DENT Fun. I - Basics and Intro to Cells
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Element
A substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances
Compound
A substance made up of 2+ elements joined by chemical bonds
About ____ of the 92 elements are essential to life.
25
Chemical behavior of an atom is determined by its ____.
valence electrons
Elements with a full valence shell are chemically ____.
inert
Covalent Bond
Chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
Noncovalent Bond
Chemical bond due to donated/accepted electrons
Electronegativity
The ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons
Electronegativity increases going ____ and ____ on the periodic table.
up/right
Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
Electrons are shared equally
Polar Covalent Bonds
- Unequal sharing of electrons
- Causes polarity: Partial Charges
What are the 3 Noncovalent Bonds?
- Hydrogen
- Ionic
- Van der Waals
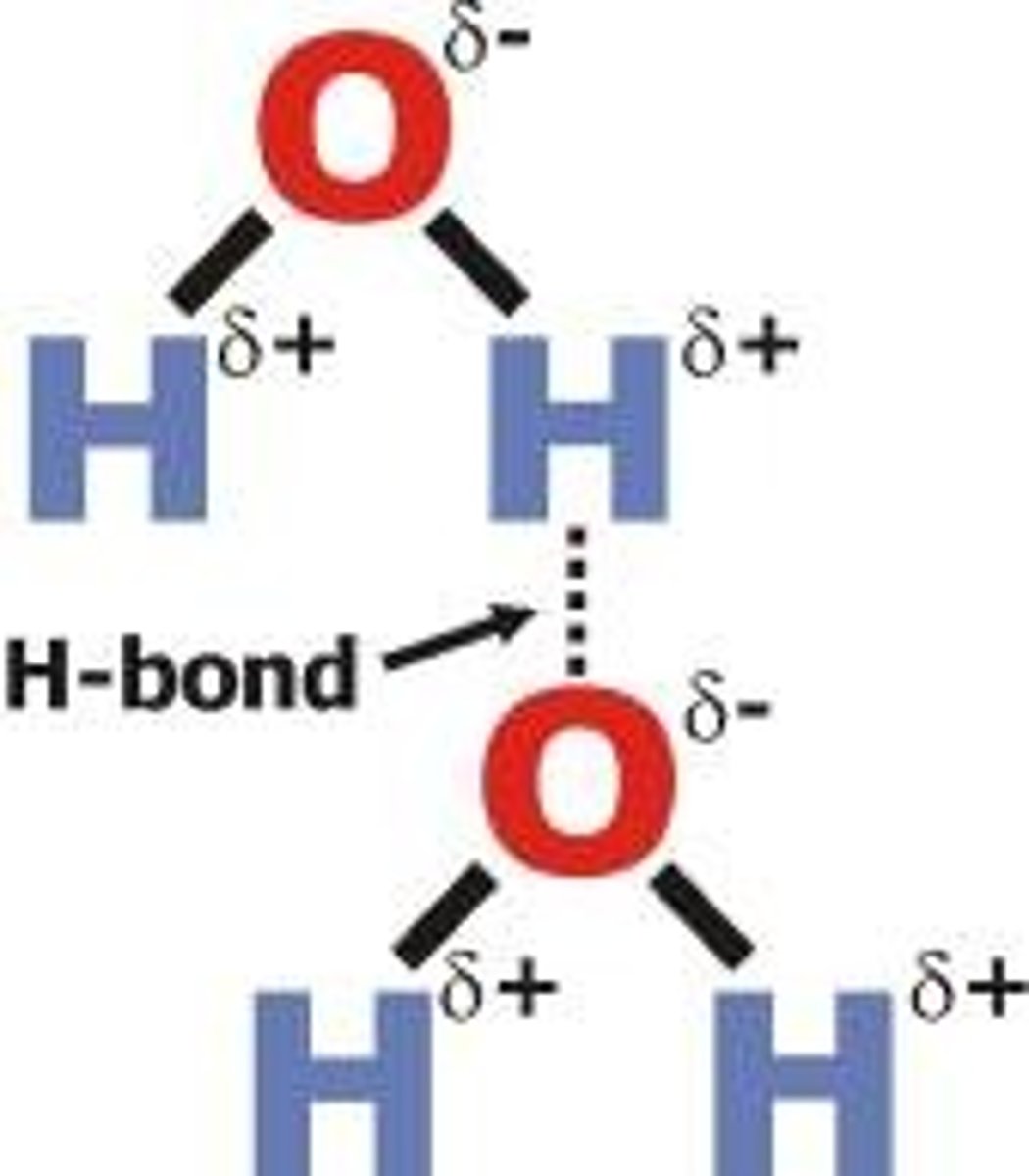
Hydrogen Bonds
Weak attraction between a hydrogen atom and another electronegative atom
Ionic Bonds
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
Van der Waals Interactions
Attractions between atoms with asymmetrically distributed electrons
Biological molecules recognize and interact with each other based on ____.
