HL PDA III Exam I - Principles of Neuropharmacology LOs
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What are the 3 structural elements of a neuron?
dendrites, cell body (soma), and axon
What is a dendrite?
the part of the neuron that receives input/information from other neurons
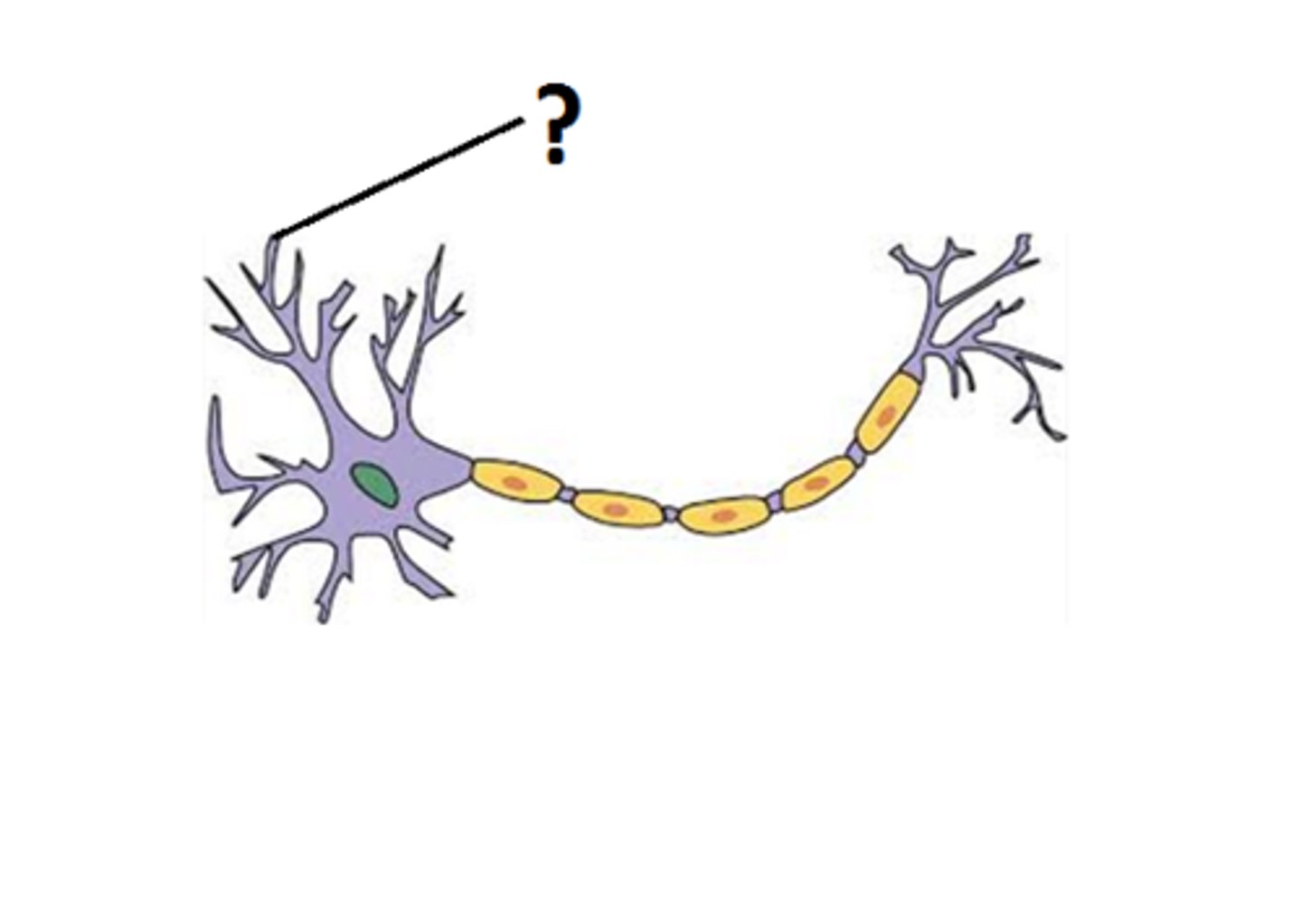
What is a cell body?
