Physio I Exam 3
1/198
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
199 Terms
What are the parts of the CNS?
Brain and spinal cord.
What are the 2 parts of the PNS?
Somatic and autonomic
Where are afferent nerve signals sent?
To the brain
Where are efferent nerve signals sent?
To the periphery
Which type of cells are more numerous?
Neurons vs Non-neuronal
Non-neuronal
True/False: Neurons can undergo cell division but non-neuronal cells can’t.
False, non-neuronal cells can but neurons can’t
What are the functions of the non-neuronal cells/neuroglia? (6 main ones)
Myelin formation
Control of extracellular environment
Axon development/regen
Immune function
BBB system
Synapse formation/removal
What are the non-neuronal cells in the PNS?
Satellite cells and Schwann cells
What are the non-neuronal cells in the CNS?
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes
Microglia
Ependyma
What shape are astrocytes?
Star-shaped
Where are astrocytes present?
Between nerve cells and blood vessels
What are the functions of the astrocytes?
Provide nutrients & regulate conc. of ions (Calcium)
Structural support for synapses
Forms blood brain barrier
What shape are oligodendocytes?
Marble shaped
What is the function of oligodendrocytes?
Form myelin sheaths around axons in CNS
What is the difference between myelination in the CNS vs in the PNS?
In the CNS, one axon can be myelinated by many olig. or one olig. can myelinate many axons.
In the PNS, one Schwann cell myelinates one axon.
What happens when there is a disruption to the oligodendrocytes?
Myelin sheath disorders occur, like multiple sclerosis
What is the function of microglia?
Scavenge and degrade dead cells & protect from invading microorganisms
What is the function of the ependyma cells?
Produce CSF and line fluid filled ventricles in the brain and central canal of spinal cord
What are the coverings for the CNS?
The cranium and the meninges
What makes up the meninges from top to bottom?
Top - Dura mater
Middle - Arachnoid mater
Bottom - Pia mater
What is meningitis?
A bacterial/viral/fungal infection leading to inflammation of the meninges that can cause paralysis and mental retardation
What layers does meningitis affect?
The arachnoid mater and pia mater
Who is most susceptible to meningitis?
Children and infants
What are the cerebral ventricles from top to bottom?
Top - Lateral ventricles
Middle - Third ventricle
Bottom - Fourth ventricle
Which ventricle is closest to the spinal cord?
The fourth ventricle
Which ventricle is the largest?
Lateral ventricle
What is the lateral ventricle made of?
Anterior, posterior, and inferior horns
What is the function of the third ventricle?
Communicate with lateral ventricle via interventricular foramens
What is the fourth ventricle bound by?
Bound ventrally by pons and medullar oblongata and dorsally by the cerebellum
What is the opening in the fourth ventricle for?
For CSF to exit the ventricular system
What happens when there is damage to the fourth ventricle?
Detrimental for walking and movement
Where is the choroid plexus?
In the ventricles of the brain
What is the choroid plexus made of?
Modified ependymal cells surrounding capillaries and loose connective tissue
What is the function of the choroid plexus?
Produce and secrete most of the CSF in the CNS
What is the source of CSF?
Cerebral ventricles and choroid plexus
What is the rate of CSF formation and the total volume of CSF?
0.5 mL/min and 140-200 mL
Where does the CSF drain to?
The cisterna megna to subarachnoid space to be absorbed into veins at arachnoid granulations
What are the functions of CSF? (4)
Buoyancy for brain and membranes
Mix with brain ECF
Maintain intracranial pressure
Protection during sudden movements
What is hydrocephaly?
An imbalance of CSF produced vs absorbed, causing buildup in the cavities of the brain, putting pressure on the brain and causing damage
Who most commonly suffers from hydrocephaly?
Children and infants
What is hydrocephaly most commonly characterized by?
Head enlargement from fluid buildup
What is the treatment for hydrocephaly?
A tube/shunt inserted in the lateral ventricle for drainage
What do the 2 internal carotid arteries form?
The Circle of Willis
What do the two vertebral arteries form?
The basilar artery
What percentage of total oxygen consumption does the brain account for?
18%
What causes cerebral ischemia?
An occlusion in the carotid in old people
What two properties affect cerebral blood flow?
Blood pressure and cerebrovascular resistance
What happens when arterial BP drops below 70 mmHg?
Cerebral flow is compromised, causing orthostatic hypotension (feeling faint after lying or sitting too much)
What is polycythemia?
A type of blood cancer where there is a high number of RBC in blood, making the blood thick
What is unique about cerebral capillaries?
They are non-fenestrated with tight junctions between their endothelial cells
What are cerebral capillaries surrounded by?
