The Vertebral Column
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What makes up the spinal column?
33 bones called vertebrae
Vertebrae extend from ___ to ___
skull to pelvis
What are the 4 joints of the vertebral column?
costotransverse
costovertebral
intervertebral
zygapophyseal
What are the 4 functions of the spinal column?
encloses and protects the spinal cord
supports the trunk of the body
supports the skull
provides for attachment for muscles of the back
The spinal cord extends from ___ to ___
foramen magnum (medulla oblongata) to lower border of L1
What are “true” vertebrae?
the 24 bones of the spinal column that remain separate during life
What is another term for true vertebrae?
moveable vertebrae
What are “false” vertebrae?
5 vertebral bones that fuse to form the sacrum
4 vertebral bones that fuse to form the coccyx
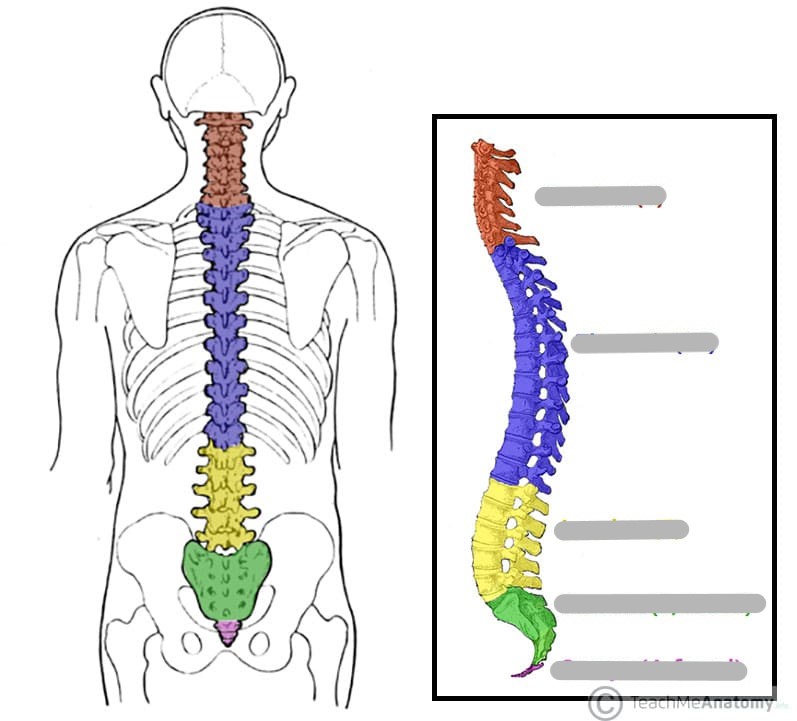
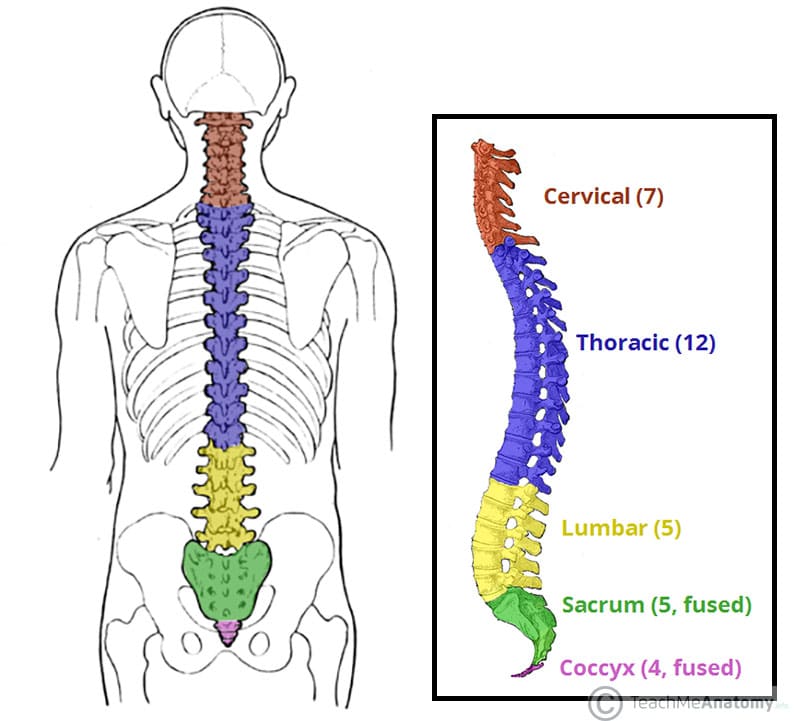
What are the regions of the vertebral column, and how many bones are present in each?
