Zebra fish techinques and diseases
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Most common areas for blood collection in ZF
Dorsal aorta or posterior cardinal vein (survival), decapitation or dorsal aorta through transverse incision of anal and caudal fins (terminal)
Monitoring fish under anesthesia
operculum movement tail fin pinch
Stage 1 anesthesia
teens disoriented, sedated
Stage 2 anesthesia
excited in your 20s
Stage 3 anesthesia
Stage 3 – loss muscle tone in your 30’s
Stage 4 anesthesia
Stage 4 – down hill in your 40’s – no muscle tone
Only FDA approved anesthetic for fish:
MS222
Important notes of MS 222 regarding solubility, acidity and heat
Important notes of MS 222: soluble in water, acidic so requires buffering, potentancy increases with heat
Can you give isoflurane with MS222 in fish?
Yes, provides a nice surgical plane of anesthesia in 90 minutes, fast recovery,
What is the dose for MS222 for surgical anesthesia?
140 – 164 mg/ L
What is the dose for isoflurane for anesthesia in fish?
325 mg/L
What is the safety margin of isoflurane in fish?
Narrow safety margin, 30% mortality at 350 mg/L.
Eugenol, cost, safety, induction time, and solubility
Important components of eugenol: low cost, wide safety margin, fast induction, metabolism. Require ethanol to become soluble.
Side effects of eugenol
Side effects: long recovery time and can cause adverse effects
Does Metatomidate provide analgesia?
no
side effects of metatomidate?
Side effects: long recovery, can see fasiculations, decrease cortisol and glucose, increase pigmentation
Can you cool fish for anesthesia?
Yes, get water to 10 - 12 C, for quick nonpainful procedures.
Does quinaldine have any analgesic properties?
Yes, but minimal
Immersion techniques for acceptable euthanasia?
Immersion: MS222, benzocaine, lidocaine, quinaldine sulfate, 2-phenoxyenthanol
Can chilling be an acceptable form of euthanasia?
Rapid Chilling (2-4°C)
What are the acceptable with conditions of euthanasia for fish?
a. Immersion: CO2, eugenol/clove oil
b. Rapid Chilling (2-4°C): small-bodied tropical/sub-tropical
c. Maceration
d. Decapitation + pithing
e. Manual blunt force trauma + pithing/exsanguination
Examples of unacceptable methods of euthanasia?
a. Flushing
b. Slow chilling or freezer
c. Anoxia / dessication by removal from water
d. Caustic chemicals
e. Prolonged trauma
f. Metomidate (illegal for extralabel euthanasia
Rapid chilling components based on age: adults
10 minutes
Rapid chilling components based on age: fry (4-14 dpf)
20 minutes
Rapid chilling components based on age: <3dpf
<3dpf: add-in sodium/calcium hypochlorite

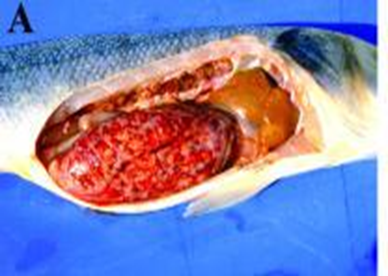
What is being shown here?
pericardial effusion

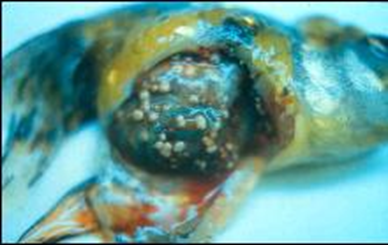
What is being shown here?
Dropsy, edema
Most common mycobacterium in ZF:
M. chelonae (nonpathogenic)
Most common pathogenic mycobacterium in ZF:
M. marinum, and M. haemophilum
Common clinical signs of Mycobacterium haemophilum
Poor growth, wasting, emaciation
Most common clinical signs of M. marinum:
dropsy, edema
Most common generic clinical signs of mycobacteriosis in fish:
Granulomas (external and internal), Spinal curvature, muscle deformities
What likely pathogen causes this gross pathology?
mycobacteriosis

