Chapter 6 - Emotional Intelligence: Emotion Appraisals, Experience, and Regulation
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Appraisal
The brain’s judgement of a situation that leads to an emotional response
Stein et al Sequence of Appraisals
Proposed order the brain processes its appraisal of the situation
An event happened (usually unexpected)
What happened?
Challenges in beliefs
What do you think?
Plans are formed to decide whether or not to support or go against it
What to do next?
Primary Appraisals
The first and automatic judgment from the brain
First movement (helps survival)
Decides if rewarding or threatening
Also called automatic evaluations
Murphy & Zajonc Study
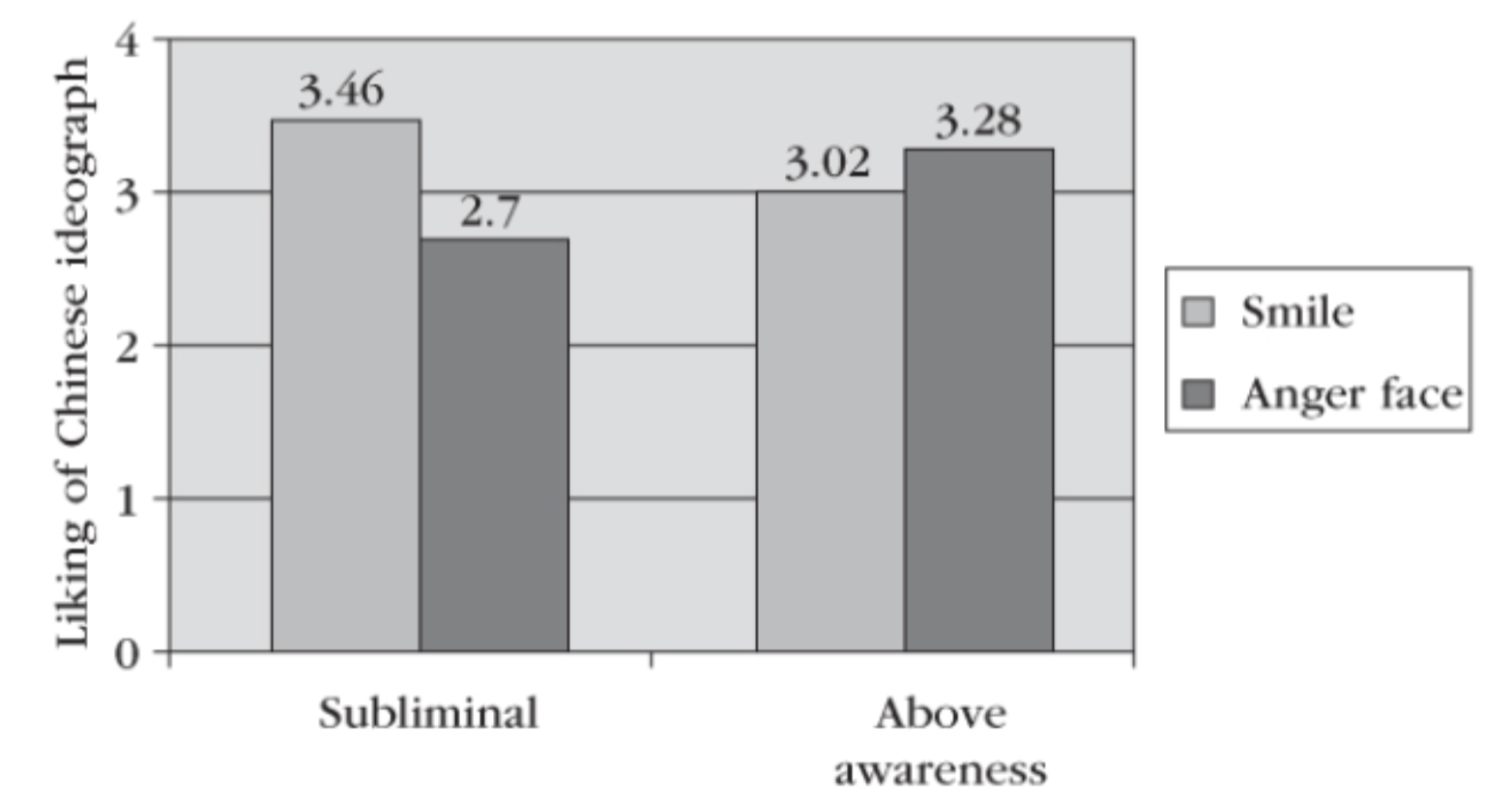
The study was conducted with flashing images of Chinese ideographs for either 4 milliseconds or 4 seconds
Subliminal graph displays those who only saw it for 4 milliseconds
Above awareness graph displays those who saw it for 4 seconds
Results: The subliminal graph shows more smiling faces, while Above Awareness shows angry faces
