Edexcel IGCSE Physics: 1 Forces and Motion
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
How do you calculate the speed from a distance-time graph ?
the speed/velocity is the gradient
State the equation for average speed
average speed = distance travelled /time taken
v[m/s]=s[m]/t[s]
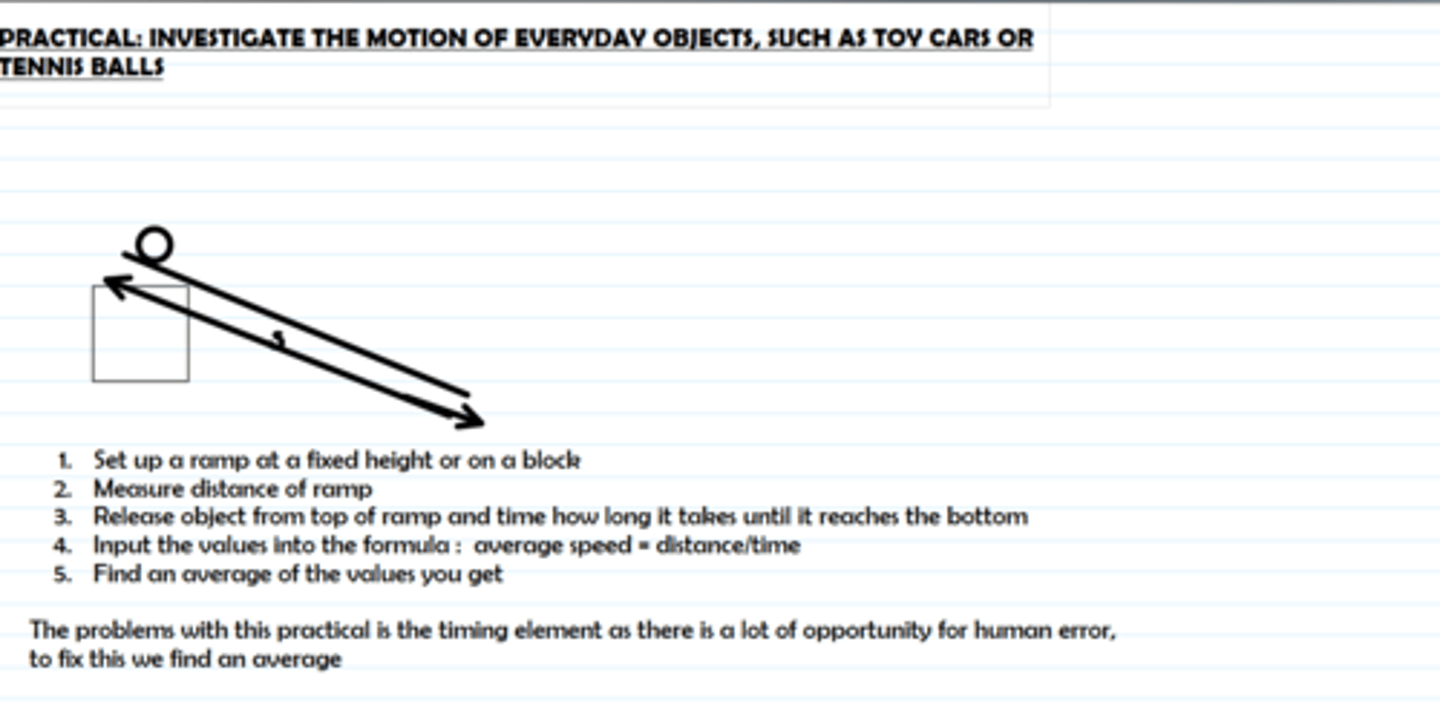
Practical: investigate the motion of everyday objects such as toy cars or tennis balls
state the equation for acceleration ( using velocity and time)
acceleration = change in velocity / time taken
a[m/s/s] = (v-u)[m/s]/t[s]
How do you calculate the distance from a velocity time graph?
The distance is the area under the graph
How do you calculate the acceleration from a velocity time graph?
The acceleration is the gradient of the graph
State the equation for final speed
final speed squared [m/s] = initial speed squared [m/s] + 2 x acceleration[m/s/s] x speed [m/s]
What are the effects of a force?