the part of the neuron that is also called the soma
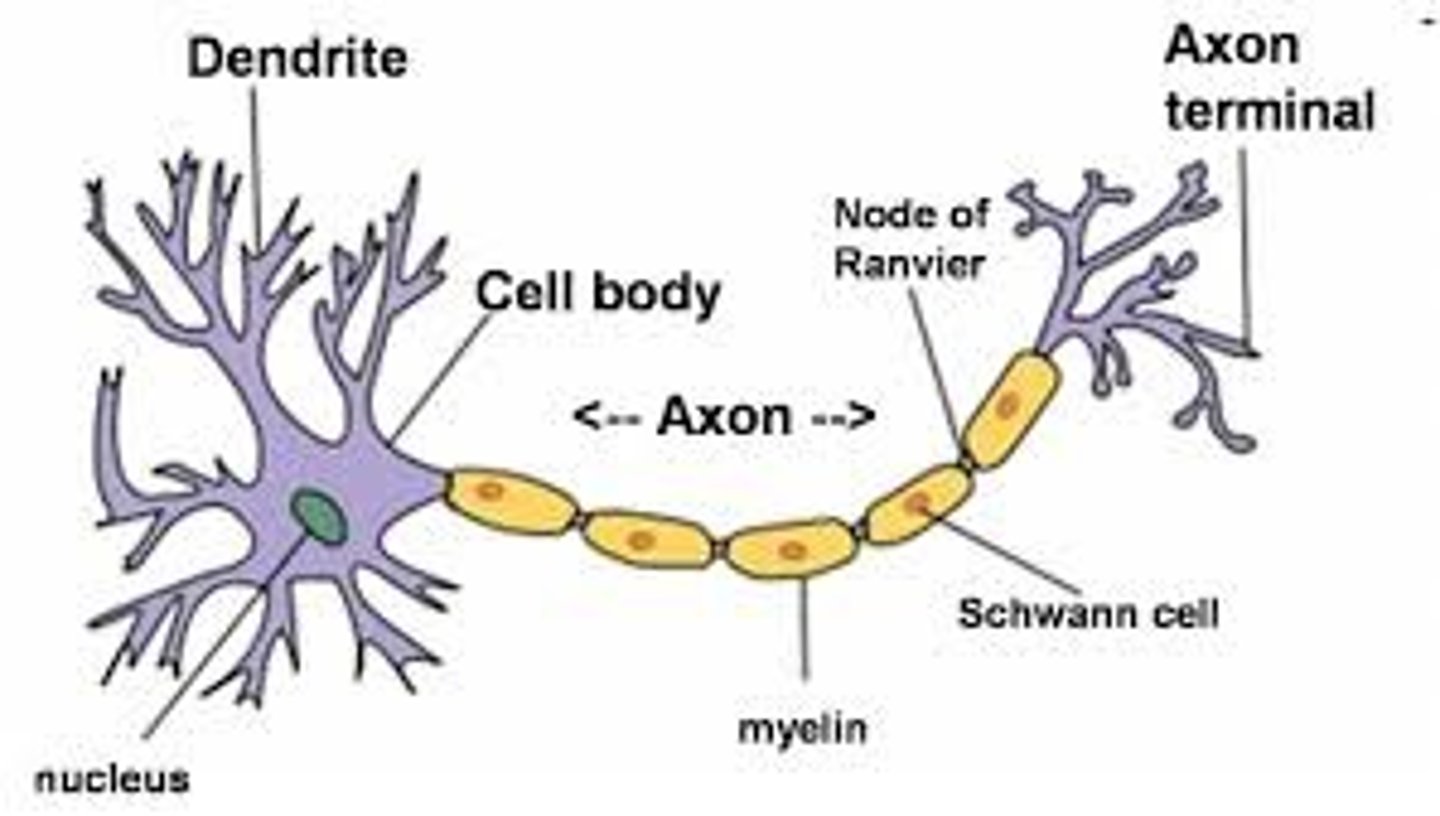
