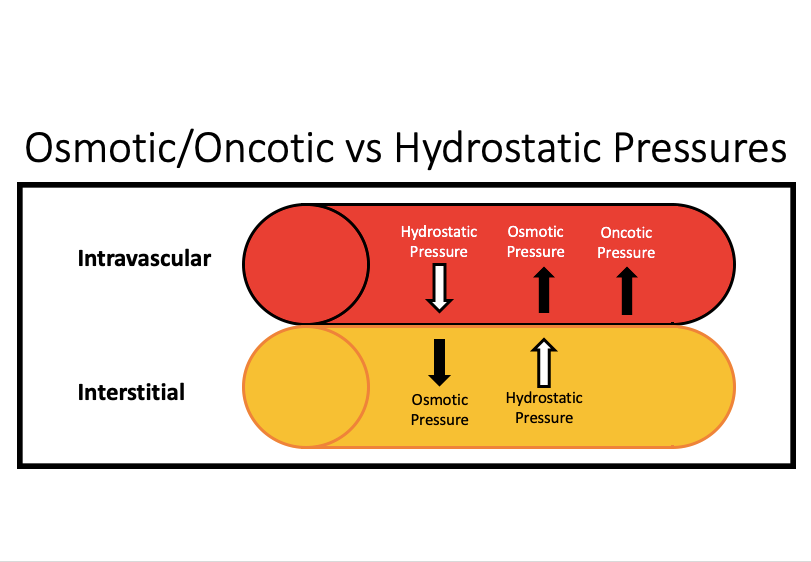
Forces pushing and pulling fluid into the capillary (maybe only Y1)
pushing: interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure
pulling: capillary oncotic pressure
(nutrient exchange at capillaries)
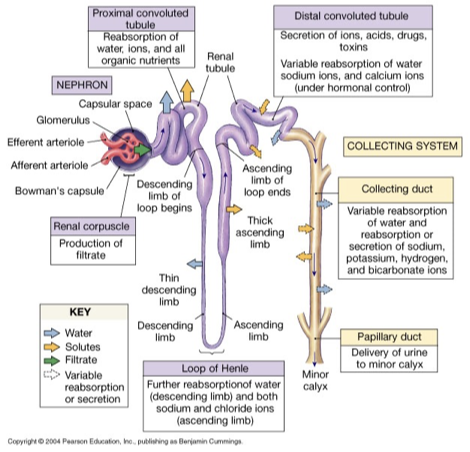
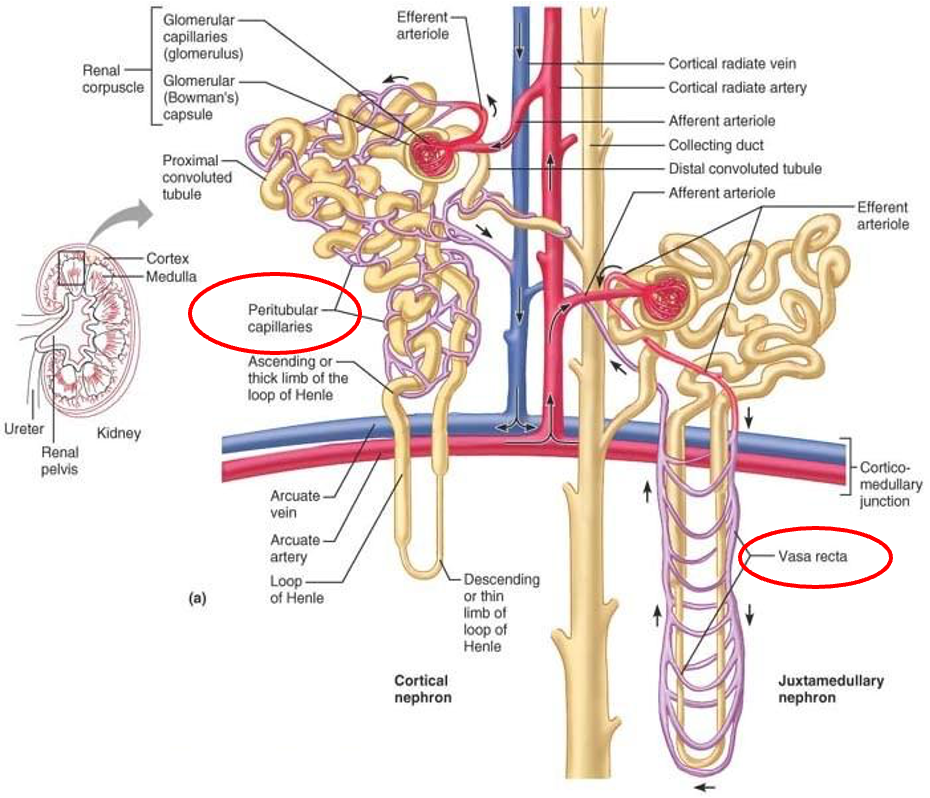
nephron
structural and functional unit of the kidney
glomerulus: high pressure capillary bed, fluid and dissolved solutes diffuse from blood into glomerular/bowman’s capsule
produced filtrate passes through renal tubule (composition continues to be altered)
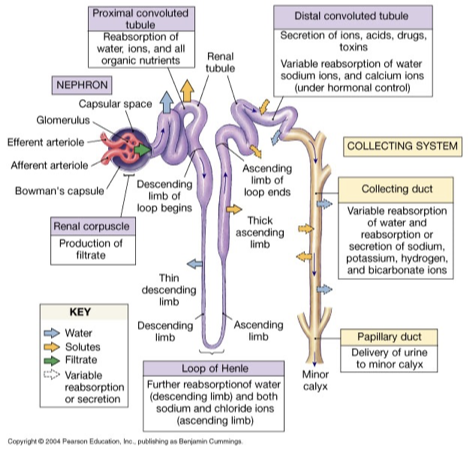
renal tubule
proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
substantial water and solute reenters bloodstream (reabsorbs)
loop of Henle (descending and ascending limb)
descending: only water permeable/reabsorbed (lots of aquaporins)
ascending: only solutes reabsorbed (little to no aquaporins)
distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
hormonal control for what is being reabsorbed
collecting duct
hormonal control for what is being reabsorbed
cortical nephrons
most abundant
found in cortex (outside) of the kidney (except loop of henle that dips into medullary portion)
