Quiz 4: Biomedical Sciences - Anderson
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
What are the primary roles and functions of cellular membranes?
- barriers that separate the cell from its environment and compartments within the cell
- regulate movement of small molecules and ions into/out of cells or organelles
- provide biochemical features that influence diffusion, transport, and signaling
Which types of molecules have high permeability through lipid bilayers?
Lipid‐soluble (hydrophobic) molecules
Which types of molecules have very low permeability through lipid bilayers?
Charged molecules like ions
Classify these molecules from highest to lowest lipid bilayer permeability.
- large uncharged polar molecules
- hydrophobic molecules
- small uncharged polar molecules
- ions
1. hydrophobic molecules (highest)
2. small uncharged polar molecules
3. large uncharged polar molecules
4. ions (lowest)
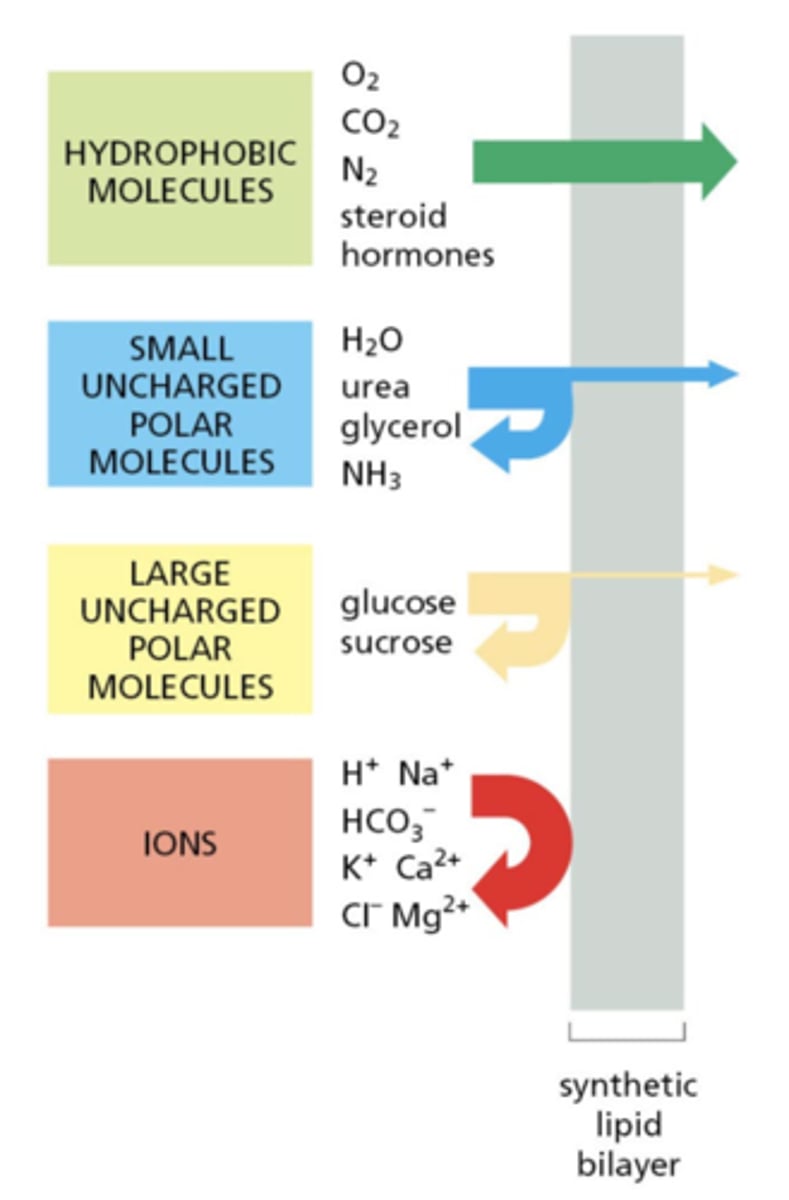
What determines how rapidly a molecule crosses the bilayer?
The smaller the molecule and the less strongly it interacts with water, the faster it crosses
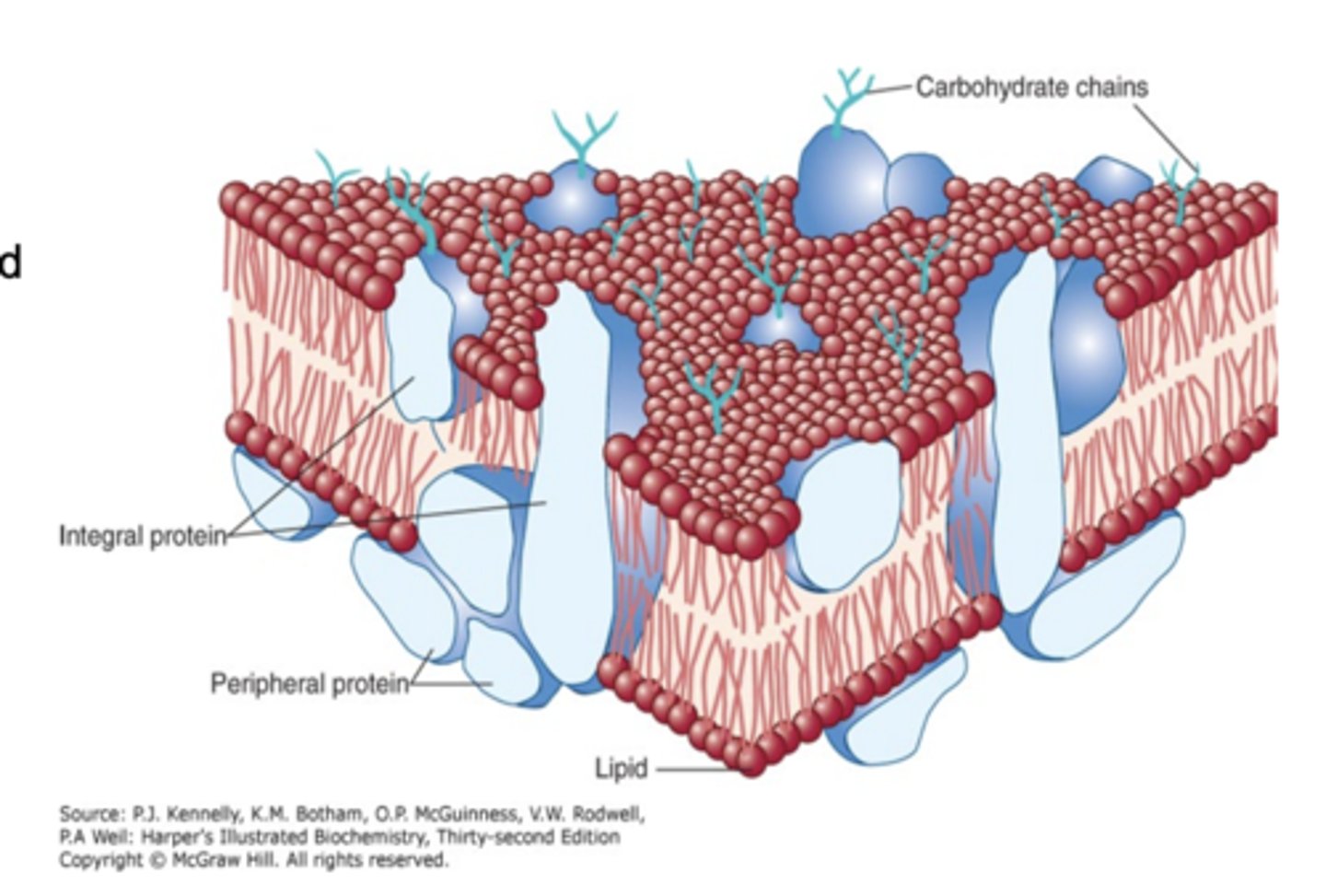
What are the two key features of the fluid mosaic model of membranes?
