Physics II Lesson 2: Waves
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
CRB Fill in the blanks: Recall that Longitudinal waves have particles oscillate parallel to the direction the wave travels. ________________ Pushes the medium's molecules closer together, and _____________ is the decompression that follows.
(A) Compression, Relaxation
(B) Compression, Rarefaction
(C) Suppression, Relaxation
(D) Suppression, Rarefaction
(B) Compression, Rarefaction
Recall that Longitudinal waves have particles oscillate parallel to the direction the wave travels. Compression Pushes the medium's molecules closer together, and Rarefaction is the decompression that follows.
CRB True or false? The Principle of Superposition states then when 2 waves interact with each other, the net displacement of the resultant is equal to the difference of the two waves.
False. The Principle of Superposition states then when 2 waves interact with each other, the net displacement of the resultant is equal to the Sum of the two waves.
CRB Fill in the blanks: When the waves are perfectly out of phase, then the waves completely counter-act, and is called __________________. When the waves are perfectly in phase, then the resultant is equal to the sum of the two waves' amplitudes, which is known as ____________________.
(A) Destructive Interference, Constructive Interference
(B) Antiphase Interference, In-phase Interference.
(C) Destructive Interference, In-Phase Interference
(D) Antiphase Interference, Constructive Interference
(A) Destructive Interference, Constructive Interference
When the waves are perfectly out of phase, then the waves completely counter-act, and is called Destructive Interference. When the waves are perfectly in phase, then the resultant is equal to the sum of the two waves' amplitudes, which is known as Constructive Interference.
CRB True or false? If the difference in frequencies is about 10 Hz, then there is a "wobbling" resultant wave that sometimes is in phase and sometimes out of phase, producing equally spaced moments of constructive interference, which will be quieter, called "Beats".
False. If the difference in frequencies is about 10 Hz, then there is a "wobbling" resultant wave that sometimes is in phase and sometimes out of phase, producing equally spaced moments of constructive interference,which will be louder, called "Beats".
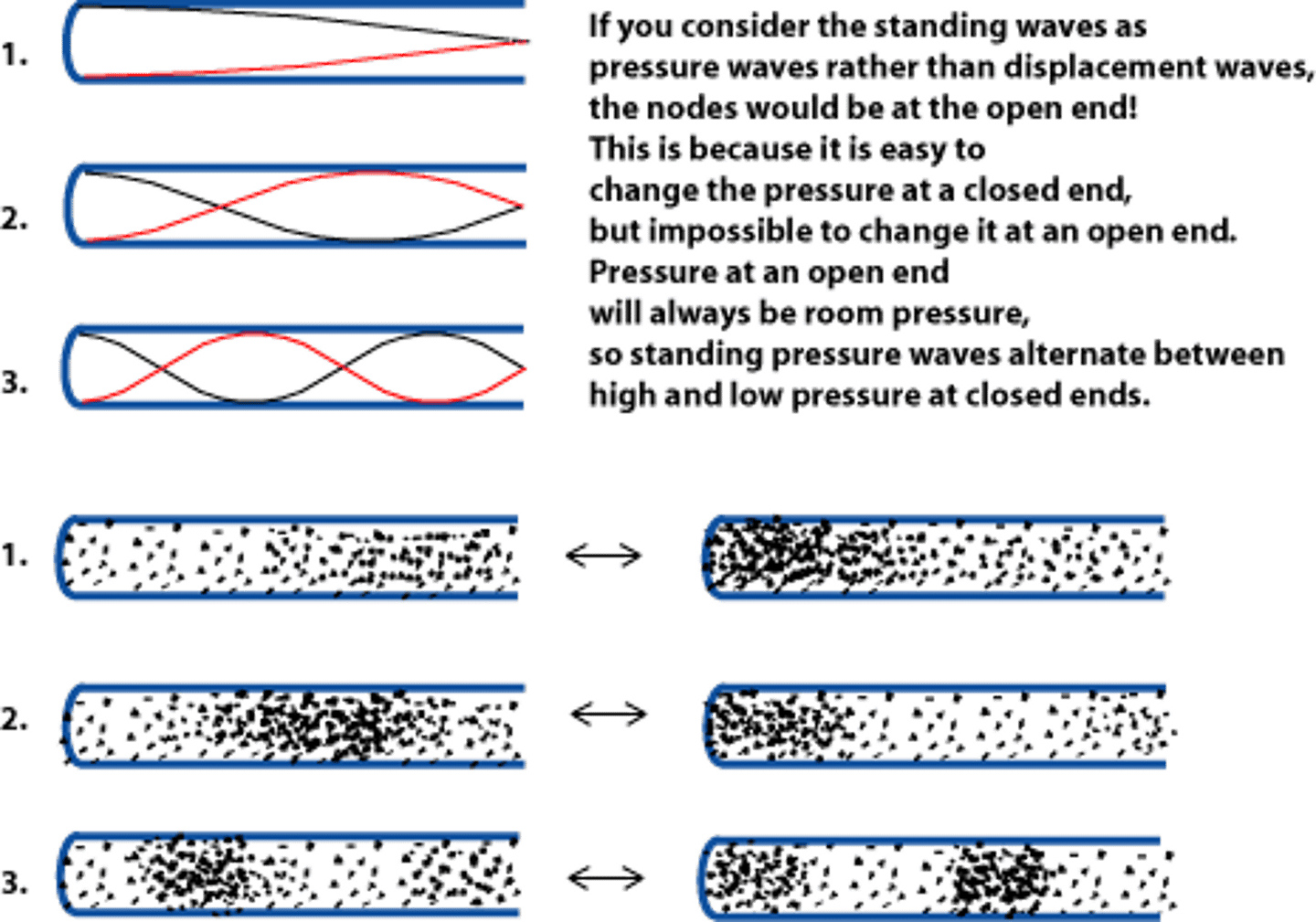
Give an example of a closed-closed tube/container? Open-closed? Open-open?
Closed-closed container -
guitar string, etc.
Open-closed tube - Soda Bottle, clarinet, etc.
Open-open tube - Flute, Harmonica, Organ Pipe, etc.
Air can oscillate freely at which end(s)? Open, closed or both?
Air oscillates freely at the open end. Air doesn't oscillate at the closed end and is considered fixed at that point.
Points at which air can oscillate freely (at maximum displacement) are known as ___________. Points at which air is fixed (no displacement) are known as ________________.
(A) nodes, anti-nodes
(B) anti-nodes, nodes
(C) maximi, minimi
(D) minimi, maximi
(B) anti-nodes, nodes
Points at which air can oscillate freely (at maximum displacement) are known as anti-nodes. Points at which air is fixed (no displacement) are known as nodes.
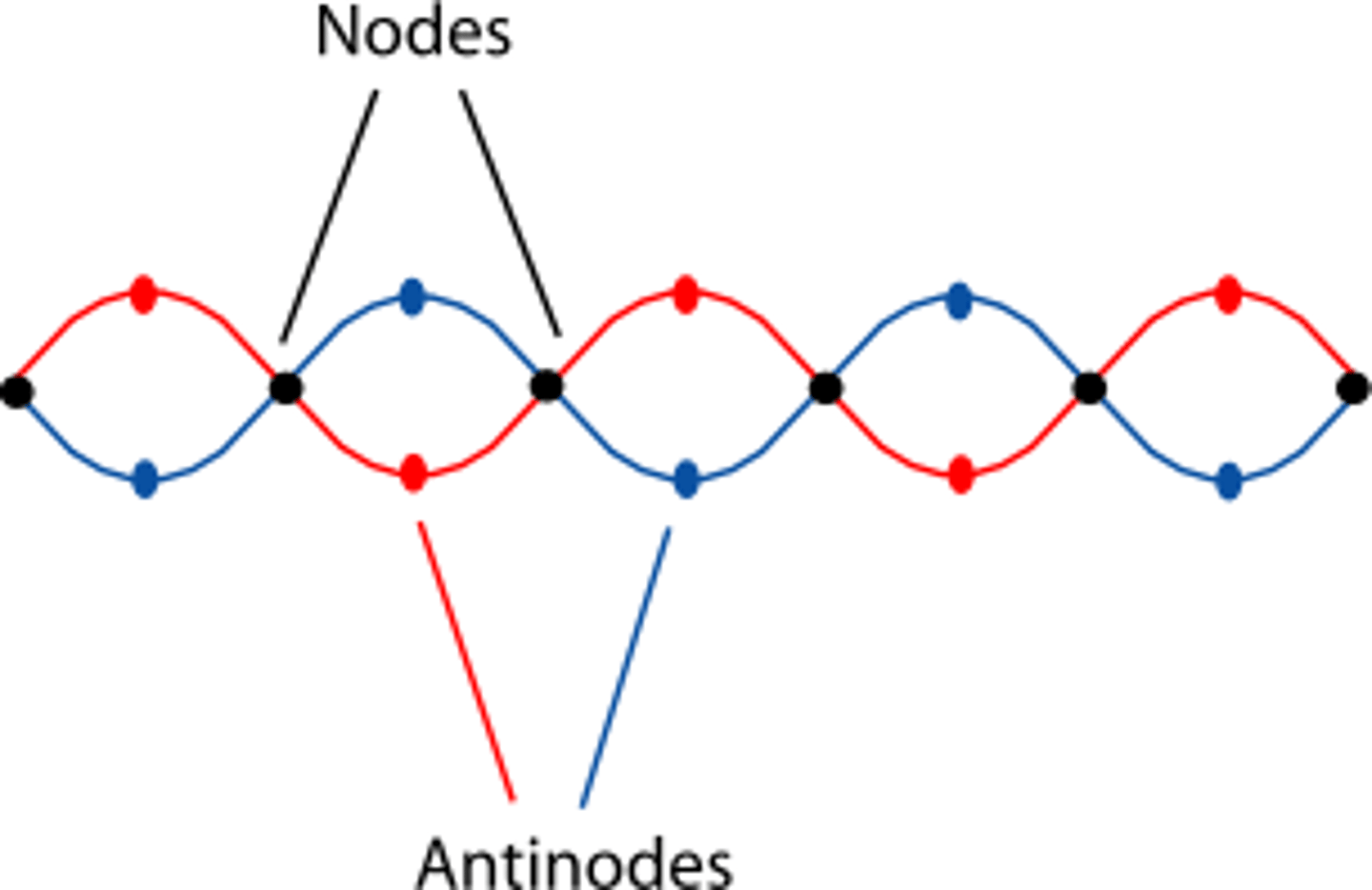
Why are waves in tubes considered "standing waves"?