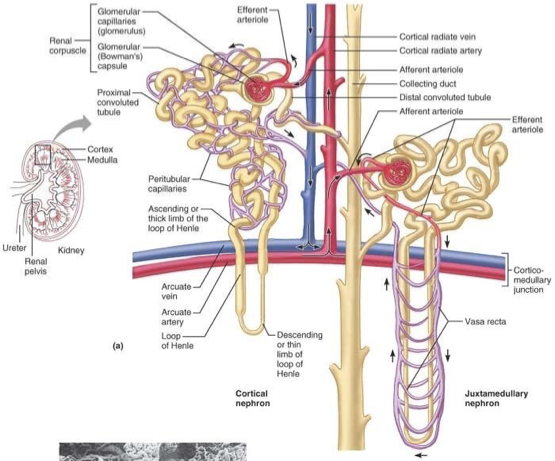
juxtamedullary nephron
less common
glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule arise near cortex-medullary junction
loops of Henle deeply invade renal medulla
important in producing concentrated urine
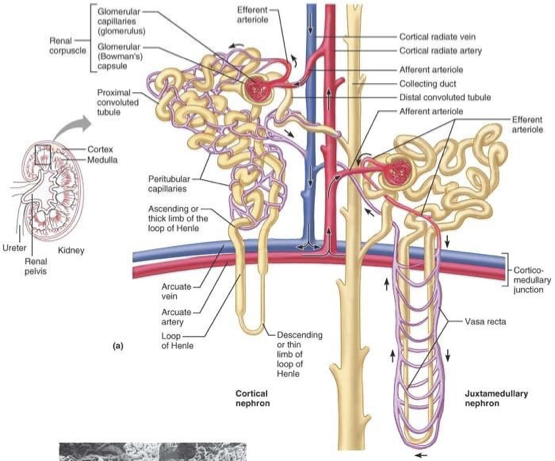
glomerulus
high pressure capillaries
site of filtration
fluids and solutes forced into glomerular capsule
fed by afferent arterioles
drained by efferent arterioles
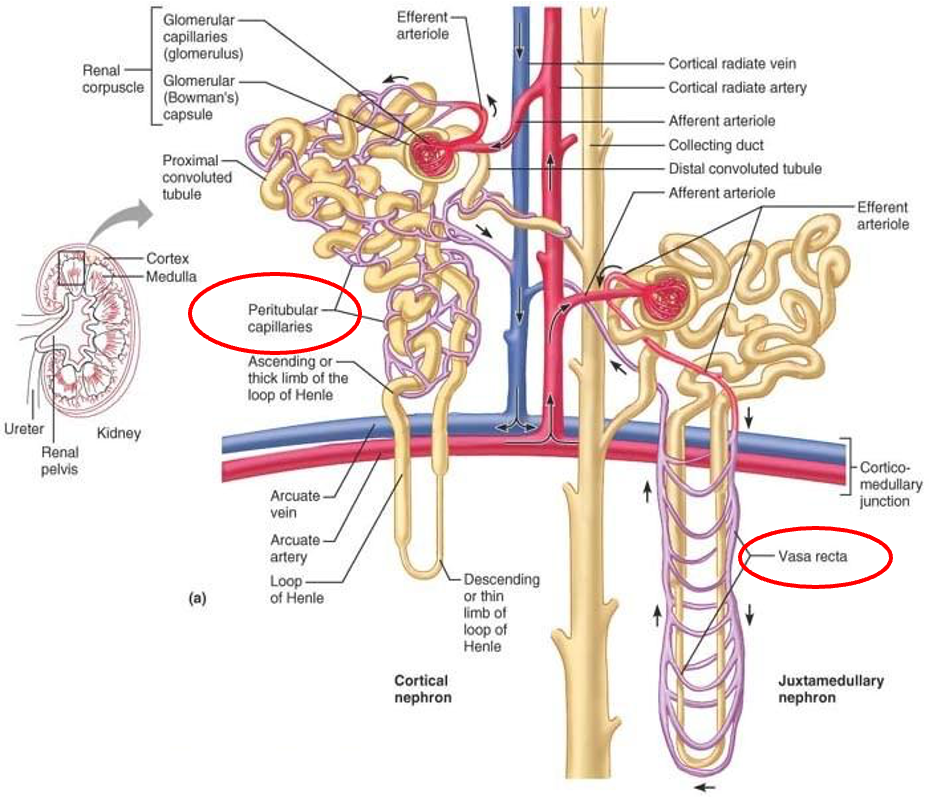
peritubular capillaries
arise from efferent arteriole
low pressure porous capillaries
filter waste from blood
reabsorb water and solutes from filtrate back into blood
vasa recta - long straight vessels serving juxtamedullary nephrons
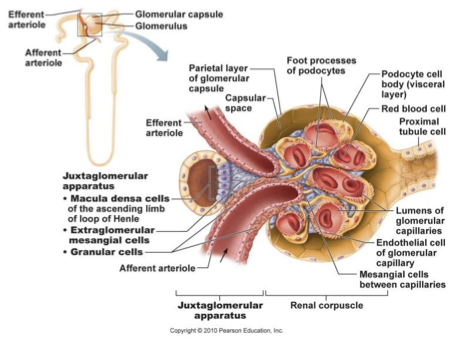
juxtaglomerular apparatus
region where distal portion of ascending limb lies against afferent arteriole
contains:
juxtaglomerular/granular cells
macula densa
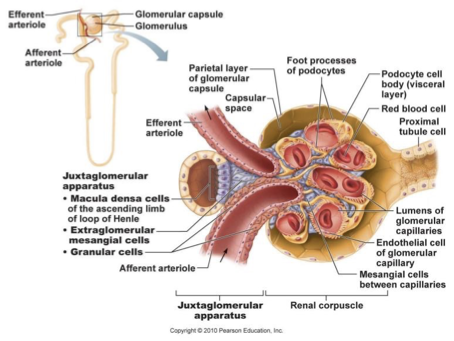
juxtaglomerular/granular cells
enlarged smooth muscle cells
secretory granules producing and storing renin
mechanoreceptor that sense BP in afferent arteriole (low BP increases renin release)
controls arteriole diameter to regulate blood flow