1. Membrane consists of a lipid bilayer with proteins inserted or bound to its surface
- proteins have different functions based on their locations
2. The membrane is fluid
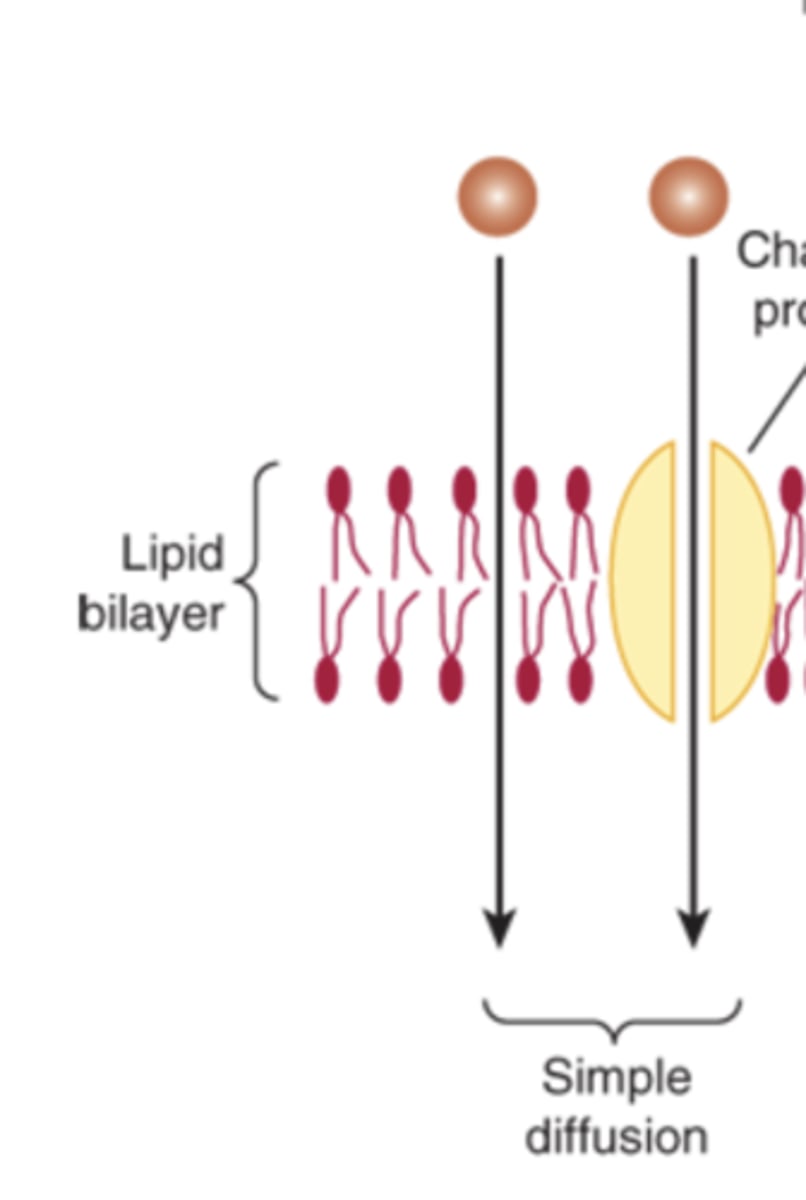
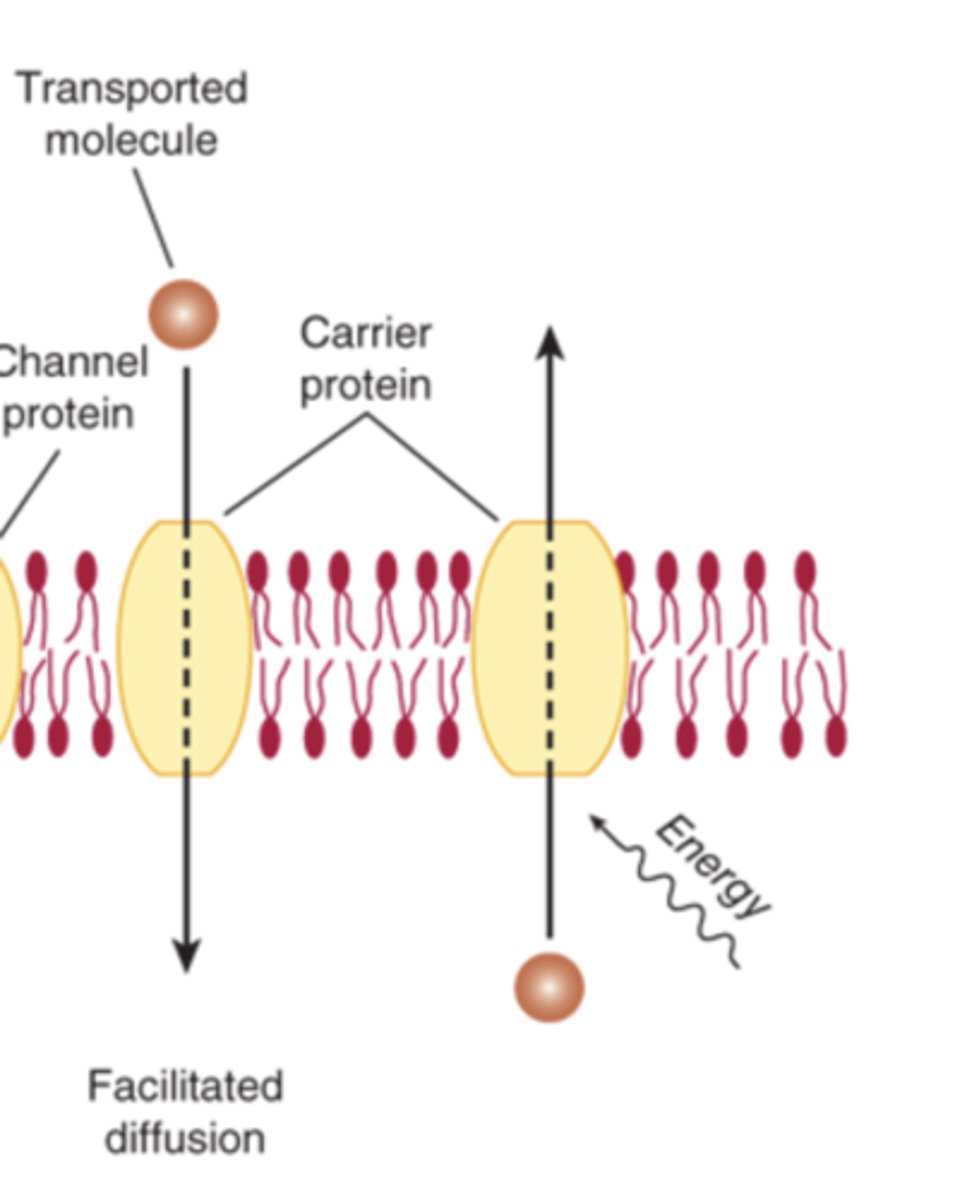
What are the three main types of membrane transport of small molecules?
facilitated diffusion, simple diffusion, active transport
How do transporters move solutes across the lipid bilayer?
- bind solutes
- undergo conformational changes and move them across the membrane
**they may use facilitated diffusion or active transport slower than ion channels
How do ion channels differ from transporters?
- form pores across the bilayer
- allows for rapid passive diffusion of ions down their electrochemical gradient
faster
How do small uncharged molecules pass through the bilayer?
By simple diffusion or through channels
How do transporters move solutes?