cervical: bones of the neck (7)
thoracic: bones of the thorax (12)
lumbar: bones of the abdomen (5)
pelvic: sacrum (5) and coccyx (4)
What are the 2 curves of the spine?
primary (kyphotic) and secondary (lordotic)
Explain primary (kyphotic) curves of the spine
present at birth
convex posterior
concave anterior
thoracic and pelvic region
Explain secondary (lordotic) curves of the spine
develops within 1st year of life
concave posterior
convex anterior
cervical and lumbar region
What is kyphosis?
an exaggeration of the thoracic curve of the spine (caused by degeneration of disc spaces or poor posture)
What is lordosis?
an exaggeration of the lumbar curve of the spine (caused by obesity or quick weight gain)
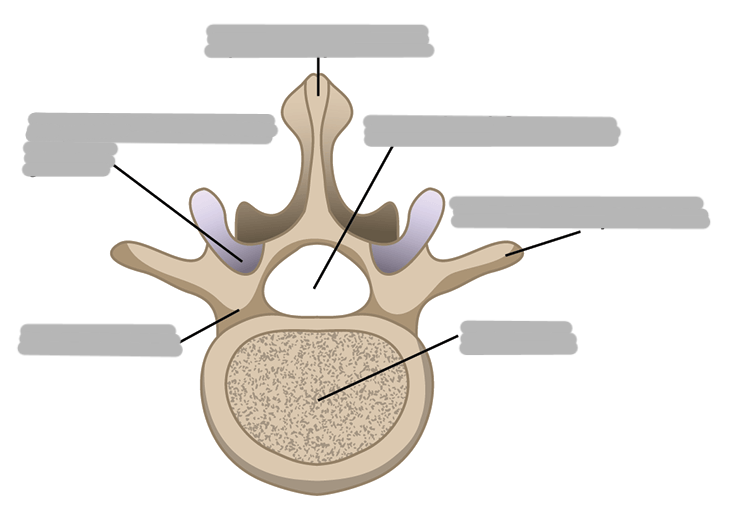
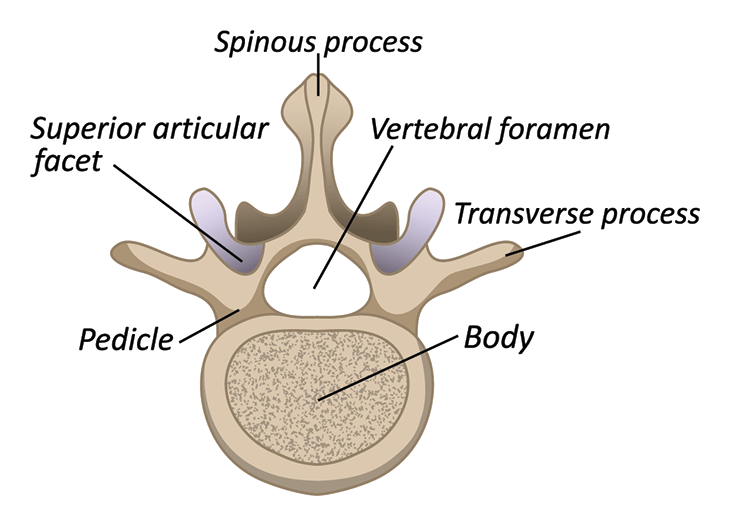
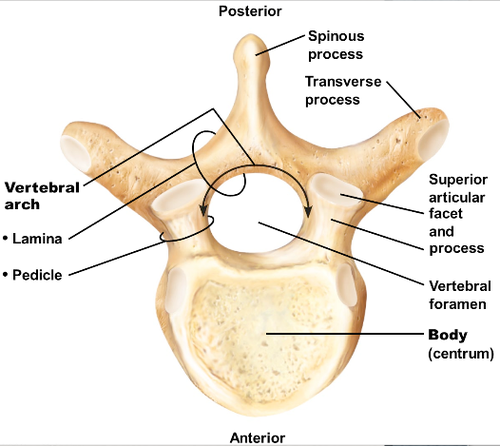
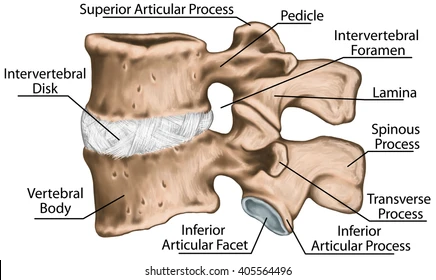
What are the 2 main parts of a singular vertebra?
