Microbio Lab Practicum 1
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
facultative aerobe
Both aerobic and anaerobic growth; more growth in the presence of oxygen.
-gradient down, mostly at the top
-SOD and Catalyse
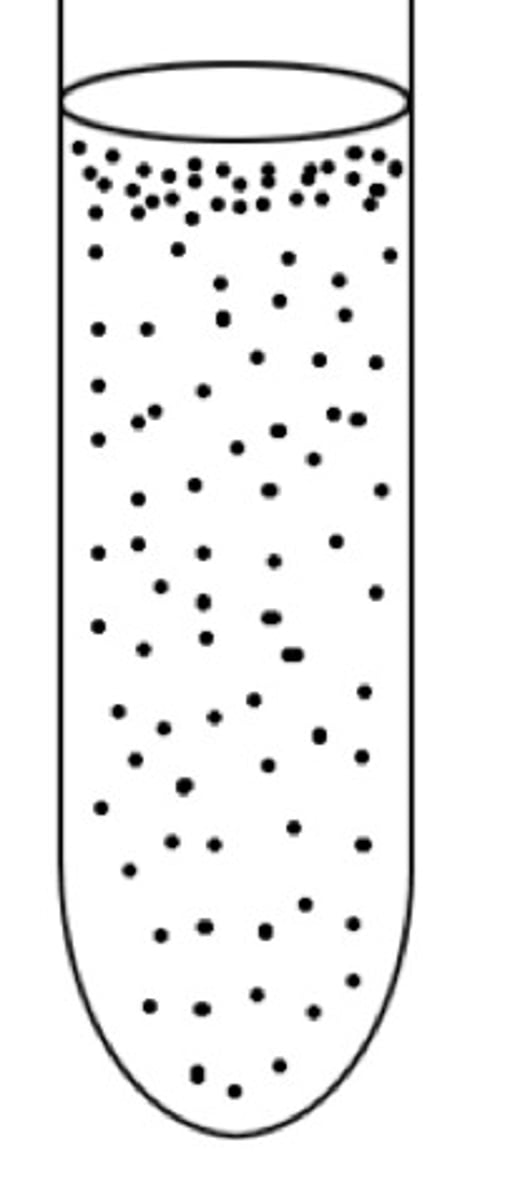
aerotolerant anaerobe
Only aerobic growth, but grows in the presence of oxygen.
-even distribution
-SOD and Peroxidase
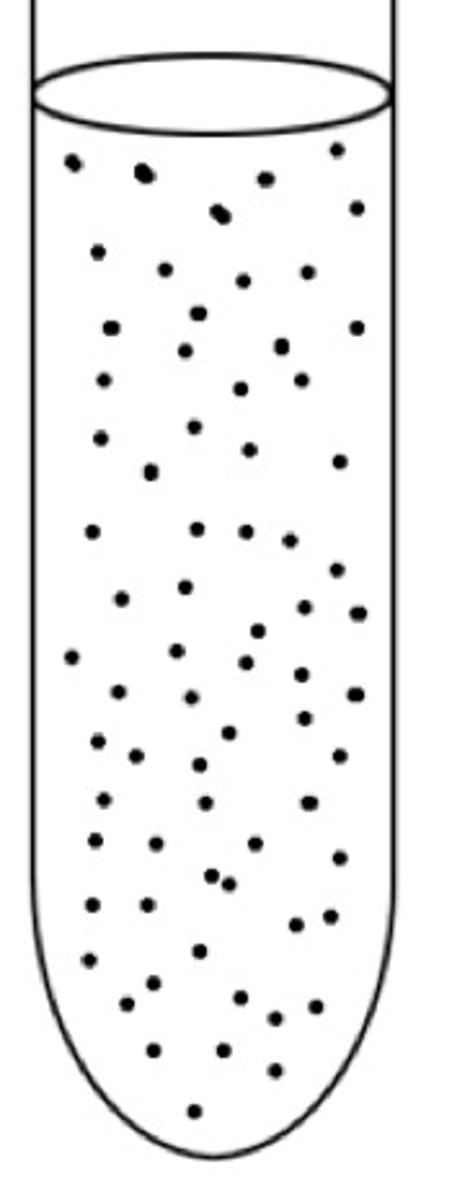
gas pack reaction
2H2 + O2 = 2H2O
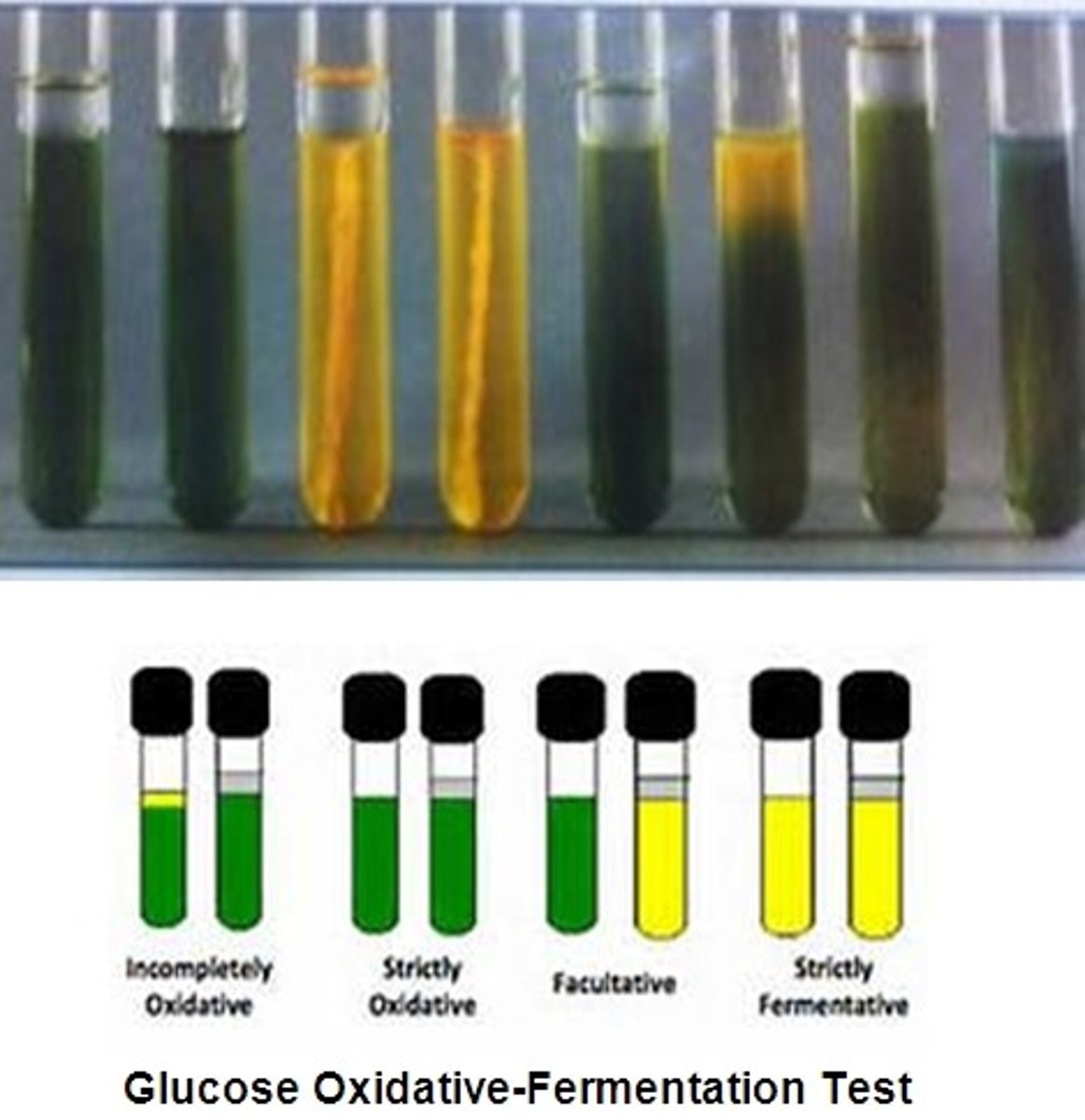
What is the OF test?
determine whether a bacteria uses oxidative or
fermentative carbohydrate metabolism or is inert
-indicator = bromthymol blue
- yellow = positive, green = negative (no color change)
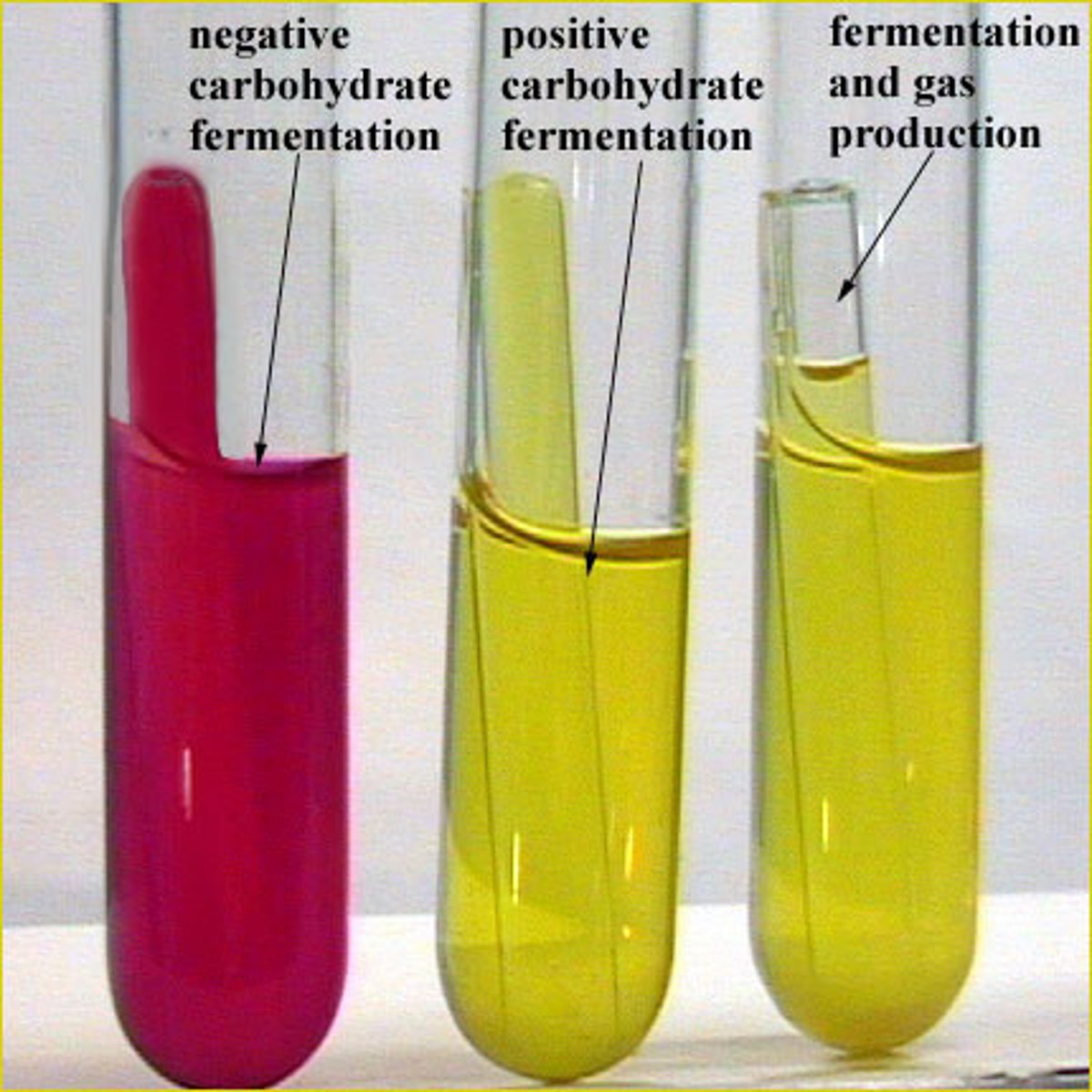
What is the sugar fermentation test?