1. can change the speed of an object
2. can change direction an object is travelling in/ can rotate an object
3. can change shape of an object
List the different types of forces:
1. Gravity/Weight
2. Reaction Force
3. Electrostatic Force
4. Thrust
5. Drag/Air Resistance
6. Friction
7. Lift
8. Tension
9. Magnetic
10. Nuclear
What is the difference between a vector quantity and a scalar quantity?
a scalar quantity only has magnitude (size) whereas a vector quantity has magnitude(size) and direction
How do you calculate the resultant force of forces acting on a line ?
you add up the forces in each direction
You subtract the larger force from the smaller force, to get the resultant force
The resultant force acts in the direction of the larger force
What is friction ?
a force that opposes motion
State the equation for force (using mass and acceleration)
force = mass x acceleration
F[N] = m[Kg] x a[m/s/s]
State the equation for weight
Weight (N) = mass (kg) x gravitational field strength (N/kg)
W[N]=m[Kg] x g[m/s/s]
What is stopping distance and how do you calculate it ?
the distance a vehicle travels from the second a hazard is detected till the car stops
stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance
What factors affect stopping distance?
speed
mass
road condition
reaction time
Describe the forces acting on a falling object
*CHECK
1. initially v=0 and drag=0 , only weight acting on it
2. Then as it falls it will experience drag , however initially the weight force is higher
3. the object will begin to move faster towards the ground, simultaneously the force of drag increases
4. the weight and drag forces balance out so there is no resultant force on the object and it reaches(constant) terminal velocity
Practical: Investigate how extension varies with applied force for helical springs, metal wires and rubber bands
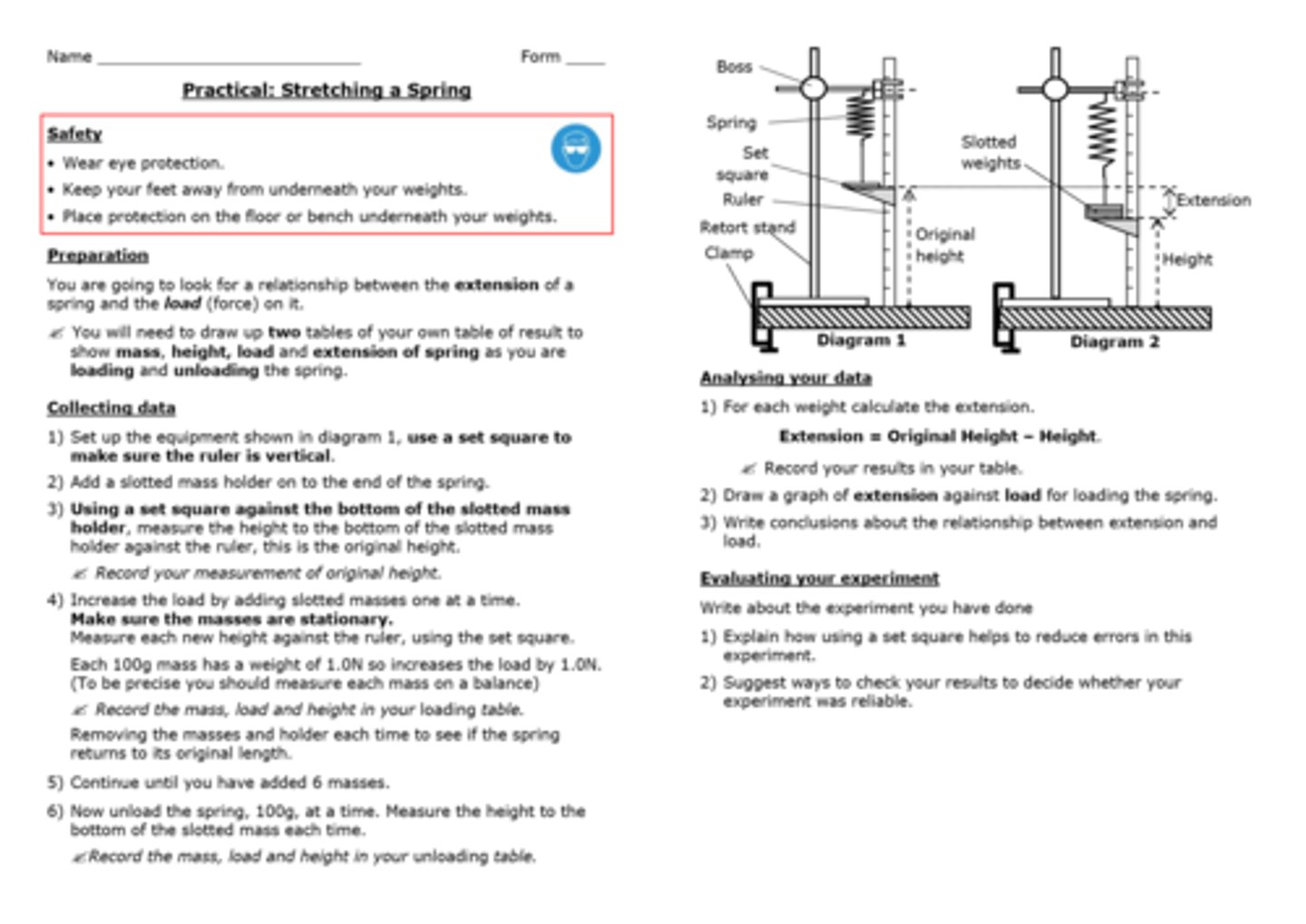
What is Hooke's law?