NA
→ ß1 receptors
→ renin secretion
macula densa cells
specialised epithelial cells
closely packed cells of ascending limb
chemoreceptors - monitor changes in NaCl in distal part of nephron
responsible for vasoconstricting afferent arteriole to regulate blood flow/filtrate into glomerulus
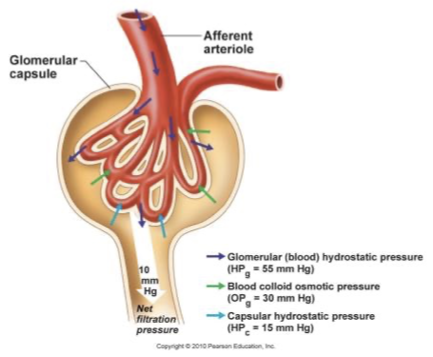
glomerular filtration
BP forced fluids and solutes across glomerular capillaries into glomerular capsule
passive process
leaky glomerular capillaries made of fenestrated endothelial cells (open windows)
high pressure and large surface area increases filtration efficiency
small molecules move down pressure gradient across filtration membrane
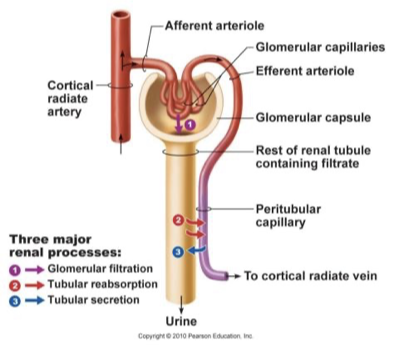
glomerular blood pressure
filtration rate mainly dependent on BP
afferent arterioles: short, large diameter
efferent arterioles: smaller diameter
therefore high rate of blood flow into glomerulus, low rate out of glomerulus
glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
indicator of kidney function: volume of filtrate produced by all the glomeruli in both kidneys per minute
Intrinsic mechanisms (renal autoregulation) maintain stable filtration under normal conditions.