microbes ferment glucose to produce gases,mainly carbon dioxide and hydrogen, can use the sugar provided for carbon, hydrogen, and energy
-indicator = phenol red
- yellow = positive, red = negative, gas = positve
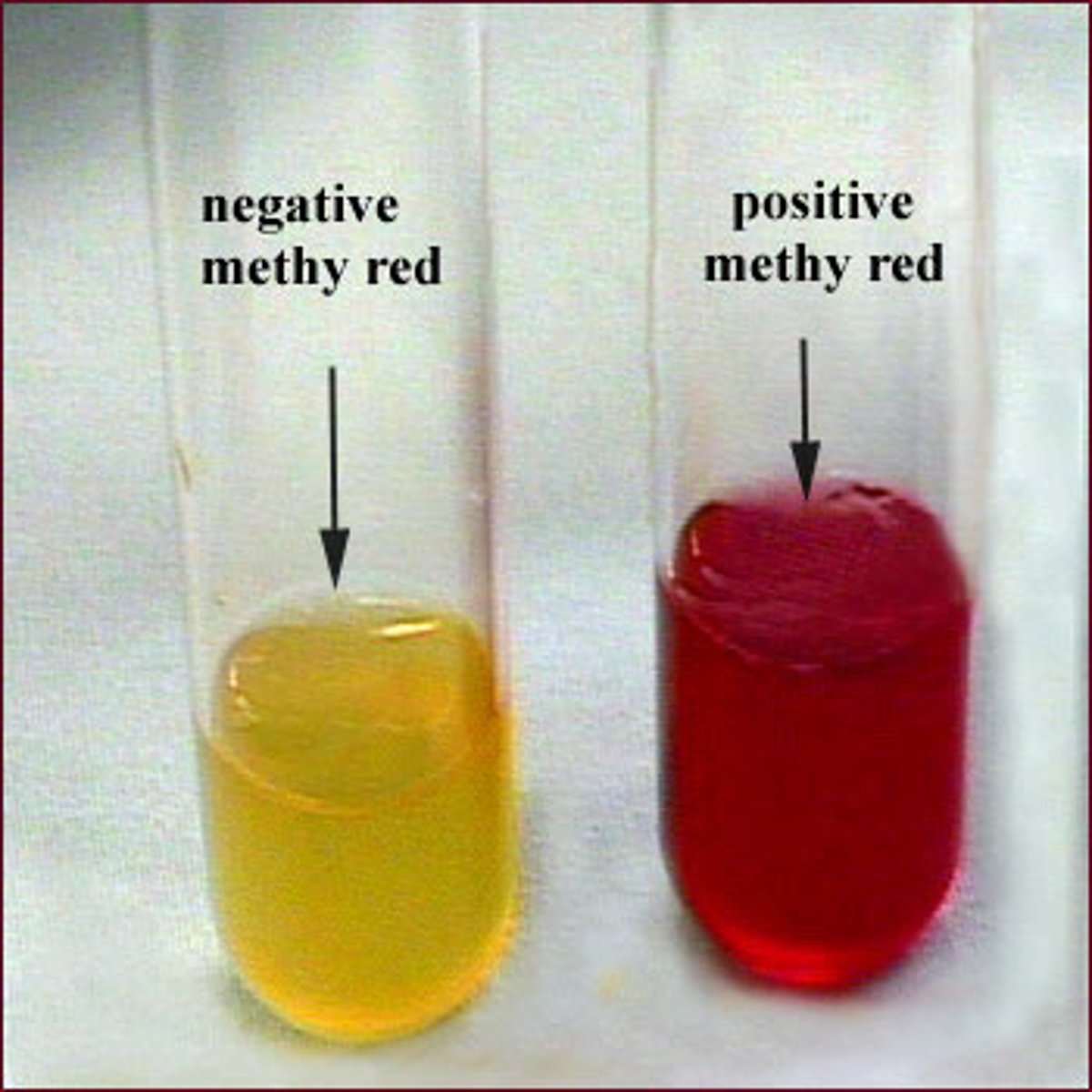
What is the Methyl Red (MR) test?
dentifies enteric bacterial ability to produce stable acid end products bymeans of a mixed-acid fermentation of glucose
-indicator = methyl red
- positive = red, negative = yellow

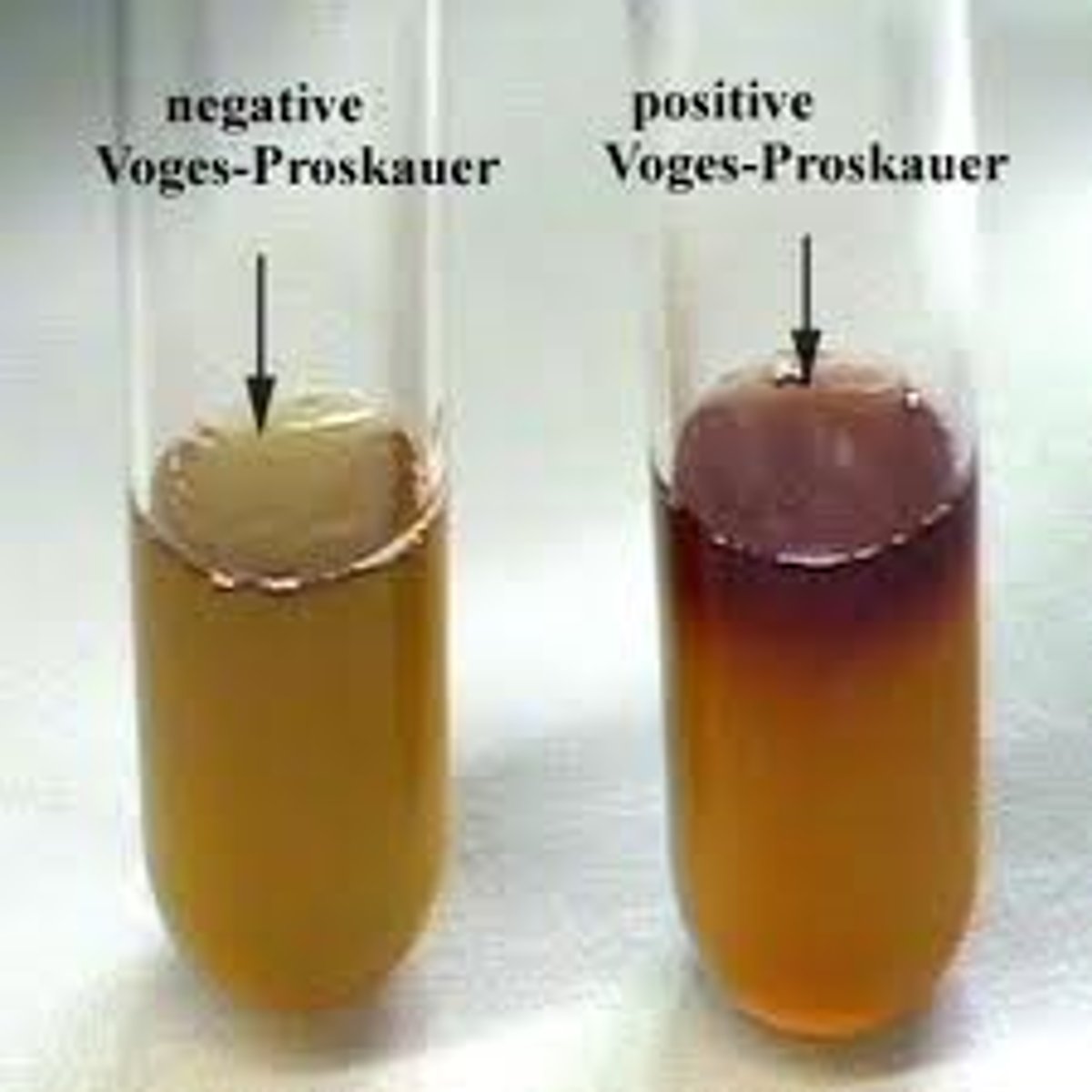
What is the VP test?