Astrocyte feetsies
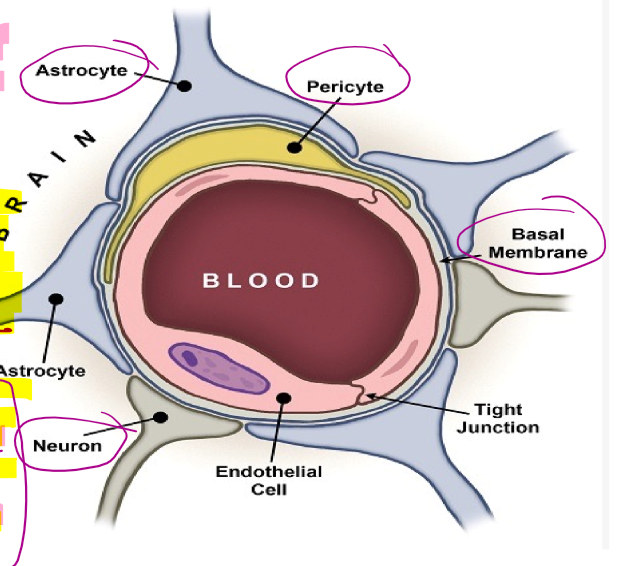
What can pass easily through the cerebral capillaries?
CO2, O2, and water
What is the blood brain barrier?
A highly selective semipermeable border of endothelial cells
What forms the blood brain barrier?
Endothelial cells of capillary walls
Astrocyte end feets
Pericytes in capillary basement membranes
What is the function of the blood brain barrier?
To prevent passage of pathogens, toxins, and solutes into the brain, and also to insulate the brain from damage
What is the definition of a circumventricular organ?
An area in the brain in and around the hypothalamus where the BBB doesn’t exist
What are the circumventricular organs?
PP-ASS:
P- post pituitary
P- pineal body
A- area postrema
S- supraoptic crest
S- subfornical organ
What could breakdown the BBB?
Infection, irradiation, tumors, sudden increases in BP
What is a column of nervous tissue continuous with brain?
The spinal cord
Where does the spinal cord begin and end?
Begins just outside cranial cavity and ends between 1st and 2nd lumbar vertebrae
How many segments of the spinal cord are there, and what are the categories?
31 total segments
Cervical (8)
Thoracic (12)
Lumbar (5)
Sacral (5)
Coccygeal (1)
What kind of matter is the spinal cord made of?
Gray matter with posterior, lateral, and anterior horns
What are the functions of the spinal cord? (2)
Conduction of info to and from brain
Integrative center for reflexes (patellar, withdrawal, evacuation)
Where does sensory information travel on the ascending tracts?
From the periphery to the brain
Where does sensory information travel on the descending tracts?
From the brain to the periphery
What are the parts of the ascending tract of the spinal cord, and what sensations do they account for?
F. gracilis & cuneatus - touch, pressure, and body movement
Spinothalamic - pain and temperature
Spinocerebellar - muscle coordination in legs and trunk
What are the parts of the descending tract of the spinal cord, and what impulses do they account for?
Corticospinal (pyr) - voluntary movement
Reticulospinal (expyr) - muscle tone and sweat
Vestibulospinal (expyr) - equilibrium and posture
Rubrospinal (expyr) - muscle coordination and posture control
Tectospinal (expyr) - head and eye movements
What would happen if there were an injury to the corticospinal tract of the spinal cord, and is this in the ascending or descending tract?
Descending. The person would experience flaccid paralysis
Contrast the symptoms of flaccid and spastic paralysis
Flaccid - loss of muscle tone and muscle atrophy
Spastic - increased muscle tone (stiffness) and no atrophy
What are the 4 parts of the brain?
Brain stem
Diencephalon
Cerebellum
Cerebrum
Where does the brain stem start and end?
Starts: base of cerebrum
Ends: foremen magnum
What type of matter is the brain stem composed of?
White and grey matter
What are the three parts of the brain stem?
Medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
Pons (metencephalon)
Midbrain (mesencephalon)
What do the visceral activity centers of the medulla oblongata regulate?
Cardiac, vasomotor, respiratory, and swallowing activities
What is the bulging area of the brain?
The pons of the brain stem
The reticular activating system (RAS) connects what parts of the brain?
The hypothalamus to higher brain centers
What acts as a sensory gating system for ascending and descending tracts of the brain?
RAS formation
What is the RAS formation associated with?
Sleep/wake cycles
What formation is affected by hypnotics and anesthetics?
RAS formation
What part of the brain is the hypothalamus and limbic cortex located in?
The diencephalon
What is associated with the hypothalamus?
Hunger/thirst, body temp control, water and electrolyte balance
What is associated with the hippocampus?
Learning/memory
What is the function of the cerebellum?
Coordination of skeletal muscle activities
How many lobes are in the cerebrum and what are they called?
Four: Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital
What comprises the cerebrum?
Cortex, white matter, and basal ganglia
What does the motor area of the cerebrum regulate?
Skeletal muscle movement
What does the sensory area of the cerebrum regulate?
Reception of sensations
What does the association area of the cerebrum regulate?
Higher order thinking like learning to speak
Which hemisphere of the brain is usually dominant in humans?
The left
What two areas regulate our ability to talk?
Broca’s area and Wernicke’s area
What are defects in the Broca’s area associated with?
Trouble speaking properly
What part of the basal ganglia of the cerebrum is associated with Parkinson’s disease?
The substantia nigra
What system is the amygdala and hippocampus a part of?
The limbic system
What is the fear center of the brain?
Amygdala
What is the learning and memory center of the brain?
Hippocampus