Income Taxation
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Inherent Powers of State
Taxation
Power of Eminent Domain
Police Power
Taxation (1)
Power by which the sovereign raises revenues to defray the necessary expenses of the government.
Power of Eminent Domain
Refers to the power of the government or those to whom the power has been delegated to take private property and convert it into public use upon paying the owners a just compensation to be ascertained by law.
Police power
Enact laws in relation to persons or property to promote public health, public morals, public safety and general welfare of the people.
Inherent Powers of State - Similarities
They are inherent in the state.
They exist independently of the Constitution.
They constitute the three methods by which State interferes with private rights and property.
They are legislative in nature and character.
Each presupposes equivalent compensation.
Taxation - As to Purpose
Support of government.
Police Power - As to Purpose
General welfare.
Eminent Domain - As to Purpose
Public purpose.
Taxation - As to Authority Who Exercise the Power
Government only.
Police Power - As to Authority Who Exercise the Power
Government only.
Eminent Domain - As to Authority Who Exercise the Power
Government and public service companies or public utilities.
Taxation - As to Persons Affected
Community of class of individuals.
Police Power - As to Persons Affected
Community of class of individuals.
Eminent Domain - As to Persons Affected
Individuals as owners of property.
Taxation - As to Benefits Received
In form of protection/ benefit.
Police Power - As to Benefits Received
No direct benefit.
Eminent Domain - As to Benefits Received
MV of property taken-compensation.
Taxation - As to Effect
Taxes become public funds.
Police Power - As to Effect
Regulate rights/ property.
Eminent Domain - As to Effect
Transfer of ownership.
Taxation - As to Imposition
No limit.
Police Power - As to Imposition
Limited to cost of license or regulation.
Eminent Domain - As to Imposition
No imposition. Owners is paid by government.
Taxation - As to Non Impairment of Obligation Clause of Constitution
Inferior to the clause.
Police Power - As to Non Impairment of Obligation Clause of Constitution
Superior to the clause.
Eminent Domain - As to Non Impairment of Obligation Clause of Constitution
Inferior to the clause.
Taxation (2)
A process or act of imposing a charge by the government authority on property, individuals or transactions to raise money for public purposes.
Taxation (3)
It is also defined as the act of levying a tax, i.e. the process or means by which the sovereign, through its law-making body, raises income to defray the necessary expenses of government. It is a method of apportioning the cost of government among those who, in some measure, are privileged to enjoy its benefits and must therefore bear its burdens.
Purposes of Taxation
Revenue or Fiscal
Non-revenue or Regulation
PURPOSE OF TAXATION: Revenue or Fiscal
The primary purpose of taxation on the part of the government is to provide funds or property with which to promote the general welfare and the protection of its citizens and to enable it to finance its multifarious activities.
PURPOSE OF TAXATION: Non-revenue or Regulation
Taxation may also be employed for purposes of regulation or control.
a. Imposition of tariffs on imported goods to protect local industries.
b. The adoption of progressively higher tax rates to reduce inequalities in wealth an income.
c. The increase or decrease of taxes to prevent inflation or ward off depression.
Theory and Basis of Taxation
Necessity Theory
Benefits Received Principle
Life Blood Therory
THEORY AND BASIS OF TAXATION: Necessity Theory
The power of taxation proceeds upon the theory that the existence of government is a necessity; that it cannot continue without means to pay its expenses; and that for these means, it has a right to compel all its citizens and property within its limits to contribute.
THEORY AND BASIS OF TAXATION: Benefits Received Principle
The basis of taxation is found in the reciprocal duties of protection and support between the State and its inhabitants. In return for his contribution, the taxpayer received benefits and protection from the government.
This principle serves as the basis of taxation and is founded on the reciprocal duties of protection and support between the State and its inhabitants. Also called "symbiotic relation" between the State and its citizens.
THEORY AND BASIS OF TAXATION: Life Blood Theory
This theory constitutes the theory of taxation, which provides that the existence of government is a necessity; that government cannot continue without means to pay its expenses; and that for these means it has a right to compel its citizens and property within its limits to contribute.