detect the production of acetoin, a neutral end product of glucose fermentation
- indicators = a-napthol and postassium hydroxide (KOH)
-positive = red ring no change = negative

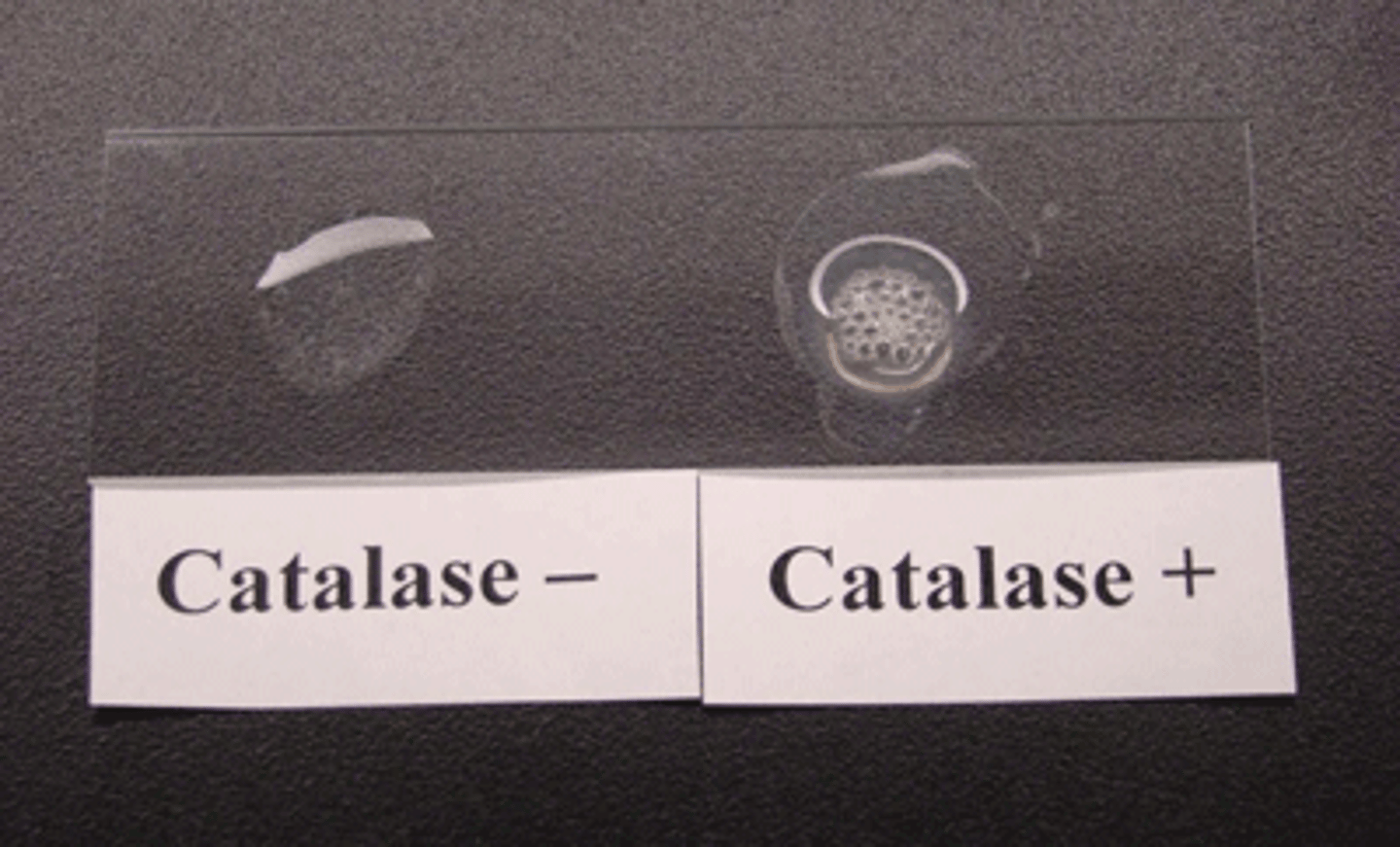
What is the catalase test?
This test detects the presence of catalase.
- indicator = hydrogen peroxide
- positive = bubbles, negative = no bubbles
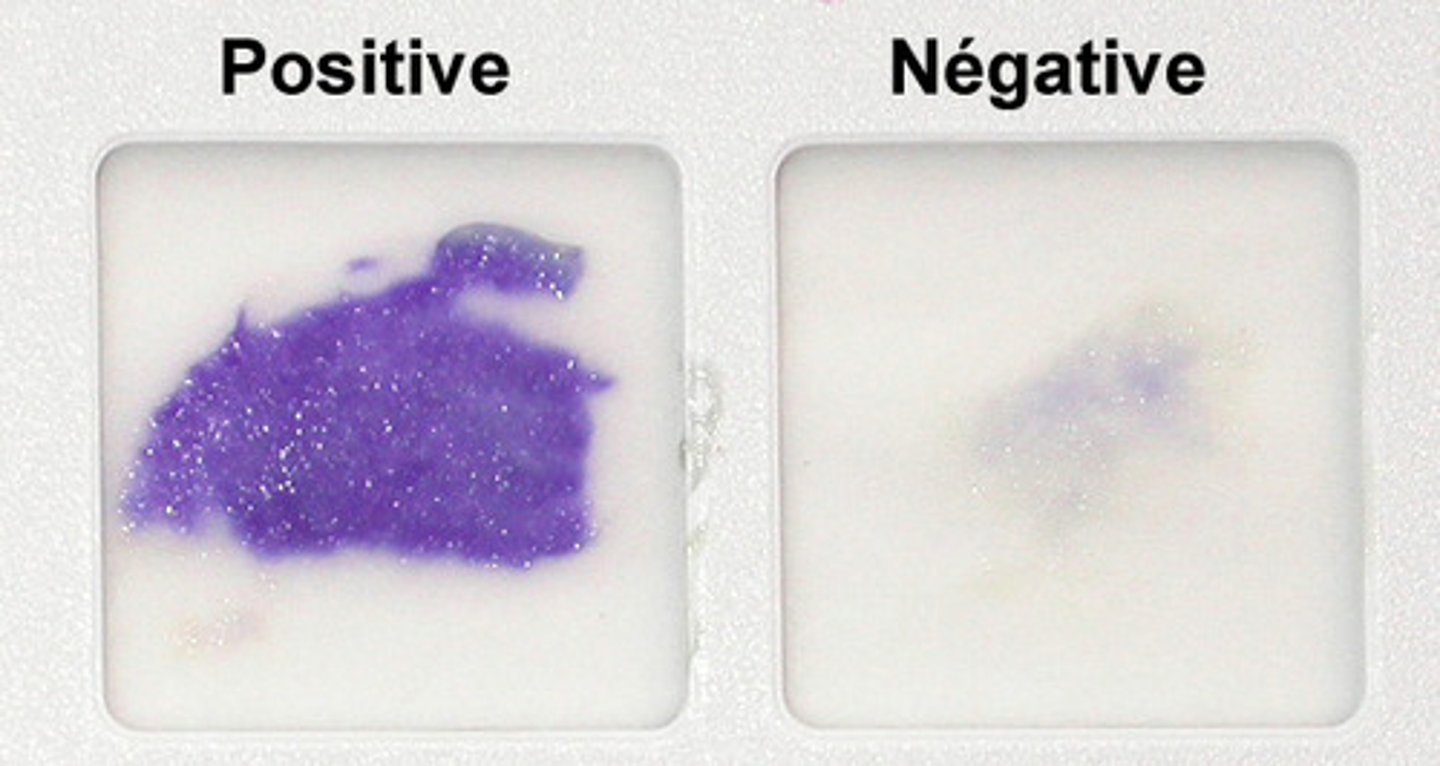
What is the oxidase test?
identifies bacteria that have cytochrome oxidase
- indicator = dimethyl-p-phenylenediaminehydrochloride
What is the nitrate reduction test?
tests for anaerobic respiration, can nitrate be reduced?
-indicator = sulfanic acid, α-naphthylamine, zinc
- initial = gas (+) no gas (-)
- add sulfanic acid/a-napth = red (+), no change/yellow (-)
-add Zn = red (-), no change (+)

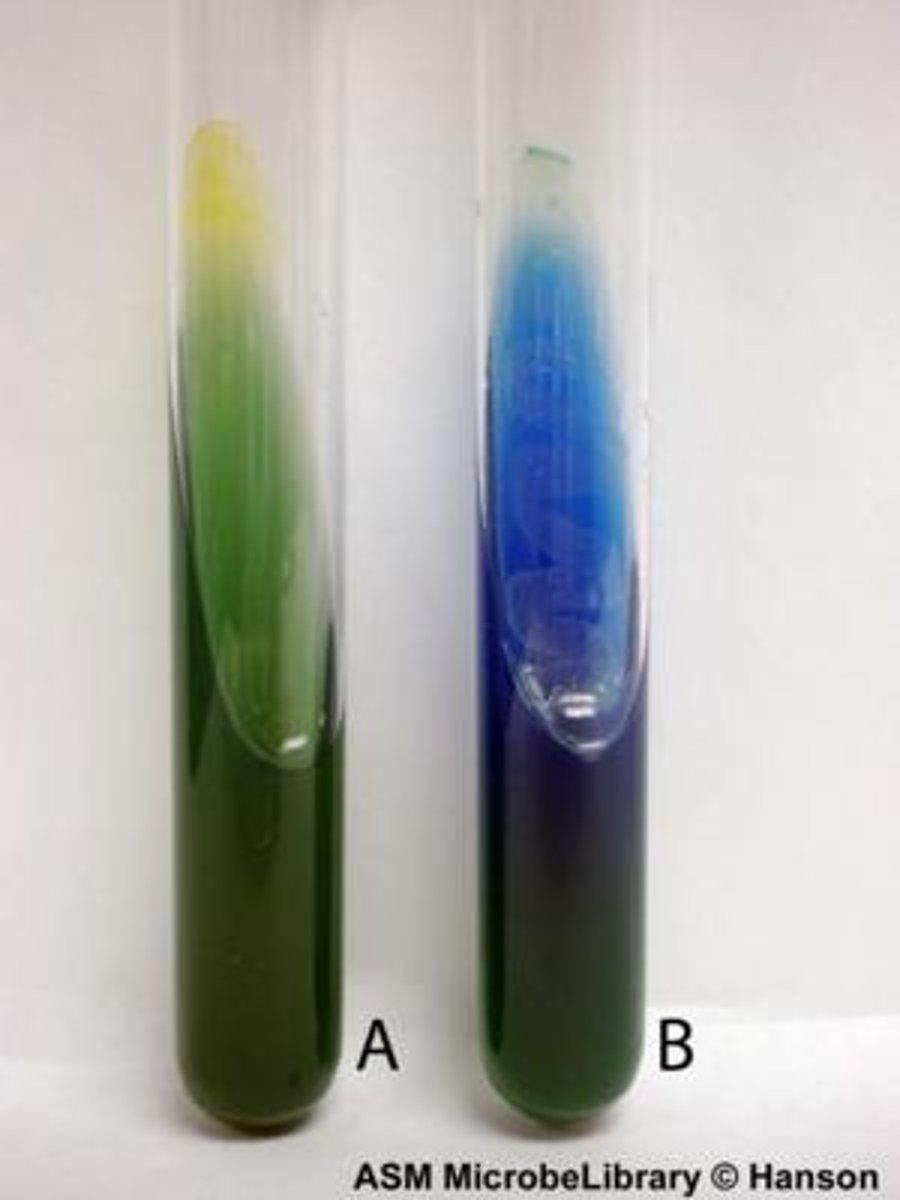
What is the citrate utilization test?
