Nervous System, Neurons, and Membrane Potential
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
CNS
brain
spinal cord
CN II (optic nerve)
neural retina
basic unit of CNS
neurons
support cell of CNS
glia cells
PNS
nerves and ganglia outside of CNS
sensory division: afferent nerve fibers
motor division: efferent nerve fibers
somatic nervous system: voluntary
autonomic nervous system: involuntary
afferent nerve fibers
signals from tissues and organs TO the CN
efferent nerve fibers
signals FROM the CNS to organs
basic elements of axon
dendrites
cell body
axon hillock
axon terminal
dendrites
receive signals (inputs) via synapses
has neurotransmitter receptors in the plasma membrane
***sensory neurons in skin fo not have dendrites, but instead receptors for physical stimuli**
axon function
carry neural signals
microtuble
transport lipids, proteins, polypeptide, mitochondria, synaptis vesciles in the cell body to the axon terminal (anterograde)
key proteins: dynein, kinesin 1 and kinesin 2
concentration gradients of 4 major species
extracellular fluid
Na+: 150 mM
K+: 5mM
Cl-: 110 mM
Ca2+: 1 mM
intracellular fluid:
Na+: 15 mM
K+: 150 mM
Cl-: 7 mM
Ca2+: 0.0001 mM
these ions are not permeable to membrane, will always need a chnanel/pump
resting membrane potential
membrane is non-permeable to ions, no traffic
electroneutrality on each side
E= -90 mV (equilibrium)
Ohm’s equation
V=RI
V= electromotive force (volts)
I= ion current (amps)
R= resistance, channel openned/closed (ohms)
conductance (G)= conductance (Siemens) is 1/R
conductance (G)
1/R
high value if channels opened
low value if channels closed
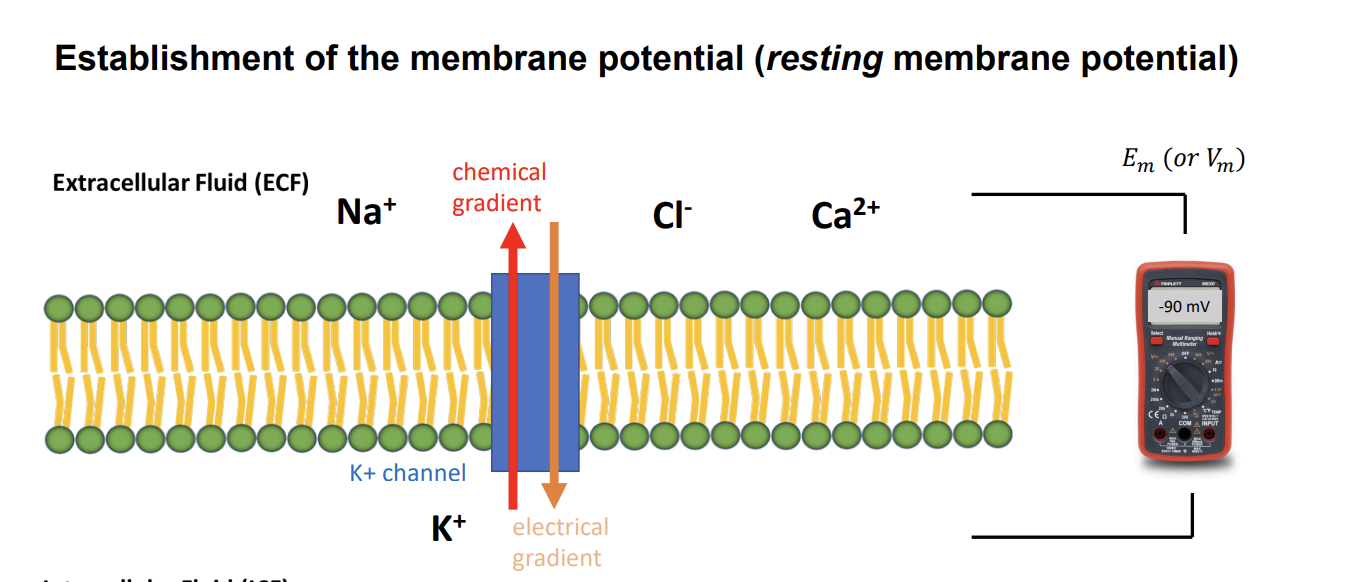
electroneutrality
ECF and ICF have equal concentration of ions
what is the E value for resting potential?