Essential Elements of a Tax
It is an enforced contribution.
It is generally payable in money.
It is proportionate in character.
It is levied on persons, property, or the exercise of a right or privilege.
It is levied by the State which has jurisdiction over the subject or object of taxation.
It is levied by the law-making body of the State.
It is levied for public purposes.
Principles of Sound Tax System
Fiscal Adequacy
Equality or Theoretical Justice
Administrative Feasibility
PRINCIPLES OF SOUND TAX SYSTEM: Fiscal Adequacy
It states that sources of revenues of govt must be sufficient to meet the demand of public expenditures regardless of business condition.
PRINCIPLES OF SOUND TAX SYSTEM: Equality or Theoretical Justice
States that tax burden must be proportionate to taxpayers ability to pay. In accordance wit Constitutions' mandate that application of taxation should be equitable.
PRINCIPLES OF SOUND TAX SYSTEM: Administrative Feasibility
Tax laws must be convenient, uniform and effective in their administration.
Stages of Taxation
Levy/ Imposition
Assessment
Collection
Scope of Power of Taxation
The power of taxation is comprehensive, plenary, unlimited and supreme.
Strongest among the Inherent Powers of State.
Limitation of Power to Tax
NATURE OF THE POWER OF TAXATION
1. It is inherent in sovereignty; hence, it may be exercised although it is not expressly granted by the Constitution.
2. It is legislative in character; hence, only the legislature can impose taxes (although the power may be delegated).
3. It is subject to Constitutional and Inherent limitations; hence, it is not an absolute power that can be exercised by the legislature anyway it pleases.
Inherent Limitations
Purpose must be public in nature.
Prohibition against delegation of the taxing power.
Exemption of government entities, agencies and instrumentalities.
International comity.
Limitation of territorial jurisdiction.
INHERENT LIMITATIONS: Purpose must be public in nature
A tax must always be imposed for a public purpose, otherwise, it will be declared as invalid.
INHERENT LIMITATIONS: Prohibition against the delegation of the taxing power
General rule - The power to tax is exclusively vested in the legislative body, hence, it cannot be delegated. (Delegata potestas non protest delegari)
Exceptions to non-delegation rule:
Delegation to the President
Delegation to local government units
Delegation to administrative agencies
INHERENT LIMITATIONS: Exemption of government entities, agencies and instrumentalities
Except government entities performing proprietary functions such as PNR.
Rationale: If the government taxes itself or if Local Government Units (LGU) tax the national government, it would be akin to taking money from one pocket to the other.
Entities or agencies exercising sovereign functions (acta jure imperii) are tax exempt, unless expressly taxed, agencies performing proprietary functions are subject to tax unless expressly exempted.
Government owned and controlled corporation performing proprietary functions are subject to taxes, except those exempted under Section 27(C) of RA 8424 as amended by RA 9337 and RA 10963, namely: GSIS, SSS, PHIC and local water district.
INHERENT LIMITATIONS: International comity
A state must recognize the generally accepted tenets of international law, they must accord each other as sovereign equals. This limits the authority of a government to effectively impose taxes on a sovereign state and its instrumentalities, as well as on its property held, and activities undertaken, in that capacity. (Vitug)
For example, a property of a foreign State or government may not be taxed by another State.
What government entities are exempt from income tax?
Government Service Insurance System (GSIS)
Social Security System (SSS)
Philippine Health Insurance Corporation (PHIC)
Philippine Charity Sweepstakes Office (PCSO)**
Local water district
**Under the TRAIN Law (effective Jan 1, 2018), PCSO is removed from tax exempt GOCCS.
Under TRAIN LAW; Sec 7, amending Sec 27 of NIRC, provides that: (C) Government-owned or -Controlled Corporations, Agencies or Instrumentalities - The provisions of existing special or general laws to the contrary notwithstanding, all corporations, agencies, or instrumentalities owned or controlled by the Government, except the Government Service Insurance System (GSIS), the Social Security System (SSS), the Philippine Health Insurance Corporation (PHIC), and the local water districts shall pay such rate of tax upon their taxable income as are imposed by this Section upon corporations or associations engaged in similar business, industry, or activity.