This test helps differentiate among gram-negative bacteria, and citrate-permease.
-indicator = bromothylmol blue
- blue (+), growth w/o color change (+), no growth/green slant (-)

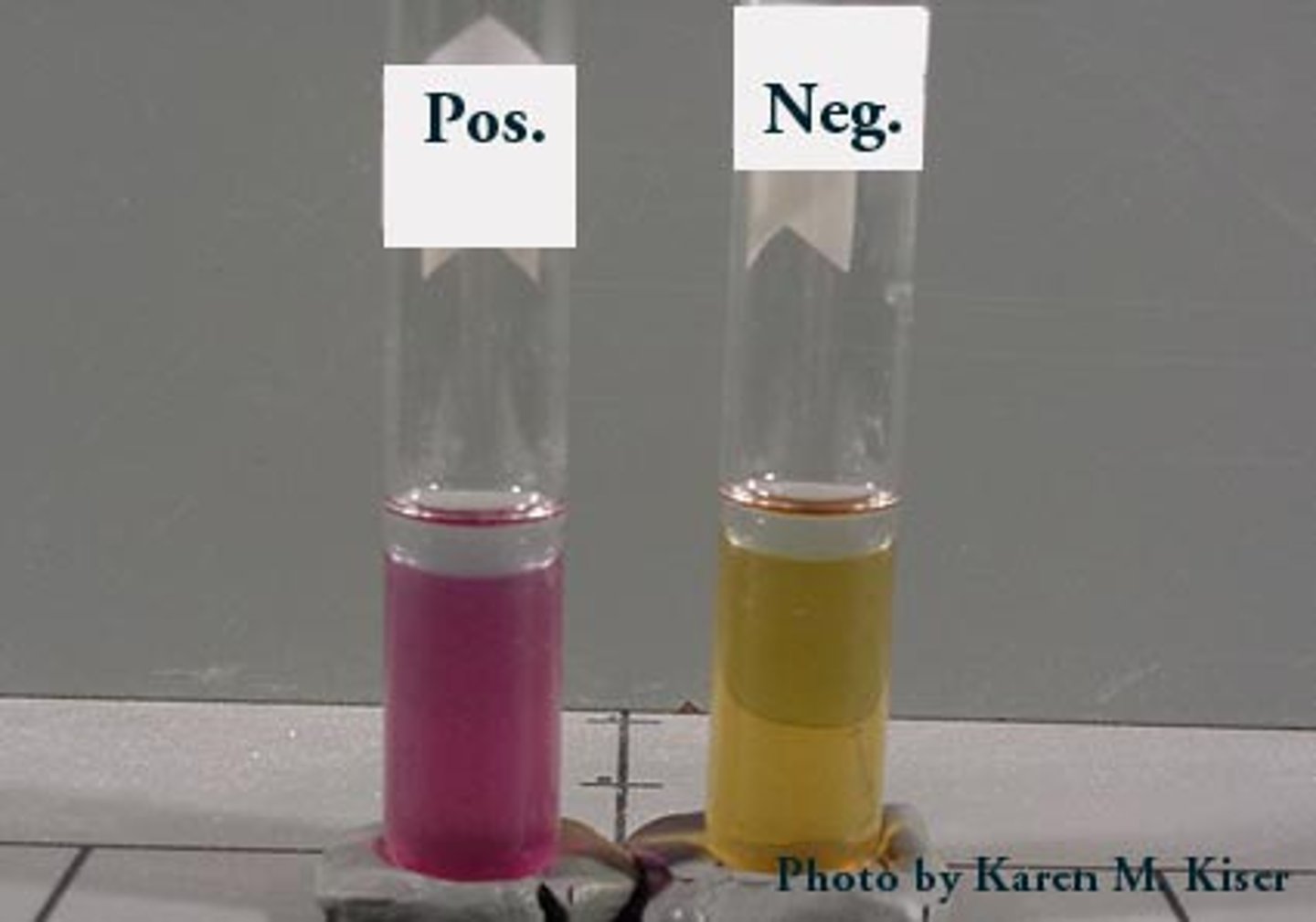
What is the decarboxylation test?
can the microbe can decarboxylate amino acids using decarboxylase.
-indicator = bromcresol purple
-purple = (+)
yellow = -

What is the Phenylalanine Deamination Test?
Detects if the organism produces phenylalanine deaminase, which removes the amino group from phenylalanine.
-indicator = ferric chloride (FeCl3)
- after adding FeCl3 = green (+) no change (-)
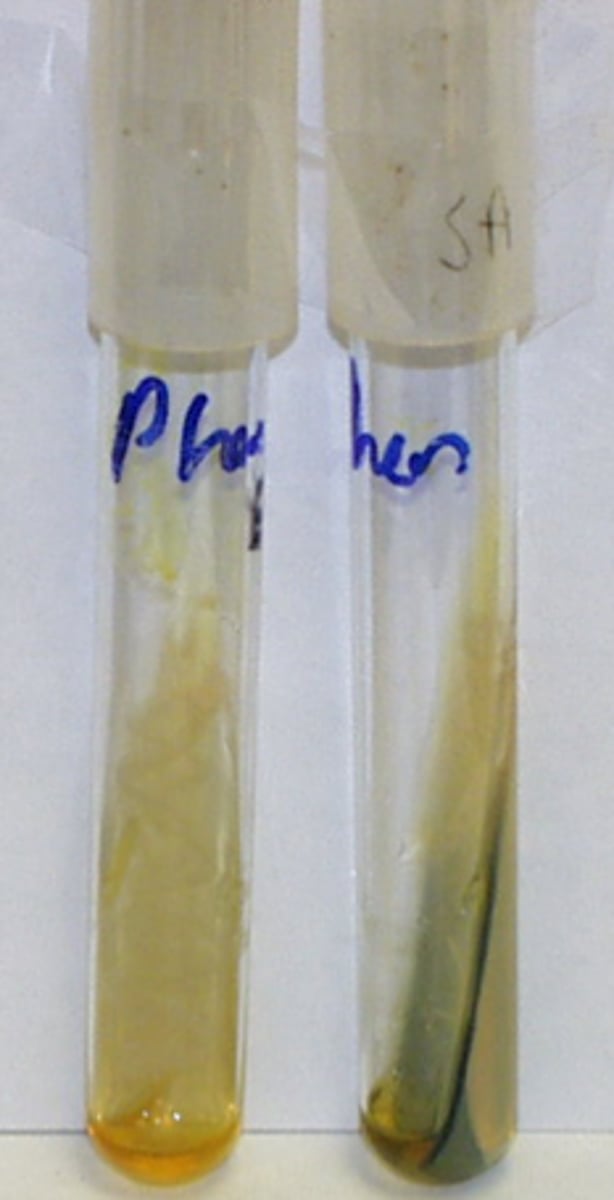

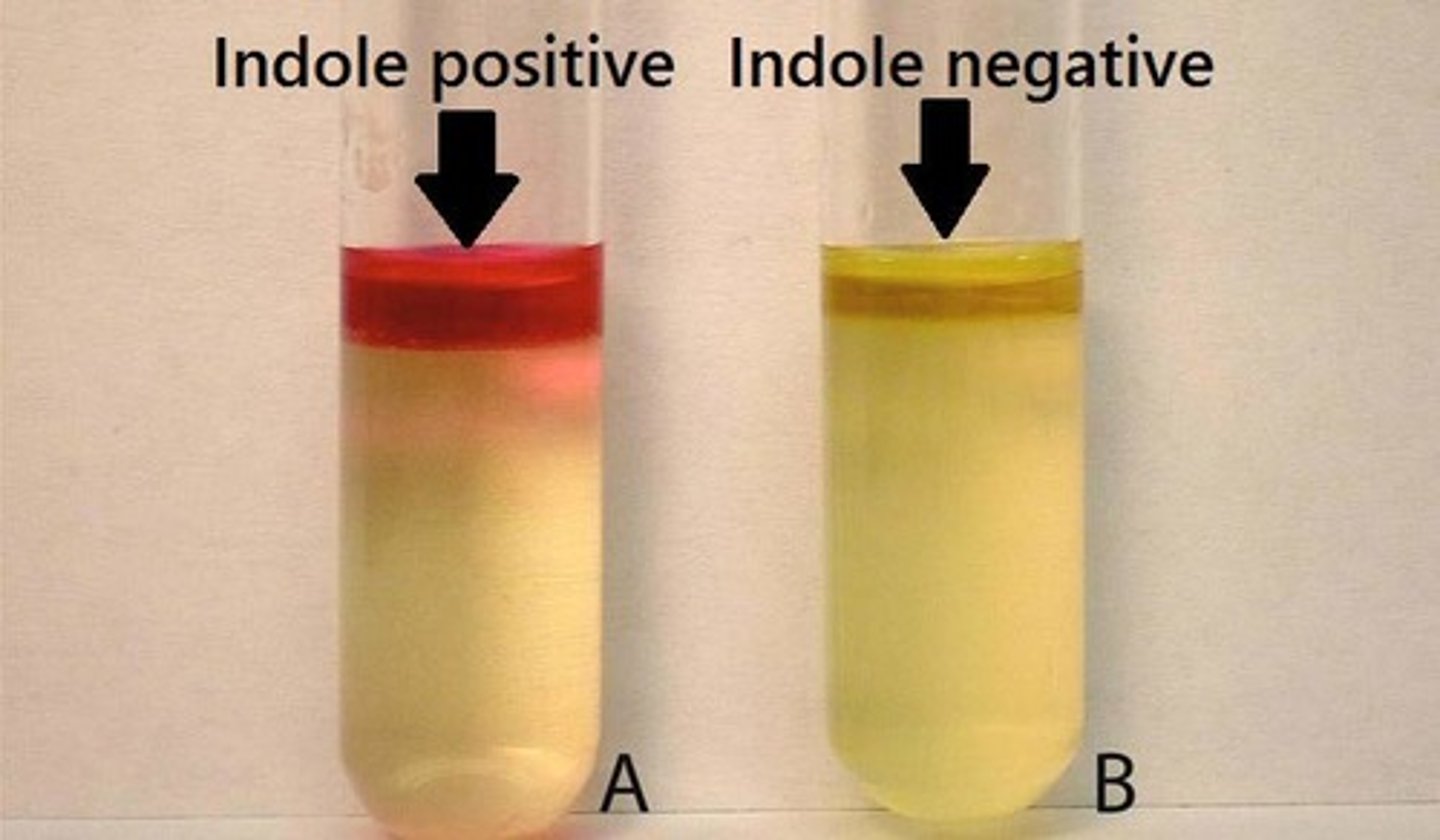
what is the Tryptophan Hydrolysis / Indole Test?