Extrinsic mechanisms prioritize systemic blood pressure and survival during emergencies, sometimes at the cost of kidney filtration
Intrinsic renal mechanisms
alter blood volume
increased blood pressure + renal blood flow increase water + sodium excretion (urine production)
two mechanisms:
pressure diuresis
high pressure
→ more filtrate formed
→ more urine formed
pressure natriuresis
sodium excretion:
filtrate is formed faster and pushed through nephron faster
not much time for sodium reabsorption
electrolytes remain in filtrate and water follows and remains so more urine formed
hormones regulating the reabsorption in distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct
Aldosterone
ADH
ANP
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
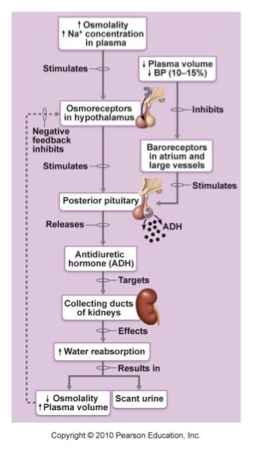
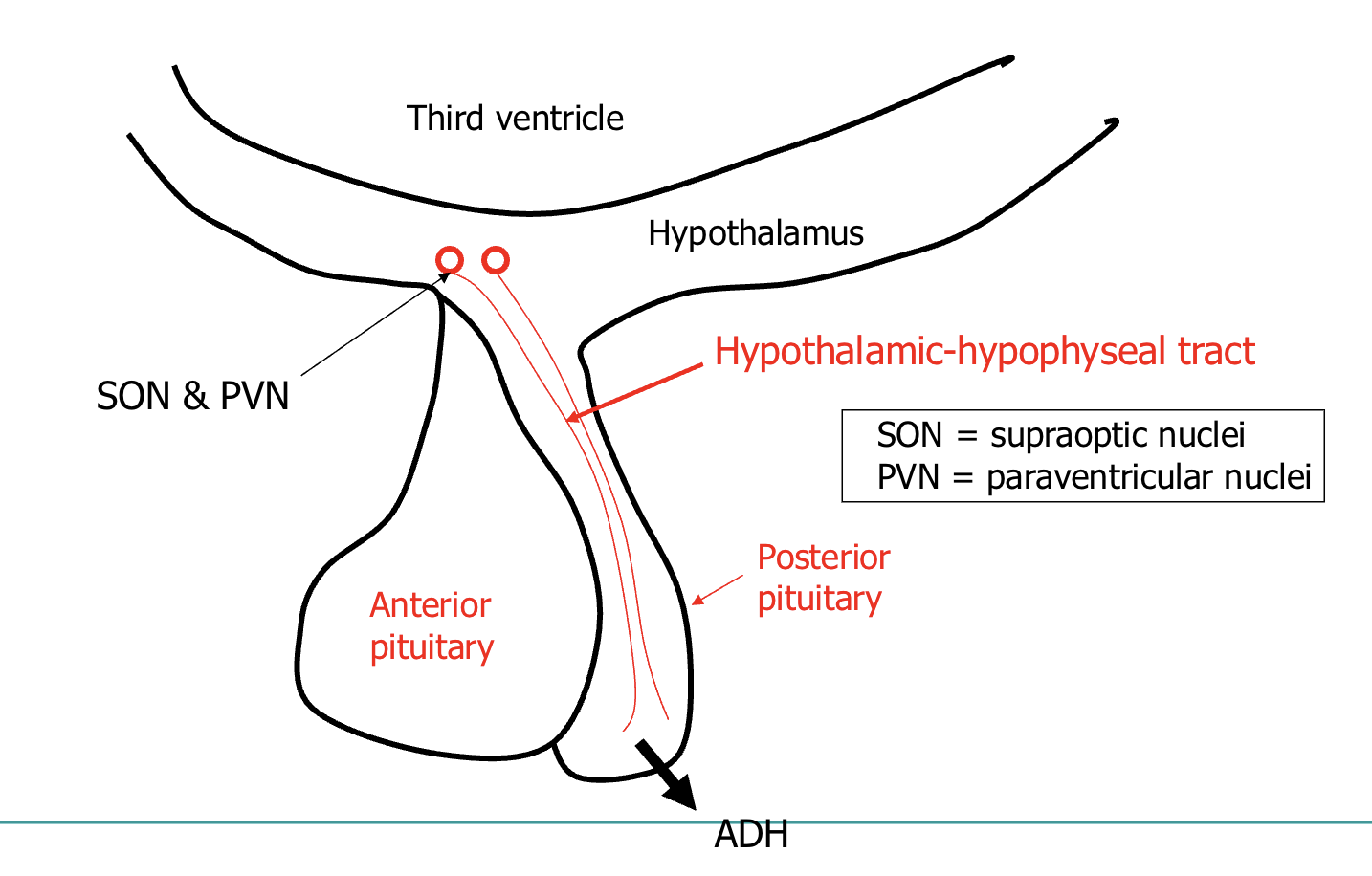
anti-diuretic hormone
Hypothalamic neurons called osmoreceptors monitor solute concentrations in the blood
If blood becomes too concentrated OR if BP is low:
ADH released by posterior pituitary
Targets collecting ducts (via cAMP system)
Water reabsorbed from filtrate
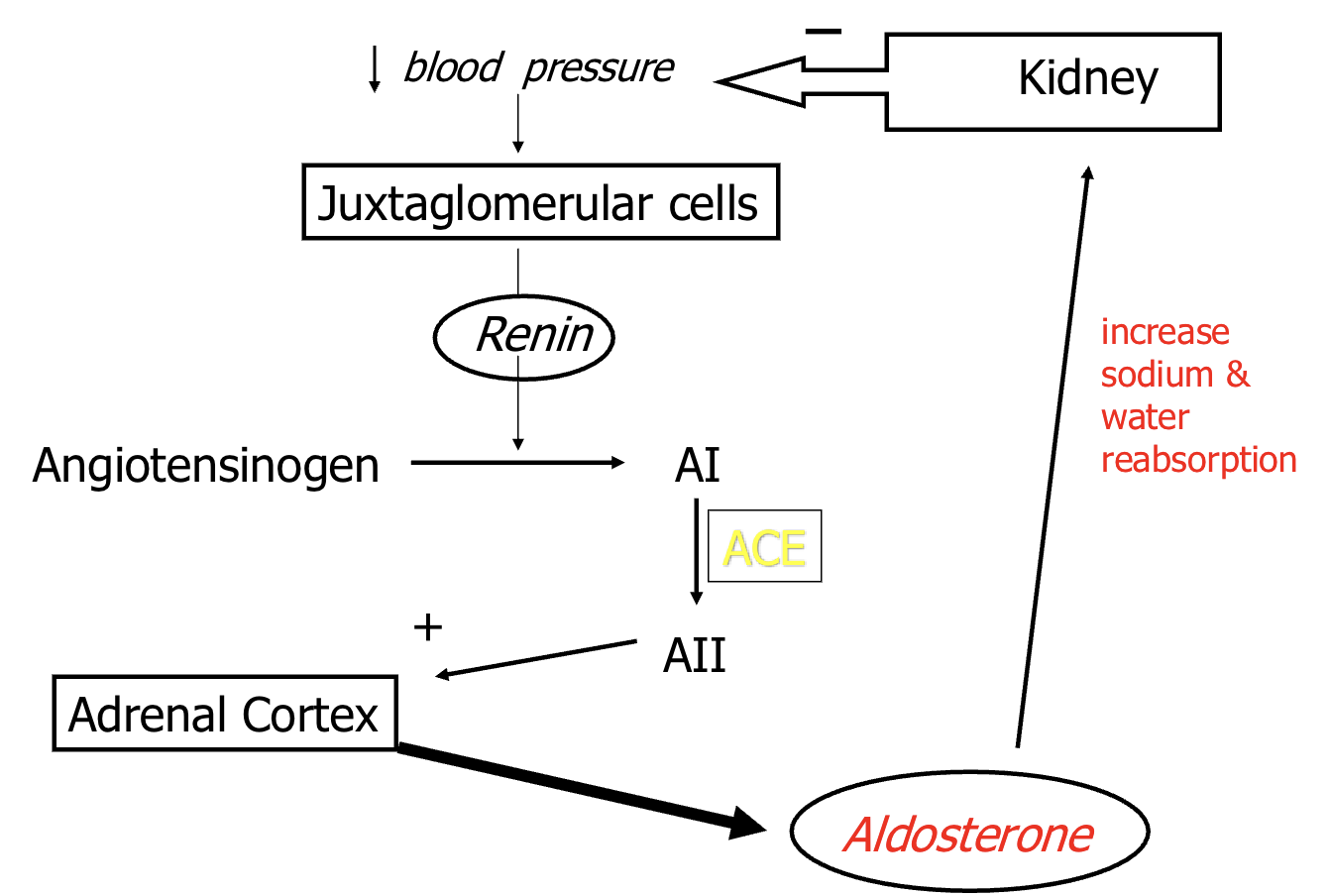
ACE
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (RAAS system)
Angiotensin I → Angiotensin II
ALSO: Bradykinin → inactive metabolites
ACE inhibitors lead to the accumulation of bradykinin in lungs → cough
found in endothelial cells of all tissues
AI → AII primarily converted in the lungs (due to their dense vasculature and high ACE expression)
RAAS system
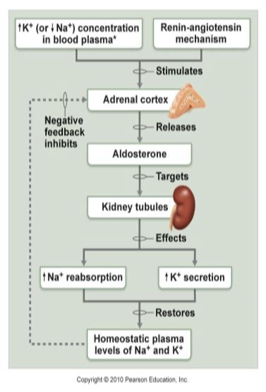
aldosterone