molecular shape
Structure = Function
Molecules that have similar shapes can have similar ____.
biological effects
Next to water, ____ and ____ are the most abundant biomolecules in the body.
proteins/triglycerides
Water is ____.
polar; has a positive and negative pole (dipole)
Cations
Positive ions
Anions
Negative ions
Properties of Water
- Solid is less dense than Liquid
- High Specific Heat
- Cohesion/Adhesion
- Solvent of Life
High Specific Heat of Water
It takes a lot of energy to heat up water due to hydrogen bonding, which allows for a stable environment
Cohesion/Adhesion of Water
Cohesion: H-Bonding between water causes a high surface tension
Adhesion: Attraction to substances other than water
Water is an excellent ____.
solvent
Water is polar covalent, therefore, it interacts with anything with a charge
What happens when water interacts with nonpolar substances?
Water cannot dissolve the substance and creates micelles or membrane bilayers
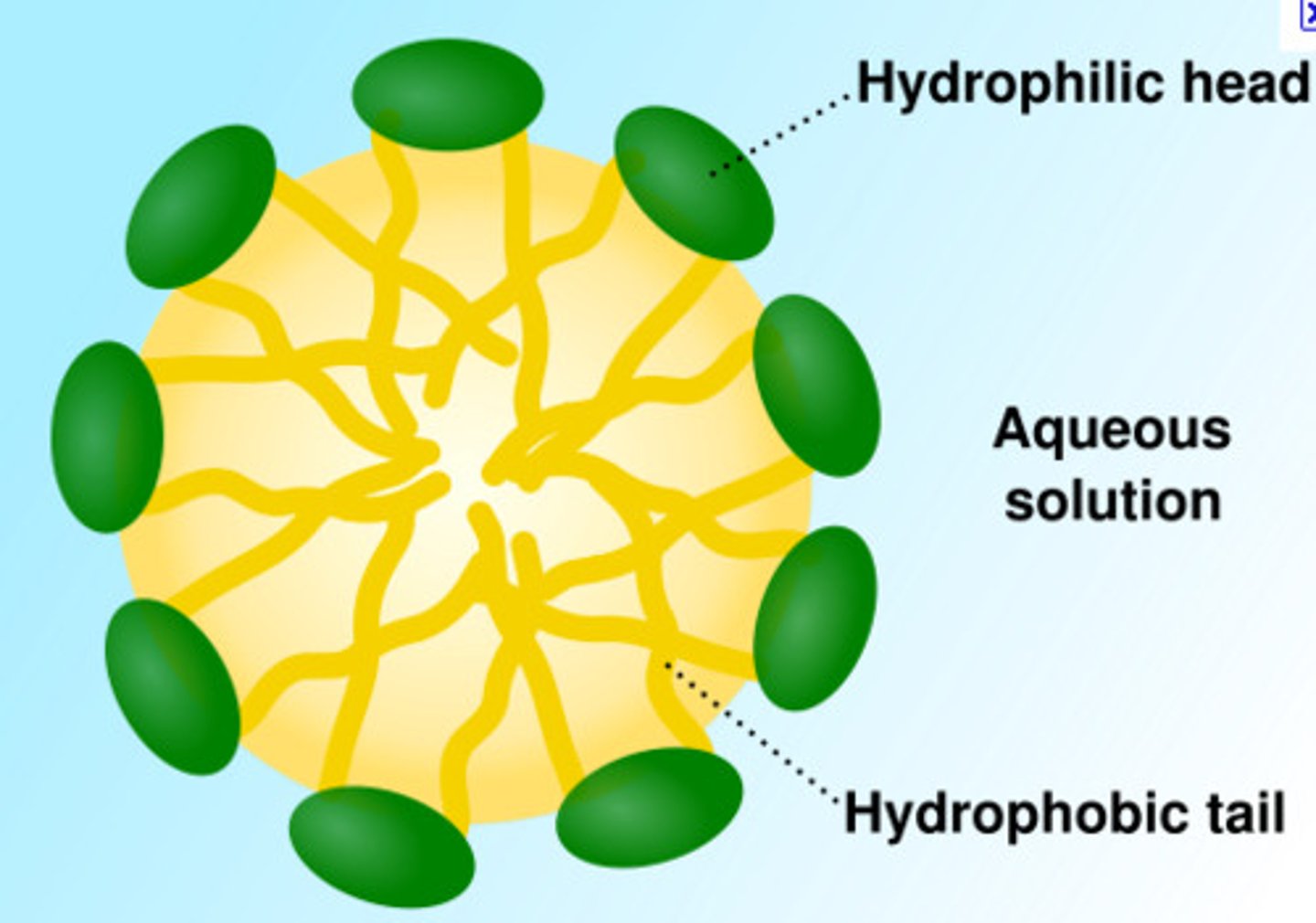
Micelles
Lipid molecules orient with polar (hydrophilic) head toward water and nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails away from water
Membrane Bilayer
Consists of two leaflets of lipid monolayers
- Hydrophilic head groups interact with water
- Hydrophobic fatty acid tails are packed inside
Water is amphoteric, which means that ____.