Tests for the enzyme tryptophanase, which breaks down tryptophan to indole.
-indicator = kovacs reagent
- red/pink on top (+)
- no change/yellow (-)
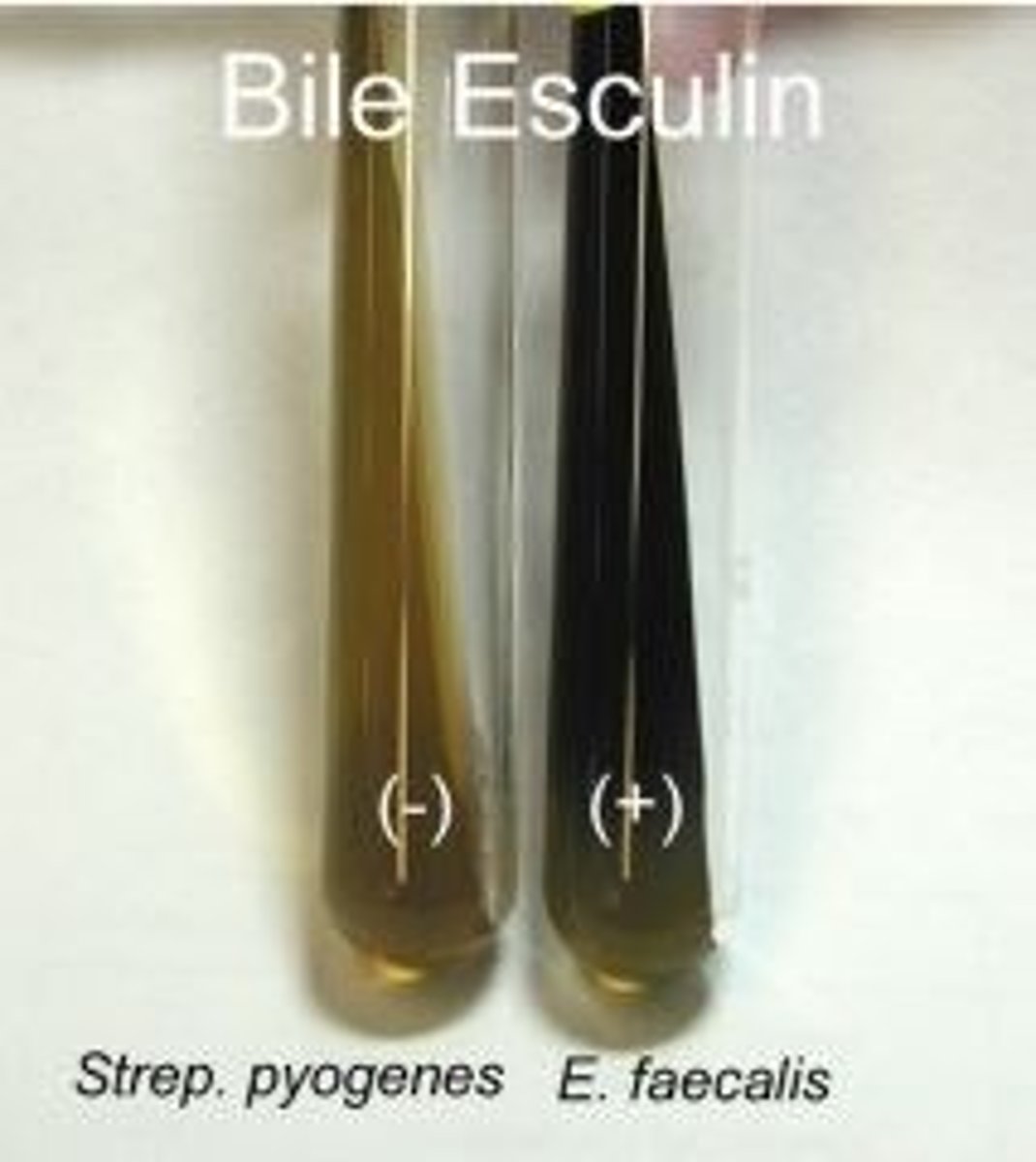
What is the hydrolytic enzyme (Bile Esculin) tests?
Tests for growth in the presence of bile salts, and
Hydrolyze esculin into esculetin and glucose.
indicator = ferric citrate
- change to dark = +
- no change = -
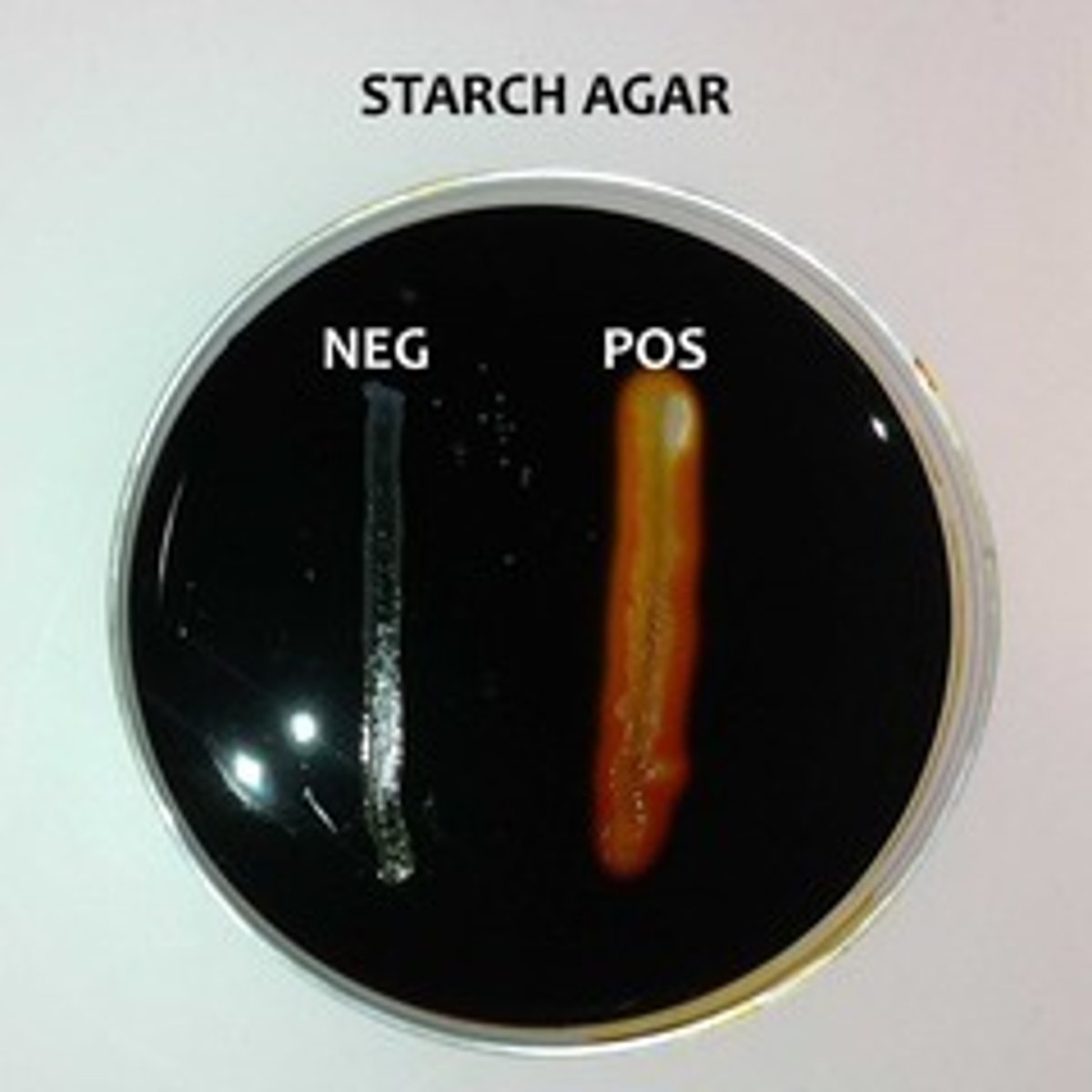
What is the starch hydrolysis test?