Waves in tubes are considered "standing waves" because their areas of compression are not propagating in a single forward direction, but rather oscillate back and forth.
CRB True or false? There are also Traveling waves, which will be reflected and inverted when it hits a fixed boundary.
True. There are also Traveling waves, which will be reflected and inverted when it hits a fixed boundary.
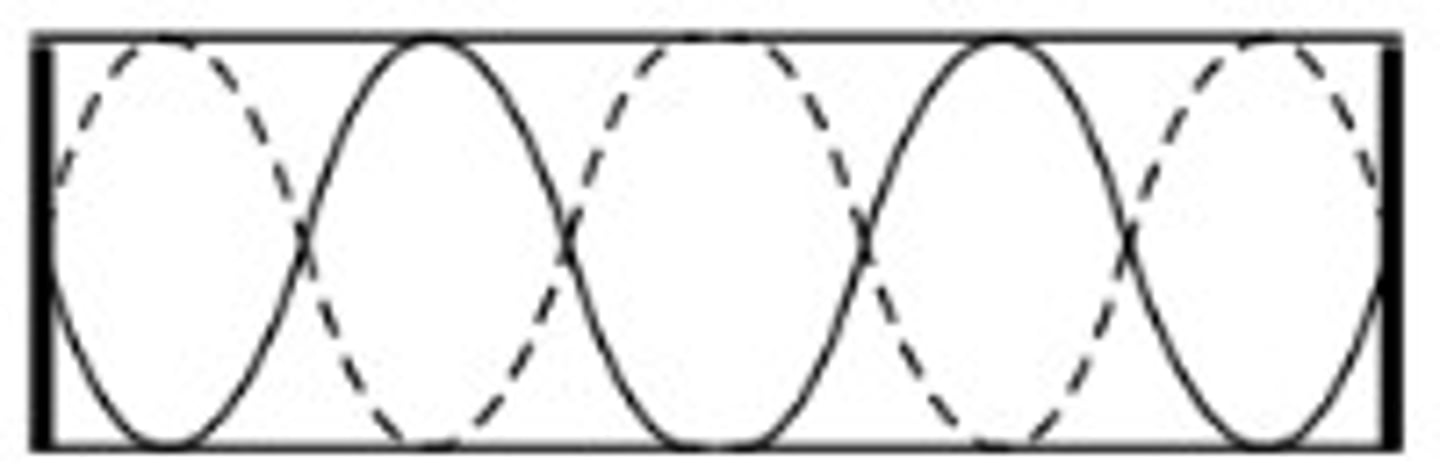
Air particles within a tube will oscillate up and down (vertically) or side to side (horizontally) within a tube?
The air particles will oscillate side to side (horizontally). Yet, we depict this displacement on a graph vertically. Don't get confused. The air particles are actually oscillating side to side (horizontally).
A wave starts at a displacement of -5 units, moves to 0 displacement (point A), then moves to +5 displacement (point B), moves to 0 displacement again (point C), and finally moves back to -5 displacement once again (point D). At which point does the wave complete a single wavelength?
(A) Point A
(B) Point B
(C) Point C
(D) Point D
(D) Point D
A full wavelength occurs when a wave goes from an initial point of maximal displacement back to that very same point. It can be considered the unit that repeats itself in a wave.
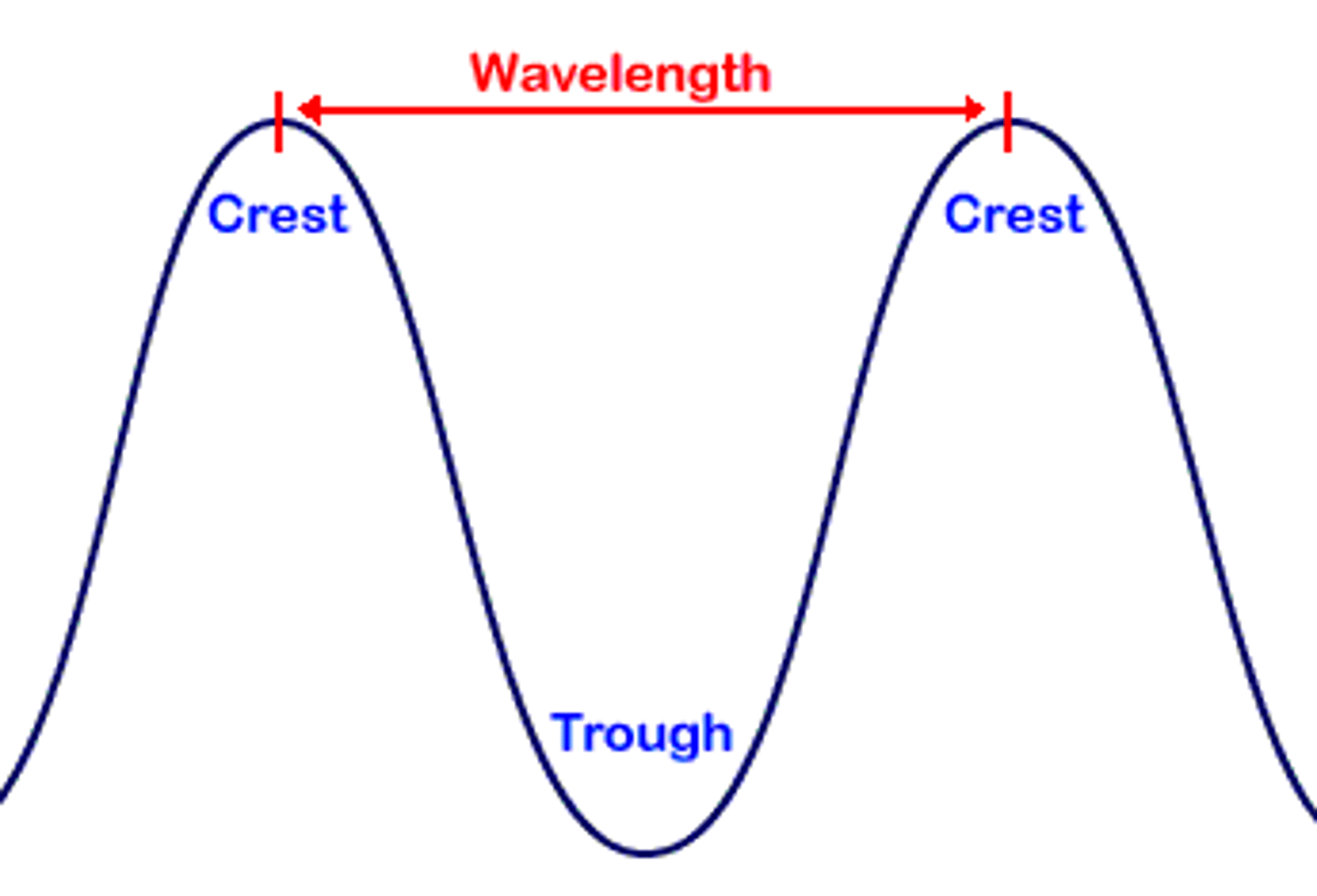
If you blow over a tube, you will hear the Fundamental Wavelength. What is that?
(A) The wave with the smallest displacement that can still fit in the tube.
(B) The wave with the largest displacement that can still fit in the tube.
(C) The wave with the smallest wavelength that can still fit in the tube.
(D) The wave with the largest wavelength that can still fit in the tube.
(D) The wave with the largest wavelength that can still fit in the tube.
In this image, it would be the top wave.