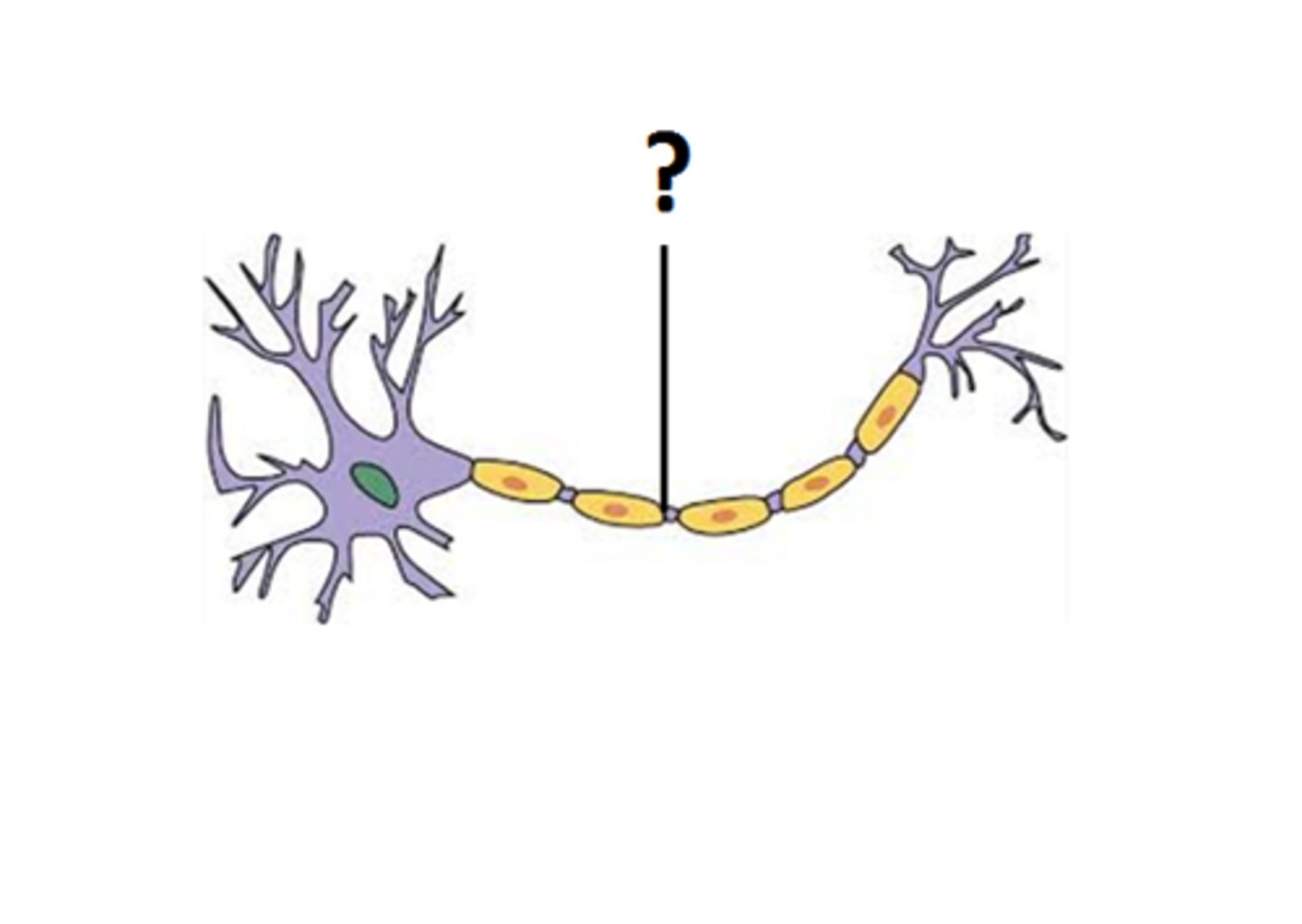
What is an axon?