Which mycobacterium species cause the gross pathology in A, B, and C?
A / B: M. marinum C. M. haemophilum
Stains used for staining acid fact mycobacterium?
Fite-Faraco, Ziehl-Neelsen, Kinyoun
What organs of the fish are best for diagnostic staining for mycobacterium?
spleen and kidney
How long does it typically take to grow M. marinum and M. haemphilum:
a. M. marinum (10 – 14 days)
b. M. haemophilum (6-8 wks)
What type of bacteria and what is the stain?
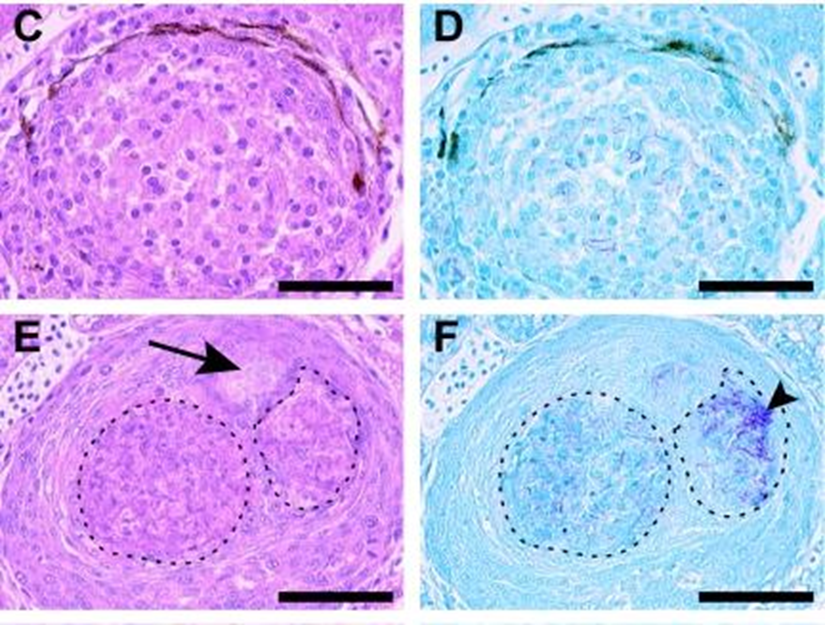
Mycobacterium and Ziehl-neelsen
Control of mycobacterium
eradicate completely and bleach. M. marinum is zoonotic and cause fish handler granulomas.
Which mycobacterium species is zoonotic for fish? And what does it cause in humans?
M. marinum, cause fish handler granulomas on the fingers, where broken skin is. Usually in immunocompromised people
Edwardsellosis gram stain and what is the name of the disease in catfish (there are two)?
Gram negative. hole in head disease / enteric septicemia in cat fish
Which species of edwardsellosis is most common in ZF and what is the severity of the disease?
E. ichtaluri can cause severe mortality and morbididty in ZF.
CS of E. ichtaluri
CS of edwardsellosis: acute presentation w/septicemia=> lethargy, raised scales, dropsy, skin ulceration, hemorrhage in skin near eyes/opercula, fins, ventral abdomen

What pathogen is likely the cause of this presentation? There was a rapid and almost 100% mortality in the tank of this fish.
Edwardselli ichtaluri
Aeromonas hydrophila and sobria gram stain and what is another name of this disease in fish (reflects the clinical signs)?
Aeromonas hydrophila and sobria: gram negative, ulcer disease


What is the pathogen that could cause these clinical signs of ulcerations?
Aeromonas spp.
Clinical signs of Aeromonas in ZF
Clinical signs in ZF: petechial hemorrhages of skin, fins, oral cavity, muscle
Treatment and prevention of aeromonas in ZF
Treatment: remove stressors, antibiotics (oxytetracycline, nifurpirinol)
Is A. hydrophila zoonotic?
yes low zoonotic risk.
Flavibacterium branchiophilum (BGD) and F. columnare (Columnaris) gram stain and common names
gram negative, bacterial gill disease, cotton wool, fin rot
Which pathogen is opportunistic and is commonly seen with shipping stress in zf?
Flavibacterium branchiophilum (BGD) and F. columnare (Columnaris)
CS of BGD (Flavibacterium bronchiophilum)
labored breathing, surface swimming
CS of Flavibacterium columnare
Saddleback, loss of pigment and scales.
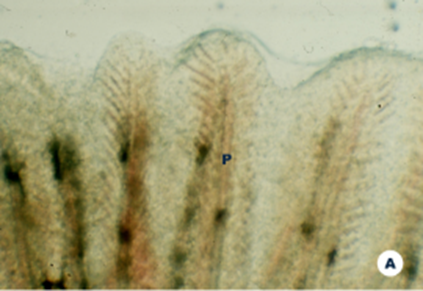
What pathogen is the picture describing?
F. bronchiophilum
Diagnosis of BGD?
Diagnosis: Wet mounts of gills: filmentous bacteria, fused secondary lamella