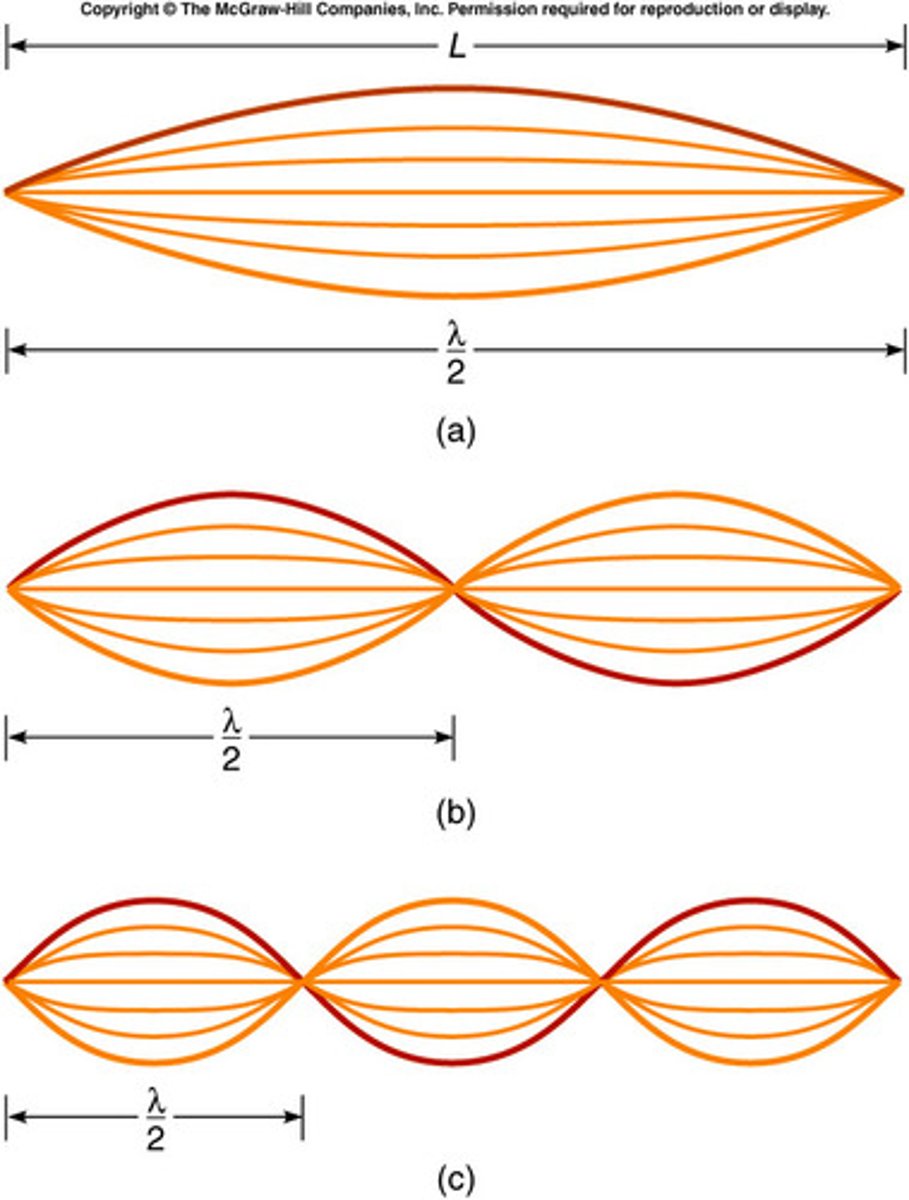
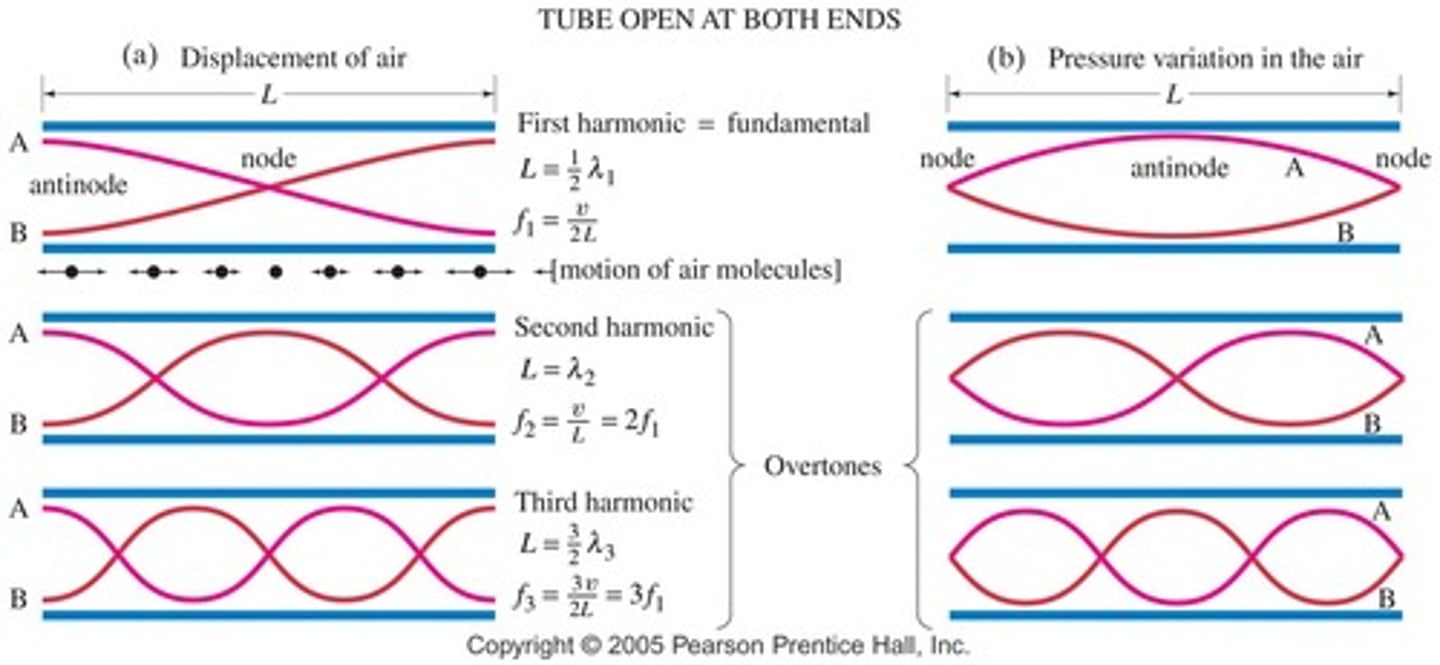
The Fundamental Frequency is also known as the First Harmonic. Draw the First, Second, and Third Harmonic for an open-open container/tube. Describe how the harmonics relate to one another.
To draw the second harmonic based on the first, simply draw the wave with the next largest wavelength that can possibly fit in the container. You can do this by adding another node within the container. Keep in mind that both ends must always be anti-nodes as they are open.
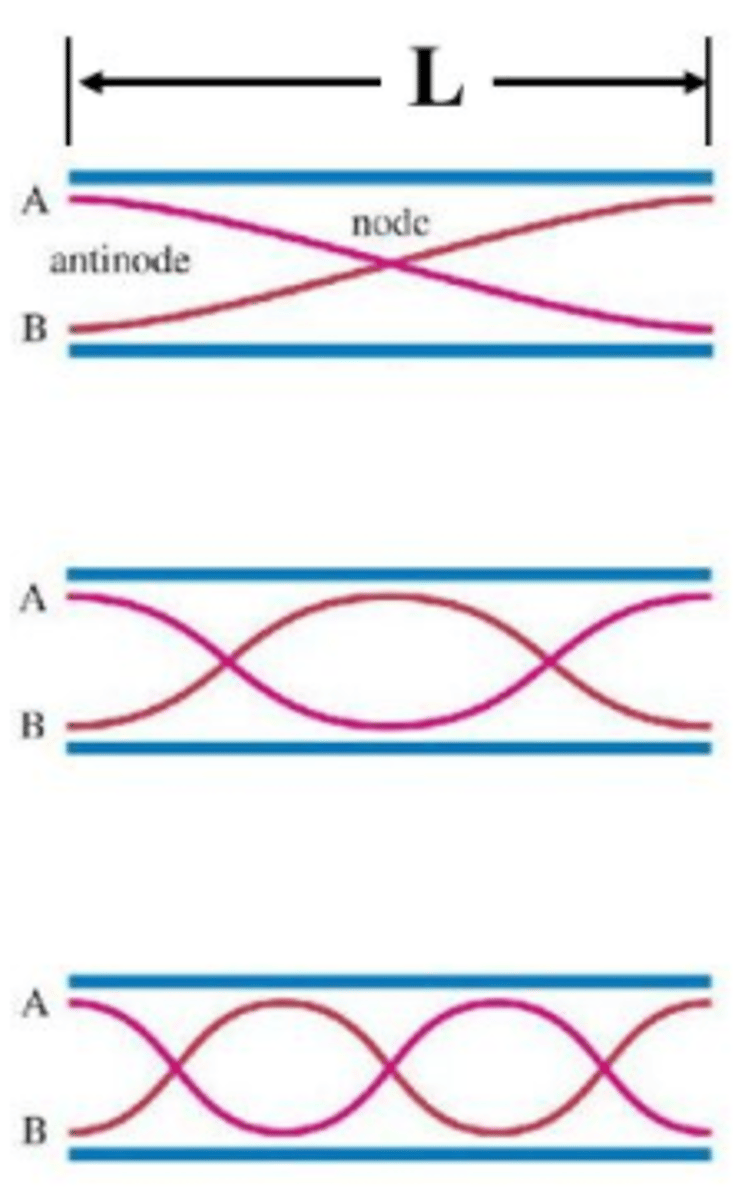
What equation can be used to relate length of the tube (L), wavelength (λ), and harmonic number (n) for an open-open tube? Show how you might derive this equation based on the images you drew in the previous question.