the body and the arch
Adjacent vertebral foramen form the ___
spinal canal
Where are intervertebral disk joints located?
between the bodies of the vertebrae C2-S1
What is the function of the intervertebral disk joints?
acts as a cushion for the spinal column
What is the classification of the intervertebral (disk) joints?
cartilaginous, amphiarthrodial, symphysis
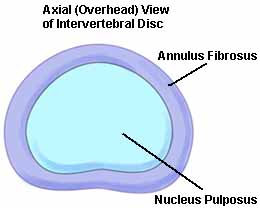
The outer ring of the vertebral disks is called the ___
The inner ring of the vertebral disks is called the ___
outer: annulus fibrosis
inner: nucleus pulposus
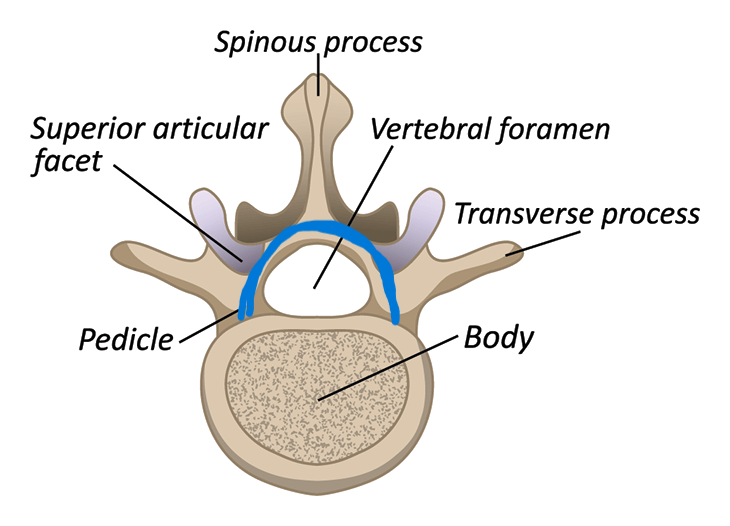
What does the blue line represent?
vertebral arch
What does HNP stand for?
herniated nucleus pulposus
What is an HNP?
