ANSC 512 Urinary System - Urine Concentration and Outflow Tracts
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
descending limb is permeable to water but not NaCl, tubular fluid increases in osmolarity (NaCl concentration) as it descends, thick segment of ascending limb is impermeable to water but has pumps for Na, K, and Cl, water remains in tubule but salt leaves, making hypertonic medulla ECF
What is the countercurrent multiplier flow?
osmolarity drives the reabsorption of water in peritubular capillaries that run adjacent to the tubules, as well as excretion of extra water to the urethra
How does the countercurrent multiplier work?
Na/K/Cl cotransport pumps 60%, urea recycling 40%
What dictates the countercurrent multiplier?
water is pushed into the extracellular fluid, salt is reabsorbed into blood
What happens when the descending limb descends into the medulla?
water diffuses into the blood and salt travels into the extracellular fluid
What happens when the limb ascends out of the medulla?
cortex, medulla, renal papilla
What is the path of the loop and collecting ducts?
urine becomes concentrated
What occurs when the medullary collecting duct is more permeable to water than solutes?
dehydration, loss of blood volume, rising blood osmolarity
Baroreceptors/osmoreceptors are triggered by what?
works on principal cells of DCT/CD to make collecting duct more permeable to water and make more aquaporins to retain more water
What does ADH do?
a steroid from the adrenal cortex that is triggered by low salt concentrations that makes Na/K pumps to retain more NaCl (which in turn retains more water)
What does aldosterone do?
water diuresis, cortical CD reabsorbcs NaCl, water remains as ewll, high volume of hypotonic urine
What happens when you are overhydrated?
hormonal control is stimulated by high blood osmolarity to increase water permeability, BP drops, BFR decreases, more water is reabsorbed and low volume of hypertonic urine is produced
What happens when you are dehydrated?
metabolic water (aerobic respiration), cutaneous transpiration (diffusion of water through epidermis), obligatory water loss (minimum unavoidable water loss)
What are the three aspects of fluid balance?
dry mouth (redirection of water away from saliva production) and quenching of thirst (30 min delay, cool/moistening of mouth, distension of stomach)
How can the body regulate water intake?
loss of water and Na equally
What is hypovolemia?
loss of water over loss of Na
What is dehydration?
circulatory shock and neurologic disfunction
What can fluid deficiency cause?
water intoxication and hypotonic extracellular fluid
What can happen if there is too much water intake?
excess fluid in a particular location
What is sequestration?
any chemical that increases urine volume
What are diuretics?
increase GFR, inhibit ADH, inhibit Na/K/2Cl cotransporter
How can a diuertic work?
2 ureters, 1 urinary bladder, 1 urethra
What is the general anatomic composition of outflow tracts?
extension of renal pelvis
What is a ureter?
adventitia, muscularis (two layers of smooth muscle), mucosa (transitional epithelium)
What are the three layers of the ureter?
keep ureters in one spot in the body
What does the adventitia do?
umbrella cells that are impermeable to urine that protect epithelial cells
What does the transitional epithelium consist of?
ureters
what is structure 1?