the part of the neuron where NT is released (electrical → chemical signals)
True or False: axo-dendritic are the most common axons
True
Explanation: terminal buttons of an axon can form synapses with dendrites and these are known as axo-dendritic
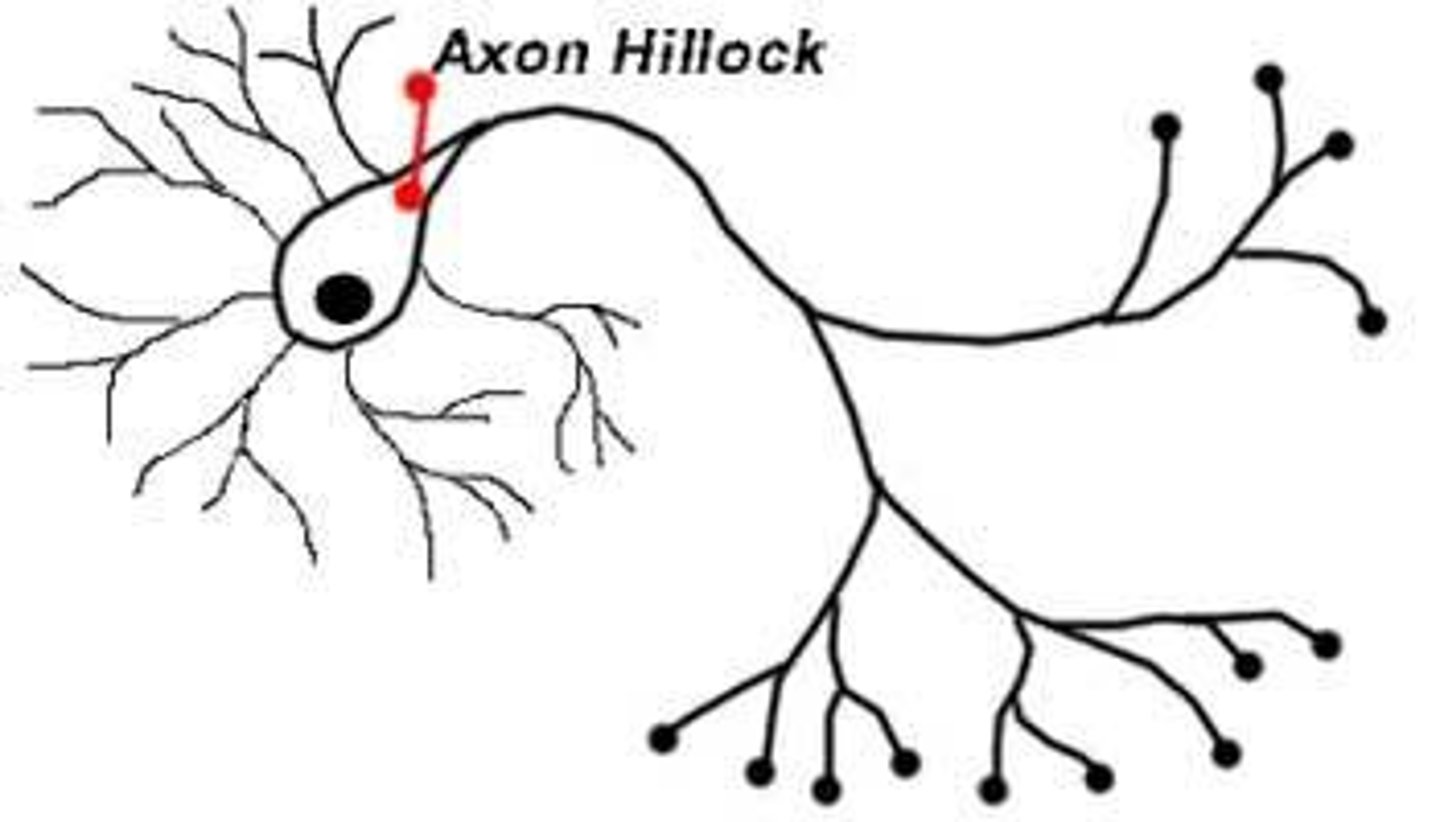
What is an axon hillock?