Conclusion: Those in the subliminal graph did not have enough time to perceive the ideographs as a threat to their system 1 thinking so they remained with a smiling face, while those in the above awareness graph had enough time to perceive it and felt threatened with an angry face
System 1
The automatic processing of the brain
Initially determines threat or no threat
Processes all the facts at the same time
Negativity bias
System 2
The conscious processing of the brain
Takes in one aspect at a time
Generally slower
Conscious Processing Track
Emotional reactions that we are aware of and can interpret
System 2 in other words
Autonomous Processing Track
Emotional reactions that happen unconsciously
System 1 in other words
Negativity Bias
We naturally react stronger to negative stimuli we perceive as threatening
A survival instinct
Discrete Approach
Appraisals that trigger distinct emotions
Dimensional Approach
The various appraisals that shape how the stimulus is perceived
Primary Approaches help survival
Secondary Approaches place multiple labels
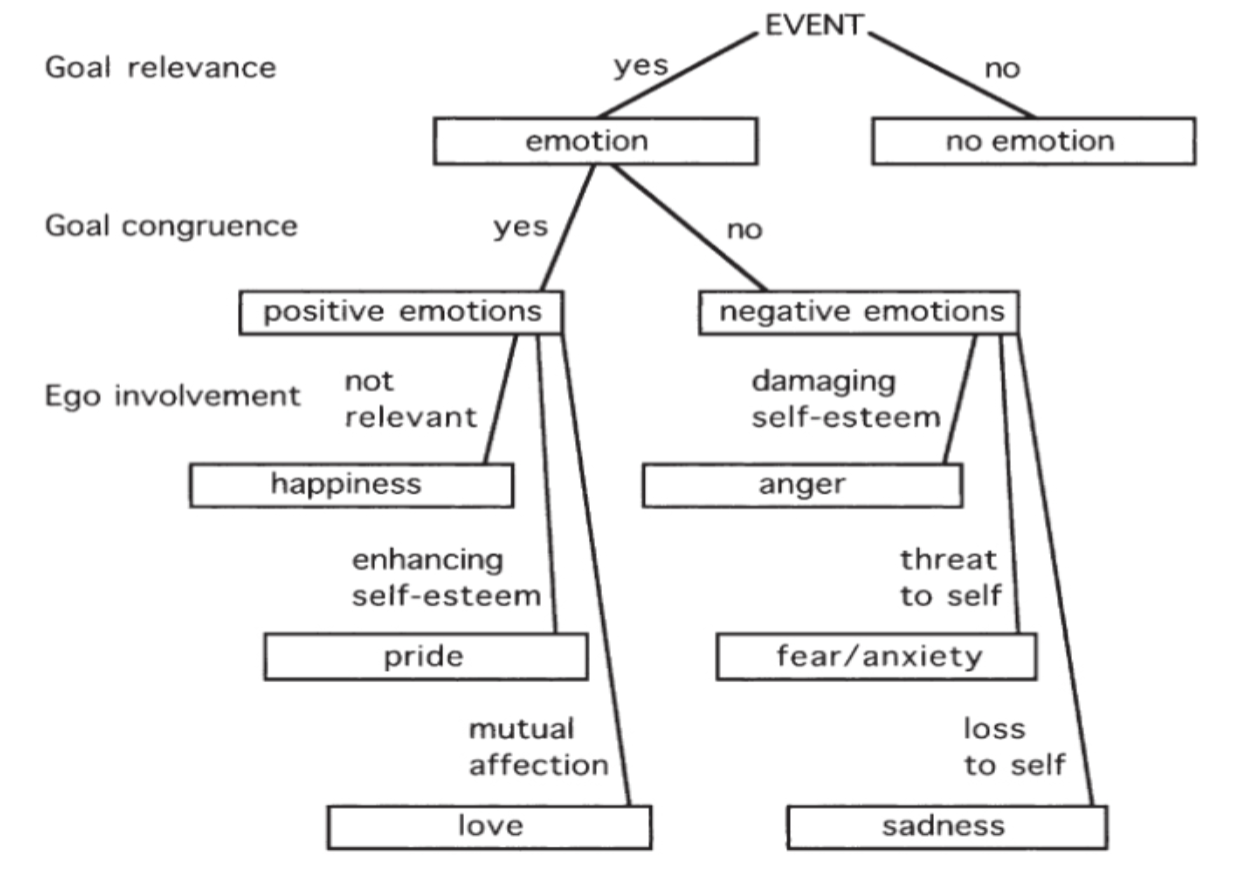
Lazarus’ Appraisal Stages
Proposed that discrete approach happens like this:
Emotional event happens
Positive or Negative?
Does it involve ego?
Irrelevant?
Self-esteem?
Survival?
Mutual Affection?