regulates amount of Na+ reabsorption (Na+ decrease = aldosterone release)
Zona Glomerulosa in adrenal cortex releases aldosterone in response to
Decreased blood volume or BP
renin-angiotensin system
Angiotensin II
Increased Potassium
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
Atrial natriuretic peptide
action: DCT (distal convoluted tubule) and collecting duct
Increases blood volume
Na+ reabsorption
Water reabsorption
K+ & H+ excretion
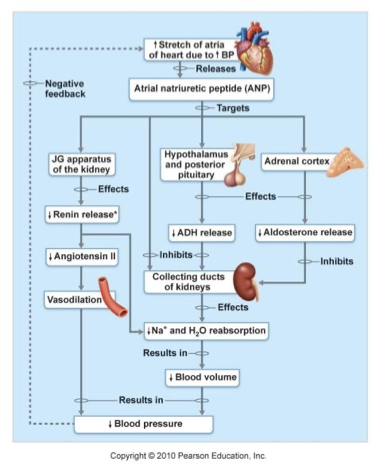
atrial natriuretic peptide
secreted by specialized cardiac muscle cells in the atria
triggered by increased BP
Inhibits the renin-angiotensin system and release of aldosterone
Inhibits Na+ and water reabsorption
↓ blood volume and BP
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)/vasopressin
