Gluconeogenesis
1/32
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What are the 3 major sources of Carbon in humans?
Lactate
Glycerol
Alanine
RBCs undergo aerobic or anaerobic glycolysis? Why?
Anaerobic
Because they lack Mitochondria!
What is produced by anaerobic glycolysis in tissues?
Lactate is produced from glucose through anaerobic glycolysis in tissues, especially in Muscle and Red blood cells.
What is released from adipose stores of TAG?
Glycerol
What is a major gluconeogenic amino acid produced from other amino acids?
Alanine
What are the 3 irreversible steps of gluconeogenesis? *
Pyruvate to Oxaloacetate (Pyruvate carboxylase)
Oxaloacetate to PEP (Phosphoenolpyruvate) (PEP carboxykinase)
Fructose 1,6 bisphosphate to fructose 6 phosphate (Fructose 1,6 bisphosphate)
List down the steps of Gluconeogenesis
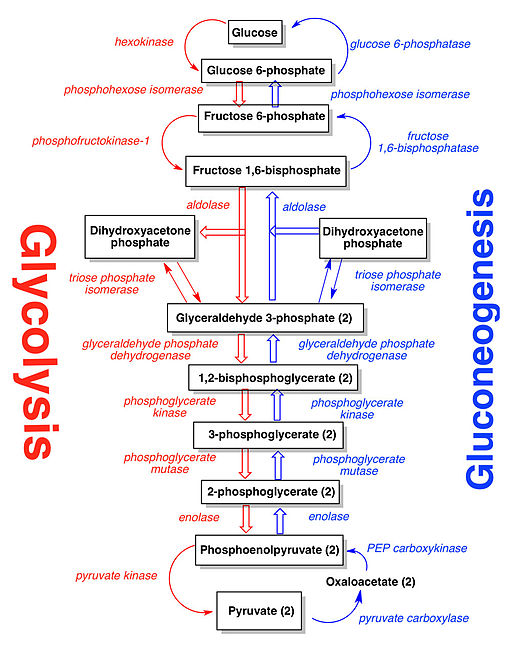
What does the conversion of Pyruvate to oxaloactetate require? What is it allosterically activated by?
Biotin and ATP. Allosterically activated by Acetyl CoA
During gluconeogenesis, the pyruvate used will come from ___ and ___, NOT ____.
From Alanine and Lactate
Not PEP
How does OAA leave the mitochondria?
Through the malate shuttle.
OAA is reduced to malate with the help of? ___
NADH
Why are there no overlapping enzymes in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis?
During gluconeogenesis, glucagon increases which is also responsible for breaking down lipids -> FA -> AcetylCoA + ATP
AcetylCoA and ATP from FAs inhibit Pyruvtae Kinase
AcetylCoA also stimulates Pyruvate carboxylase
No pyruvate dehydrogenase = no conversion of pyruvate to acetylCoA
Describe the mitochondrial pathway of the conversion of OAA to PEP
Utilizes pyruvate carboxylase and PEPCK
Describe the Cytosolic pathway of the conversion of OAA to PEP
Utilizes PEPCK
Lactate, a gluconeogenic substrate is converted into pyruvate and prefers which pathway?
Mitochondrial Pathway, which utilizes Pyruvate carboxylase.
The Malate-Aspartate shunt is another pathway on how ____ is converted into ___. This involves the formation of ___ through the process of ___
OAA, pyruvate, malate, gluconeogenesis.
What are the 2 substrates that can leave the mitochondria freely?
Malate and Aspartate
Which two amino acids are Ketogenic?
Leucine and Lysine
What is the most important regulator of Gluconeogenesis? And Why?
Glucose
High Glucose = Insulin, which regresses gluconeogenic enzymes
T/F Epinephrine, which is released by the kidneys during starvation state is a Gluconeogenic Hormone.
True, as it promotes gluconeogenesis to increase glucose availability during fasting.
Explain IREB’s action
____ triggers the activation of IREB
IREB sticks to the PEPCK gene and ____ the production of PEPCK
Less PEPCK =____ sugar produced
Insulin triggers the activation of IREB
IRED sticks to the PEPCK gene and INHIBITS the production of PEPCK
Less PEPCK = Less sugar produced
Explain CREB’s action
When blood sugar is low, ___ is activated and triggers the activation of CREB
CREB sticks to the PEPCK gene and ____ it to produce ____ PEPCK
When blood sugar is low, glucagon is activated
Glucagon triggers the activation of CREB
CREB sticks to the PEPCK gene and stimulates it to produce more PEPCK
Does insulin increase or decrease CAMP and PKA? Why?
Decrease
insulin's actions are largely counter-regulatory to glucagon.
Glucagon's signaling pathway involves the activation of adenylyl cyclase, which increases the production of cAMP, leading to the activation of PKA
What happens when there is increased NADH due to breakdown of ethanol?
Instead of converting lactate to pyruvate, it will favour Pyruvate to Lactate = lactic acidosis.
Which organ promotes the production of insulin?
The pancreas is the organ that promotes the production of insulin, specifically by the beta cells in the islets of Langerhans.
Which organs form glycogen?
The liver and muscle tissues.
The liver is acted on by ___ enzyme to form glycogen
GlucoKinase
Skeletal muscle is acted on by ____ enzyme to form glycogen
Hexokinase
Why is glycogen not used/ produced in Muscles?
Muscles do not have glucose 6 phosphatase
Does gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis occur at the same time?
Yes they can. But one is alway predominant.
Glycogenolysis is preferred in early fasting state. Glycogenesis only peaks after all glycogen is depleted.
Explain Diabetic Ketoacidosis
In DM type 1 patients, Beta cells, which produce ___, are _____.
Therefore they are always in a ___ state.
In DM type 1 patients, this process predominate? ______ which causes the build up and formation of ____?
How can you tell if a patient is undergoing diabetic keto-acidosis?
Explain Hyperglycemia in DM
In Type 2 DM patients, Insulin ____ are defective, causing the decreased up-regulation of glucose transporters.
Inc. or Dec. glucose uptake?
Inc. or Dec Lipogenesis?
Therefore there is inc. / dec. (?) glucose absorption in muscles as Glucose remains in the ___ causing Hyperglycemia.
In Type 1 DM patients, due to the autoimmune destruction of ___ cells, there is ___ insulin release and there will be inc. / dec. (?) glucose absorption in muscles.
Since muscles are “hungry”, the hunger center of the brain is activated causing an increase in this process _______, which eventually causes Hyperglycemia.
Glucosuria, which occurs when the glomerular filtrate contains more glucose than reabsorbed, occurs when the ____ threshold for glucose is exceeded.