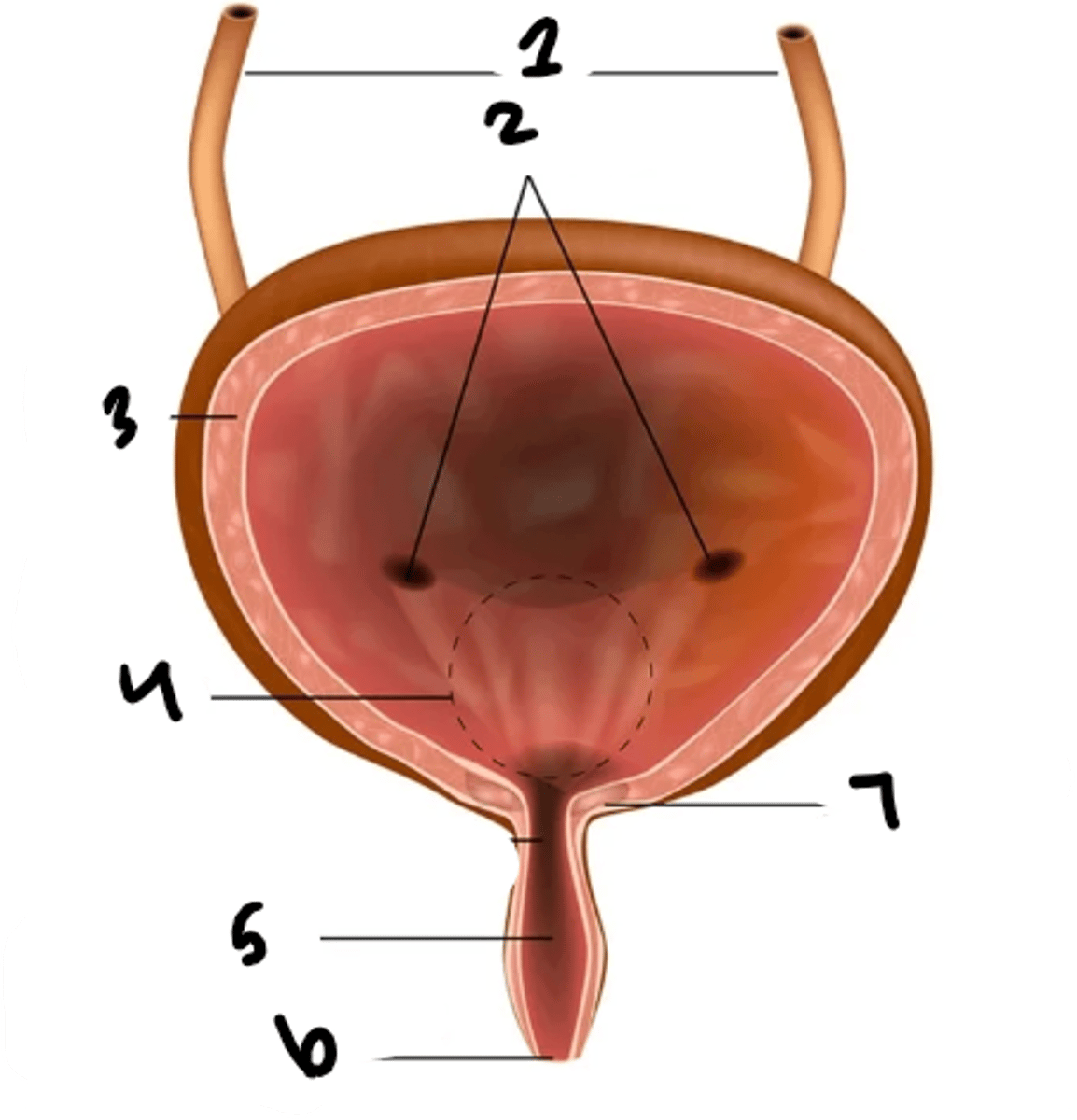
uretral openings
What is structure 2?