λ = 2L / n
λ = Wavelength
L = Length of Tube
n = Harmonic Number
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
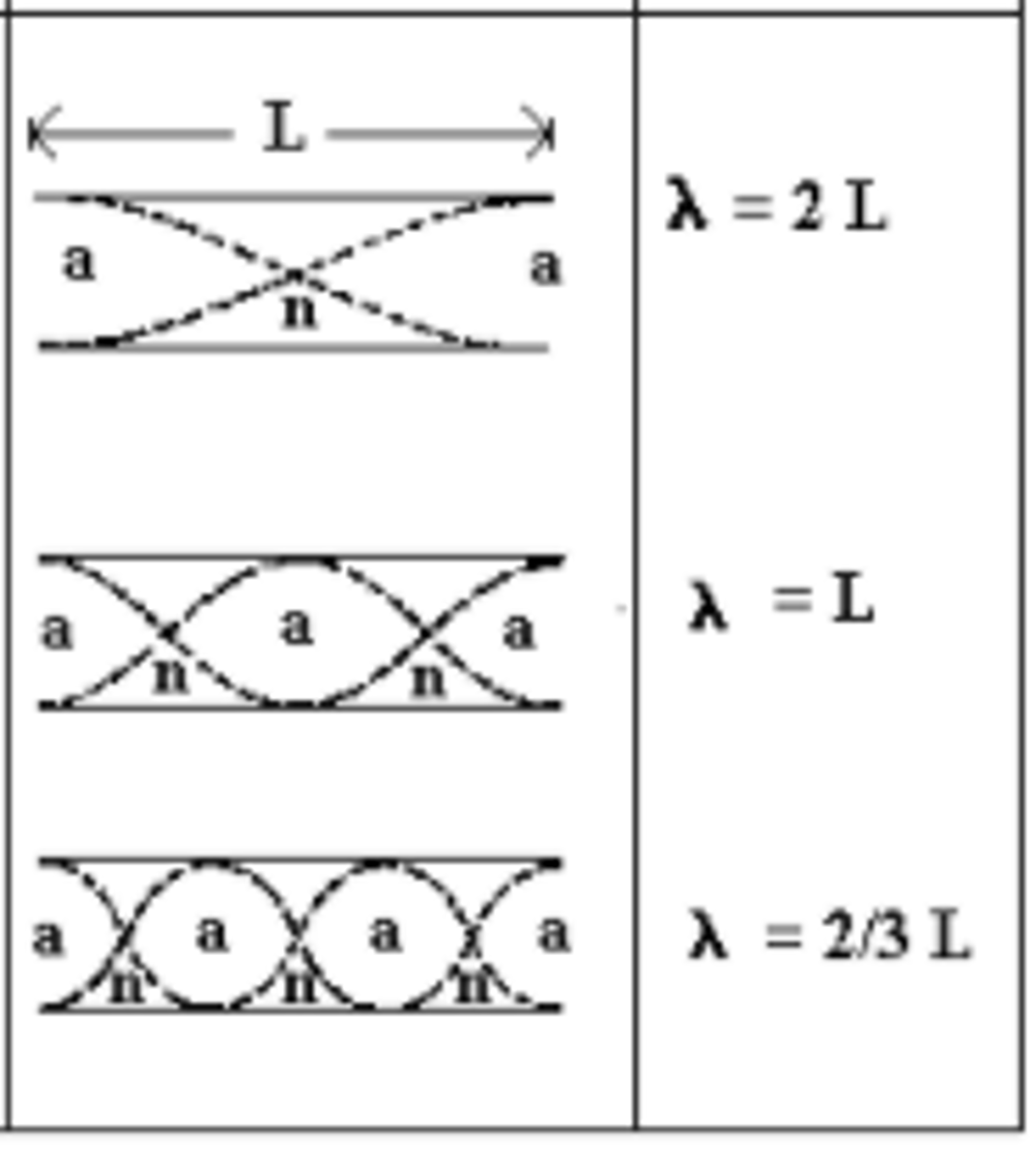
Draw the First, Second, and Third Harmonic for an open-closed container/tube. Describe how the harmonics relate to one another.
TRICK QUESTION! Even-numbered harmonics do not exist for open-closed tubes!
Draw the First, Third, and Fifth Harmonic for an open-closed container/tube. Describe how the harmonics relate to one another.
To draw the second harmonic based on the first, simply draw the wave with the next largest wavelength that can possibly fit in the container. You can do this by adding another node within the container. Keep in mind that the open end will always have an anti-node and the closed end will always have a node.
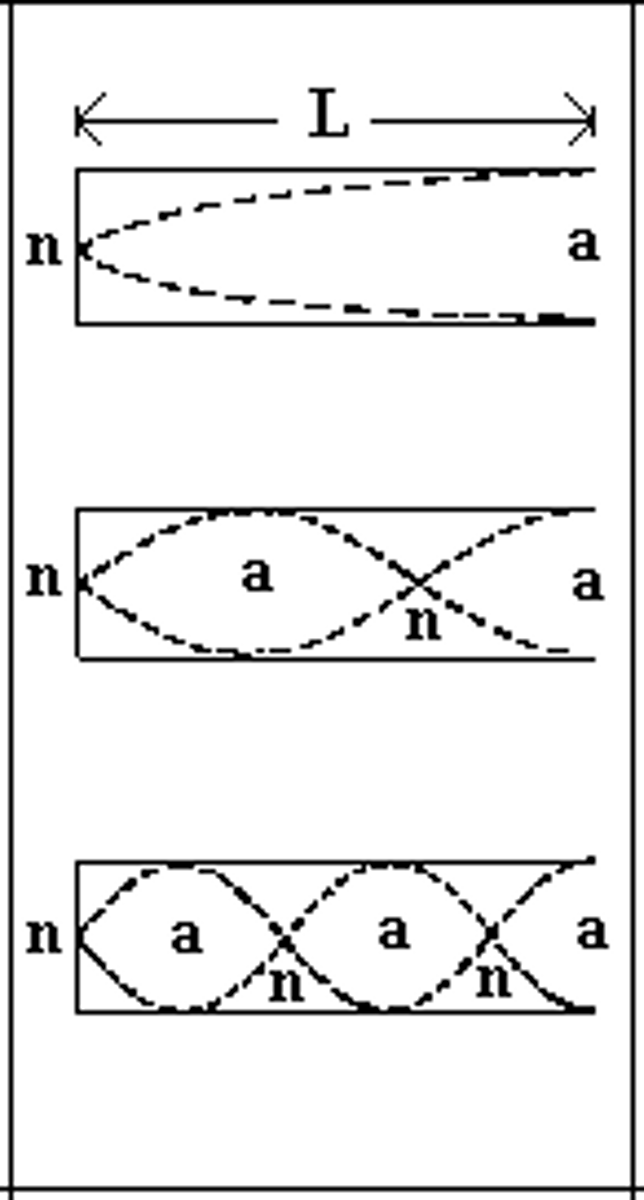
What equation can be used to relate length of the tube (L), wavelength (λ), and harmonic number (n) for an open-closed pipe? Show how you might derive this equation based on the images you drew in the previous question.
λ = 4L / n
λ = Wavelength
L = Length of Tube
n = Harmonic Number
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
You are observing a pipe organ in an old church. Which will play lower notes and why?
(A) Longer pipes will play lower notes due to allowing for a longer wavelength.
(B) Longer pipes will play lower notes due to allowing for a lower amplitude.
(C) Shorter pipes will play lower notes due to allowing for a longer wavelength.
(D)Shorter pipes will play lower notes due to allowing for a lower frequency.
(A) Longer pipes will play lower notes due to allowing for a longer wavelength.
Longer wavelengths correspond to lower frequencies, which correspond to lower pitches.
Draw the First, Second, and Third Harmonic for a closed-closed container/tube. Describe how the harmonics relate to one another.
To draw the second harmonic based on the first, simply draw the wave with the next largest wavelength that can possibly fit in the container. You can do this by adding another node within the container. Keep in mind that both ends must always be nodes as they are closed.