tests for amylase starch breakdown
indicator = iodine
results = clear zone = positive blue/black = negative
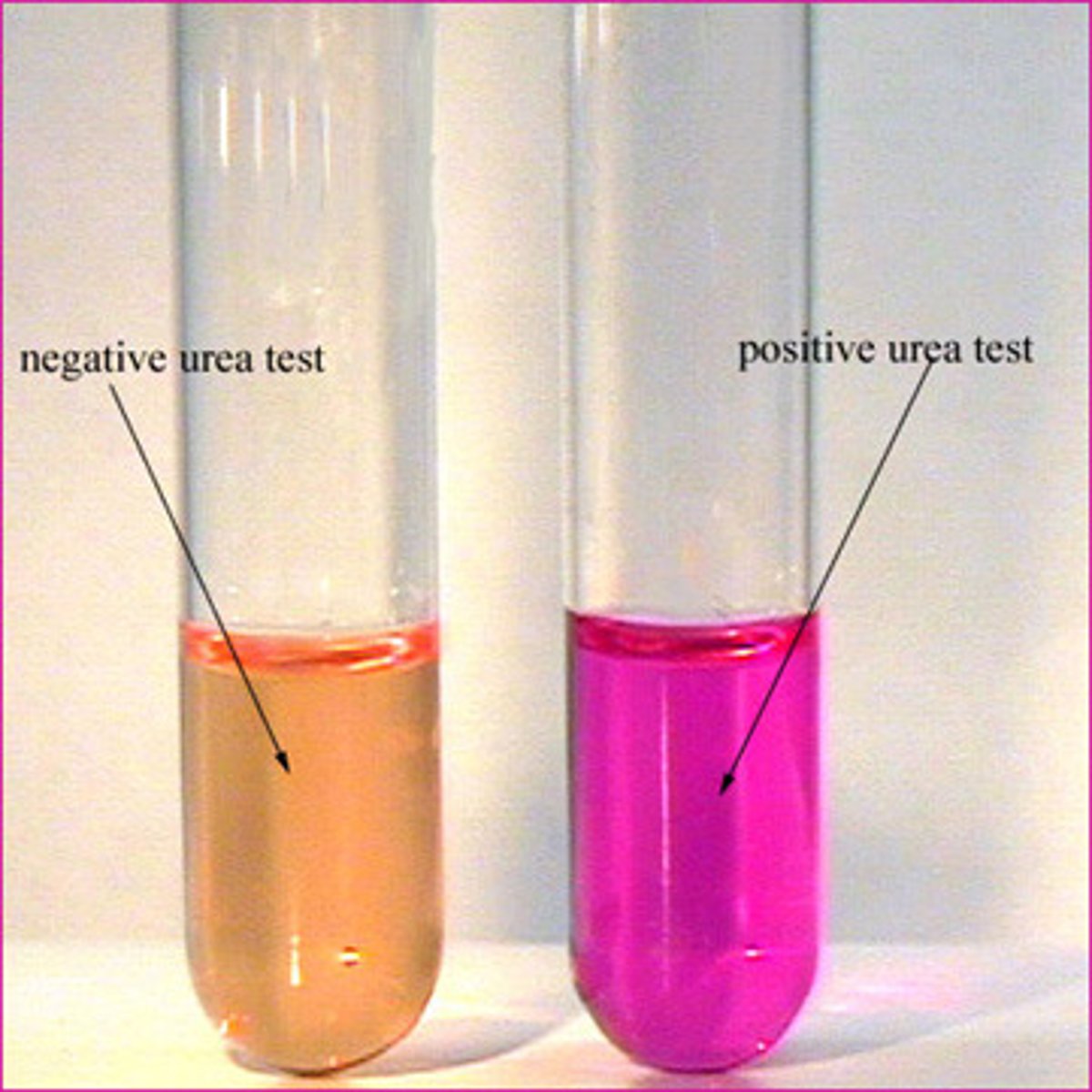
What is the urea hydrolysis test?
tests for urease, which breaks down ammonia to co2
- indicator = phenol red
- pink = positve yellow = negative

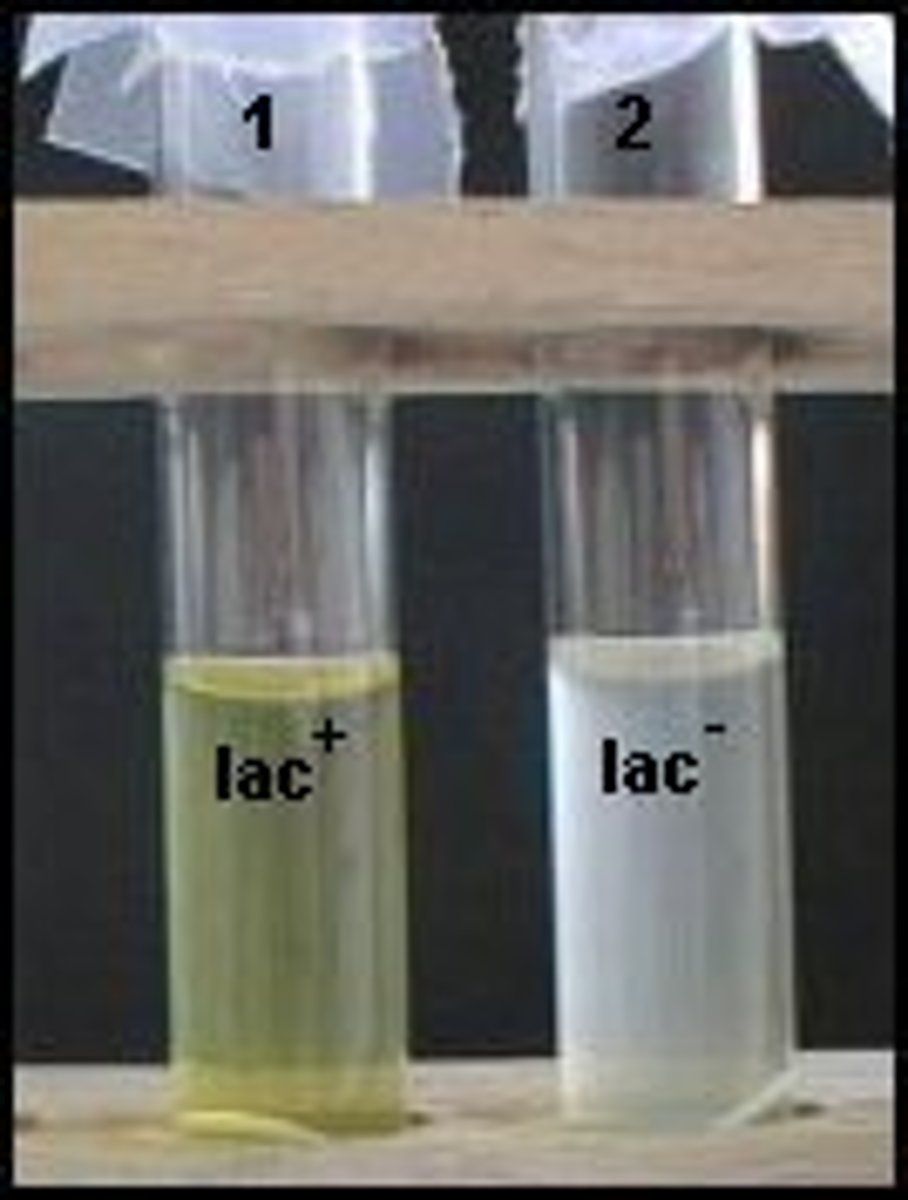
What is the OPNG test ?
Tests for β-galactosidase activity
indicator = ortho-nitrophenol
yellow=+
no color = negative

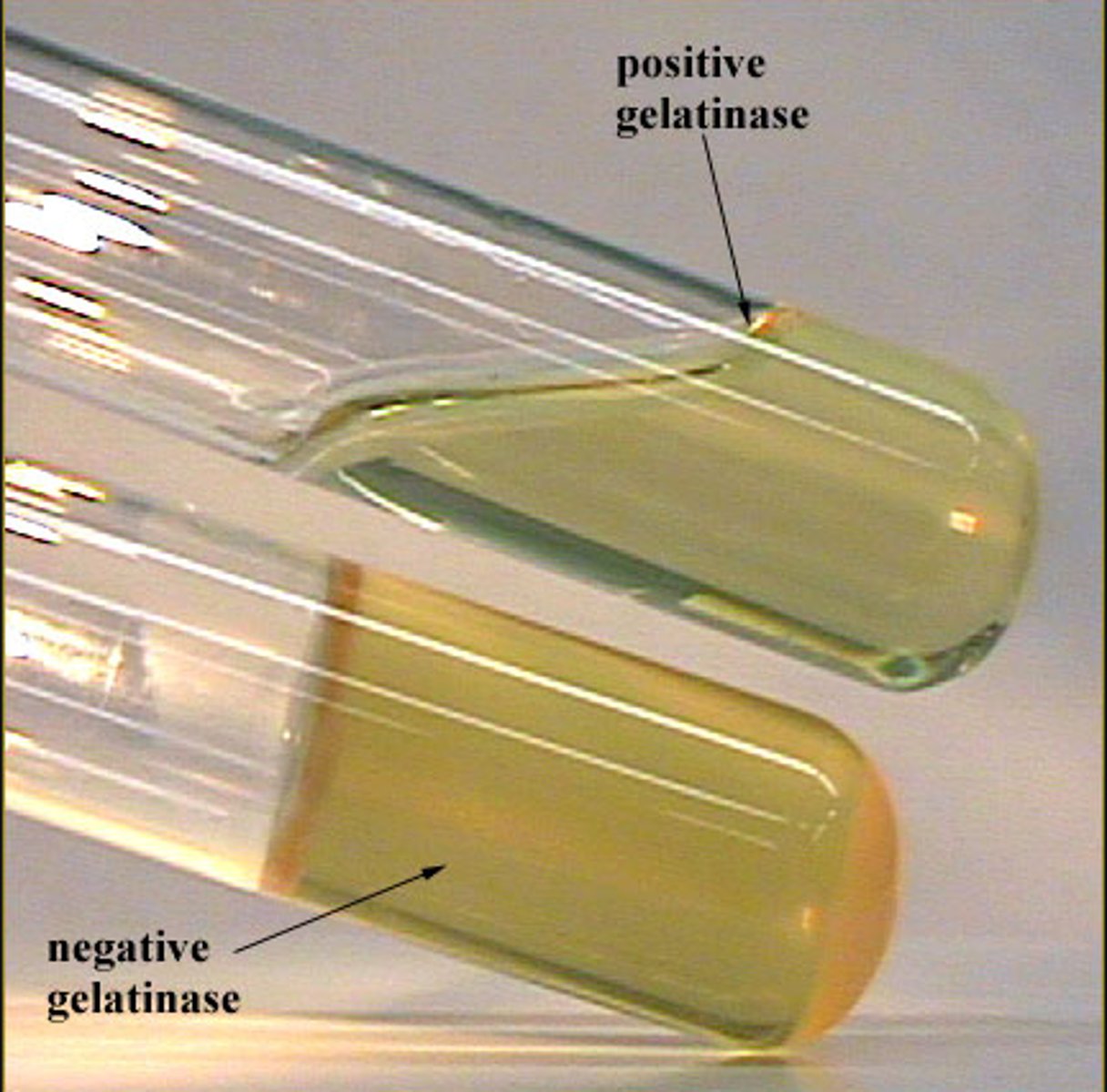
What is the gelatin hydrolysis test?