Via facilitated diffusion or energy-dependent mechanisms, often following a concentration gradient
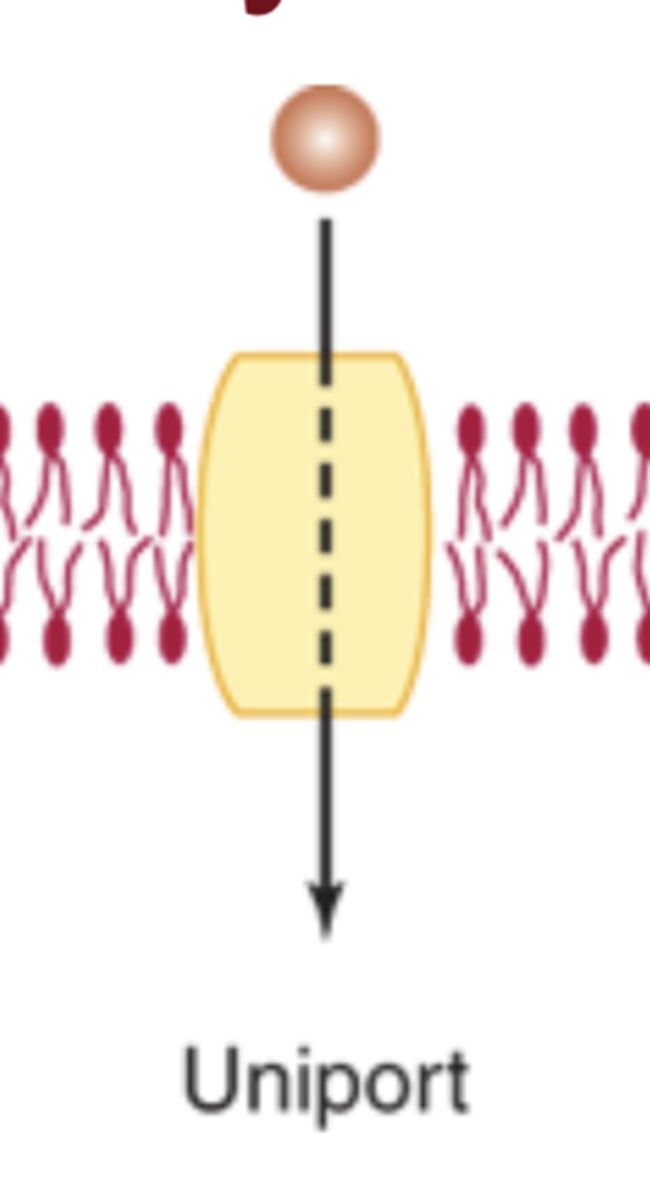
Uniport
Moves one solute in one direction
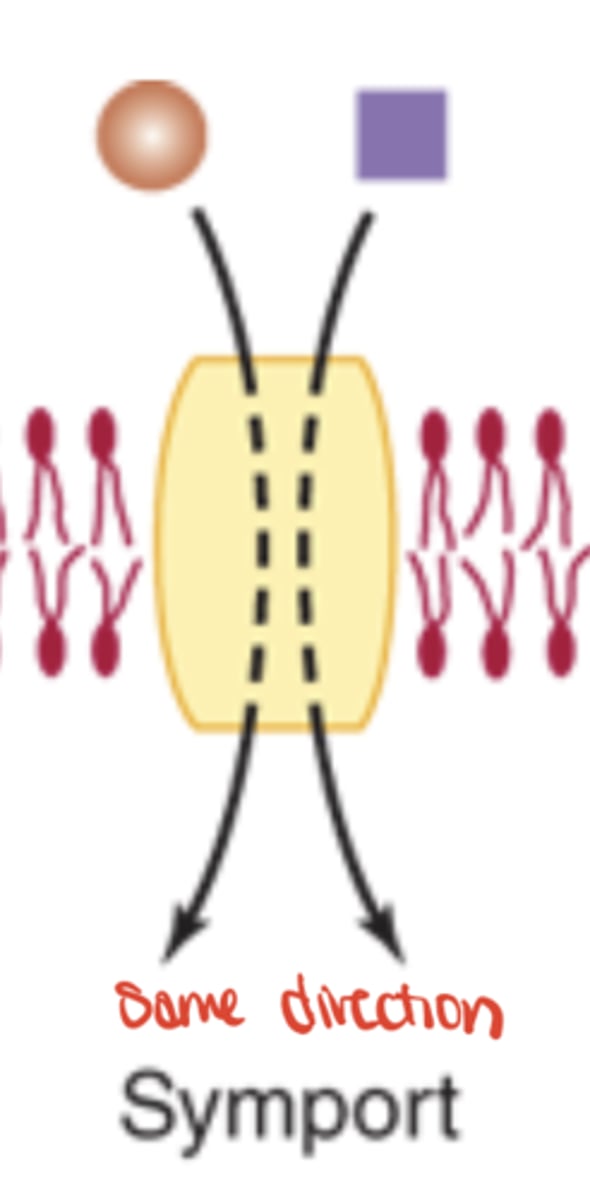
Symport
Moves two solutes in the same direction
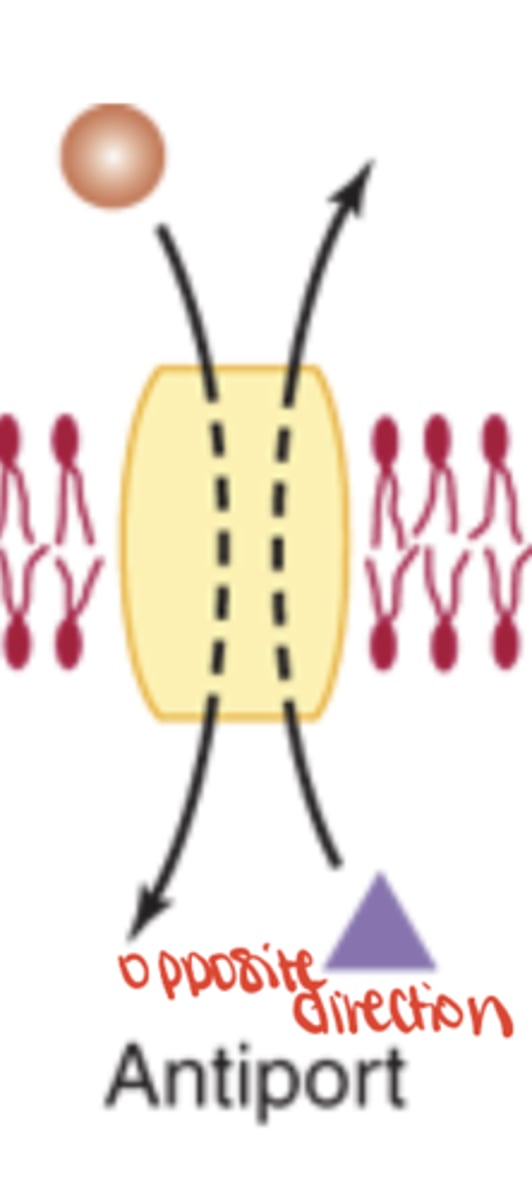
Antiport
Exchanges solutes in opposite directions (ex. Na+/K+ ATPase)
How is sodium distributed across the plasma membrane?
High outside, low inside
How is potassium distributed?
High inside, low outside
Why is calcium tightly regulated inside cells?
intracellular calcium must remain very low so that small changes trigger signaling cascades
What are the key properties of ion channels?
