topic 4 : river processes
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
topic 4: the uk's evolving physical landscape
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
freeze thaw
when rainwater enters gaps in rocks and freezes, the ice puts pressure on the rock and causes it to break
acid rain
rain containing high amounts of chemical pollutants such as nitric and sulfuric acids, which when it falls can react with the minerals in the ground and cause dissolving and decay.
biological weathering
when the roots of plants grow into cracks of gaps and pushes the rock apart
soil creep
individual particles of soil move slowly down a slope due to gravity
slumping
when the bottom of a valley side is eroded, the slope becomes steeper and the material slides downwards
hydraulic action
sheer force of water hitting the river bed and banks, wearing them away
abrasion
material scraping or rubbing along the banks and bed of the river
solution
river water is slightly acidic so can dissolve some rocks and minerals
attrition
particles in the river bashing into each other, wearing each other down and becoming smaller and rounder
traction
stones rolling along the river bed
saltation
smaller particles bouncing along the river bed
suspension
the water flow carries silt and sand particles
erosion
the breaking away and removal of materials by a moving force e.g. river, wave, glacier
four types of erosion?
hydraulic action, abrasion, attrition & solution
weathering
the breakdown & decay of rock by natural processes acting on rocks, cliffs & valley sides
three types of weathering?
physical, chemical, biological
mass movement
the movement of material down a slope due to gravity
four types of mass movement?
falls, slumps/slides, creeps and flows
mudflow
saturated soil flows down a slope
landslide
large blocks of rock slide downhill
rockfall
bits of rock fall off the cliff face, usually due to freeze-thaw weathering
transportation
the carrying of sediment downstream from the point where it has been eroded to where it is deposited
four types of transportation?
solution, suspension, saltation, traction
deposition
when a river loses energy it drops/deposits the sediment it has been carrying
freeze-thaw weathering
water enters cracks in the rock.
when air temperature drops below freezing, the water will freeze and expand by 9-10 percent putting pressure on the rock
the ice will melt and contract when the temperature rises above freezing
what happens if the process of freeze thaw weathering is repeated?
the rock will weaken and eventually shatter into angular fragments - the fragments may then be deposited as scree at the foot of a slope
onion skin weathering/exfoliation
when a rock's outer layer peels off due to extreme variations in temperatures
describe what happens with different temperatures in exfoliation
when temperature is high, the rocks expand e.g in desert areas, when temperature drops during the night, the rocks contract
describe how river processes of erosion, transportation and deposition change downstream (8 marks)
"You need to start at the upper course, then talk about the middle and lower course. Don't forgot to mention deposition. You must use correct terms."
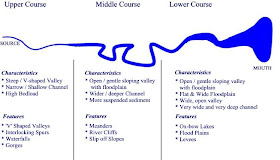
what is the upper course like?
narrow/shallow channel
high bedload
steep/v-shaped valley
what is the middle course like?
open/gentle sloping valley with floodplain
wider/deeper channel
more suspended sediment
what is the lower course like?
open/gentle sloping valley with floodplain
flat and wide floodplain
very wide and deep channel
upper course features
interlocking spurs
gorges
waterfalls
‘v’ shaped valleys
middle course features
meanders
river cliffs
slip off slopes
lower course features
ox-bow lakes
floodplains
levees
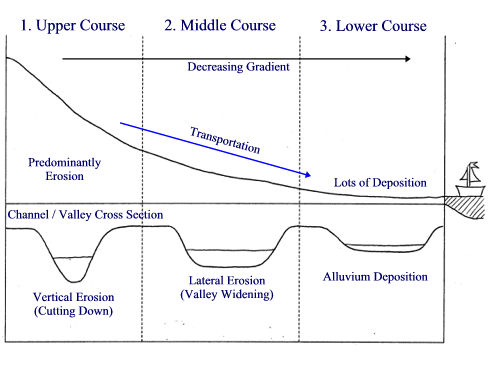
why certain fluvial processes occur at different places along the river?
modal answer:
firstly, deposition processes predominantly occur in the lower course, e.g by the mouth of the river, this is because the river is moving slowly and will lose energy, causing it to drop sediment.
secondly, vertical erosion ocurs mainly in the upper course, for example by a waterfall - shown in the figure, this is because the water is travelling down a steep gradient and therefore erode downwards.