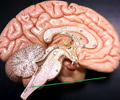
BSC2085L E.15 Brain and Cranial Nerves
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/40
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
1
New cards
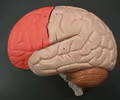
frontal lobe
• The most anterior region of the cerebral cortex.
• Separated from the parietal and temporal lobes by the central and lateral sulci, respectively.
• Associated with conscious thought, motor control, memory storage, judgement, problem solving, and emotion.
• Separated from the parietal and temporal lobes by the central and lateral sulci, respectively.
• Associated with conscious thought, motor control, memory storage, judgement, problem solving, and emotion.
2
New cards
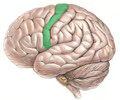
precentral gyrus
• Prominent gyrus of the frontal lobe lying anterior to the central sulcus.
• Sends motor commands to skeletal muscles.
• Also known as the primary motor cortex.
• Sends motor commands to skeletal muscles.
• Also known as the primary motor cortex.
3
New cards
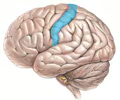
postcentral gyrus
• Prominent gyrus of the parietal lobe lying posterior to the central sulcus.
• Receives somatic sensations of touch, pressure, pain, vibration, and temperature.
• Also known as the somatosensory area.
• Receives somatic sensations of touch, pressure, pain, vibration, and temperature.
• Also known as the somatosensory area.
4
New cards
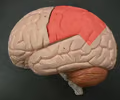
parietal lobe
• The most superior region of the cerebral cortex.
• Separated from the frontal and temporal lobes by the central and lateral sulci, respectively.
• Associated with analyzing sensory stimuli.
• Separated from the frontal and temporal lobes by the central and lateral sulci, respectively.
• Associated with analyzing sensory stimuli.
5
New cards
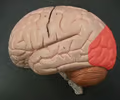
occipital lobe
• The most posterior region of the cerebral cortex.
• Associated with receiving visual stimuli.
• Associated with receiving visual stimuli.
6
New cards
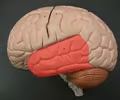
temporal lobe
• The most lateral region of the cerebral cortex.
• Separated from the frontal and parietal lobes by the lateral sulcus.
• Associated with receiving auditory stimuli.
• Separated from the frontal and parietal lobes by the lateral sulcus.
• Associated with receiving auditory stimuli.
7
New cards
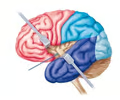
insula
• The lobe of the cerebrum deep to the lateral sulcus.
• Associated with receiving gustatory and olfactory stimuli.
• Associated with receiving gustatory and olfactory stimuli.
8
New cards
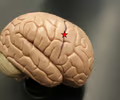
central sulcus
• Separates the frontal and parietal lobes.
• The precentral gyrus lies anterior to it; the postcentral gyrus lies posterior to it.
• The precentral gyrus lies anterior to it; the postcentral gyrus lies posterior to it.
9
New cards
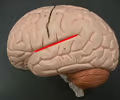
lateral sulcus
• Separates the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe.
• Superficial to the insula.
• Superficial to the insula.
10
New cards
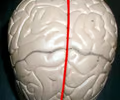
longitudinal fissure
An especially deep sulcus that separates the cerebral hemispheres.
11
New cards
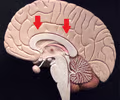
cingulate gyrus
• Deep to the cerebral cortex and superficial to the corpus callosum.
• Appears as one continuous gyrus around the corpus callosum.
• Appears as one continuous gyrus around the corpus callosum.
12
New cards
corpus callosum
• Deep to the cingulate gyrus and longitudinal fissure; superficial to the septum pellucidum.
• A large bundle of nerves connecting the two cerebral hemispheres together.
• A large bundle of nerves connecting the two cerebral hemispheres together.
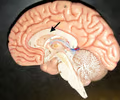
13
New cards
anterior commissure
• An anterior portion of the corpus callosum protruding inwards.
• A small bundle of nerves connecting the two cerebral hemispheres together.
• A small bundle of nerves connecting the two cerebral hemispheres together.
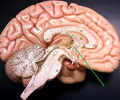
14
New cards
septum pellucidum
• Deep to the corpus callosum and superficial to the fornix.
• A thin membrane separating the lateral ventricles at the midline.
• A thin membrane separating the lateral ventricles at the midline.
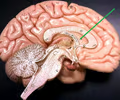
15
New cards
fornix
• Deep to the septum pellucidum.
• Connects structures of the limbic system.
• Connects structures of the limbic system.
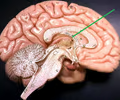
16
New cards
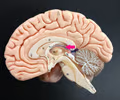
choroid plexus
• Located in the roof of the third ventricle.
• Produces cerebrospinal fluid.
• Produces cerebrospinal fluid.
17
New cards
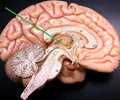
thalamus
• Located near the center of the brain.
• The relay center of incoming signals.
• Contains an intermediate mass.
• The relay center of incoming signals.
• Contains an intermediate mass.
18
New cards
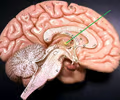
intermediate mass
• Located within the thalamus.
• Connects both sides of the thalamus medially.
• Connects both sides of the thalamus medially.