E= -90 mV to -70 mV
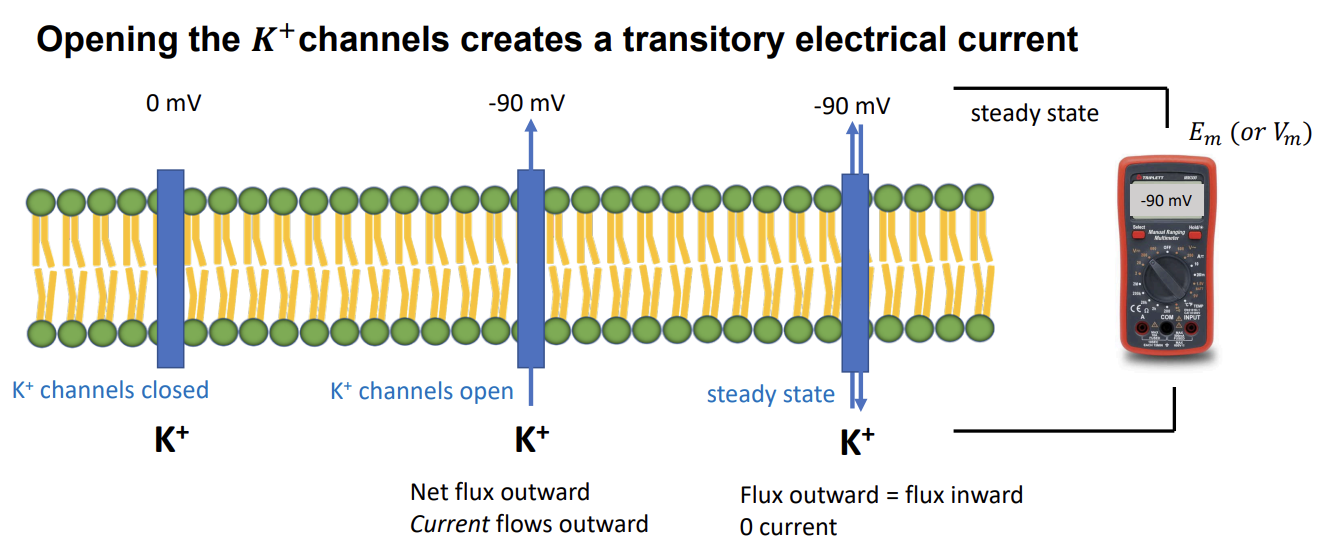
K+ channel opens
create transitory electrical current
K+ from ICF flows outward
net flux is electrical current (in amps)
Ik+ = Gk+(Em-Ek+)
Em-E = driving force
the direction is (+)
compare G value of species at rest
Gk > Gcl > Gna > Gca
Nernst Equation
calculate electrochemical equilibrium potential for an ion
E= (RT/z)ln(ion outcside/ion inside)
R= 8.314 JK-1mol-1
T= absolute temp (K=C+273.15)
F= 98485 Cmol^-1
z= valence of ion
what is standard body temperature?
37*C
chord equation
don’t have remember the equation, just the logic
does not take into account of temperature
goldman-hodgkin-Katz equation
When membrane is permeable to several different ions, the resting membrane potential depends on permeability, charge, and concentrations of all the ions and temperature.
Pion in the GHK equation is relative conductance of that ion.