the part of the neuron where we transition from soma to axon
True or False: if the summation of local potentials at the axon hillock reach -70mV, an action potential is generated
False
Explanation: it is at -50mV! also an AP is defined as a rapid change in membrane potential that's propagated down the axon
What happens when the membrane potential reaches -50mV?
Depolarization
Explanation: large numbers of voltage-gated Na+ FAST channels open causing the membrane potential to rise by Na influx to reach +40mV which is considered the rising phase of the AP
What is the definition of depolarization in regards to Na+?
influx of Na+ that causes the membrane potential to be more positive
What happens when the membrane potential reaches +40mV?
Absolute Refractory Period
Explanation: the Na+ channels close and CANNOT open, it is impossible to stimulate further/again
True or False: during the absolute refractory period, voltage-gated K+ channels open for influx
False
Explanation: when these channels are open, K+ efflux occurs which leads the membrane potential to become more negative (-70mV)
What happens when the membrane potential reaches -70mV?
Relative Refractory Period: can stimulate again with a large enough stimulus
Hyperpolarization: K+ efflux causing more negative membrane potential
True or False: after the membrane potential reaches -70mV, all voltage-gated channels close and the neuron returns to resting membrane potential
True
True or False: if an AP has propagated down the neuron and arrives at the axon terminal, voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open during chemical transmission
True
Explanation: this leads to Ca2+ influx and a more positive membrane potential
What happens in chemical transmission after voltage-gated Ca2+ open?
Ca2+ interacts with proteins on the membrane of synaptic vesicles to stick to the presynaptic cleft causing release of NTs
True or False: Ca2+ interacting with proteins on the membrane of synaptic vesicles to stick to the presynaptic cleft causing release of NTs is known as a "Ca2+ dependent process"
True
What is exocytosis during chemical transmission?
release of NTs
True or False: NTs may diffuse across the synapse and bind to ionotropic receptors which opens the ion channel causing a change in the membrane potential within the presynaptic neuron
False
Explanation: everything is true except it's within the POSTsynaptic neuron
What is depolarization within chemical transmission?
positive change in membrane potential to reach threshold and the postsynaptic neuron will fire an AP
True or False: chemical transmission within a neuron is linked to electrical transmission between neurons
False
Explanation: chemical transmission is BETWEEN neurons and electrical transmission is WITHIN a neuron
What happens after depolarization during chemical transmission?
NTs go crazy lol
True or False: NTs may diffuse across the synapse and bind to G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs)
True
Explanation: GPCRs produce biochemical changes in the postsynaptic neuron
True or False: NTs can also bind to presynaptic inhibitory autoreceptor, undergoreuptake, can be broken down by an enzyme, AND/OR be moved by transporters on glial cells
True
Explanation: "Reuptake" is when NTs are grabbed by an NT transporter → back into the presynaptic neuron. Transporters on glial cells → glia is ONLY glutamate and GABA
What are the 2 types of extracellular receptors?
ionotropic and metabotropic
What are ionotropic receptors?
Ion channel receptors
Example: ligand-gated ion channels
What are metabotropic receptors?
Biochemically coupled to effectors/second messengers & have enzymatic activity
Example: G-protein coupled receptors
True or False: G-proteins are heterotrimers with alpha, beta, and gamma subunits
True
True or False: the alpha subunit of a G-protein is bound to GDP
True
True or False: during GCPR signaling, an agonist ligand binds to the extracellular domain of GCPR
True
What is an example of an agonist ligand?
NT or a drug
What happens once an agonist ligand binds to extracellular domain of GCPR?