it can act as an acid or base
H2O + H2O <--> H3O+ + OH-
pH = ____
-log[H+]
Bronsted Acid
Proton (H+) Donor
Bronsted Base
Proton (H+) Acceptor
Dissociation Constant (Kd)
Kd = [H+][A-]/[HA]
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
pK + log[A-]/[HA]
The pK value represents the pH value at which the ionizable group is ____.
half-protonated
Arterial Blood pH
7.4
Venous Blood pH
7.35
More Carbonic Acid
Carbonic Acid
H2CO3
Bicarbonate Buffer System
CO2 (g)+ H2O(l)↔H2 CO3 (aq)↔H+ (aq)+HCO3- (aq)
What enzyme aids CO2 and H2O to create H2CO3?
Carbonic Anhydrase
Buffers
Substances that minimize pH change
All ____ and ____ buffer the pH of the solution at pH values close to their pK values.
weak acids/weak bases
Acidemia
pH < 7.35
Alkalemia
pH > 7.45
Respiratory Acidosis
A drop in blood pH due to hypoventilation (too little breathing) and accumulation of CO2
Respiratory Alkalosis
A rise in blood pH due to hyperventilation (excessive breathing) and loss of CO2
Metabolic Acidosis
High [H+] in the extracellular fluid caused by either an increase in [H+] or a decrease in [HCO3-]
Metabolic Alkalosis
High pH and high [HCO3-] due to loss of acids from the body (vomiting)
What are the 3 lines of defenses to attempt to restore normal Blood pH?
(1) Buffer Systems
(2) Respiration
Acidosis: Increased ventilation
Alkalosis: Decreased ventilation
(3) Kidneys
Acidosis: Remove [H+]
Alkalosis: Remove [HCO3-]
Eukaryotic
Membrane-Enclosed Organelles
Prokaryotic
No Membrane-Enclosed Organelles
Pathogens can only be prokaryotic (T/F)
False; prokaryotic, eukaryotic, or neither (viruses)
Features of All Cells
- DNA
- Cytosol
- Ribosomes
- Plasma Membrane
Features of Prokaryotes
- Cell Walls
- Flagella
- Pili
Features of Eukaryotes
- Nucleus
- Extensive Membrane System (Golgi, Smooth/Rough ER)
Plasma Membrane
Selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of cells
Also acts as a surface for biochemical reactions to occur
The prokaryotic plasma membrane is surrounded by the ____ and is folded to provide ____.
cell wall/a complex of membranes that allow for metabolic reactions to occur
Cell Wall
- Plant: Cellulose
- Fungus: Chitin
- Bacteria: Peptidoglycan
Gram Positive
- Purple
- Thick peptidoglycan layer
Gram Negative
- Pink
- Thin peptidoglycan layer
Since eukaryotic cells do not have cell walls, it allows for the formation of ____.
tissues
Organ and tissue mechanical/functional properties are determined by ____ and ____.
cytoskeletal components/intercellular junctions
What 3 filaments make up the Cytoskeleton?
- Microfilaments (Actin)
- Intermediate
- Microtubules
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
Fluid outside the cell that interacts with the glycoproteins of the plasma membrane
Functions include...
- Support
- Adhesion to other Cells
- Movement
- Regulation
- Communication
Components of the ECM
- Collagen Fibers
- Elastic Fibers
- Proteoglycans
- Glycoproteins
ECM proteins bind to ____.
integrins
Protein receptors important in communication
Cellular Communication
(1) Reception
(2) Transduction
(3) Response
Direct Cellular Communication
- Proteins bind membrane proteins
- Cytosolic molecules through gap junctions
Indirect Cellular Communication
Communication via signal molecules
- Autocrine
- Paracrine
- Endocrine
What are the 8 possible ligands of Cellular Communication?
- Proteins
- Lipids
- Carbs/Glycoproteins/Glycolipids
- ECM Components
- Growth Factors
- Hormones
- Neurotransmitters
- Gases
Signal Transduction
A series of molecular changes that converts a signal on a target cell's surface to a specific response inside the cell
In connective tissues, where cells are not in close proximity, what is critical for cellular adhesion and communication?
Extracellular Matrix
Integrins binding fibronectin is an example of which type of communication?
direct