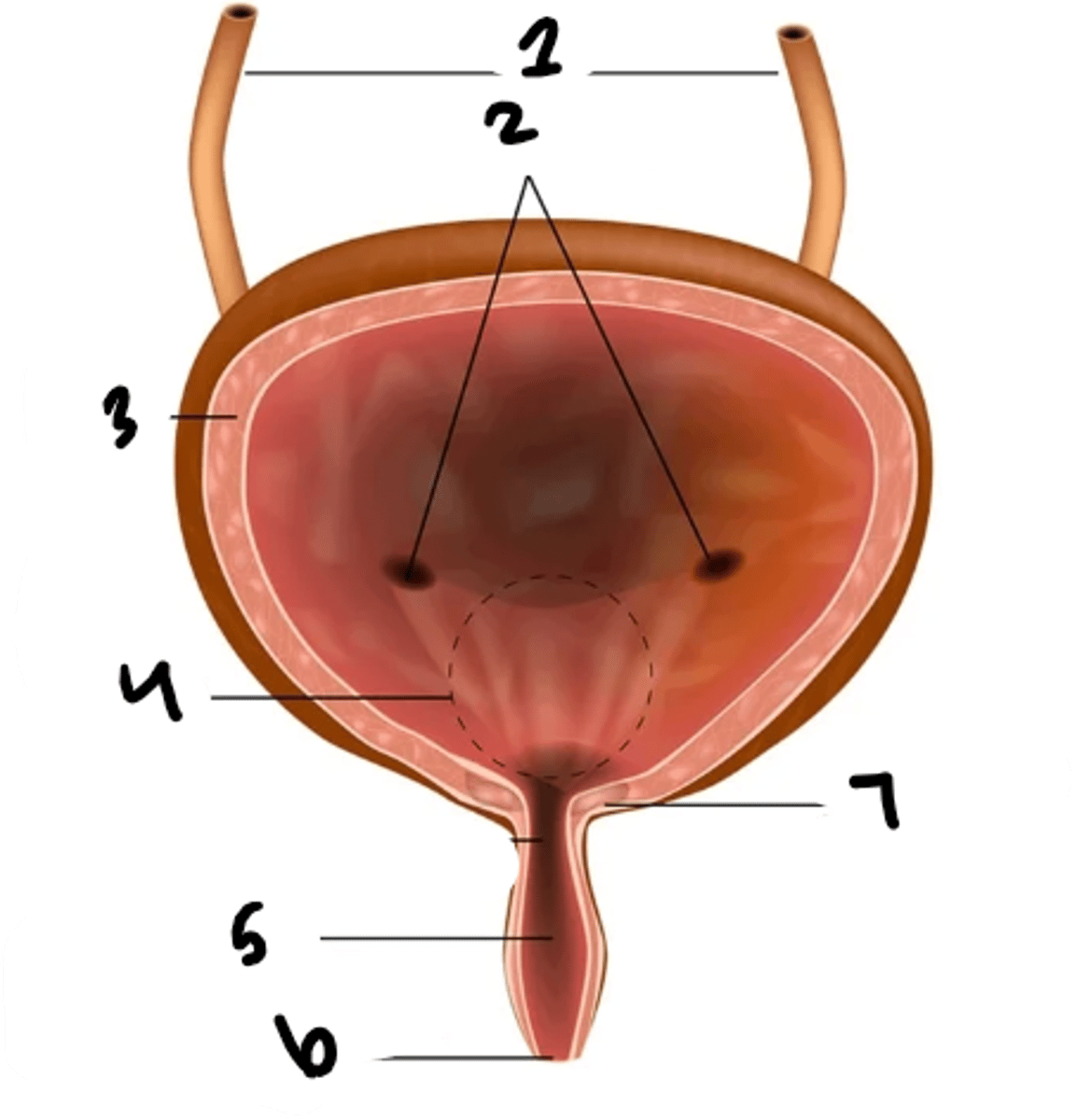
detrusor muscle
What is structure 3?