The extension of a spring is directly proportional to the force applied up until the limit of proportionality
Define the term elastic behaviour
the ability of a material to recover its original shape after the forces causing deformation have been removed
State the equation for momentum
momentum = mass x velocity
p[kgm/s]=m[kg] x v[m/s]
Explain how safety features in a car work , with respect to momentum
Airbags&Seatbelts
1. Absorbs energy from the impact, 2.increases time taken for the force to act on the passenger
3. Since force = change in momentum/ time taken , and time increases = the force decreases
Crumple Zones
1. part of the car which collapses during a collision
2. Increases time during which the car is decelerating
3. And since force = change in momentum / time , and if time increases force felt on the passenger decreases
State the principle of conservation of momentum
momentum before collision = momentum after collision
total initial momentum = total final momentum in an elastic reaction
elastic reaction , a reaction where initial KE = final KE
State the relationship between force and momentum
force = change in momentum / time taken
F[N] = (mv-mu)[kgm/s]/t[s]
Explain Newton's third law
if object A exerts a force on object B then object B exerts an equal and opposite force on object A
State the equation for a moment
moment = force x perpendicular distance
m[Nm] = F[N] x d [m]
Where does weight act on a body?
through the centre of gravity (the centre of the object)
How do you calculate the moment for parallel forces acting in one plane?
you use the moment formula and calculate the distance from the pivot of both of the forces
You then subtract the smaller moment from the larger moment to give the total moment which is in the direction of the larger moment
You may use:
F1 x d1 = F2 x d2
Then rearrange if asked to find a particular force or distance
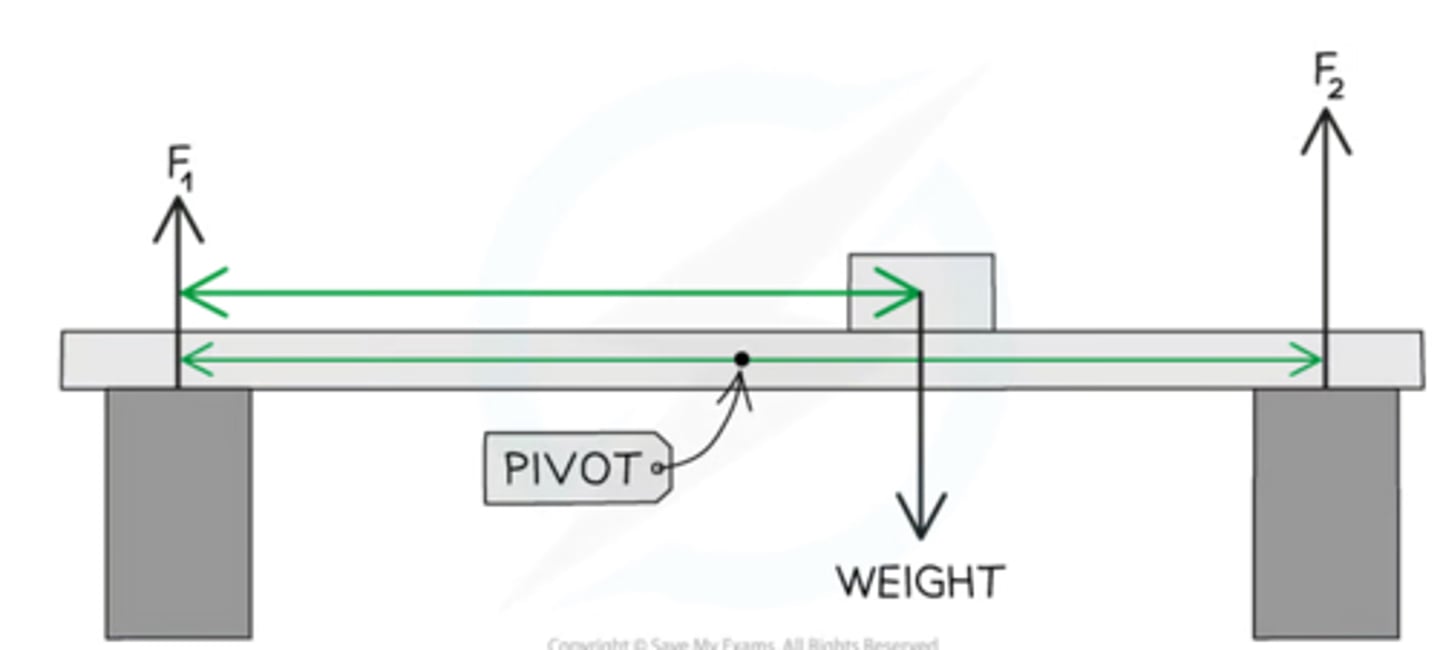
Describe how the upward forces on a light beam supported at its ends vary with position of a heavy object placed on the beam
If a beam is supported at ends A and B
(take centre as pivot )
As the mass moves towards A :
Upwards Force on A increases
Upwards force on B decreases
As the mass moves towards B:
Upwards force on A decreases
Upwards force on B increases
This is because the CW moment must equal the ACW moment to secure the beam