tests for gelantinase - breaks down gelatin
indicator = state of gelatin
liquid = positive
solid = negative
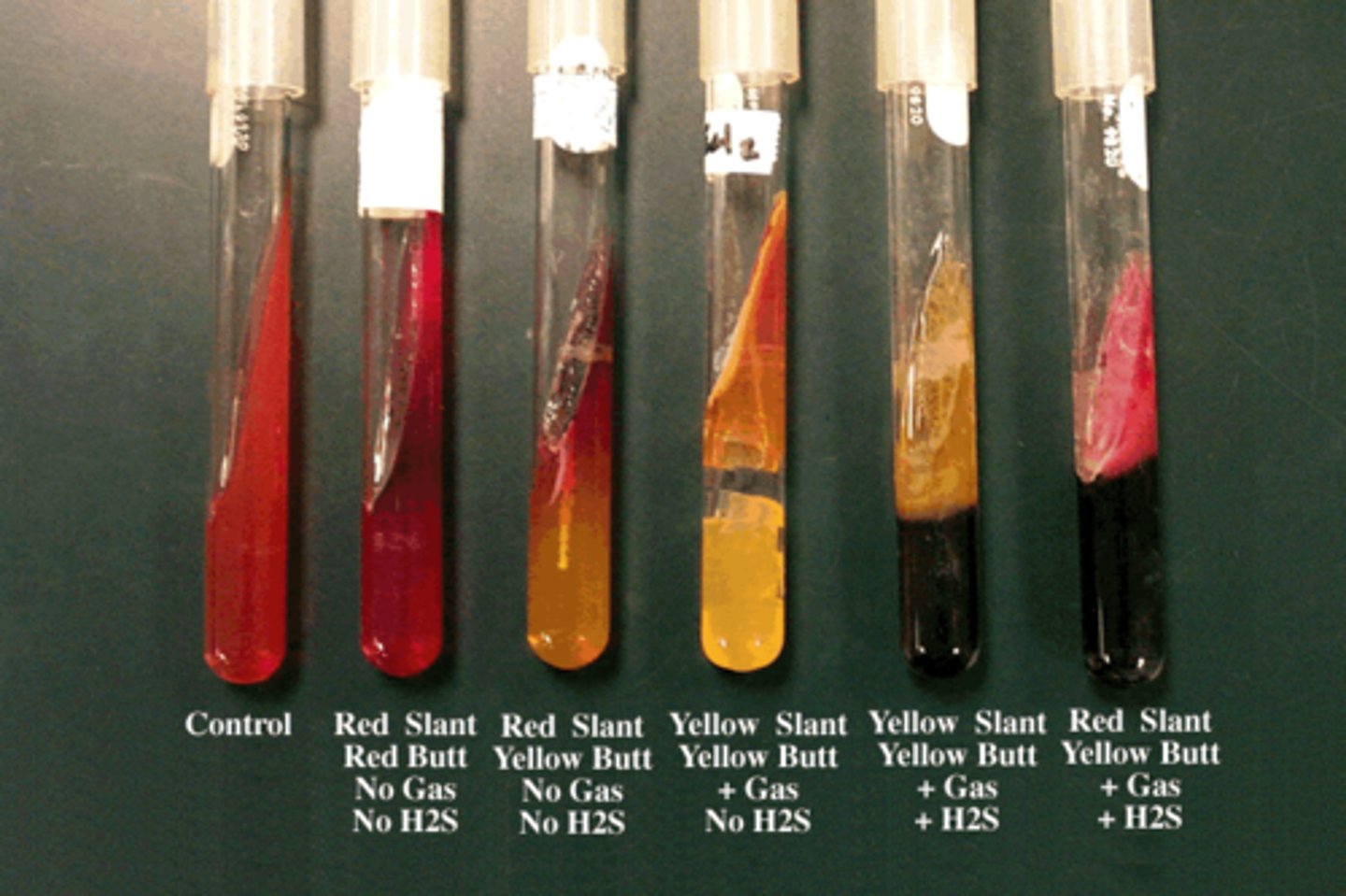
What is the Kligler's Iron Agar (KIA) test?
Tests for glucose and lactose fermentation and hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) production.
indicators = glucose, lactose, and phenol red
yellow butt, red slant = glucose fermentation
all yellow = glucose and lactose
pink/orange = no fermentation
black precipitate, bubbles, cracks = H2S

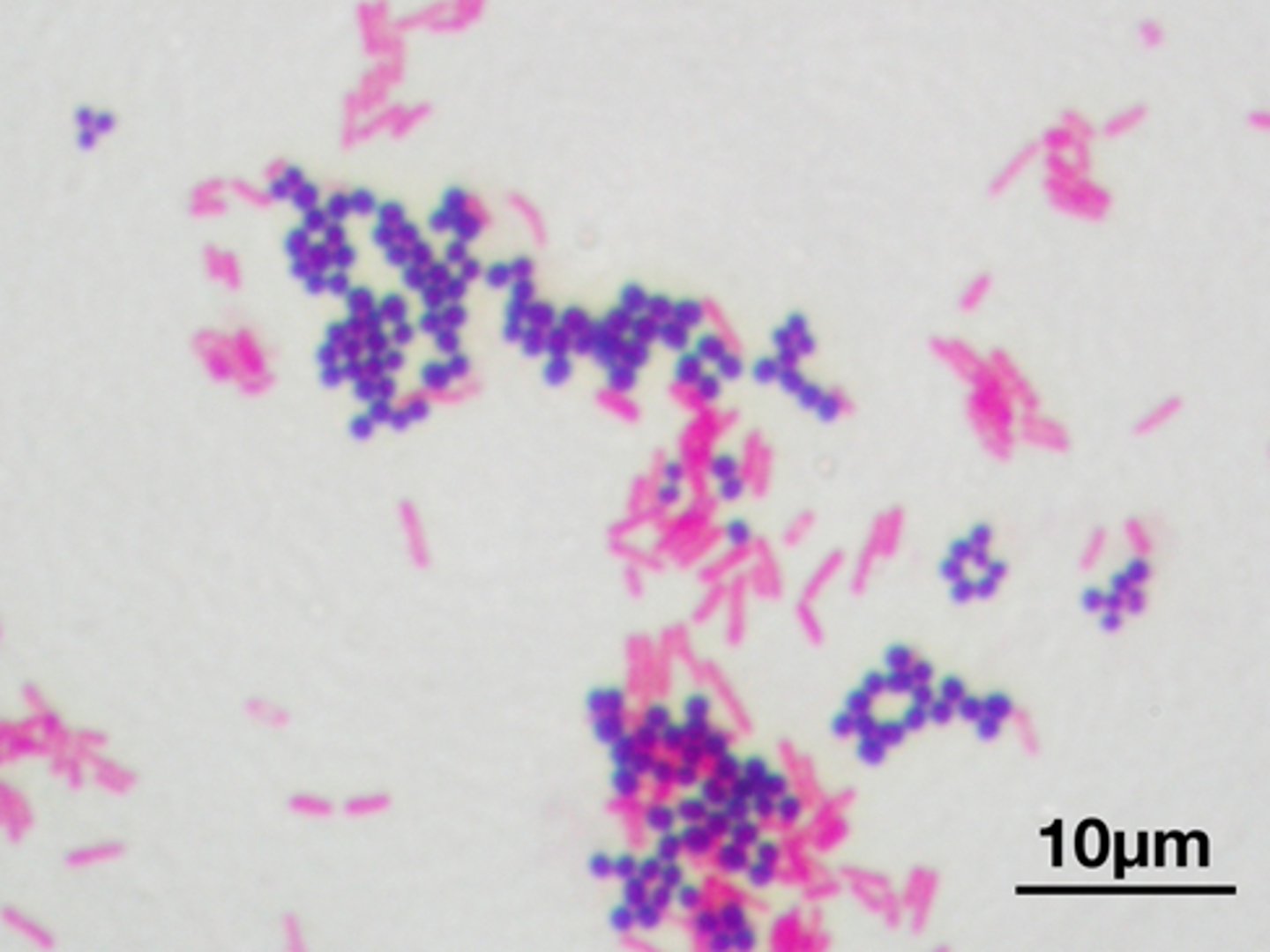
Gram Stain
Purpose:To differentiate bacteria based on the structure of their cell wall — specifically, the thickness of peptidoglycan.
Indicator/Dye System:
Crystal violet (primary stain)
Iodine (mordant)
Alcohol/acetone (decolorizer)
Safranin (counterstain)
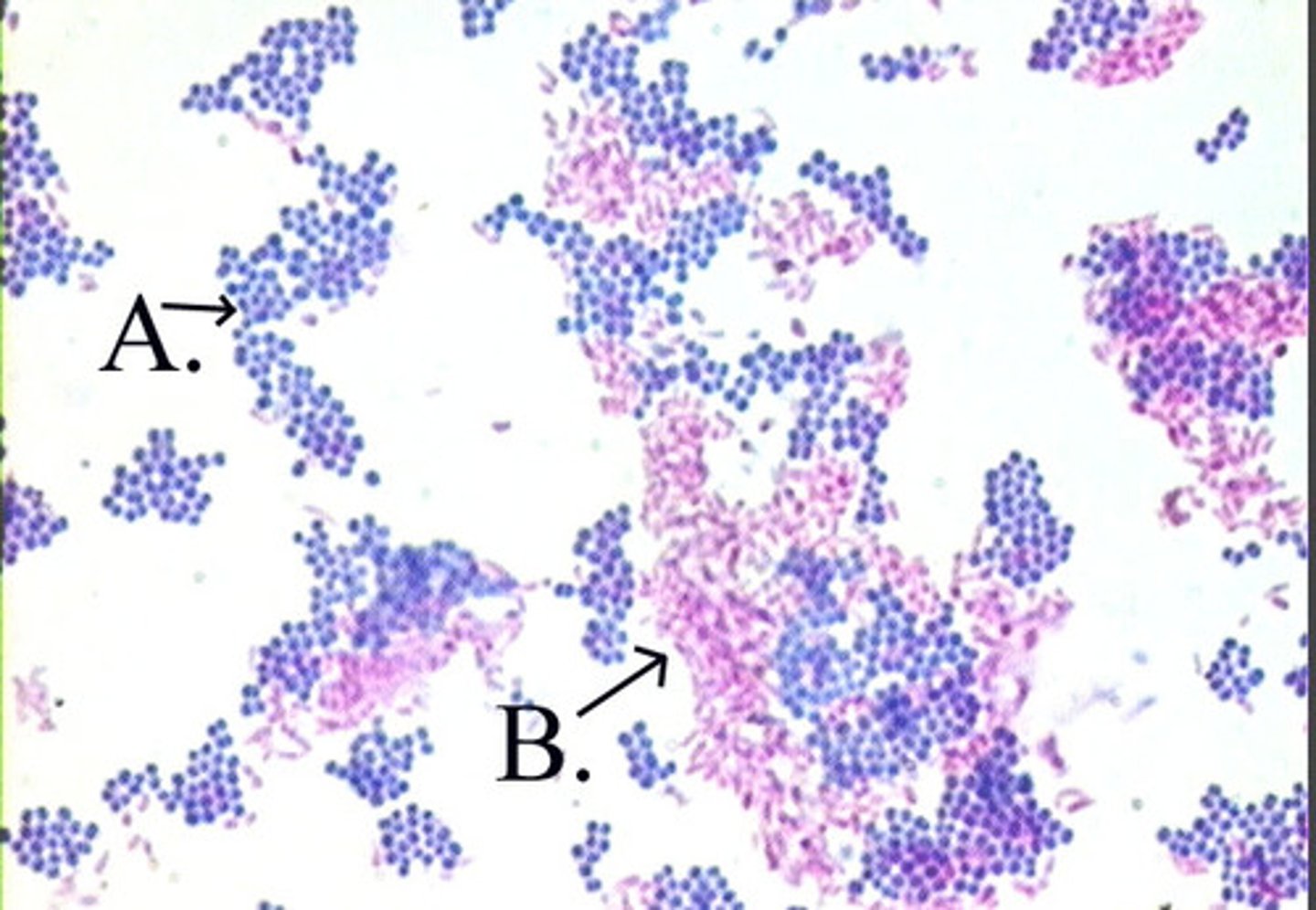
Acid-Fast Stain (Ziehl-Neelsen or Kinyoun method)
Purpose:To identify bacteria with waxy, mycolic acid-rich cell walls (e.g., Mycobacterium species).