Constitutional Limitations
NOTE: A tax that violates the constitution has no legal force.
Due process of law
Equal protection of laws
Rule of uniformity and equity in taxation
Prohibition against imprisonment for non-payment of poll tax (example is Community Tax)
Prohibition against impairment of obligation of contracts
No public money shall be appropriated for religious purposes
Prohibition against appropriation of proceeds of taxation for the use, benefit, or support of any church
Prohibition against taxation of religious, charitable and educational entities
Prohibition against taxation of non-stock, non-profit educational institutions
Others
Prohibition on use of tax levied for special purpose
President's veto power on appropriation, revenue, and tariff bills
Flexible tariff clause
Doctrines in Taxation
Prospectivity of Tax Laws
Imprescriptibility of Taxes
Double Taxation
Escape from Taxation
Doctrines in Taxation: Prospectivity of Tax Laws
This principle provides that a tax law must only be applicable and operative prospectively, except when expressly provided by law to be imposed retroactively.
Doctrines in Taxation: Imprescriptibility of Taxes
Although the NIRC provides for the limitation in the assessment and collection of taxes imposed, such will only be applicable to those taxes where a tax return is required. Unless otherwise provided by the tax law itself, taxes in general are imprescriptible.
Doctrines in Taxation: Double Taxation
Two types:
a. Indirect Duplicate Taxation
b. Direct Duplicate Taxation - This is double taxation in strict sense. It is prohibited because it comprises imposition of tax to same property/person- same period-same purpose- same tax rate and same taxing authority.
Double Taxation
Indirect Double taxation (Broad sense)
The SC held that there is no constitutional prohibition against double taxation in the Philippines. (Villanueva v. City of Iloilo, G.R. No. L-26521, 1968) Therefore, it may not be a valid defense against the validity of a tax measure. (Pepsi-Cola v. Tanauan, G.R. No. L-31156, 1976) What is prohibited is direct double taxation.
Tax treaties as relief from double taxation
Modes of Eliminating Double Taxation
i. Provide for exemptions or allowance of deduction or tax credit for foreign taxes;
ii. Enter into treaties with other states (e.g., former Phil-Am Military Bases Agreements as to income tax); or
iii. Apply the principle of reciprocity.
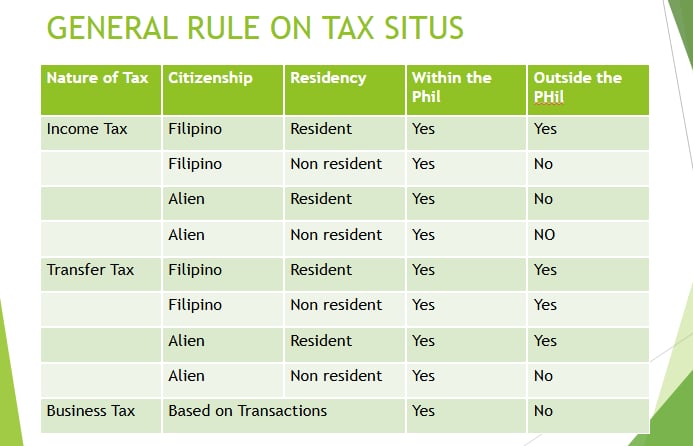
Situs of Taxation (Income)
Situs is the place of taxation; power to tax is limited to the territorial jurisdiction of the taxing state. It is the place or authority that has the right to impose and collect taxes.
SITUS OF TAXATION

GENERAL RULE ON TAX SITUS
Classification of Taxes
As to Subject Matter or Object
As to Purpose
As to Who Bears the Burden
As to Scope of the Tax
As to the Determination of Amount
As to Gradation or Rate
CLASSIFICATION OF TAXES (As to Subject Matter or Object)
Personal, poll or capitation tax - Tax of a fixed amount imposed on persons residing within a specified territory, whether citizens or not, without regard to their property or the occupation or business in which they may be engaged.