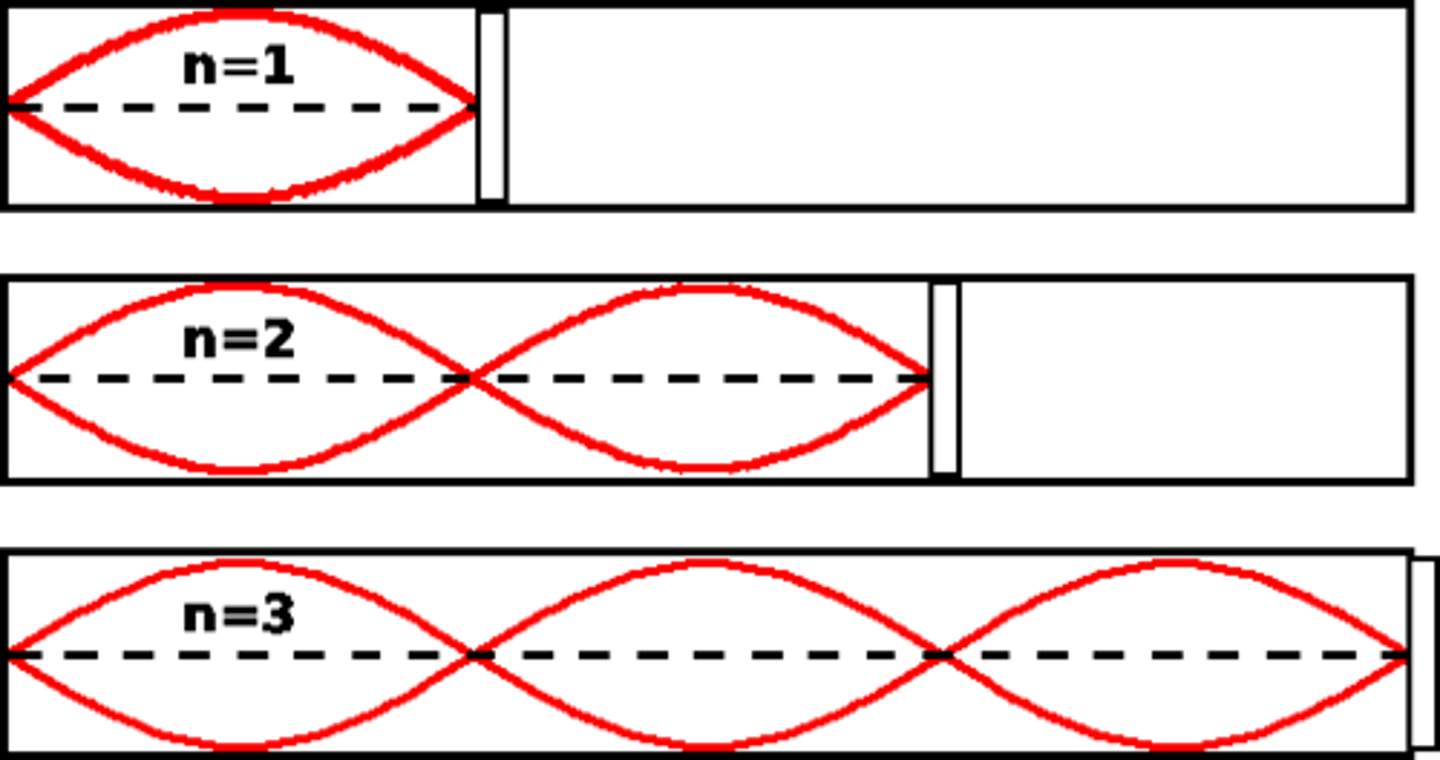
What equation can be used to relate length of the tube (L), wavelength (λ), and harmonic number (n) for an closed-closed pipe? Show how you might derive this equation based on the images you drew in the previous question.
λ = 2L / n (same equation as for open-open tubes)
λ = Wavelength
L = Length of Tube
n = Harmonic Number
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
A man is playing a flute, which is open at both ends. You measure the fifth harmonic at 787 Hz. What is the length of the flute in meters?
(A) 19.6
(B) 2010
(C) 1.08
(D) 953,000
(C) 1.08
v = λf
340 m/s = λ⋅7.87⋅10^2 Hz
λ = approx. 4⋅10^-1 meters (actual: 0.432)
λ = 2L / n
0.4 = 2L / 5
L = approx. 1 m (actual: 1.08)
Note: 340m/s is the speed of sound
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
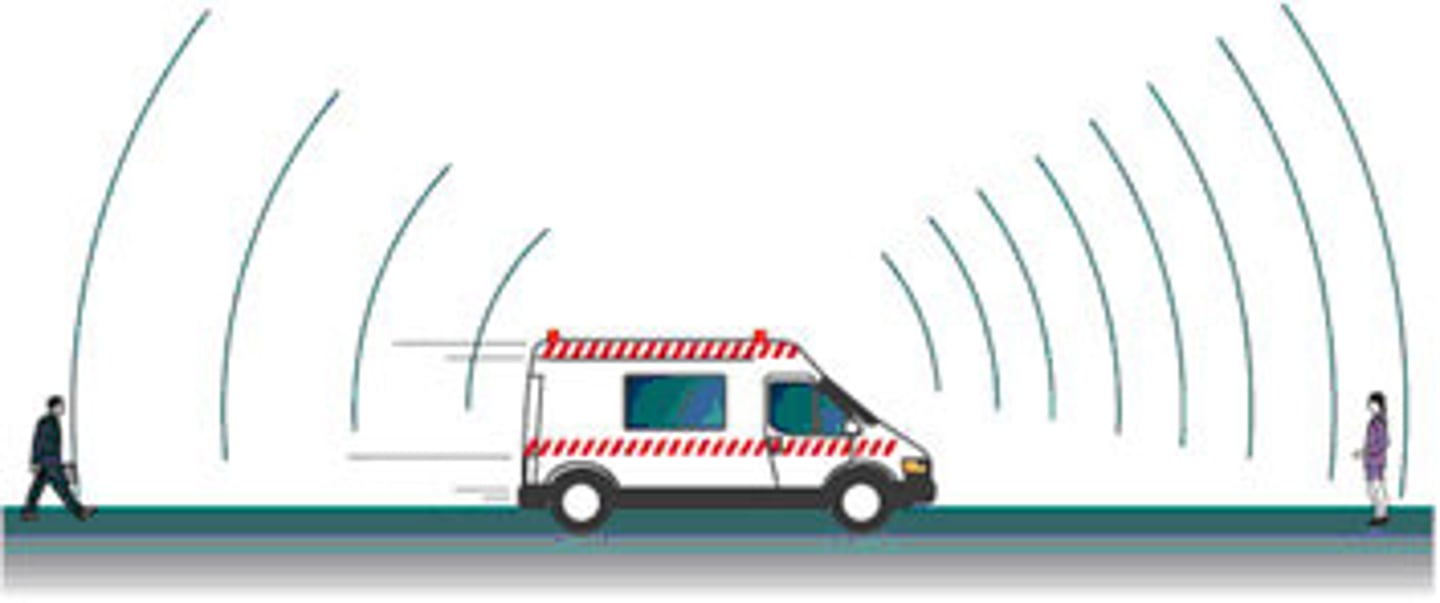
You are standing still as an ambulance drives by. As the ambulance is driving away from you, what will happen to the pitch? Why?
(A) The pitch will increase because the frequency at which the sound waves are reaching your ear increases.
(B) The pitch will increase because the frequency at which the sound waves are reaching your ear decreases.
(C) The pitch will decreases because the frequency at which the sound waves are reaching your ear increases.
(D) The pitch will decreases because the frequency at which the sound waves are reaching your ear decreases.
(D) The pitch will decreases because the frequency at which the sound waves are reaching your ear decreases.
As an ambulance is driving towards you, the sound waves get pushed closer together, resulting in a higher frequency and higher pitch. Once the ambulance drives by and travels away from you, the frequency decreases as the sound waves are essentially spread out.
CRB Which of the following terms best describe how the quality of sound is determined by the natural frequencies of the object producing the sound?
(A) Tone
(B) Brass
(C) Timbre
(D) Vibrato
(C) Timbre
Timbre refers to the fact that the quality of sound is determined by the natural frequencies of the object producing the sound.
What equation can be used to determine the new frequency due to the Doppler Effect?
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/

CRB Imagine that the Zombie Apocalypse has started. If the source, a screaming zombie, runs towards the detector, a normal human, what will that human perceive?
(A) The perceived sound will be lower-pitched, since the source velocity is increasing and in the denominator.
(B) The perceived sound will be higher-pitched, since the source velocity is increasing and in the denominator.
(C) The perceived sound will be lower-pitched, since the source velocity is increasing and in the numerator.
(D) The perceived sound will be higher-pitched, since the source velocity is increasing and in the numerator.
(B) The perceived sound will be higher-pitched, since the source velocity is increasing and in the denominator.
Recall that the denominator is (v - vs), so increasing the source velocity decreases the denominator overall!
