year 9 chemistry
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
fuels, earth and atmospheric science
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
types of non-renewable fossil fuels
natural gas, crude oil
what is a non-renewable fuel
a fuel that can run out (fossil fuels)
what are fossil fuels made from
ancient remains of animals and plants
what state is crude oil at room temperature
liquid
what is crude oil used for
to make petrochemicals
crude oil are
hydrocarbons
natural gases are
hydrocarbons in the gas state
how are crude oils separated
using fractional distillation
is a factional distillation column hotter at the top or bottom
bottom
boiling point of petrol
40
boiling point of naptha
110
boiling point of kerosene
180
boiling point of diesel oil
260
boiling point of residue
340
what is petrol used for
used in cars
what is naptha used for
used in chemical production
what is kerosene used for
used at jet fuel
what is diesel oil used for
used in diesel engines
what is reidue used for
fuel for ships
what is a homologous series
compound with the same general formula and similar properties
what’s the name for single-bond carbon atoms
alkanes c-c
what is produced when an alkane reacts with oxygen
carbon dioxide and water (and energy)
do longer chains have lower or higher boiling points
higher
complete combustion happens when
there is enough oxygen
incomplete oxygen happens when
their is not enough oxygen
what is produced during complete combustion
carbon dioxide and water (and energy)
what is produced during incomplete combustion
carbon monoxide, carbon, (soot) and water (less energy produced)
carbon monoxide
a toxic gas
is carbon monoxide acidic
yes
how is sulphur dioxide formed
When fuels containing sulphur impurities is burned
what does sulphur + water form
acid rain
effects of acid rain
plants don’t grow well, kills fish, weathers buildings,
what is the process of breaking hydrocarbons
cracking
what type of bond is made during cracking
carbon carbon bonds c=c
smaller hydrocarbons are used as
fuels
what type of hydrocarbons have c=c bond
alkenes
what was the main gas in the early atmosphere
carbon dioxide (small amounts of water vapor)
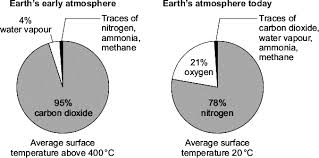
when did most gases come from
volcanic activity
how were oceans formed
water vapour condensed
how was carbon dioxide removed in earths early atmosphere
it was dissolved in oceans
what is earth atmosphere like today
78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen and small amounts of other gases
what are some green house gases
carbon dioxide, methane and water vapour
how is carbon dioxide realised into the atmosphere
by burning fossil fuels
how is methane produced
when oil and natural gas are extracted and processed, cattle, landfill sites and rice fields
what are the effects of global warming on oceans
glaciers melt
which causes sea levels to rise
which causes flooding
what are the effects of global warming on animals
some now cant handle the weather in their natural habitat so they have to find new ones
what are the effects of global warming on weather
weather events and becoming more extreme and destructive
how many carbon atoms does methane contain
1
how many carbon atoms does ethane contain
2
how many carbon atoms does propane contain
3
how many carbon atoms does butane contain
4