Example: Community tax
Property tax - Tax imposed on property, real or personal, in proportion to its value or in accordance with some other reasonable method of apportionment.
Example: Real estate tax
Excise tax - A charge imposed upon the performance of an act, the enjoyment of a privilege, or the engaging in an occupation. This is different from the excise tax of Title VI of the NIRC.
Example: Income tax, VAT, estate tax, donor’s tax
CLASSIFICATION OF TAXES (As to Purpose)
General/ fiscal/ revenue tax - A general/ fiscal/ revenue tax is that imposed for the purpose of raising public funds for the service of the government.
Special/regulatory tax - A special or regulatory tax is imposed primarily for the regulation of useful or non-useful occupation or enterprises and secondarily only for the purpose of raising public funds.
CLASSIFICATION OF TAXES (As to Who Bears the Burden)
Direct tax - A direct tax is demanded from the person who also shoulders the burden of the tax. It is a tax which the taxpayer is directly or primarily liable and which he or she cannot shift to another.
Indirect tax - An indirect tax is demanded from a person in the expectation and intention that he or she shall indemnify himself or herself at the expense of another, falling finally upon the ultimate purchaser or consumer. A tax which the taxpayer can shift to another.
CLASSIFICATION OF TAXES (As to Scope of the Tax)
National tax - A national tax is imposed by the national government.
Local tax - A local tax is imposed by municipal corporations or local government units (LGUs).
CLASSIFICATION OF TAXES (As to the Determination of Amount)
Specific tax - A specific tax is a tax of a fixed amount imposed by the head or number or by some other standard of weight or measurement. It requires no assessment other than the listing or classification of the objects to be taxed.
Ad valorem tax - An ad valorem tax is a tax of a fixed proportion of the value of the property with respect to which the tax is assessed. It requires the intervention of assessors or appraisers to estimate the value of such property before the amount due from each taxpayer can be determined.
CLASSIFICATION OF TAXES (As to Gradation or Rate)
Proportional tax - Tax based on a fixed percentage of the amount of the property receipts or other basis to be taxed.
Example: Real estate tax
Progressive or graduated tax - Tax the rate of which increases as the tax base or bracket increases.
Example: Income tax
Digressive tax rate: progressive rate stops at a certain point. Progression halts at a particular stage.
Regressive tax - Tax the rate of which decreases as the tax base or bracket increases. There is no such tax in the Philippines.
NOTE: Regressive Tax is different from Regressive Tax System.Regressive Tax System - More indirect taxes is imposed than direct taxes.
Requisites of a Valid Tax
Must be for a public purpose;
Should be uniform and equitable;
Either the person or property taxed is within the jurisdiction of the taxing authority;
Complies with the requirements of due process; and
Does not infringe any constitutional or inherent limitations.
Interpretation and Application of Tax Laws
Nature of internal revenue laws
Internal revenue laws are not political in nature.
Tax laws are civil and not penal in nature.
Income Tax
A tax on all yearly profits arising from property, professions, trades, or offices, or as a tax on a person’s income, emoluments, profits and the like. Income tax is a direct tax.
Income Tax Systems
Global
Schedular
Semi-Schedular or Semi-Global Tax System
INCOME TAX SYSTEM: Global
The total allowable deductions are deducted from the gross income to arrive at the net taxable income subject to the relevant income tax rate. All items of gross income and deductions are reported in one income tax return and a single tax is imposed on all income received or earned by a person irrespective of the activities which produced the income (i.e. compensation income, net income from business, trade or profession.)
INCOME TAX SYSTEM: Schedular
Different types of income are subjected to different sets of graduated or flat income tax rates. The applicable tax rates will depend on the classification of the taxable income and the basis could be gross income or net income (i.e. capital gains tax).
INCOME TAX SYSTEM: Semi-Schedular or Semi-Global Tax System
The compensation income, business or professional income, capital gain and passive income not subject to final tax, and other income are added together to arrive at the gross income and after deducting the sum of allowable deductions, the taxable income is subjected to the relevant income tax rate.
Philippine Income Taxation
A combination of both systems but is more schedular for individuals while more global for corporations.