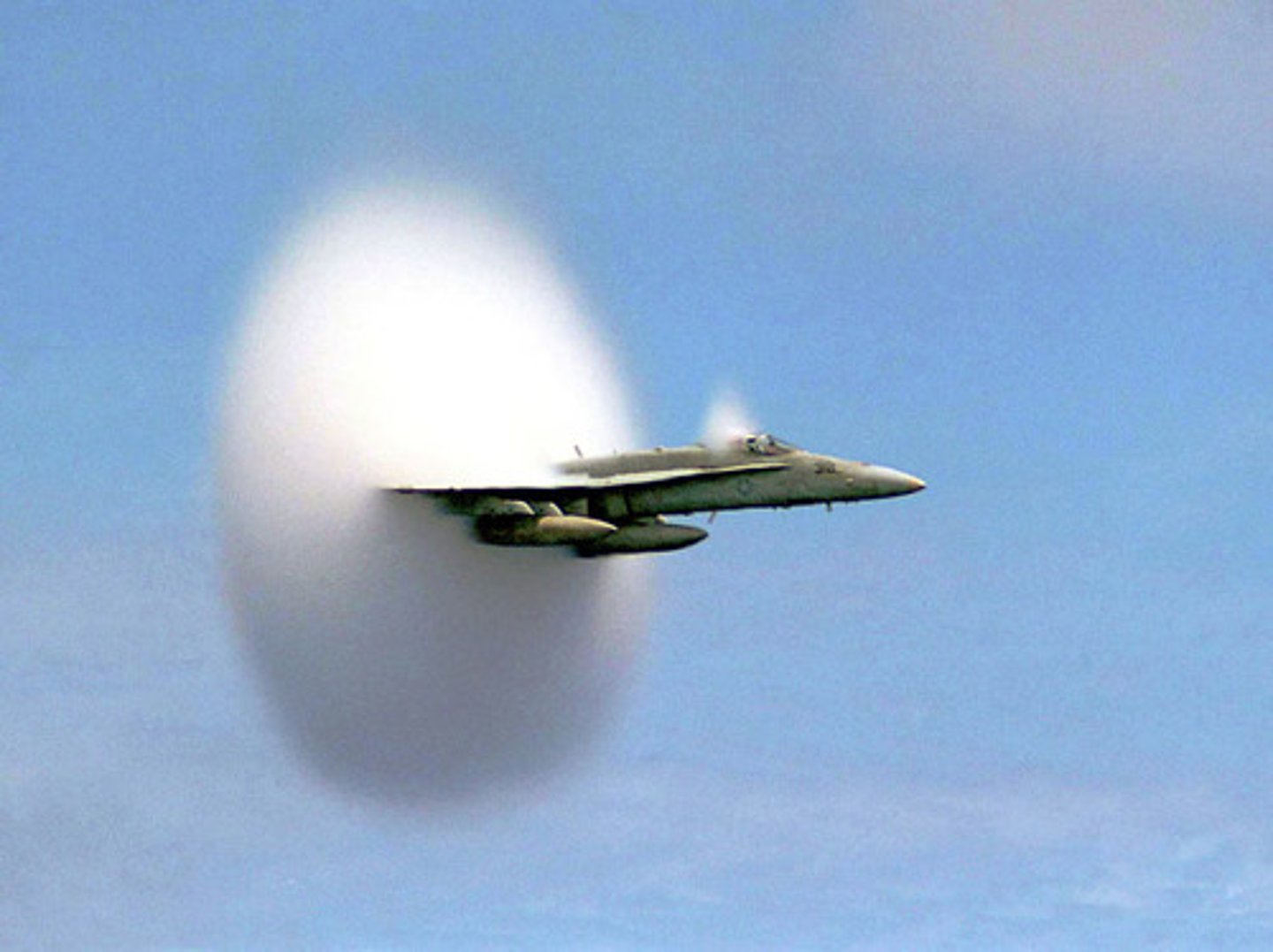
A sound wave moves at 343 m/s. As a jet emitting a sound wave approaches this speed, the frequency:
(A) Approaches 0.
(B) Approaches the Fundamental Frequency.
(C) Approaches the First Harmonic's Frequency.
(D) Approaches infinity.
(D) Approaches infinity.
A sound wave moves at 343 m/s. As a jet emitting a sound wave approaches this speed, the frequency approaches infinity.
If you were to hear a frequency close to infinity, it would create a sound that is very _________ known as a Sonic ___________.
(A) Loud, Whisper
(B) Soft, Whisper
(C) Loud, Boom
(D) Soft, Boom
(C) Loud, Boom
If you were to hear a frequency close to infinity, it would create a sound that is very loud known as a Sonic Boom.

You are singing a song as you run toward a wall. Put the following pitches in order of lowest to highest:
I. Pitch emitted as you sing
II. Pitch that hits the wall
III. Pitch that reaches your ear after reflecting off the wall
(A) I < II < III
(B) II < I < III
(C) III < II < I
(D) III < I < II
(A) I < II < III
In order of lowest to highest:
Pitch emitted as you sing < Pitch that hits the wall < Pitch that reaches your ear after reflecting off the wall
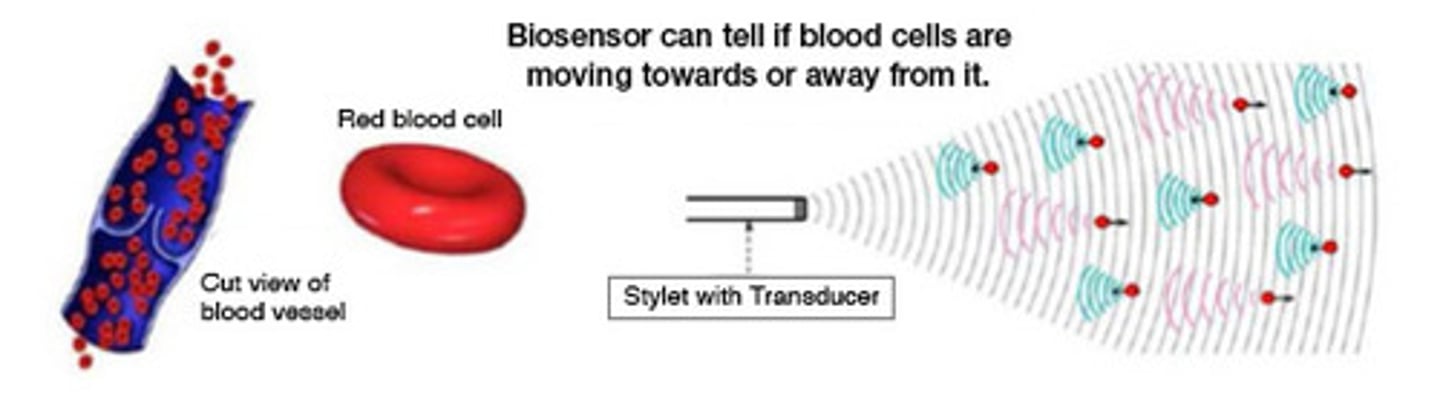
How does this idea of a double Doppler Effect relate to Doppler Ultrasound?
The Ultrasound machine takes into account the fact that the Doppler Effect works twice due to the reflection off the moving blood as it calculates the speed at which the blood is flowing.
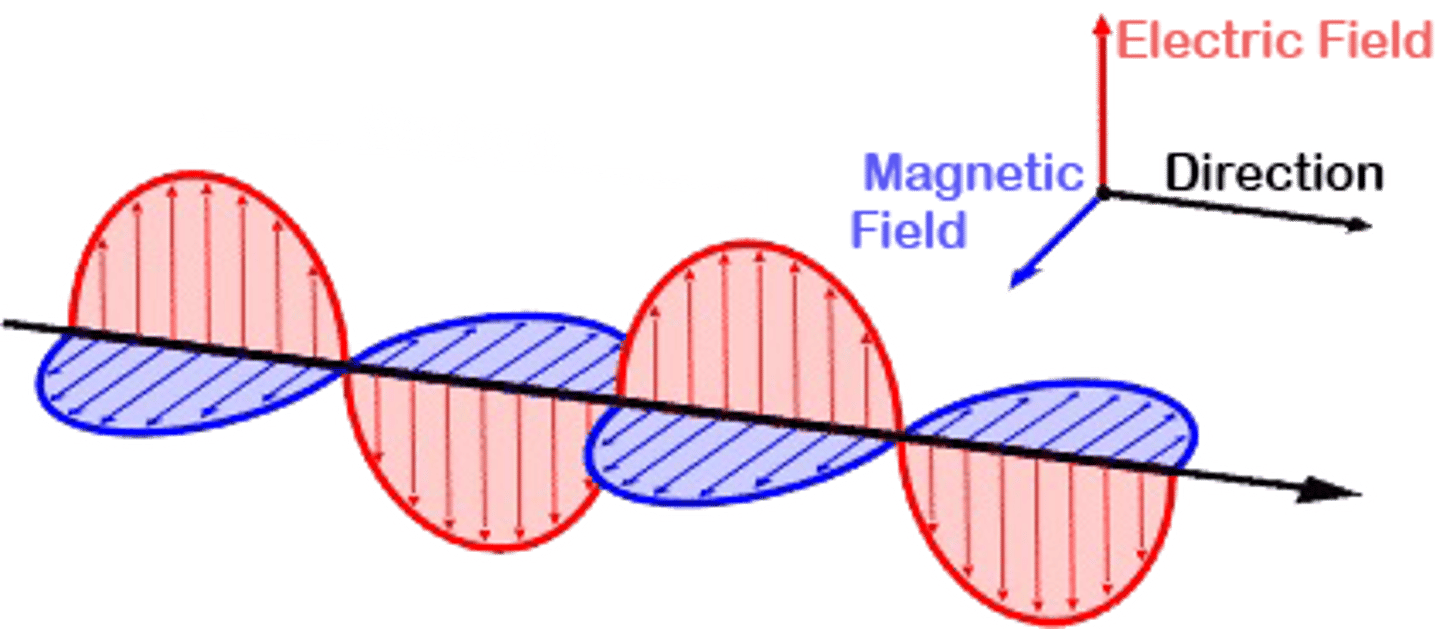
Electromagnetic Waves are based on the idea that:
(A) Electric Fields create Magnetic Fields and vice versa.