Conformational change in the receptor which leads to conformational change of the G-protein → GDP pops off of the alpha subunit to bind to GTP
True or False: there is lots of GDP floating around
False
Explanation: there is GTP floating around
What happens with the alpha subunit after it binds to GDP?
Conformational change causes the alpha to separate from beta-gamma
Explanation: alpha and beta-gamma can interact with effector molecules (enzymes that have 2nd messenger inside the cell)
What happens with the 2nd messenger in GPCR signaling?
Causes biochemical changes inside the cell
True or False: alpha subunit is NOT an enzyme that catalyzes hydrolysis of GTP → GDP
False
Explanation: it is an enzyme that does this! Also, alpha changes back to OG conformation that prefers binding to beta-gamma and its receptor
What is the function of Gs within the alpha subunit?
interacts with effector enzyme adenylyl cyclase which converts ATP → cAMP → activate PKA → phosphorylation cascade
What is the function of Gq within the alpha subunit?
interacts with effector molecule alpha Q (that's NOT adenylyl cyclase) → activates PLC → breaks PIP2 into DAG + IP3
→ IP3 releases Ca2+ from ER
→ DAG + Ca2+ activate PKC
True or False: PKC is similar to PKA
True
Explanation: they are kinase enzymes
What is the function of Gi within the beta subunit?
interacts with its effector molecule K+ channel → subunit binds → opens the channels → K+ efflux → hyperpolarization of the neuron
What are the G-protein alpha subunit subtypes?
Gs, Gi, Gq
What is the effector molecule of Gs within alpha subunit?
adenylyl cyclase (stim)
What is the effector molecule of Gi within alpha subunit?
adenylyl cyclase (inhib)
What is the effector molecule of Gq within alpha subunit?
phospholipase C (stim)
What is the 2nd messenger of Gs within alpha subunit?
cAMP (increased)
What is the 2nd messenger of Gi within alpha subunit?
cAMP (decreased)
What are the 2nd messengers of Gq within alpha subunit?
Diacylglycerol (DAG) and Inositol Trisphosphoate (IP3)
What is the altered activity of Gs within alpha subunit?
increased PKA activity from increased cAMP
What is the altered activity of Gi within alpha subunit?
decreased PKA activity from decreased PKA activity
What is the altered activity of Gq within alpha subunit?
increased PKC activity from DAG and Ca2+ release from the ER because of IP3
What is the G-protein beta-gamma subunit subtype?
Gi
What is the effector molecule of Gi within the beta-gamma subunit?
K+ channel AND voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channel
What is the altered activity of Gi within the beta-gamma subunit?
Hyperpolarization from K+ channel AND inhibits NT release from voltage sensitive Ca2+ channels
What sites and steps of neuronal activity can a drug act on to produce an effect?
Agonist molecules (i.e., drugs or NT) can alter the membrane potential by acting directly on ion channels or through G-protein coupled mechanism
What is the blood brain barrier (BBB)?
exists because of differences in morphology of endothelial cells of brain capillaries vs typical capillaries
True or False: brain capillaries have no intracellular clefts
True
Explanation: this is because adjoining endothelial cells are fused together at tight junctions
True or False: brain capillaries have fenestrations and pinocytic vesicles
False
Explanation: they have neither
What is the purpose/function of glial cells in brain capillaries?
tightly surround the capillaries to form another barrier
Is the BBB an absolute barrier?
No
True or False: BBB blocks water-soluble and ionized compounds
True
Explanation: BBB prefers lipophilic compounds BUT there are exceptions
What do specialized transporter molecules do within the BBB?
bring amino acids, glucose, and other nutrients in
What do efflux pumps do within the BBB?
pump lipophilic molecules out
True or False: the BBB has receptor mediated transcytosis
True
True or False: pericytes do not contribute to the BBB
False
What molecules typically can cross the BBB?
small, lipid-soluble (lipophilic) molecules, like gases (oxygen, carbon dioxide), certain hormones, and small non-polar molecules