Action Readiness
Acts that are usually associated with certain appraisals
With Primary Appraisals, it is automatic and acts with goals in mind
With Secondary Appraisals, results are considered
Smith & Ellsworth Study (1985)
A study with participants imagined experiencing 15 emotions and rated the imagined experience on 8 dimensions
Unique dimensions here create discrete emotions
Results: The most important dimension is agency, which is the appraisal of who or what was responsible for the event

Tertiary Appraisals
The step that comes after Primary and Secondary Appraisals
This is when feelings are verbalized to others
Intentional Objects
The external stimulus that triggers our emotions
Emotion Prototypes
The basic foundations and examples of how an emotion is like
Oatley & Duncan Study
A daily diary study with 175 emotional episodes
Appraisals did not cause 6% of them but rather experiences from the past
Conclusion: Basic emotions are something we understand and process immediately
Keltner & Cowen Study
The study with participants watching 2000 film clips and reporting discrete emotions they felt
They also reported on primary dimensions of positive and negative emotions
Emotional Regulation
The act of lessening an emotion’s intensity and duration
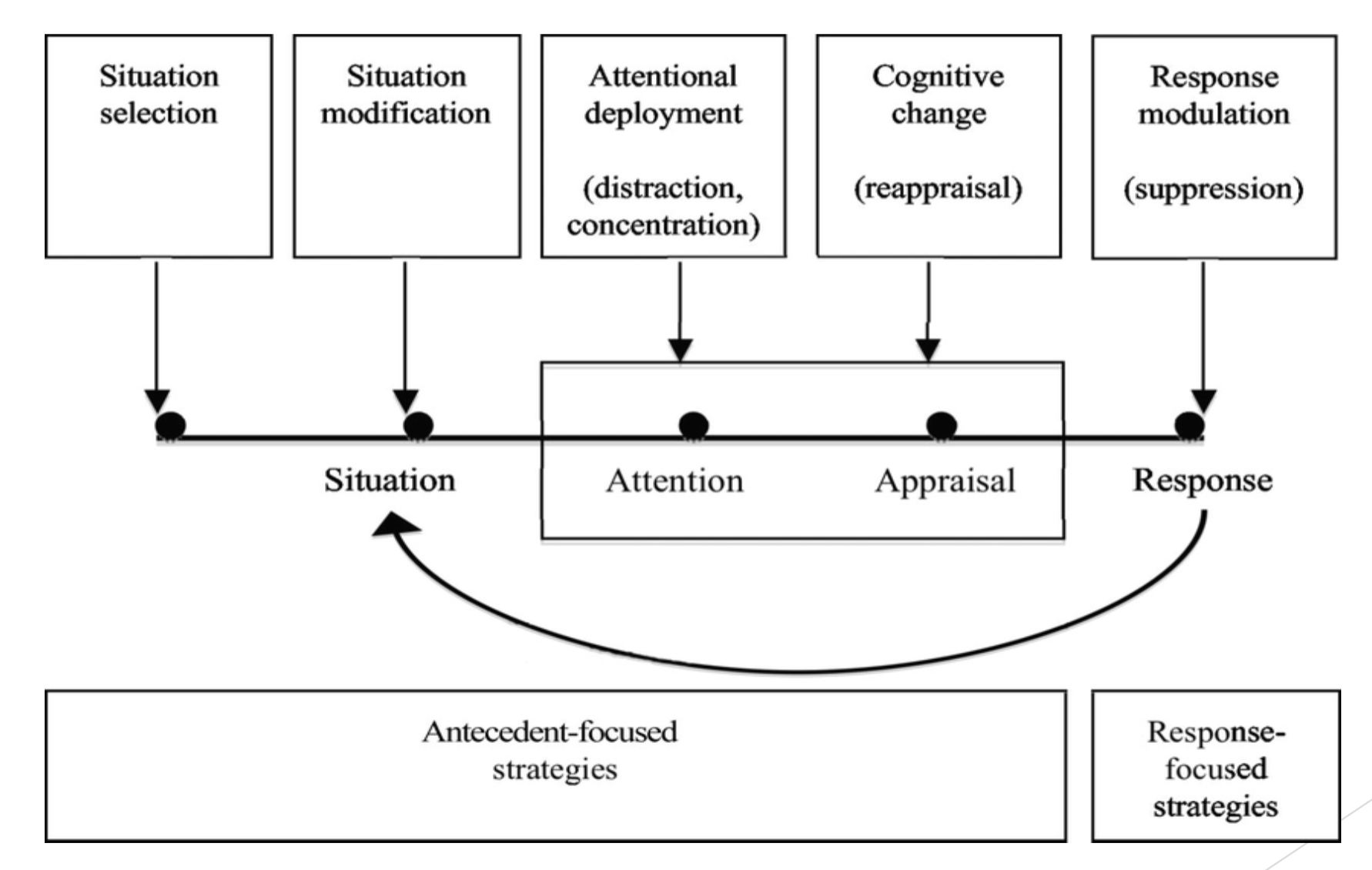
Reppraisal
Changing perspective about something
Suppression
The act of purposely blocking out an emotion
Common misconception: Suppression is bad
It is okay, as long as you eventually deal with it
Repression
The body’s unconscious act of blocking out emotional pain
In other words, a defense mechanism that prevents thoughts or feelings from entering conscious awareness, often to protect oneself from distress.