What pathogen causes this disease in fish:
F. columnare
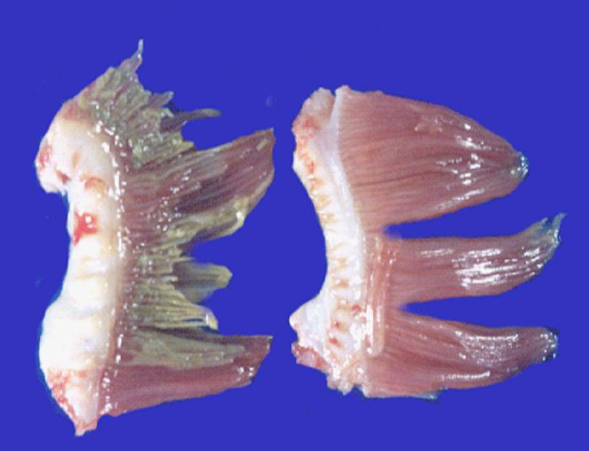
What pathogen causes this disease in fish:
F. bronchiophilum
What is the most common pathogen of ZF?
Microsporidiosis
What are the most common microsporidia of ZF:
Pseudoloma neurofilia, Pleistophora hyphessobryconis
Are pseudoloma and pleistophora intracellular or extracellular?
intracellular
How is microsporidia transmitted?
Both vertically and horizontally.
Where do pseudoloma and pleistophora preference in the body?
Pseudoloma (neuro), Pleistophora (skeletal muscle).
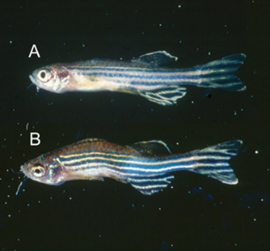
What filamentous pathogen causes this grosely?
microsporidiosis
Clinical signs of microsporidiosis:
Degenerative muscle atrophy, scoliosis, lordosis, reduced growth
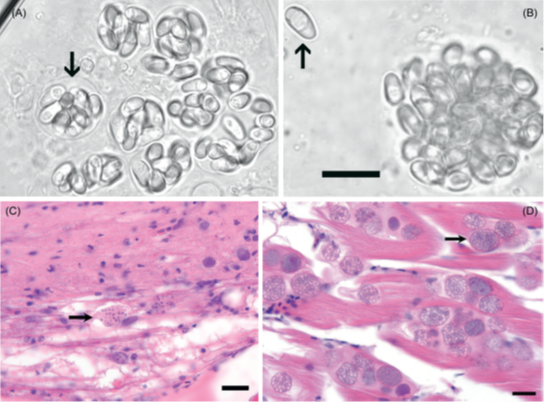
What pathogens present with this?
Pseudoloma neurophila and Pleistophora.
How long should you have sentinels to ensure SPF populations don’t have microsporidia?
3 months
Sanitation for microsporidia?
UV sterilization, Chlorine 100 ppm (>95% of spores) = useful for equipment disinfection. Can aerosolize
Are classic egg surface sterilization techniques sufficient for preventing microsporidiosis?
Egg surface sterilization practices are insufficient in inactivating spores on outside/inside embryo
What are saprolegnia
Water molds, are pseudo-fungi. Opportunistic, ubiquitous in environment.