secreted by posterior pituitary after
increased osmolality of bodily fluids
decreased volume and pressure of vascular system
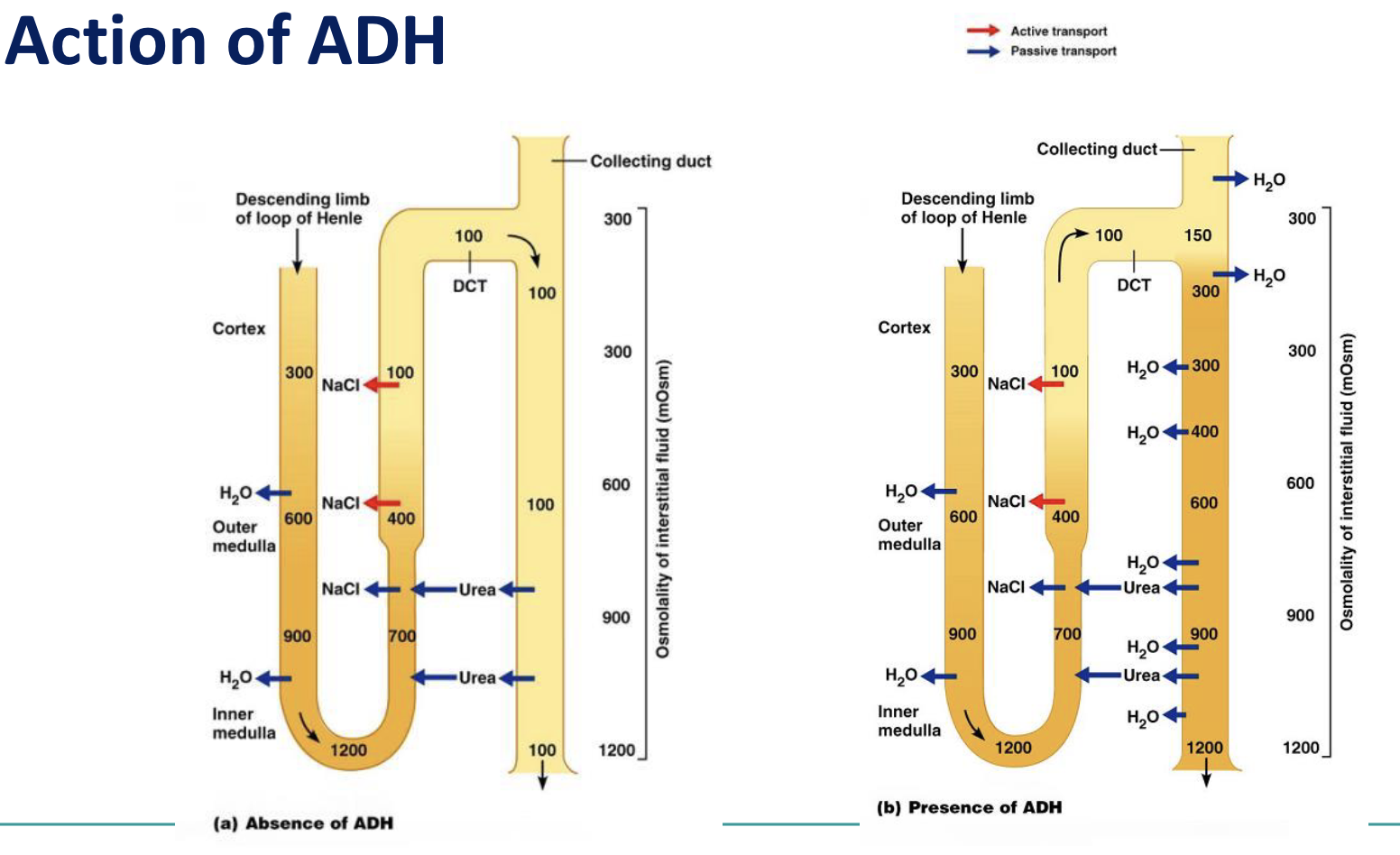
increases permeability of collecting ducts to:
water (primary action) (via aquaporins)
urea (accumulates with NaCl - adding to osmotic gradient)
stimulates reabsorption of NaCl by thick ascending limb of Loop of Henle, DT and collecting duct
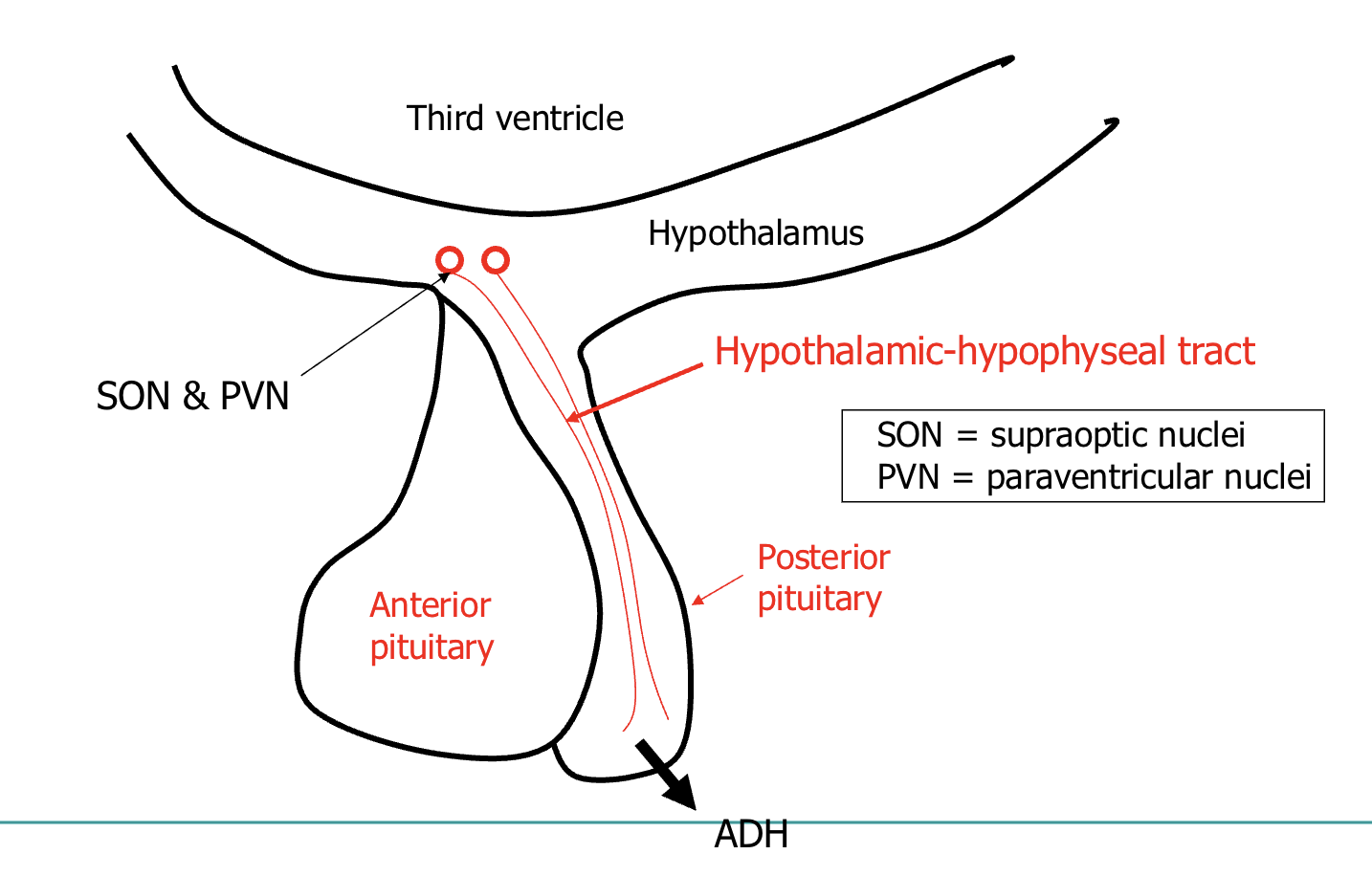
Synthesised in the hypothalamus
- paraventricular nucleus
- supraoptic nucleus
➢ Released from the posterior pituitary
➢ Acts on
➢ V2 receptors in the kidney induce water retention
➢ V1 receptors on blood vessels cause vasoconstriction
➢ Antidiuretic effect
Increases water permeability in distal convoluted
tubule and collecting ducts (by increasing number of