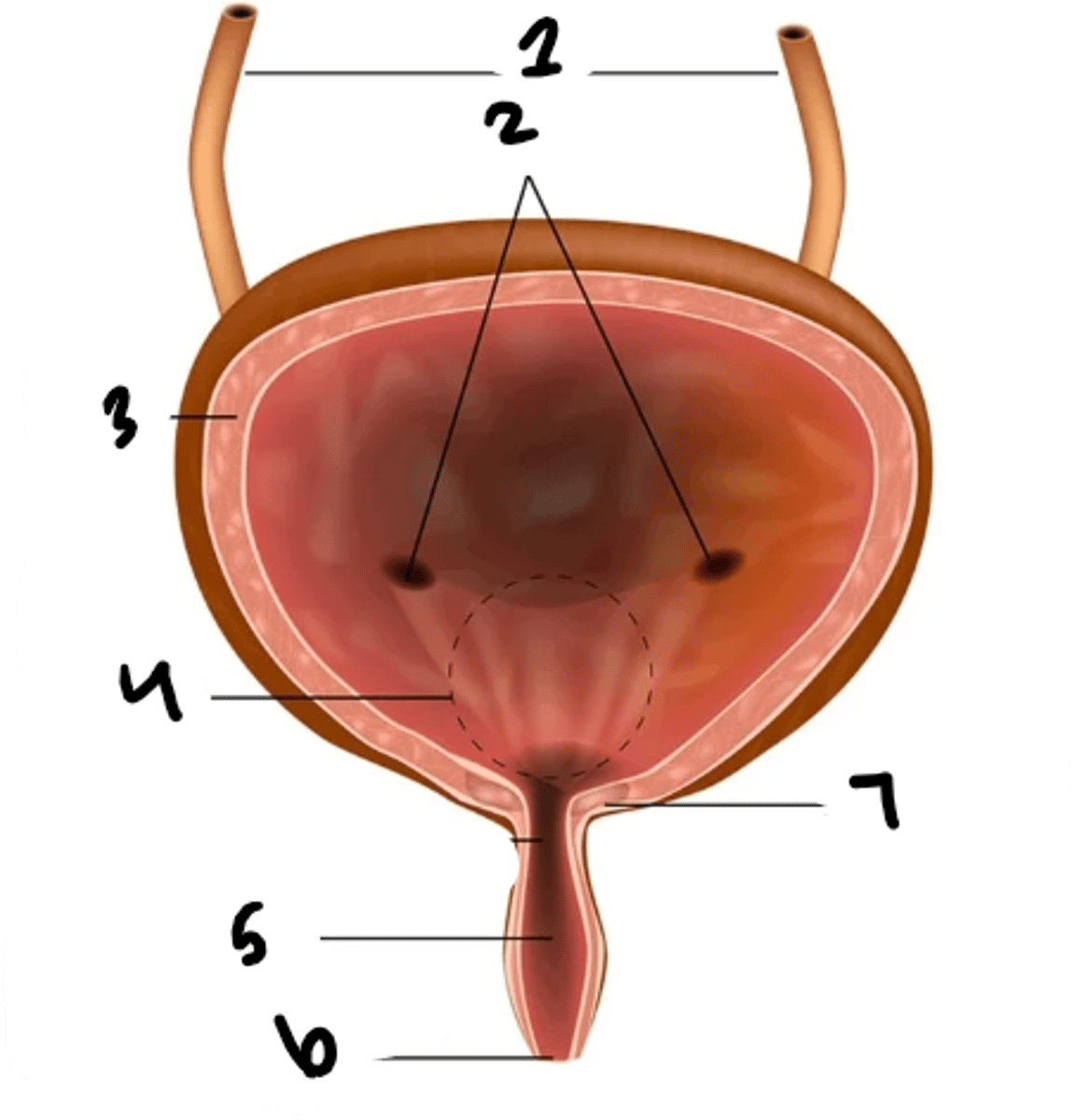
trigone
What is structure 4?