(B) Changing Electric Fields create Magnetic Fields and vice versa.
(C) Electric Fields create changing Magnetic Fields and vice versa.
(D) Changing Electric Fields create changing Magnetic Fields and vice versa.
(D) Changing Electric Fields create changing Magnetic Fields and vice versa.
How do antennas generate electromagnetic waves?
They move a charge up and down.
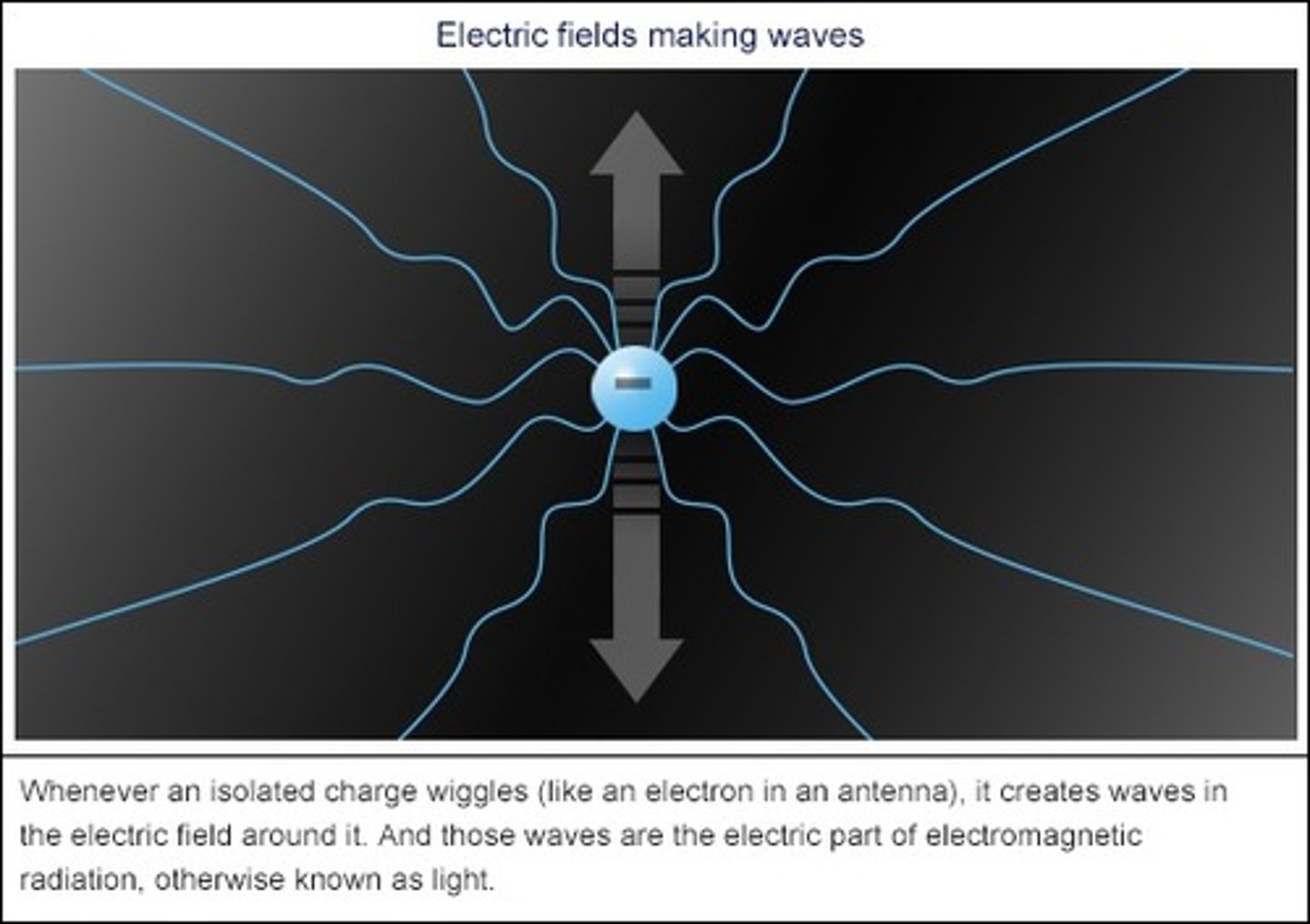
True or False. Electromagnetic Waves are similar to Sound Waves in that they cannot propagate within a vacuum.
False. Electromagnetic Waves are DIFFERENT FROM Sound Waves in that Electromagnetic Waves CAN propagate within a vacuum.
How do Electromagnetic Waves compare to Light Waves?
Light is one example of an Electromagnetic Wave.
Put the following in order of low frequency to high frequency:
I. Yellow Light
II. Green Light
III. X-rays
IV. Infrared
V. Ultraviolet
VI. Microwaves
VII. Gamma
VIII. Radio
(A) III < VII < V < II < I < IV < VI < VIII
(B) VII < III < V < II < I < IV < VI < VIII
(C) VIII < VI < IV < I < II < V < III < VII
(D) VI < VIII < IV < II < I < V < III < VII
(C) VIII < VI < IV < I < II < V < III < VII
See image.
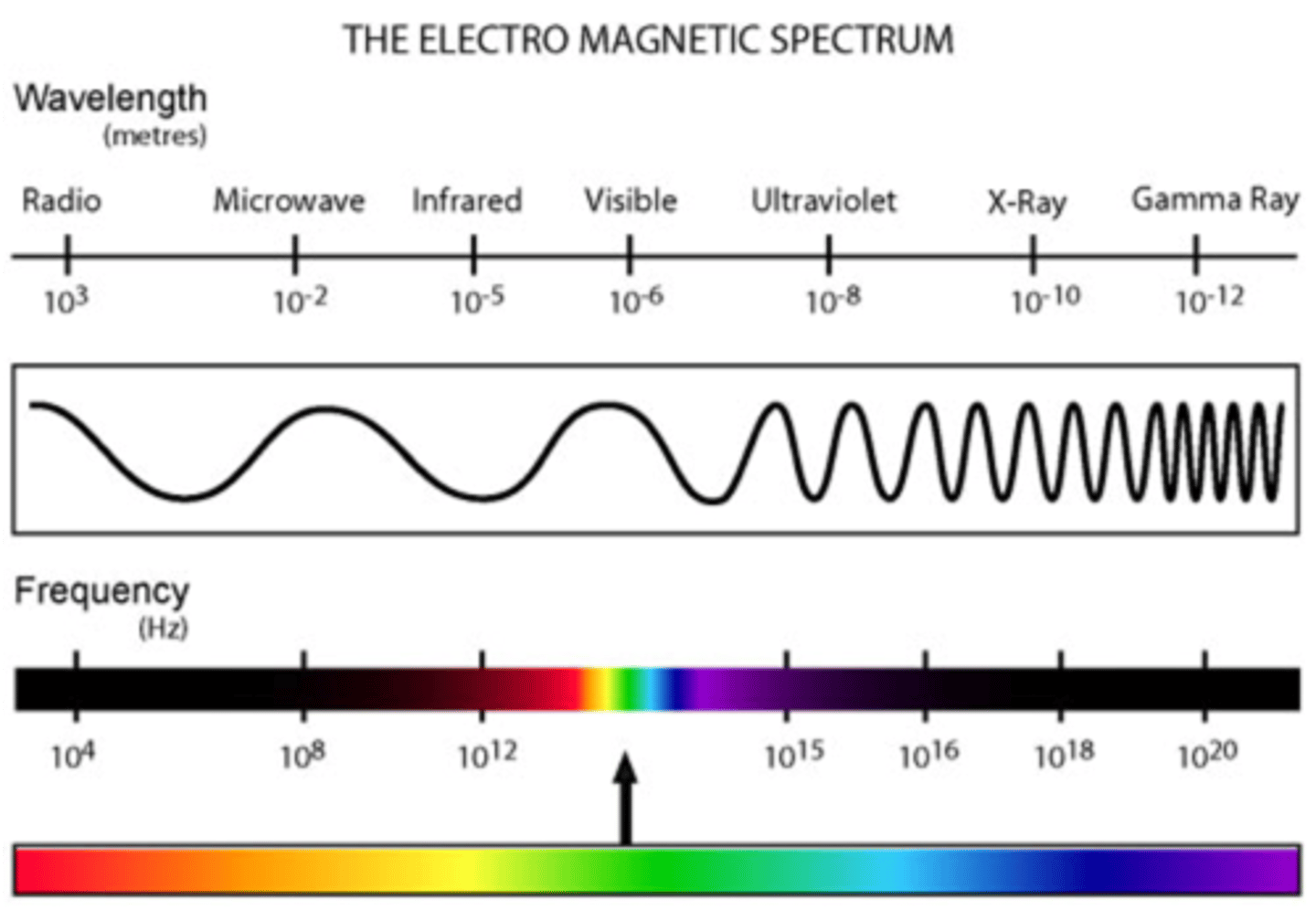
CRB Which of the following units is NOT a unit that UV, Infrared or Visible Light Waves would have describing their wavelength?
(A) mm
(B) nm
(C) pm
(D) um
(C) pm
Picometers (10^ -12 m) would be used to describe x-rays or gamma rays, not the ones asked about in this question.