Indicator/Dye System:
Carbol fuchsin (primary stain, requires heat for Ziehl-Neelsen)
Acid-alcohol (decolorizer)
Methylene blue (counterstain)
Result Interpretation:
Acid-fast: Bright pink/red (retains carbol fuchsin)
Non–acid-fast: Blue (decolorized, takes up counterstain)
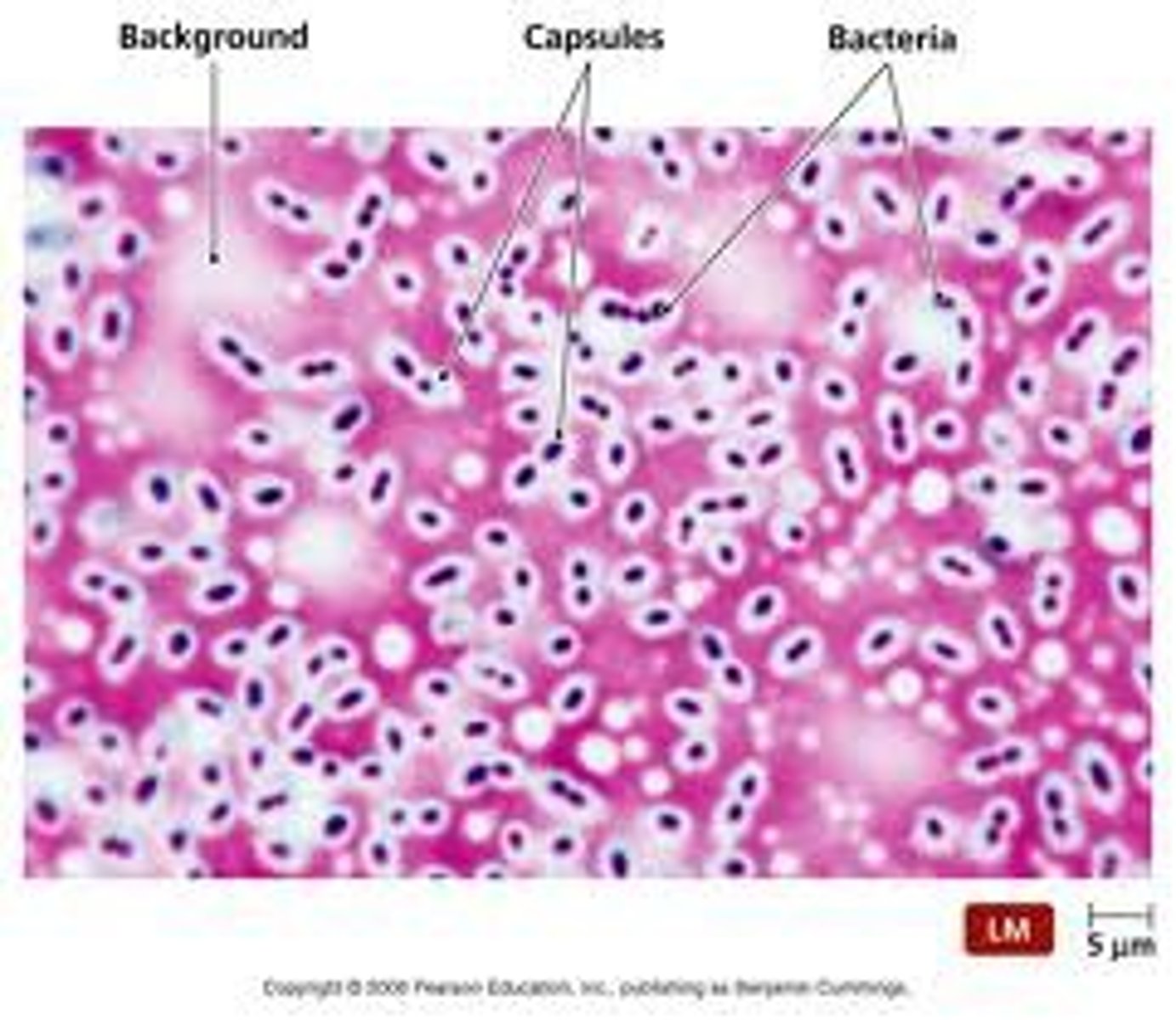
Capsule Stain (Negative stain)
Purpose:To detect bacterial capsules, which are protective layers that resist staining.
Indicator/Dye System:
India ink or nigrosin (stains background)
Crystal violet (optional, can stain the cell)
Result Interpretation:
Capsule: Appears as a clear halo around the stained cell and against a dark background
Cell: Stained; background is dark
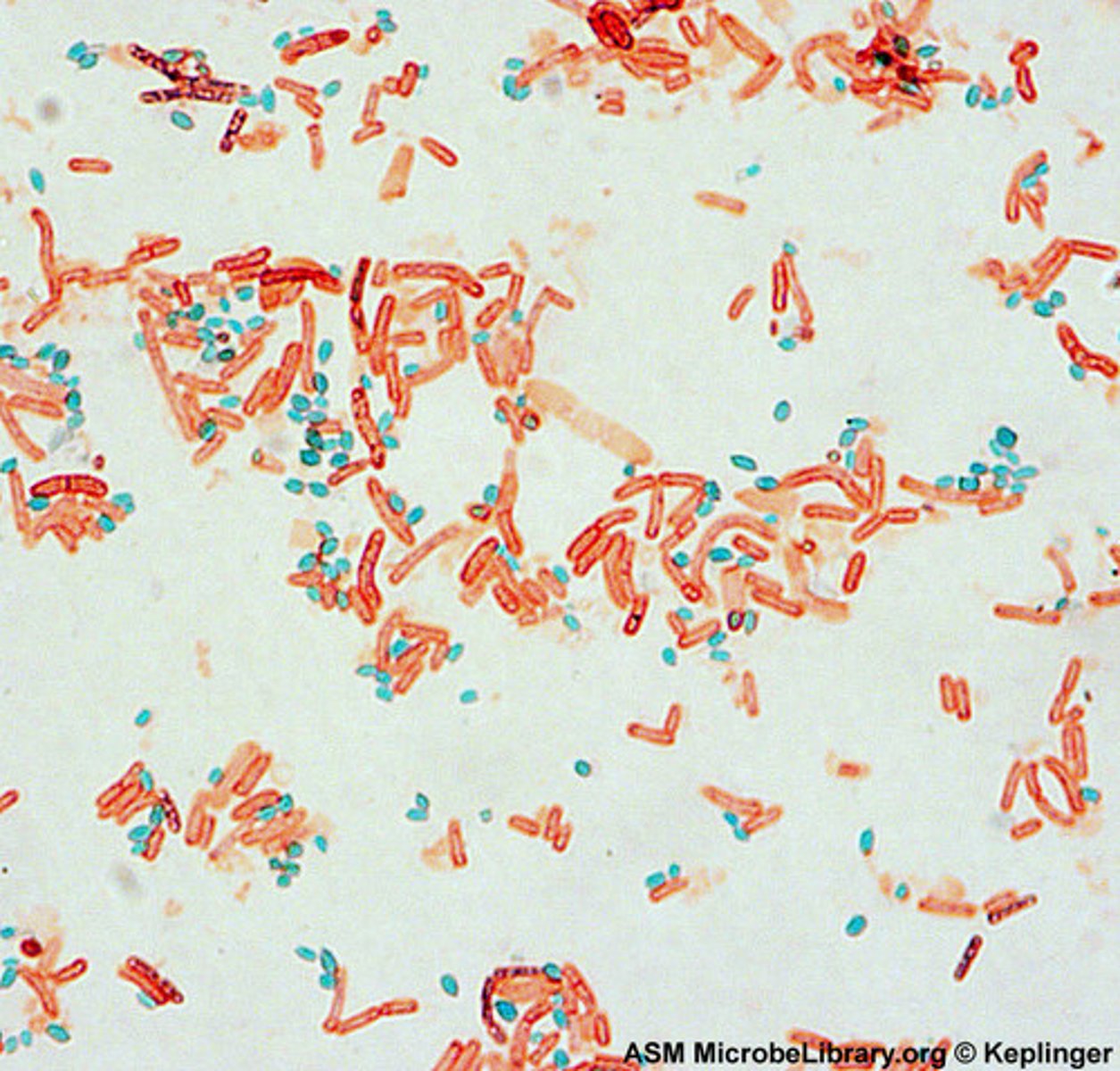
Endospore Stain (Schaeffer-Fulton method)
Purpose:To detect endospores, which are highly resistant, dormant structures produced by some bacteria (e.g., Bacillus, Clostridium).
Indicator/Dye System:
Malachite green (primary stain, applied with heat)
Water (decolorizer)
Safranin (counterstain)
Result Interpretation:
Endospores: Green
Vegetative cells: Red/pink
Microaerophiles
growth in low oxygen concentration
-growth in middle
-SOD
-Peroxidase