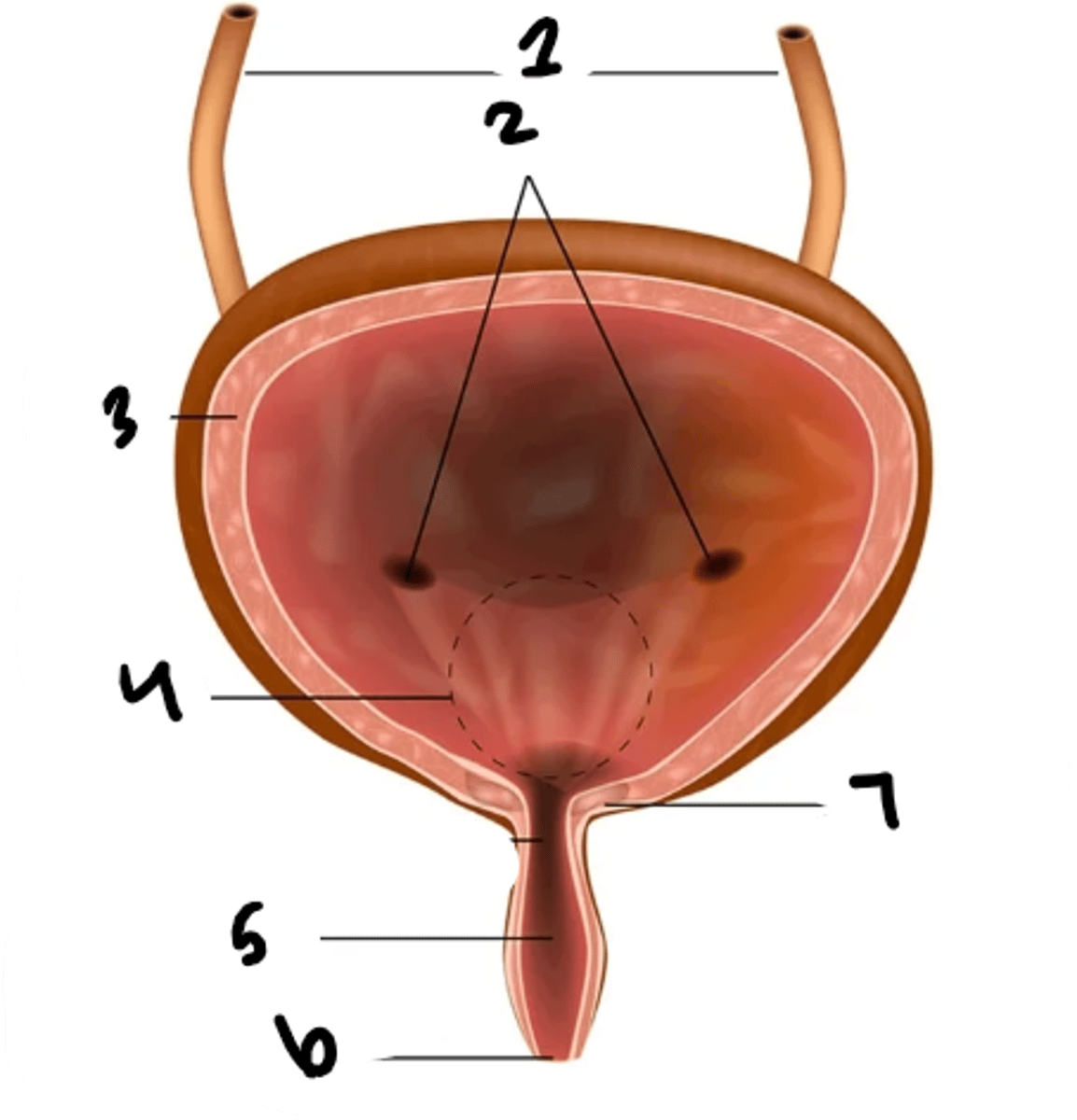
urethra
What is structure 5?