water channels (aquaporins)
how is ADH triggered to release
1% rise in osmolality can significantly increase ADH secretion
detected by osmoreceptors in hypothalamus
10% drop in blood volume stimulates low pressure baroreceptors (atria and veins) to send signals to release ADH
signal sent to synthesising cells located in hypothalamus:
supraoptic nuclei
paraventricular nuclei
released from posterior pituitary
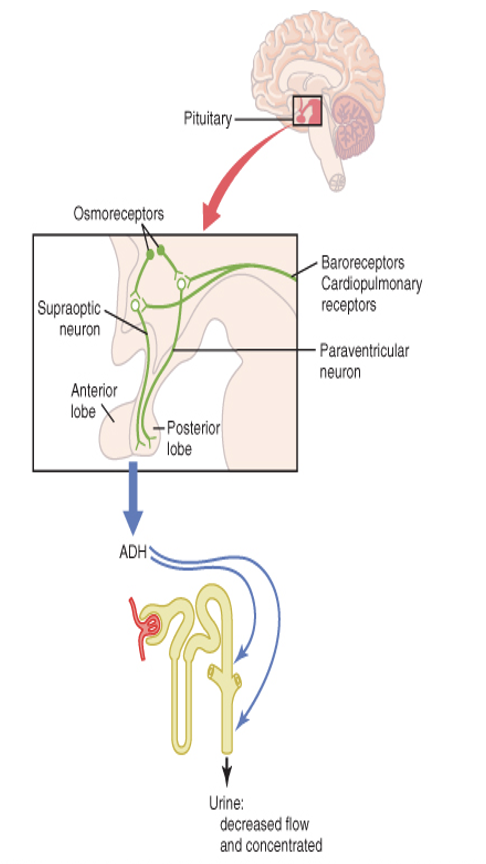
actions of ADH
V1 receptors on blood vessels cause vasoconstriction
V2 receptors in the kidney induce water retention
Increases water permeability in distal convoluted
tubule and collecting ducts (by increasing number of water channels (aquaporins)
ATP binds to
P2X receptors (pyronergic)
Adenosine binds to
A1 receptors