- composed of transmembrane protein subunits
- usually selective for a single ion
- allow impermeable ions to cross membranes
- activity can be regulated (voltage, ligands, mechanical forces)
Passive Transport
spontaneous, down concentration gradient (via diffusion, channels, passive transporters)
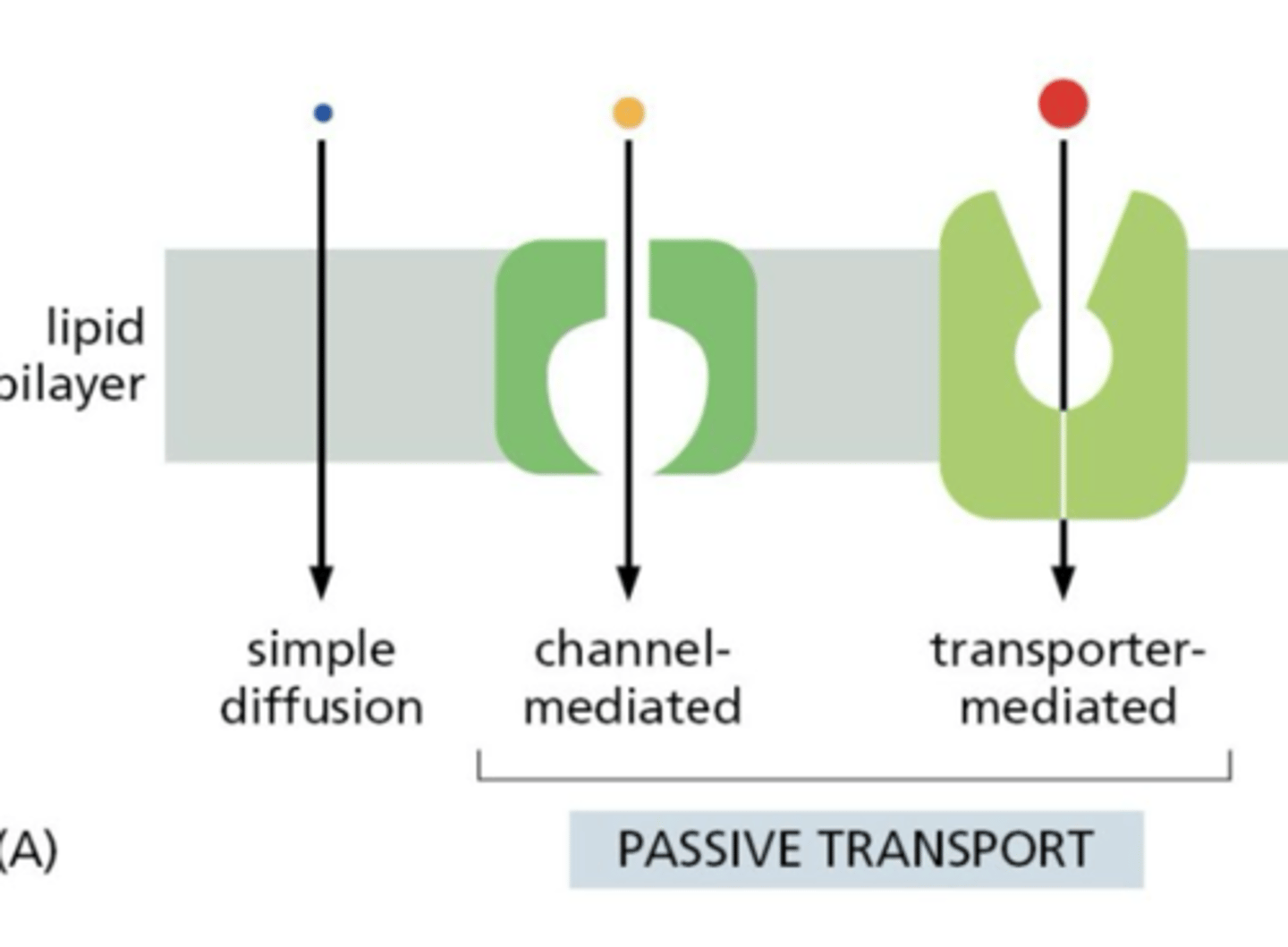
Active Transport
transport against gradient, requires ATP
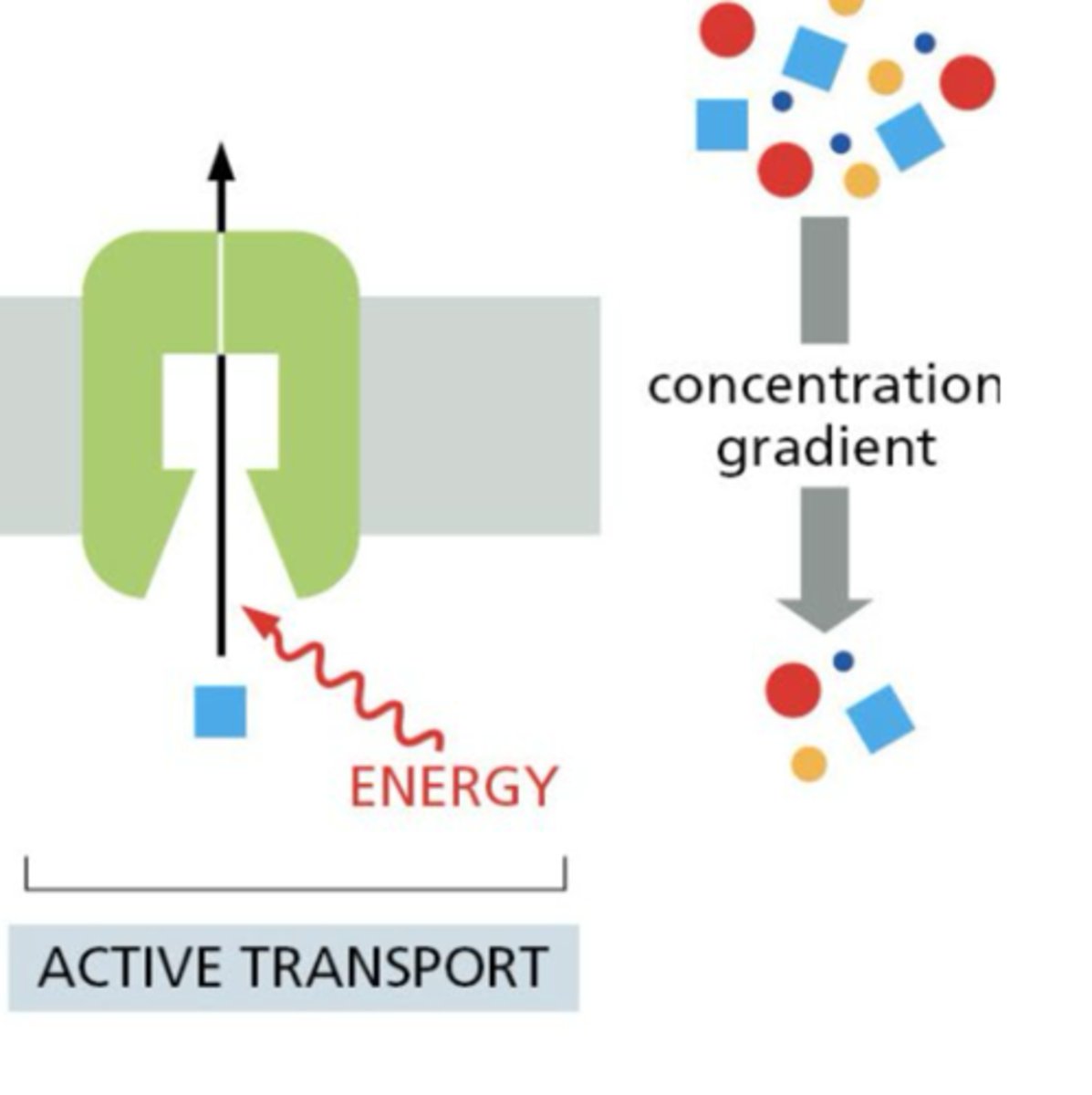
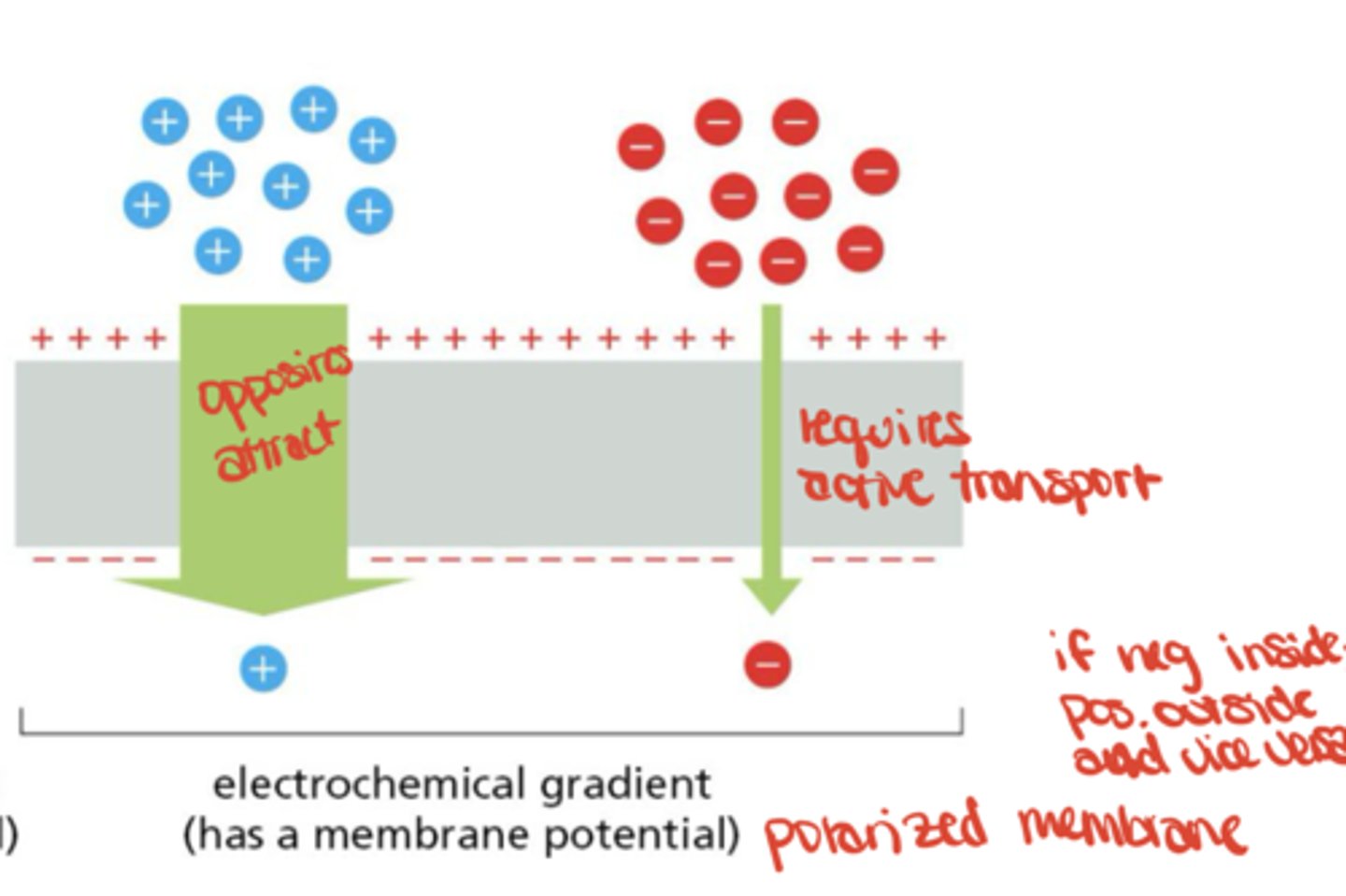
Electrochemical Transport
transport is influenced by membrane potential of charged solutes
What are ATP-driven pumps?
membrane proteins that use ATP hydrolysis to move solutes/ions against their gradients
How does ATP/ADP ratio influence them?