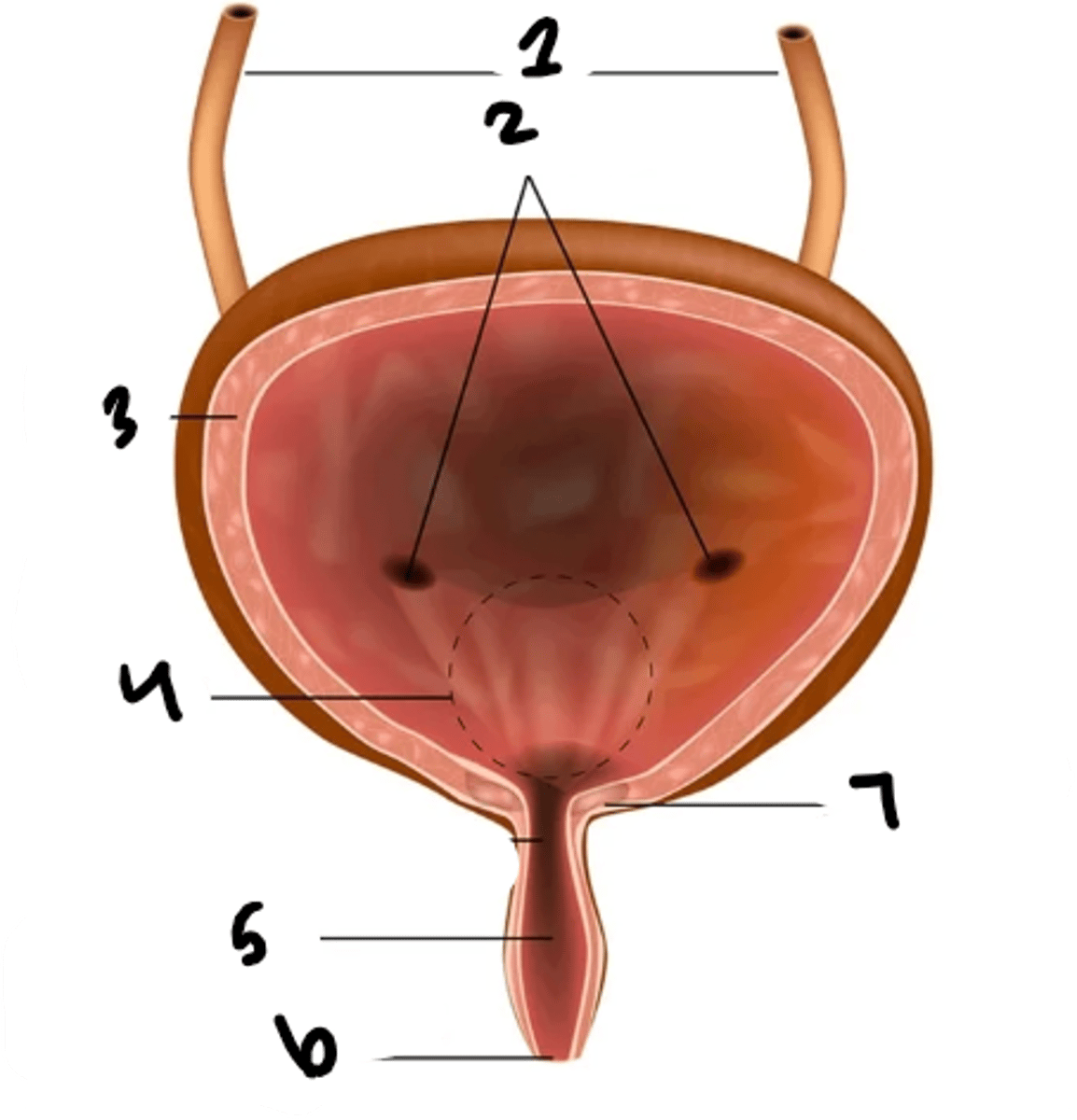
external urethral sphincter
What is structure 6?