Which light is more likely to damage your skin?
(A) Yellow Light
(B) Green Light
(C) Blue Light
(D) Orange Light
(C) Blue Light
Blue Light is more dangerous as it has a higher frequency. Think about how Ultraviolet (UV) light is dangerous and how it has a high frequency.
CRB Vantablack is a recently-popularized substance made of Carbon Nanotubes, and is the closest to ideal artificial absorber of visible light. Which of the following is Vantablack most like, and why?
(A) Captain America's Shield, since it seems impenetrable to light.
(B) Blackbodies, because it is an ideal absorber of light (within a certain spectrum) and appears completely black.
(C) Black paint, Vantablack isn't all that special.
(D) I just want to see a cool image of Vantablack on the back of this card.
(B) Blackbodies, because it is an ideal absorber of light (within a certain spectrum) and appears completely black.
Blackbodies are ideal absorbers of all wavelengths of light, not just the visible ones Vantablack absorbs!
How do 3D glasses work?
One lens of 3D glasses filters out all light but that in the horizontal direction while the other lens only lets in vertically polarized light. The movie producers make two images, one horizontally polarized and the other vertically polarized, which when combined together in your brain create a vertical image. This can also be done using oppositely circular polarized light.
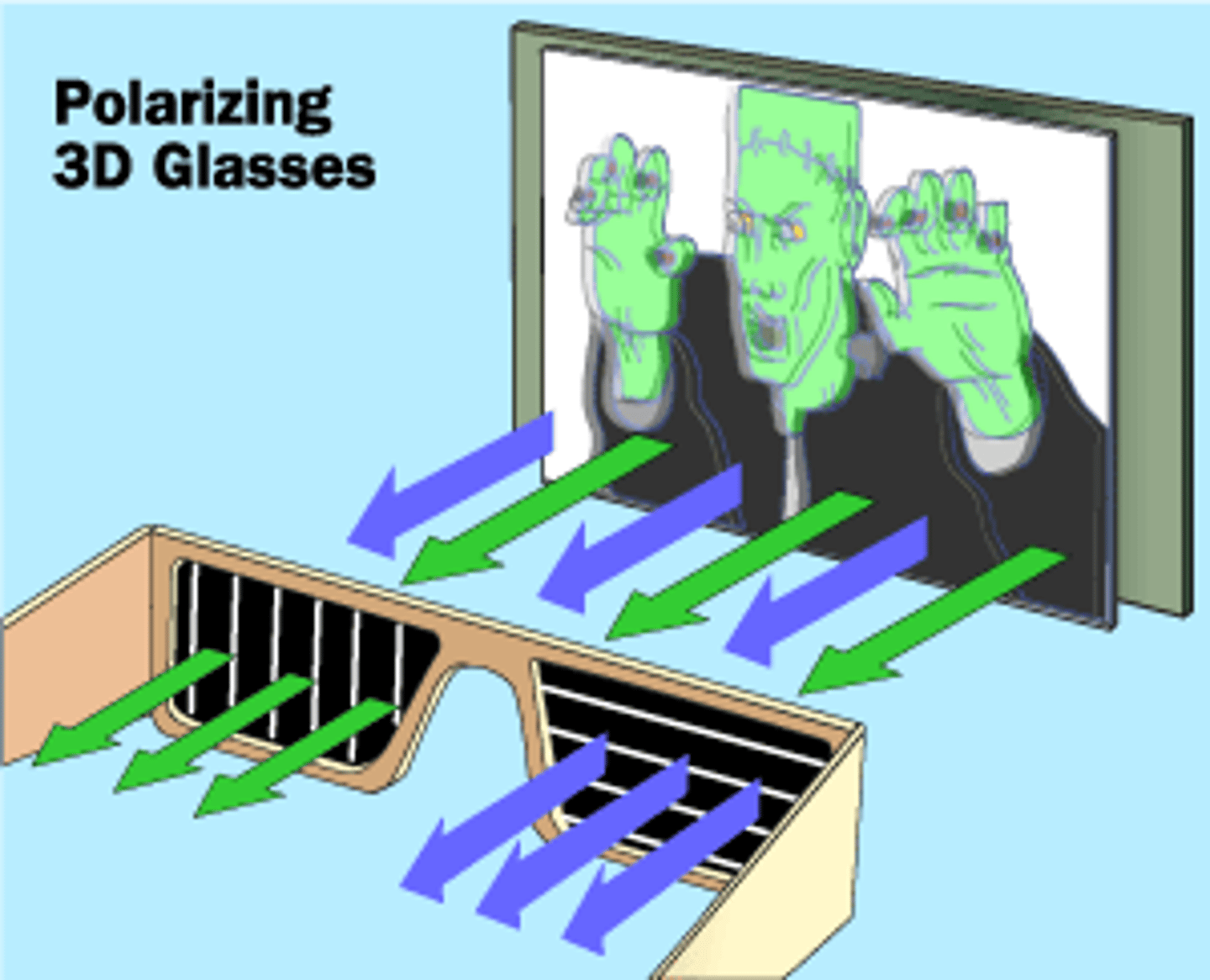
CRB True or false? The direction of Polarization of a wave is the direction that electrons would flow inside that electric field.
False. The direction of Polarization of a wave is the direction that the wave's electric field oscillates, and is often represented as a plane
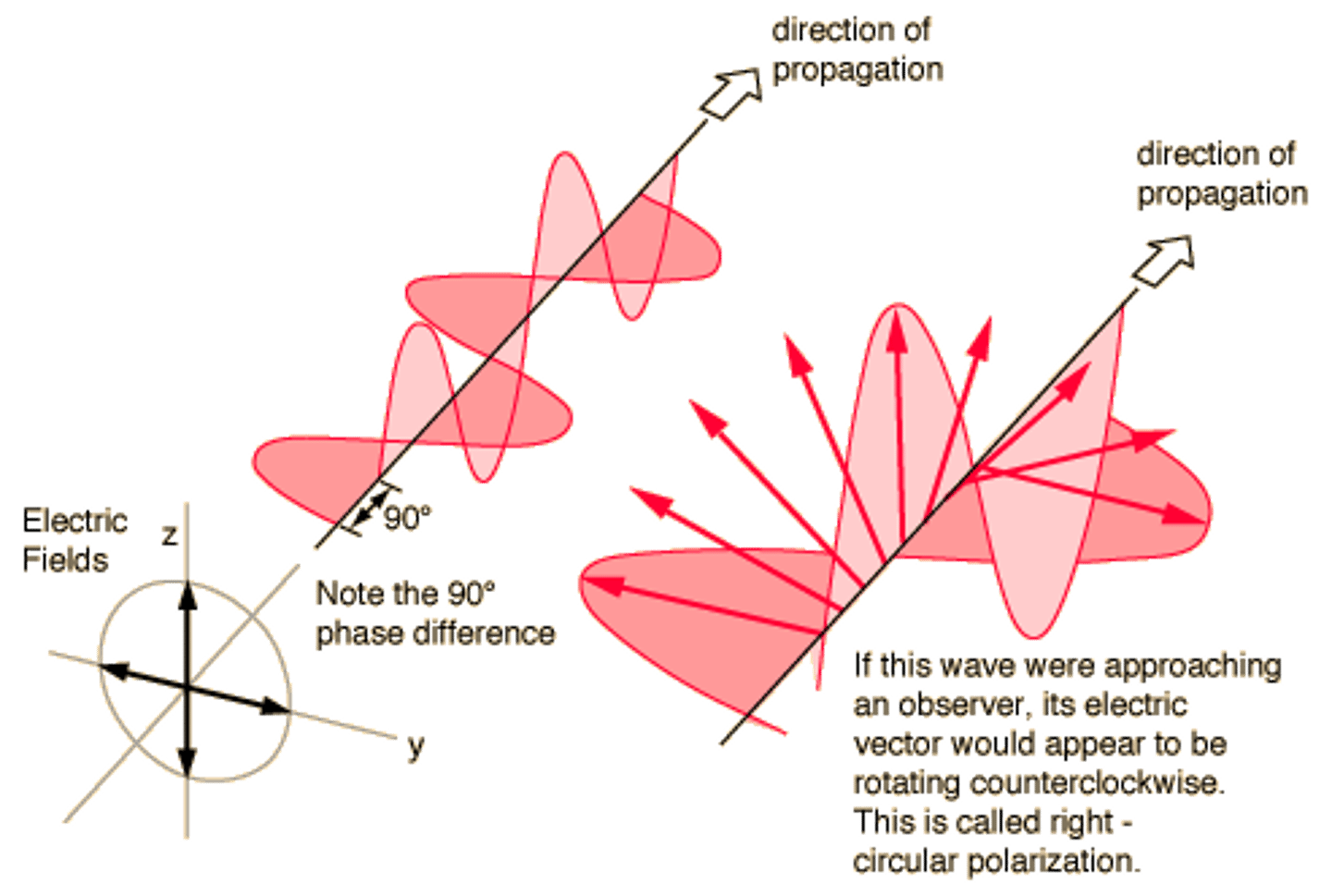
What is Circularly Polarized Light? How is it generated?
It is light whose total vectors move in a circular fashion. It is generated by having two waves set off from each other by 90 degrees.