High ATP/ADP: pumps hydrolyze ATP to move solutes
Low ATP/ADP: some pumps can synthesize ATP
What are the three functional domains of a calcium ATPase pump?
1. nucleoside binding domain (binds ATP)
2. phosphorylation domain (receives phosphate group)
3. actuator domain (conformational changes drive transport)
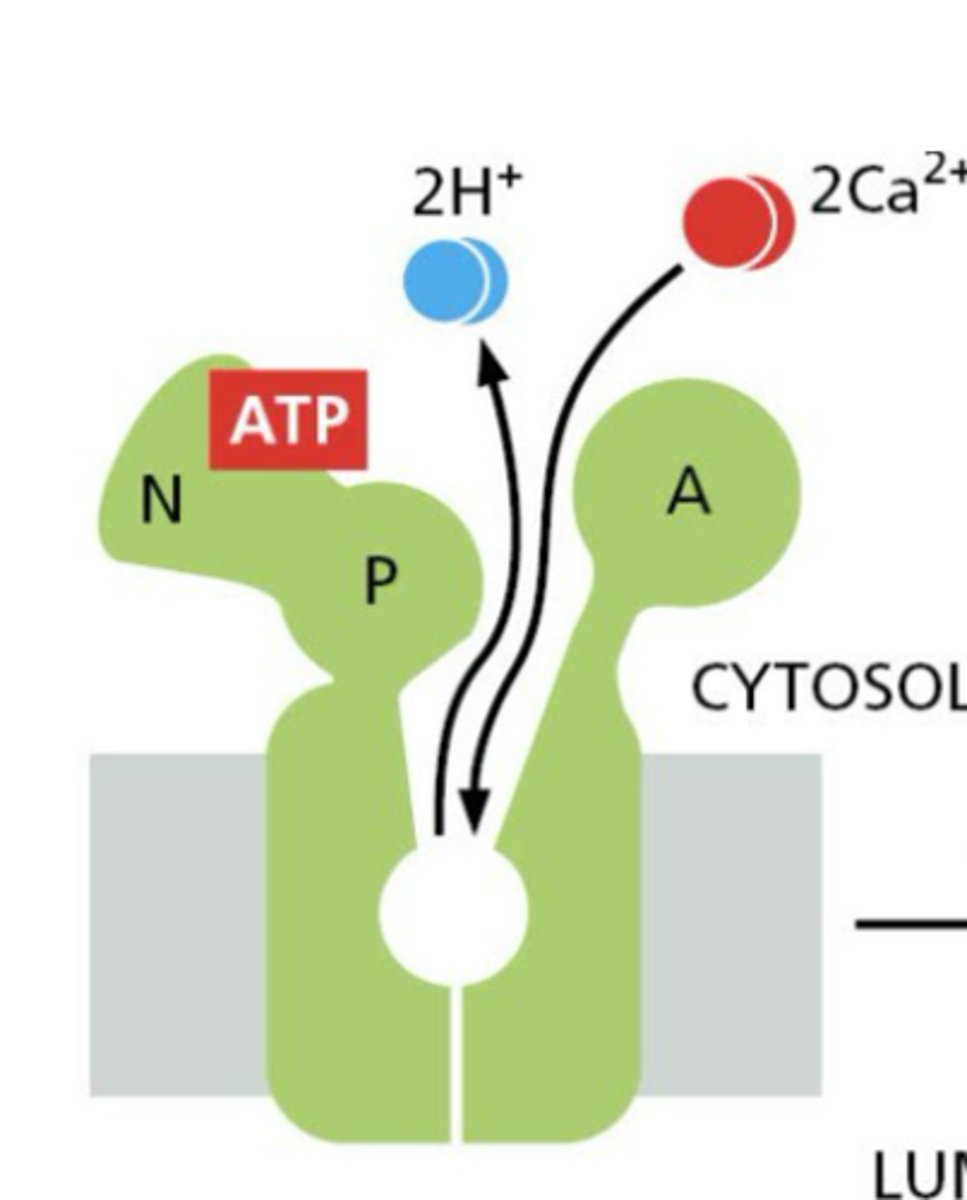
Why is calcium pumping important?
Maintains low cytosolic calcium, regulates signaling, and controls ER/SR calcium stores
What is the role of Na⁺/K⁺ ATPase pumps?
use ATP to drive sodium out and potassium in, maintaining steep gradients across the plasma membrane
Which ion is higher inside vs. outside?
Sodium: higher outside
Potassium: higher inside
How do ion channels fluctuate?
Between open and closed conformations
What gives channels selectivity?
Narrowing of the pore to atomic dimensions at one region, allowing only specific ions to pass
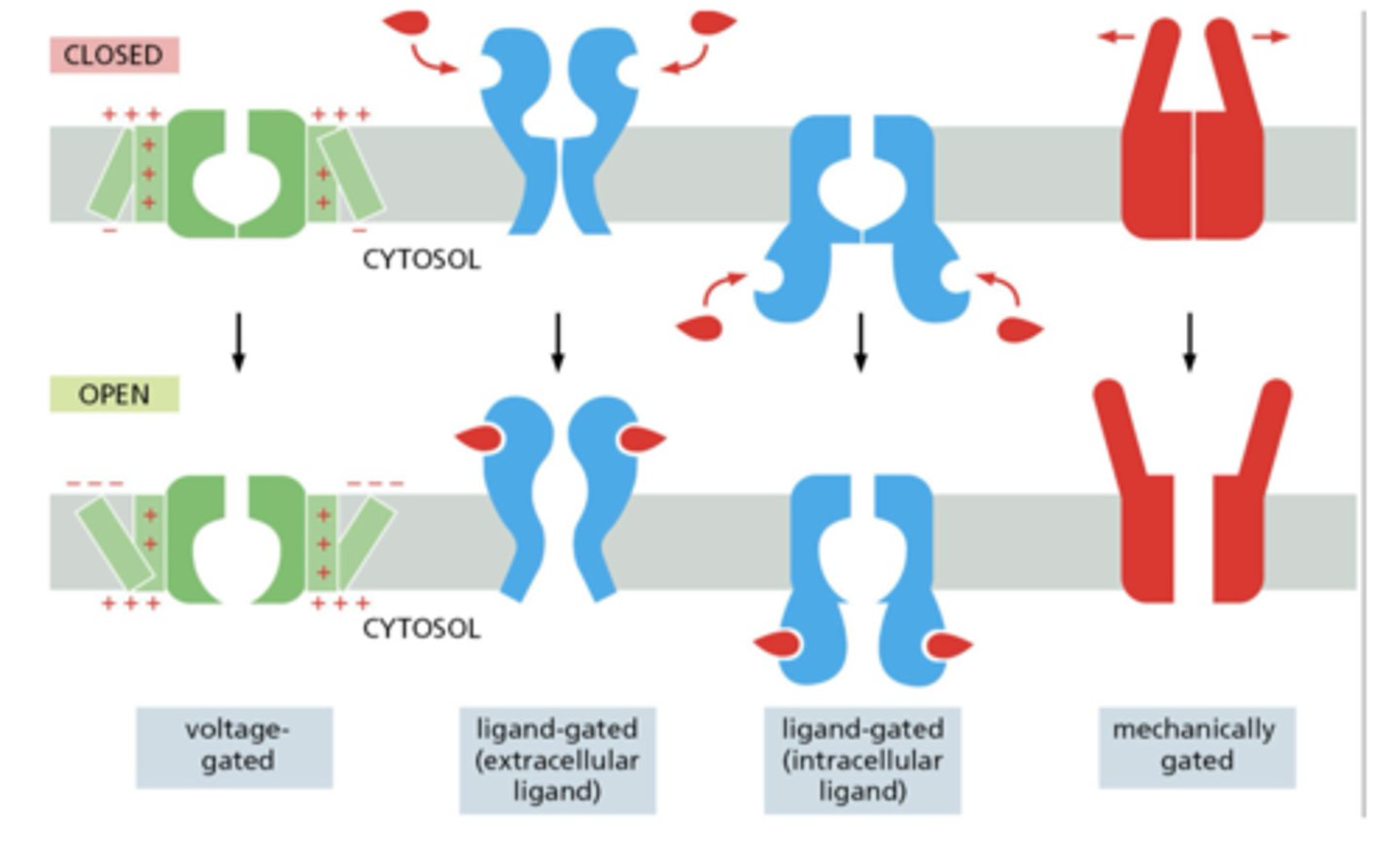
What are the main gating mechanisms of ion channels?