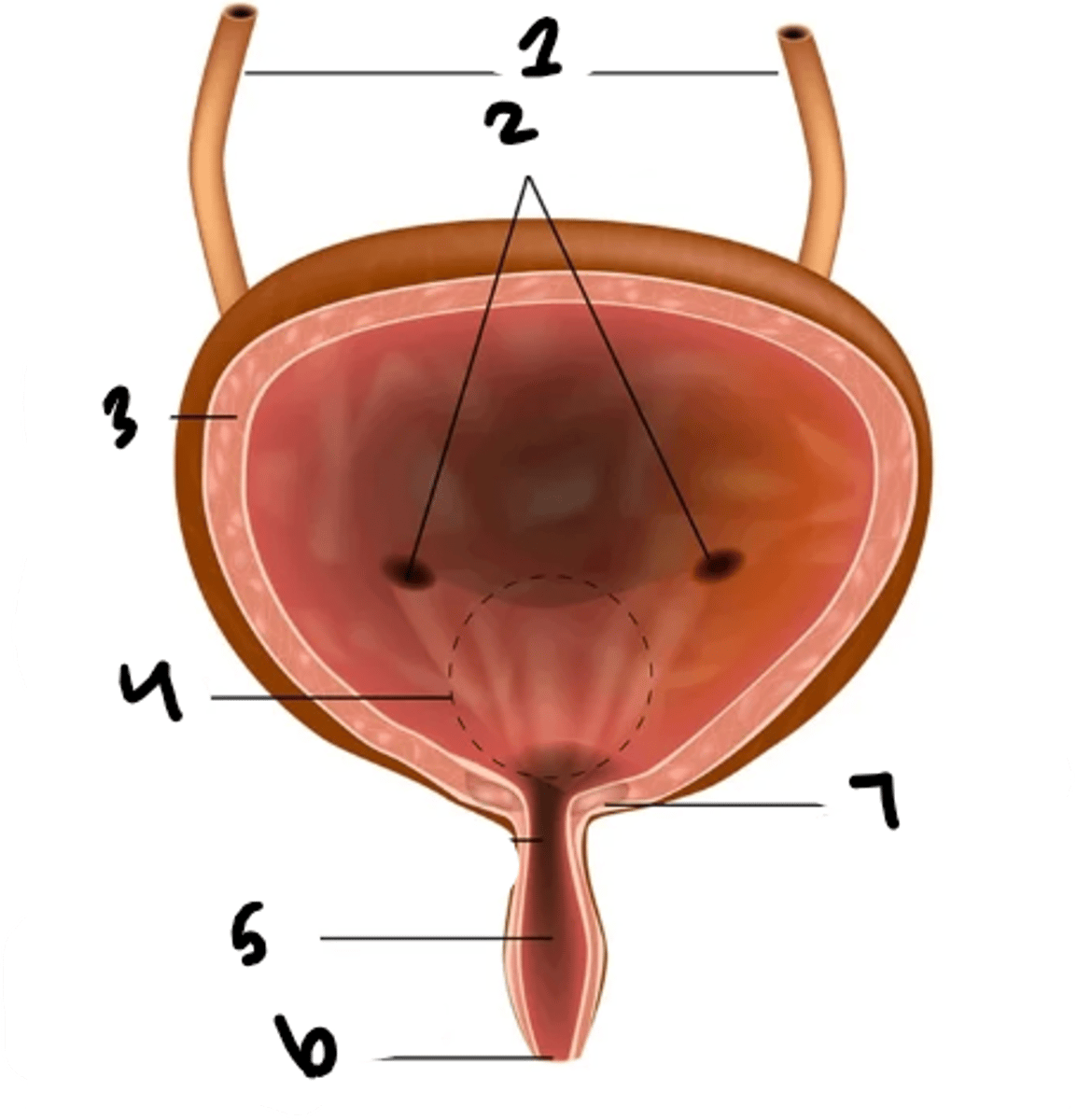
internal urethral sphincter
What is structure 7?