Pion in GHK equation = Gion/Gtotal
it iss the product of the Nernst and chord equations
neuronal organization of retina
photoreceptors (outer nuclear layer): receive input and make synapses w bipolar cells
bipolar (inner nuclear layer): receives input from photoreceptors and makes synapses w retinal ganglion cells
retinal ganglion cells (retinal ganglion cell layer): receive input from bipolar and send it to the brain for vision processing
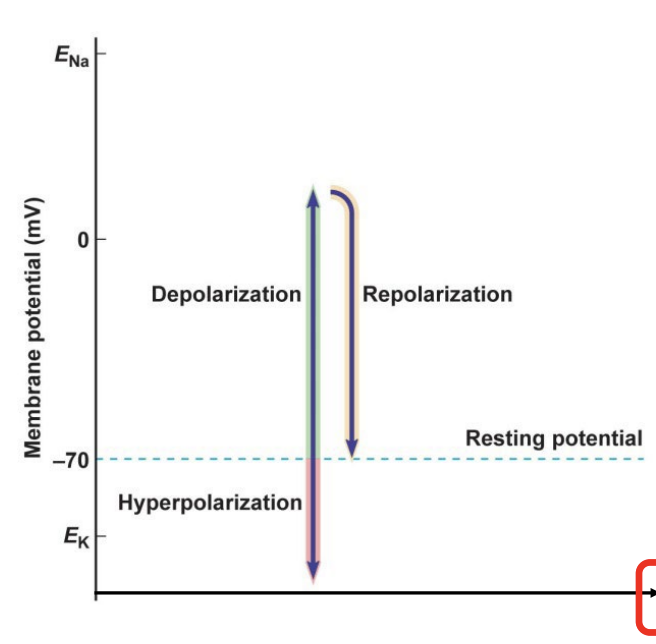
hyperpolarizing
more negative than resting potential
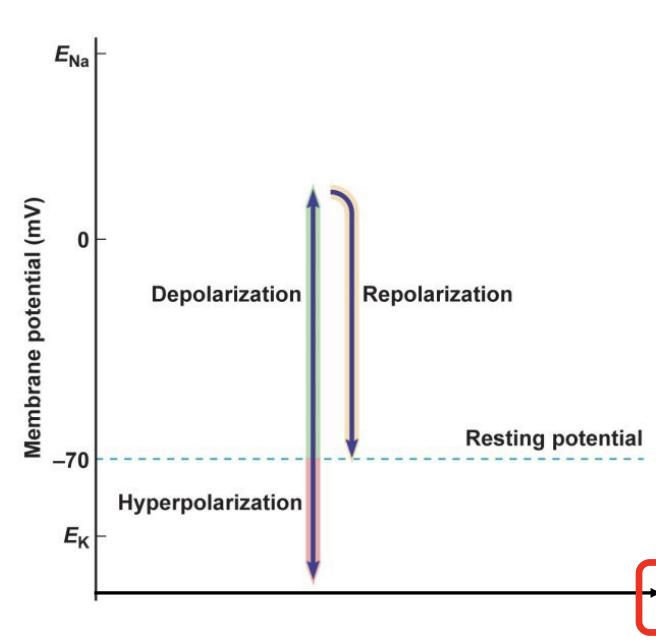
depolarizing
more positive than resting potential
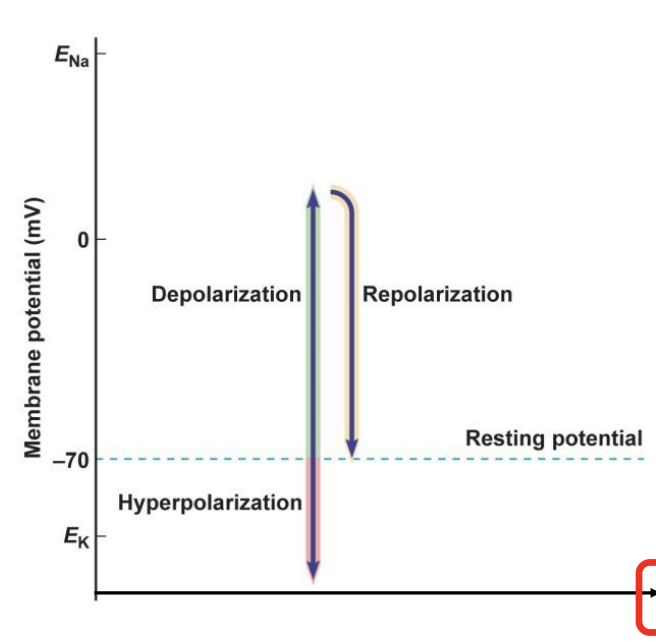
repolarizing
a change toward resting potential, from more positive or more negative potential
signaling
fluctuation of the membrane potential round its resting state
flux
net flux = electrical current (amps)
direction of electric current
defined by the direction in which the (+) charge moves (inward or outward)
the driving force
when the membrane potential to at an x current away from an ion steady state, that ion will move in a direction that will compensate the difference → generate a current