1. Voltage-gated
2. Ligand-gated (extracellular or intracellular)
3. Mechanically gated
How do ions give rise to membrane potential?
by forming surface layers of charge near the membrane, held by attraction to counterions across the bilayer
Do large numbers of ions move to generate potential?
No, very few ions move
- bulk intracellular concentration remains unchanged
How does voltage gating occur in ion channels?
by oscillation of voltage-sensing domains, exposing charged amino acids to alternate sides of the membrane
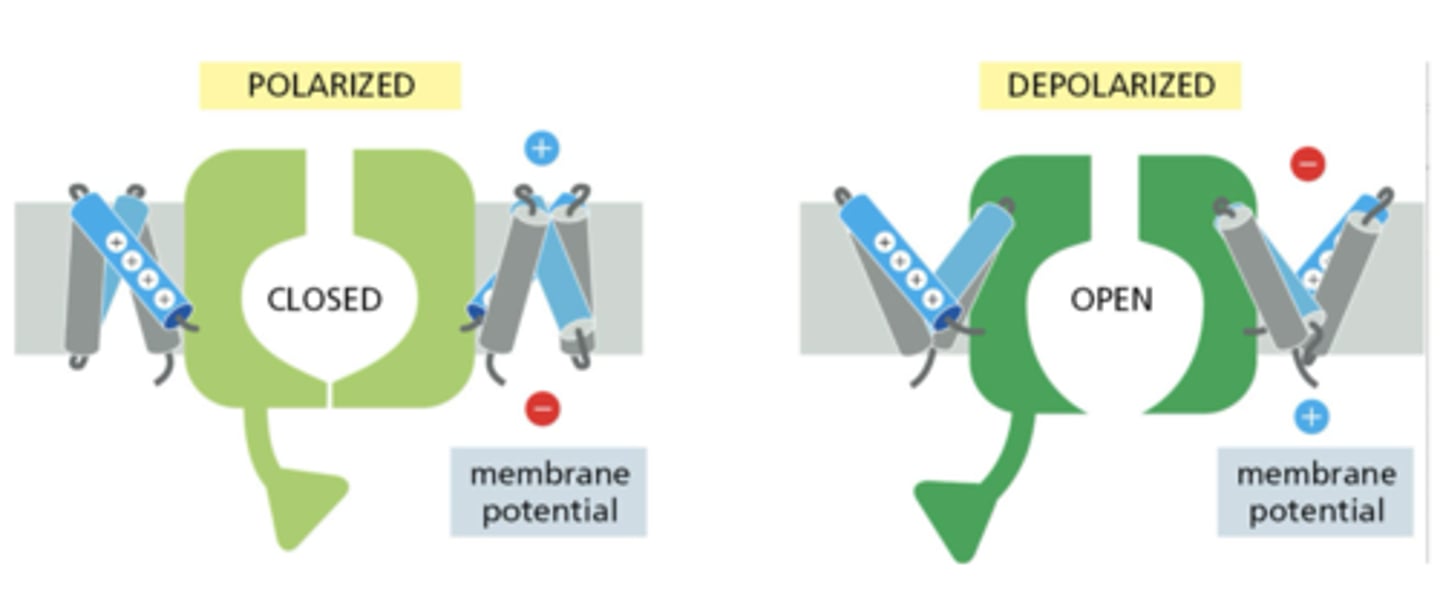
Which conformation is thermodynamically favored?
exposure of positive residues to the more negative side of the membrane
What are the main components of a signaling pathway?
- receptor (extracellular or intracellular)
- signaling molecule (ligand)
- effector proteins
- cellular responses (altered metabolism, gene expression, cell shape, movement)
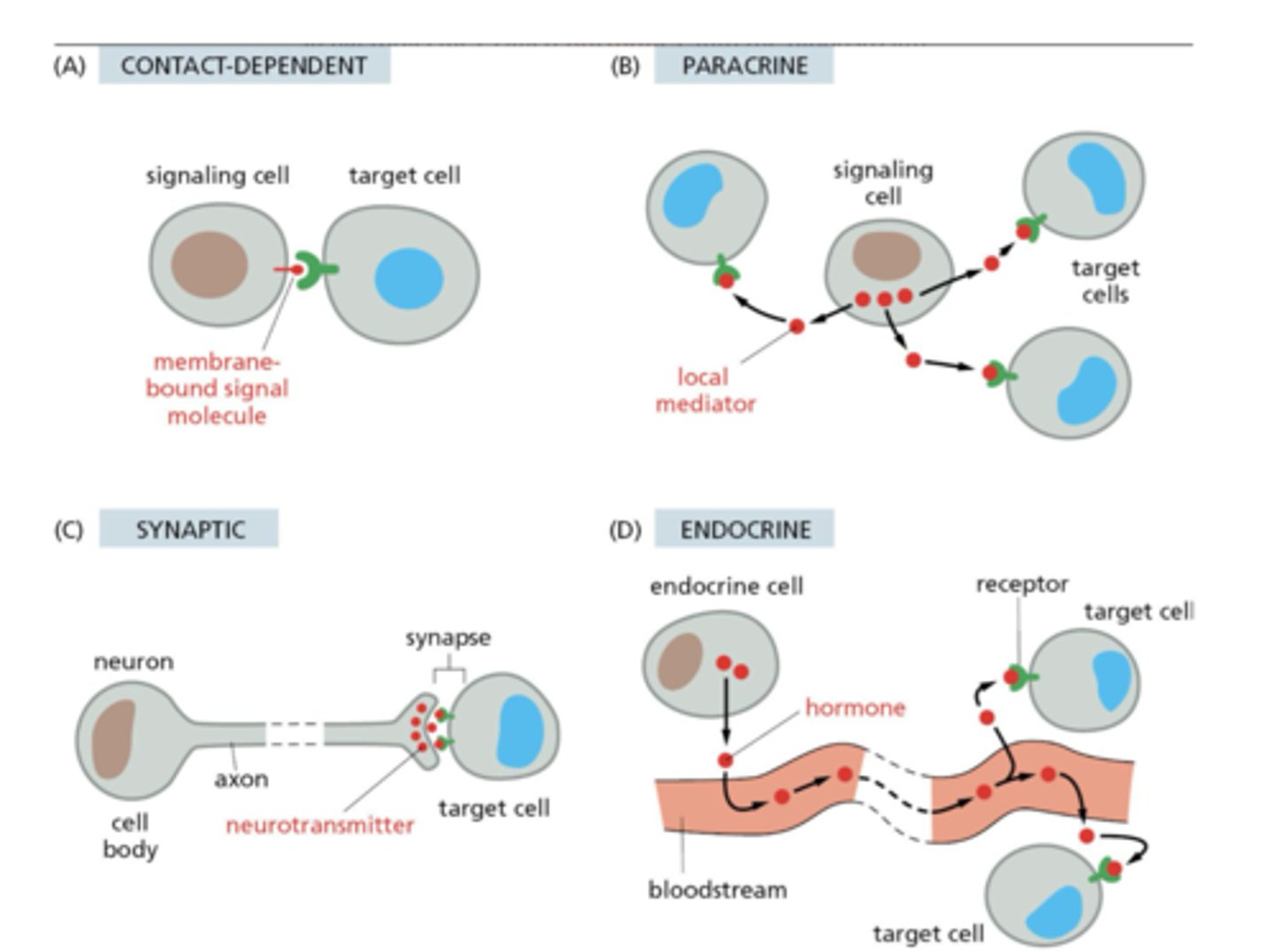
What are the four types of intercellular signaling?
