Unit 3 Presidency Terms
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
12th amendment
requires separate ballots for the President and VP, whoever gets highest votes is President, second highest is VP (outdated)
22nd Amendment
president has two terms in office only
25th Amendment
when president believes that he is incapable of performing the duties of office, he must inform Congress in writing. VP then takes over until he feels better
advice and consent
senate can review treaties and appointment of judges the president makes, say yes or no
agenda setting
power of the president to determine policy priorities for the nation
appointment power
president power to appoint cabinet members and federal judges
removal power
president power to remove appointments except head of regulatory commissions and judges
balance the ticket
VP chosen by Presidental nominees to attract groups of voters or appease party functions
Budget Reform and Impoundment Act
President proposes budget, Congress approves, but theres no need to spend all the funds constitutionally (now is illegal)
EX: Biden still has to pay for funding for Trumps fund to build the wall bc of this
Bully Pulpit
president can persuade the public to support them by interaction directly
cabinet
a group of presidential advisers not mentioned in the Constitution
Chief Diplomat
President dominates American foreign policy and create treaties and recognition towards other countries
Chief Executive
enforces the acts of Congress, the judgements of the federal courts, and treaties signed by U.S. ( backed by Take Care Clause)
Chief Legislator
President must recommend to Congress legislation that the judge necessary, State of Union Address required by Constitution every year
Chief of Staff
responsible for coordinating the office, normally one of the president’s chief advisors
Circular Model
gives the President a way to directly get information from his staff members
Commander in Chief
President controls army and navy and makes ultimate matters
Constitutional Powers
veto and sign bills
make treaties (senate approval needed)
commander in chief, chief diplomat, chief of state ,chief administrator, chief executive ,chief legislator
Power to grant reprieves and powers
appoint ambassadors and other offices
recess appointments
state of union message
Take Care Clause
faithfully execute
diplomatic recognition
the power to recognize or not recognize foreign countries
emergency powers
president can declare emergencies without anyones approval, usually during national crisis and is a inheret power
executive agreement
presidental power in foregin affairs, no senate approval required, can be secretive, expires w president
EX: biden probably has a plan with the Pres. of Ukraine to fund them
EOP (Executive Office of the President)
provides staff assistance for the chief executive and help coordinate the executive bureaucracy
Executive Order
order issued by the President that has the force of law, expires w President
Executive Privilege
inheret power that concerns the ability of the President and his executive officials to refuse to appear before, or withhold information from Congress or courts
EX: Nixon v. US
Nixon v. US
Nixon didnt want to hand over tapes recorded of his conversations, claiming executive privilege
The court ruled that it was not executive privilege and the tapes had to be handed over
Federal Register
daily publication of the U.S. Governments agenda and what they got done
Chief of State
America’s ceremonial leader and symbol of government
Impeachment
House accuses Pres., VP, or any civil officer of crime with a simple majority
Senate then conducts the actual trial (2/3 vote), if person is impeached, the Supreme Court Chief Justice hears the court
inheret power
President has the “executive power and take care that the laws be faithfully executed”
Kitchen Cabinet
very informal group of advisors, who usually are friends of the president with whom the president worked with before
Line-item Veto
the power to veto individual lines or items within a piece of legislation, rather than vetoing the entire thing (illegal now)
NSC (National Security Council)
committee links the president key foreign and military advisors
OMB (Office of Management and Budget)
makes annual federal budget that the president presents to Congress each January and approving the budget for all agencies
Pardon
legal forgiveness for a crime (constitutional, only for federal law)
Reprieve
the postpone a sentence (constitutional)
Amnesty
President constitutional ability to pardon a group of people
Communtation
reduce a sentence (constitutional)
Chief of Party
president chooses the national committee chairperson and can try to discipline part members who fail to support the presidents policies (informal power)
patronage (spoils system)
appointing individuals the president personally knows to government or public jobs (illegal now bc of Pendleton Act)
Permanent Campaign
president is always “campaigning”, even off election time
Pocket Veto
President refuses to sign the bill and Congress adjourns within 10 working days after the bill has been submitted to the president, the bill is killed
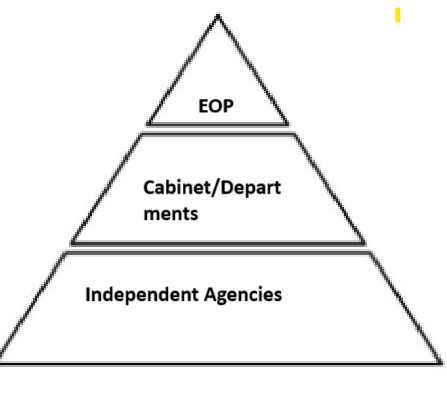
Pyramid Model
military chain of command that emphasizes a powerful Chief of Staff
Public Approval
public’s reaction to their support or opposition to president and their policies
Signing Statement
President writes a paper that confirms the signing upon a bill, official message in how he sees the law being enforced
State of the Union
required by the Constitution, given by the Chief Legislator and shares a comprehensive view of what the president wishes the legislatures to accomplish during session
Statutory Powers
Congress creates certain laws (opposed from constitution powers, which are laws made by constitution)
Take Care Clause
President should “take care that the laws be faithfully executed”
Veto Message
10-day period in which the President signs a bill or not
War Powers Resolution
requires the President to consult with Congress whenever possible prior to using military force and withdraw forces after 60 days unless Congress declares war or gives an extension
White House Office
collection of offices and organizations loosely grouped into the Executive Office of the President