19
New cards
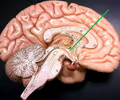
hypothalamus
• Located anteroinferior to the thalamus.
• Regulates homeostatic functions.
• Regulates homeostatic functions.
20
New cards
optic chiasma
• The superior extension connected to the hypothalamus (sagittal view).
• Appears as an X-shaped structure where the optic nerves decussate.
• Appears as an X-shaped structure where the optic nerves decussate.
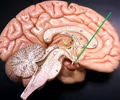
21
New cards
infundibulum
Connects the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus.
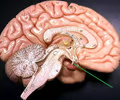
22
New cards
pituitary gland
• The inferior extension connected to the hypothalamus (sagittal view).
• The gland that influences the behavior of other glands in the endocrine system.
• The gland that influences the behavior of other glands in the endocrine system.
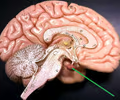
23
New cards
pineal body
• Located posterior to the thalamus between the two cerebral hemispheres of the brain; superior to the corpora quadrigemina.
• An endocrine gland.
• An endocrine gland.
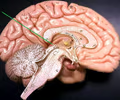
24
New cards
mammillary body
• Located inferior and posterior to the hypothalamus (or the underside of the fornix).
• Brainstem nuclei.
• Brainstem nuclei.
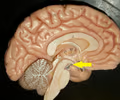
25
New cards
midbrain
• Located superior to the pons and posterior to the mammillary body.
• Connects the forebrain and the hindbrain.
• Connects the forebrain and the hindbrain.
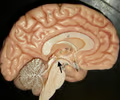
26
New cards
pons
• Located inferior to the midbrain and superior to the medulla oblongata.
• Appears as a bulge on the anterior side of the brainstem.
• Appears as a bulge on the anterior side of the brainstem.
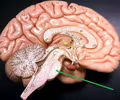
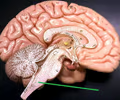
27
New cards
medulla oblongata
• Located inferior to the pons and superior to the spinal cord.
• Appears as a widening of the brainstem leading to the pons.
• Controls functions vital for life.
• Appears as a widening of the brainstem leading to the pons.
• Controls functions vital for life.
28
New cards
corpora quadrigemina
• Part of the midbrain.
• Contains a pair of superior and inferior colliculi.
• Contains a pair of superior and inferior colliculi.
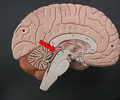
29
New cards
superior colliculus
• The superior part of the corpora quadrigemina.
• Associated with vision.
• Associated with vision.
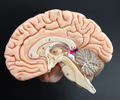
30
New cards
inferior colliculus
• The inferior part of the corpora quadrigemina.
• Associated with auditory reflexes.
• Associated with auditory reflexes.
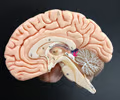
31
New cards
cerebellar cortex
• Part of the cerebellum.
• The outer layer of gray matter of the cerebellum.
• The outer layer of gray matter of the cerebellum.
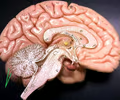
32
New cards
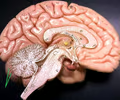
folia
• Part of the cerebellum.
• The gyri of the cerebellum separated by sulci.
• The gyri of the cerebellum separated by sulci.
33
New cards
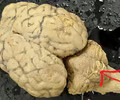
vermis
• Part of the cerebellum.
• Worm-like structure connecting the two cerebellar hemispheres.
• Worm-like structure connecting the two cerebellar hemispheres.
34
New cards
arbor vitae
• Part of the cerebellum.
• The branching white matter of the cerebellum.
• The branching white matter of the cerebellum.
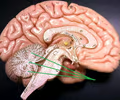
35
New cards
lateral ventricle
• One of the two superior ventricles located in either cerebral hemisphere.
• Connected to the third ventricle by the interventricular foramen.
• Connected to the third ventricle by the interventricular foramen.
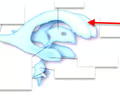
36
New cards
anterior horn
The anterior end of a lateral ventricle.
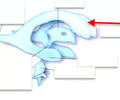
37
New cards
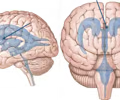
interventricular foramen
Connects the lateral and third ventricles.
38
New cards
third ventricle
• The ventricle located in the center of the brain, inferior to the lateral ventricles.
• Connected to the lateral ventricles by the interventricular foramen.
• Connected to the fourth ventricle by the cerebral aqueduct.
• Connected to the lateral ventricles by the interventricular foramen.
• Connected to the fourth ventricle by the cerebral aqueduct.

39
New cards
cerebral aqueduct
• Connects the third and fourth ventricles.
• Located between the midbrain and corpora quadrigemina (sagittal view).
• Located between the midbrain and corpora quadrigemina (sagittal view).
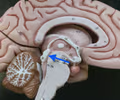
40
New cards
fourth ventricle
• The ventricle inferior to the third ventricle.
• Connected to the third ventricle by the cerebral aqueduct.
• Connected to the spinal cord by the central canal.
• Connected to the third ventricle by the cerebral aqueduct.
• Connected to the spinal cord by the central canal.
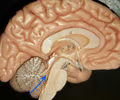
41
New cards
central canal
Connects the fourth ventricle and spinal cord.