1. Contact-dependent
2. Paracrine
3. Synaptic
4. Endocrine
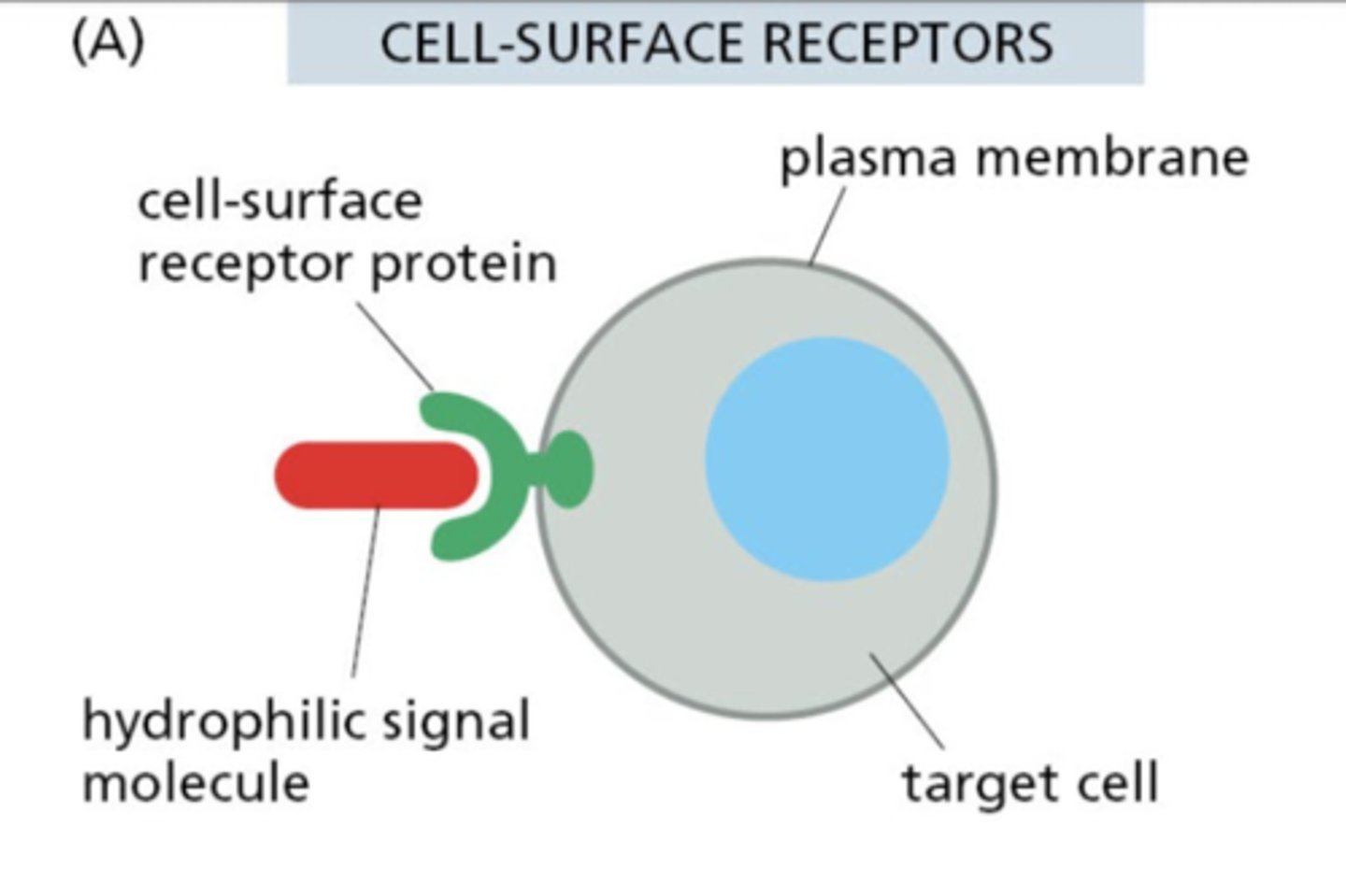
What characterizes most extracellular signal molecules?
They are hydrophilic and cannot cross membranes, so they bind extracellular receptors
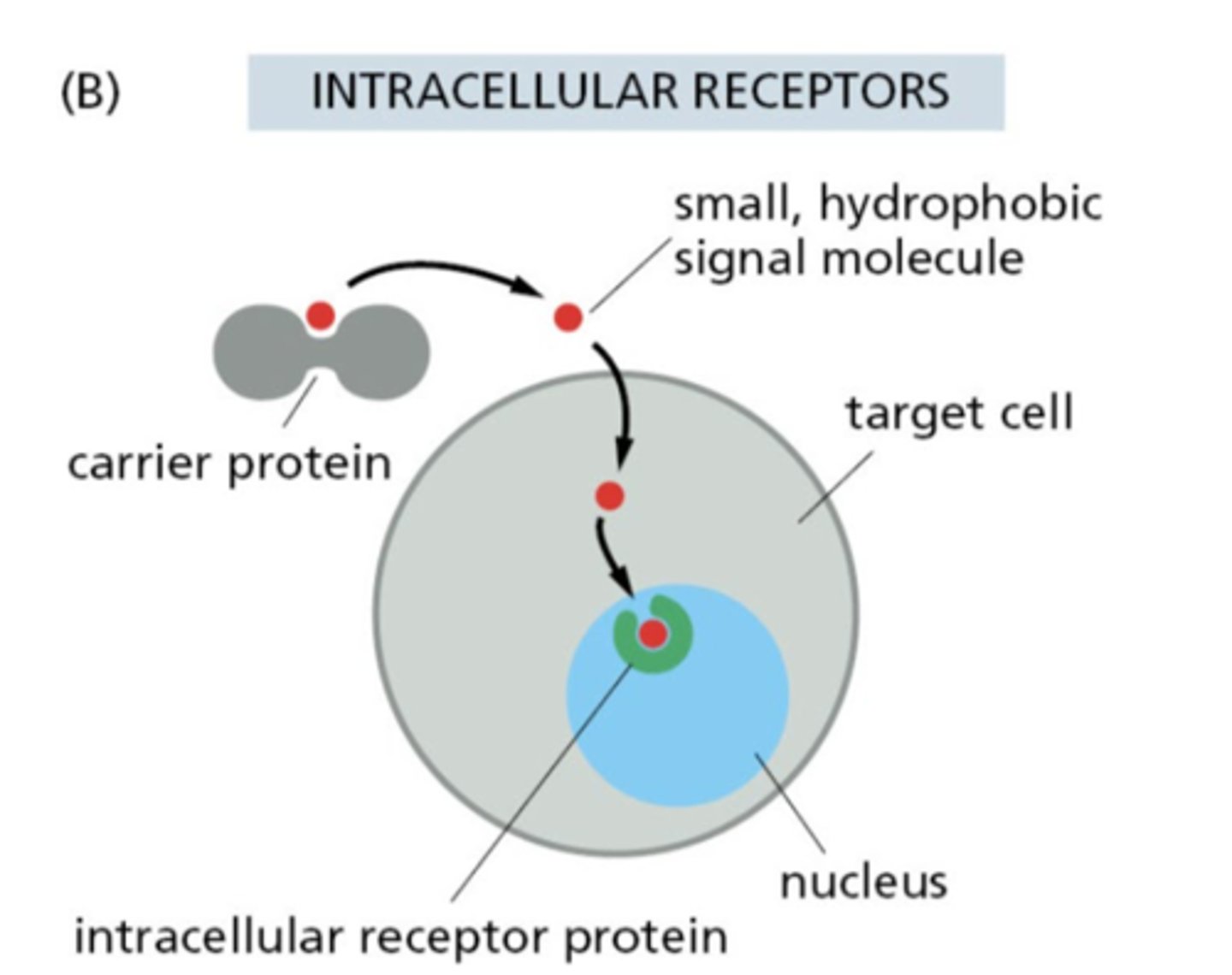
What characterizes small hydrophobic signal molecules?