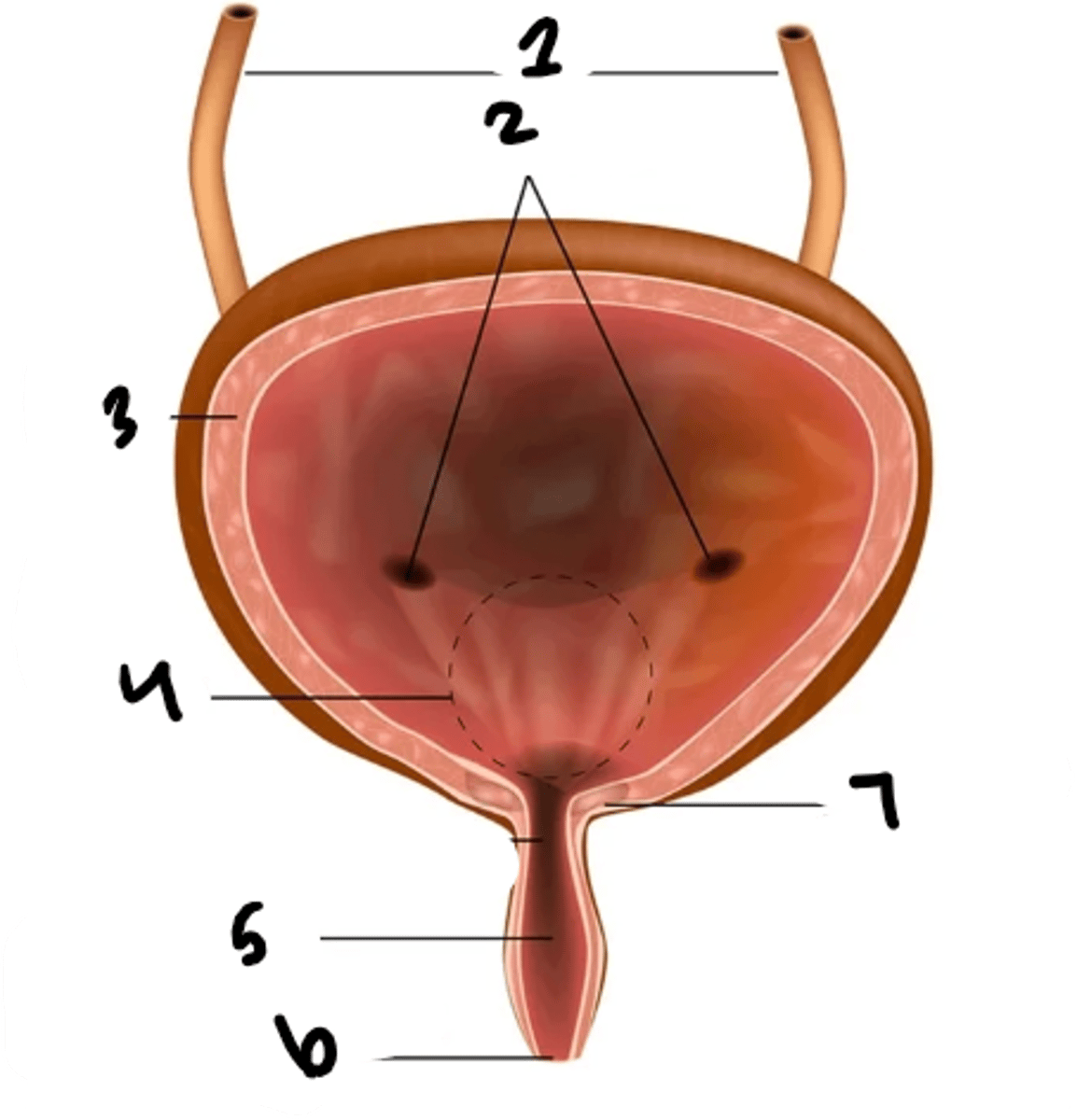
rugae
What is the term for the transitional epithelium lining the inside of the urinary bladder?
inner longitudinal, middle circular, outer longitudinal
What are the three layers of the detrusor muscle?
psuedostratified epithelium to stratified squamous epithelium
How does the transitional epithelium transition?
sympathetic stimulation to detrusor muscle to relax and somatic motor innervation to external sphincter to stay closed
What innervation allows for the bladder to fill without spilling?
stretch receptors in bladder wall stimulated, neurons travel in pelvic nerve to sacral segments of spinal cord, parasympathetic neuron travels to bladder in pelvic nerve, bladder wall contracts and urethral sphincters relax
What is the path of the micturition spinal reflex?
stretch receptor information travels up the ascending tract to the cerebrum where it decides appropriate urination or not, if appropriate reflex carries on if not stretch receptors are ignored
How is urinating voluntarily controlled?
production of normal than normal amount of urine
What is polyuria?
production of decreased amount of urine
What is oliguria?
production of no urine
What is anuria?
they have an internal urethral sphincter and three segmented parts to extend through the penis - prostatic, membranous, penile
Why do males have a longer urethra than females?
skeletal muscle around urethra controlled somatically
What is the external urethral sphincter?