What pathogen causes this?
Saprolegnia
What is the type of pathogen and common disease name of Piscinoodinium:
motile protozoa, velvet disease, gold dust disease.
What are the common species of Piscinoodinium?
P.pillulare and P.limneticum
Describe the transmission lifecycle of piscinoodinium
Horizontal transmission, Trophont feeds on skin / gills via rhizocyst projections skin / gills segments slough.
Trophont drops off sessile tomont produces infective dinospores
What is the infective stage of piscinoodinium?
dinospore, produced by sessile tomont
Clinical signs of piscinoodiumium in fish?
excess mucus, skin darkening, anorexia, depression, surface swimming, labored breathing, flashing/rubbing side of tank due to epithelial irritation/pruritis, yellow/rusty color (heavy infestation)
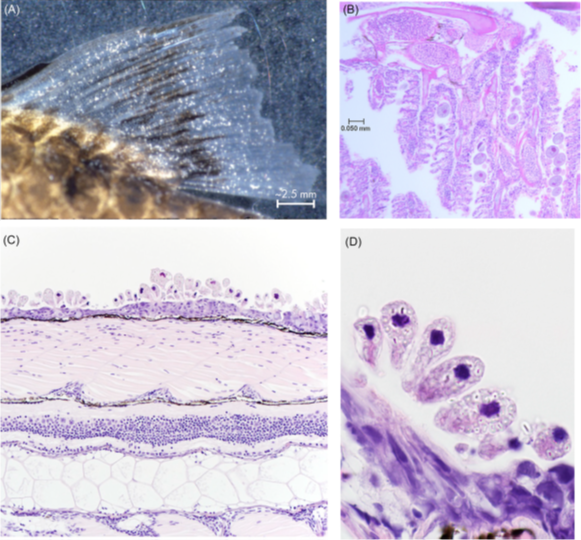
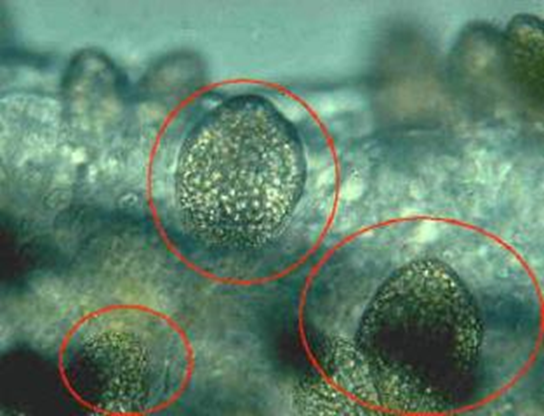
What pathogen is this in fish?
piscinoodiumium
Treatment of piscinoodinium:
Saltwater baths, Copper sulfate (dangerous), Raise water temp 33-34°C (ZF can tolerate)
Ichthyophythirius multifilis, what type of pathogen, and what is a common disease name for this species?
ciliated protozoa, causes white spot disease
Lifecycle of I. multifilis?
a. Trophonts – feed on fin, skin, gills
b. Tomonts – substrate, sticky
c. Theronts – infectious/motile

What pathogen causes this?
Ichthyophythirius multifilis
Roundworm of ZF?
Pseudocapillaria tormentosa
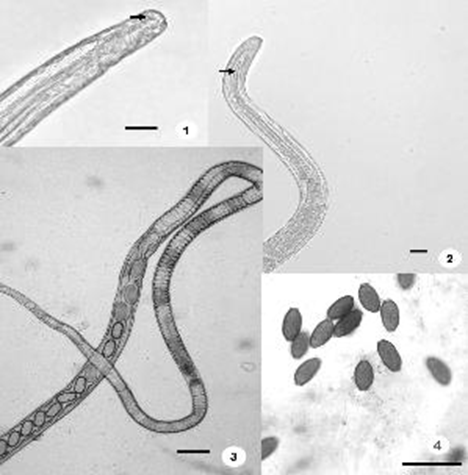
What species is this? Whats a unique characterisitic on the eggs?
Pseudocapillaria tormentosa, Bipolar plugs on eggs
Clinical signs of pseudocapillaria:
a. Wasting, ↓ fecundity, Appearing darker in color, Proliferative enteritis, Neoplasms at intestinal-esophageal junction, intestinal cell carcinomas or mixed malignant
Treatment of pseudocapillaria?
TX: Fenbendazole in Artemia
Most common neoplasm of ZF:
1. seminoma
a. Older males
b. Rarely invade locally/metastasize