slipped disc; occurs when the nucleus pulposus ruptures or protrudes into the vertebral canal, causing impinging on the spinal nerve; can be caused by improper body mechanics
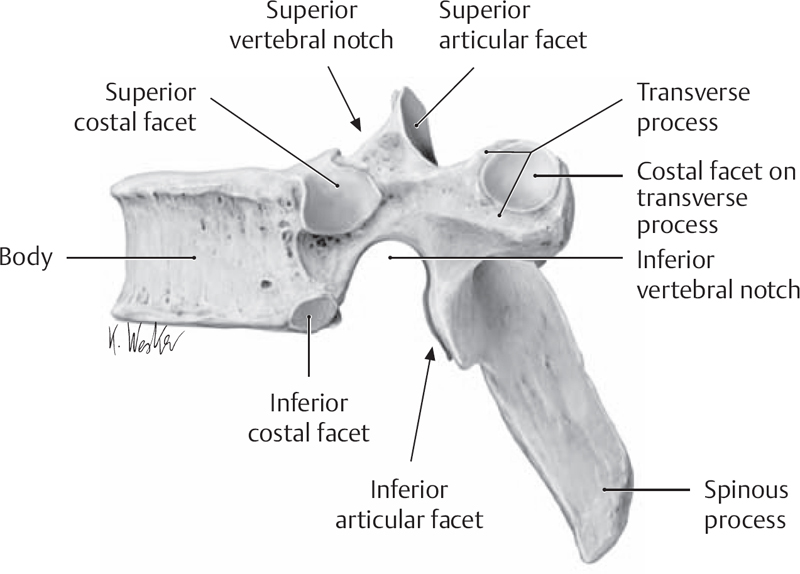
Explain the body of the vertebrae
solid anterior part shaped like a cylinder
composed of mostly cancellous bony tissue covered by a layer of compact bone
covered by a thin plate of articular cartilage (for attachment of intervertebral disc)
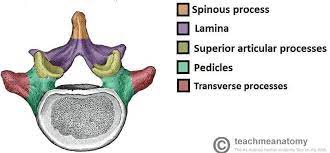
What structures make up the vertebral arch?
pedicles and laminae
The vertebral notches are located on the ___
pedicles
The lamina join together to form the ___
spinous process
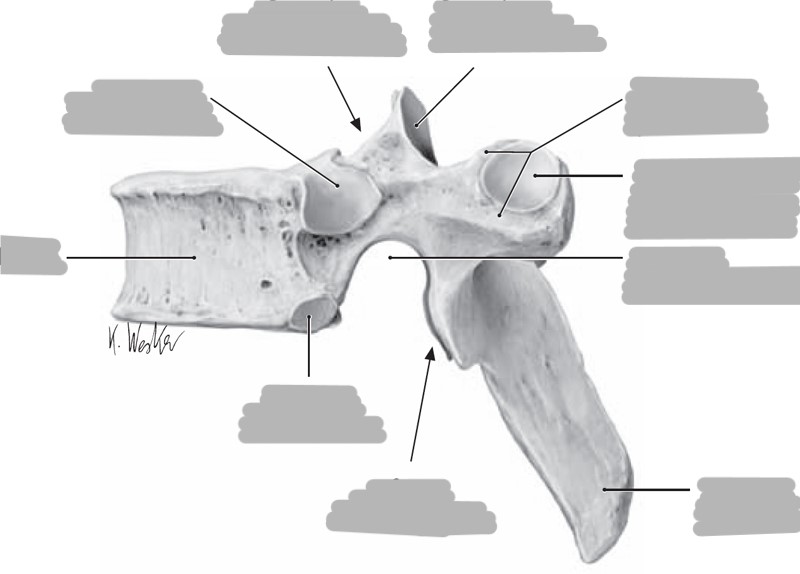
What are the intervertebral foramina?
foramen formed when vertebral notches of adjacent vertebrae come together to make a circle; transmit spinal nerves
When are intervertebral foramina seen on an x-ray of each spine segment?
C-spine: oblique
T-spine: lateral
L-spine: lateral
How many processes are there on a single vertebra? What are they?
2 transverse
4 articulating
1 spinous
(7 total)
Explain the location of the transverse processes
project laterally from the junction of the pedicles and laminae
Explain the location of the spinous process
projects posteriorly and inferiorly from the junction of the laminae in the posterior midline
The superior articulating processes have facets that face ___
The inferior articulating processes have facets that face ___
superior: face posteriorly
inferior: face anteriorly
The articulating processes contain articulating facets for ___
articulation with adjacent vertebrae
What are some other names for zygapophyseal joints?
interarticular joints and apophyseal joints
What are zygapophyseal joints?
articulations between the articular facets of the articulating processes of adjacent vertebrae
What is the classification of zygapophyseal joints?
diarthrodial, synovial, gliding
When are zygapophyseal joints seen on an x-ray of each spine segment?
C-spine: lateral
T-spine: oblique
L-spine: oblique