They can diffuse across membranes, often binding intracellular receptors; many travel bound to carrier proteins
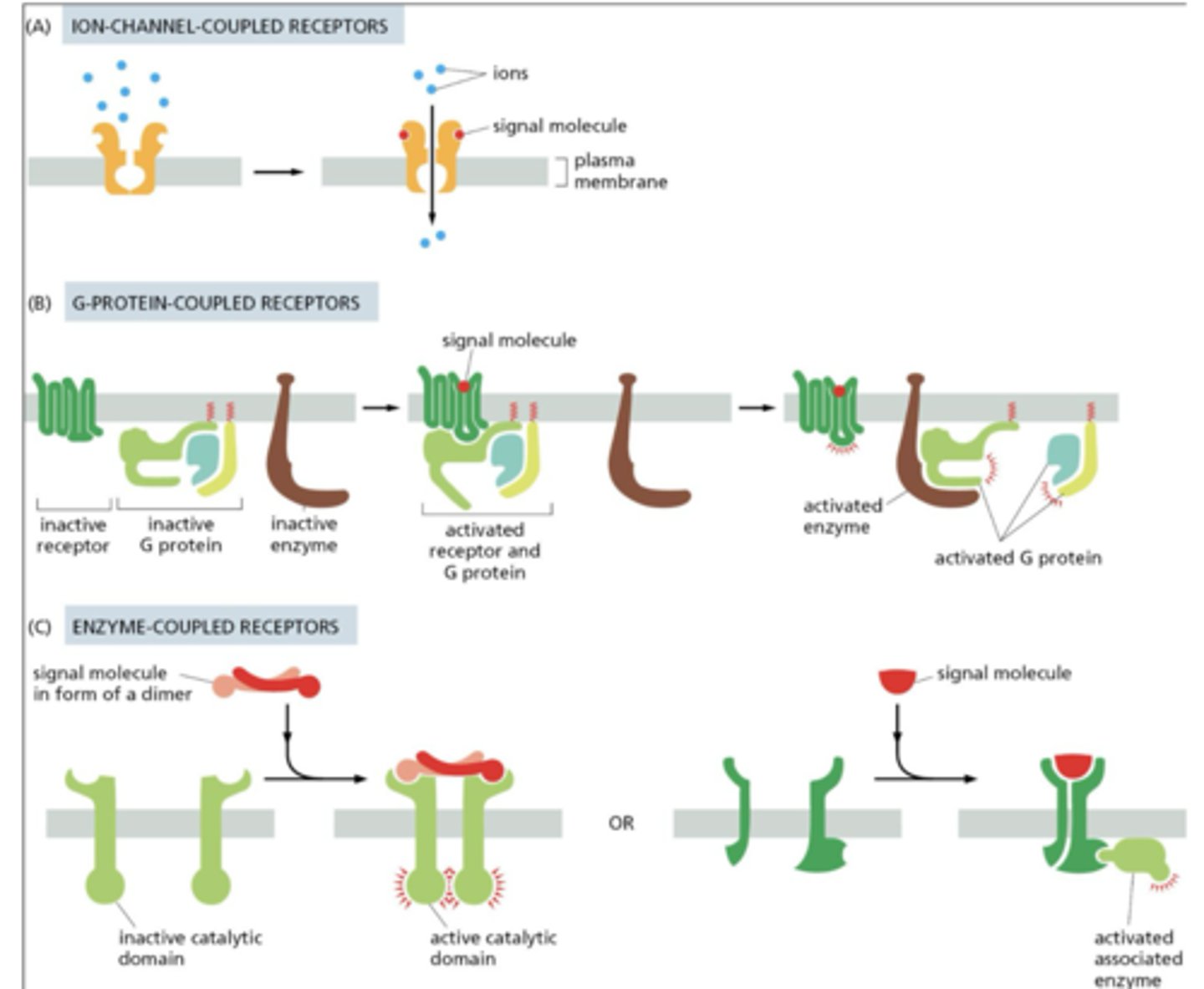
What are the three classes of cell surface receptors?
1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors (ligand-gated ion channels)
2. G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs)
3. Enzyme-coupled receptors
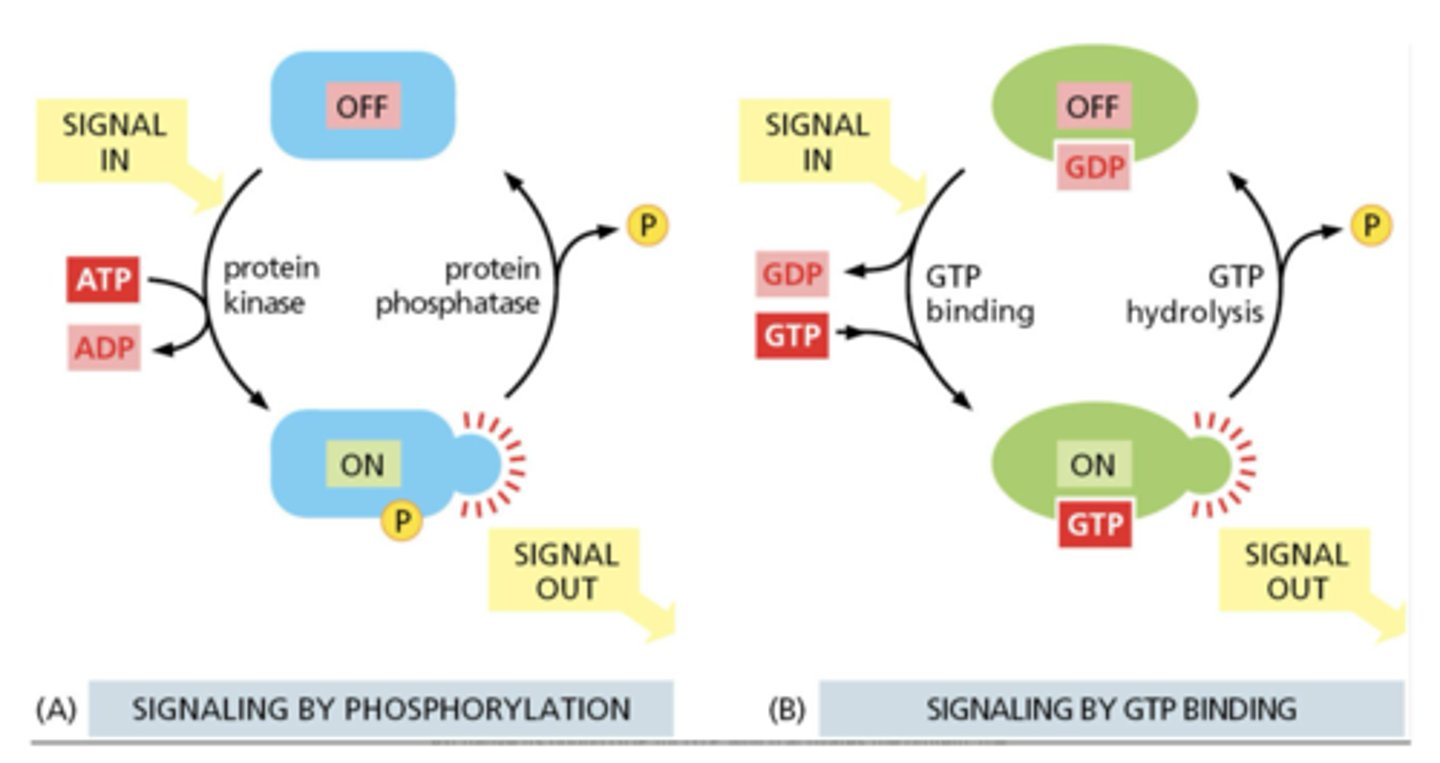
What are the two main types of intracellular molecular switches?
1. Phosphorylation (kinases/phosphatases)
2. GTP-binding (GTPases)
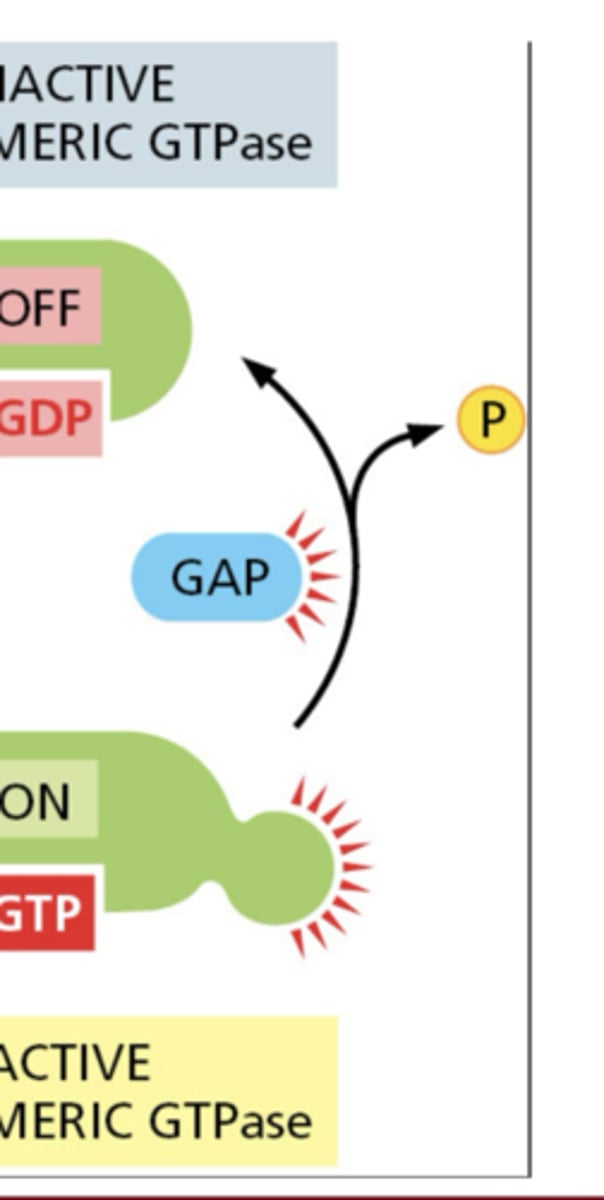
What do GAPs (GTPase-activating proteins) do?
inactivate GTPases by stimulating GTP hydrolysis to GDP
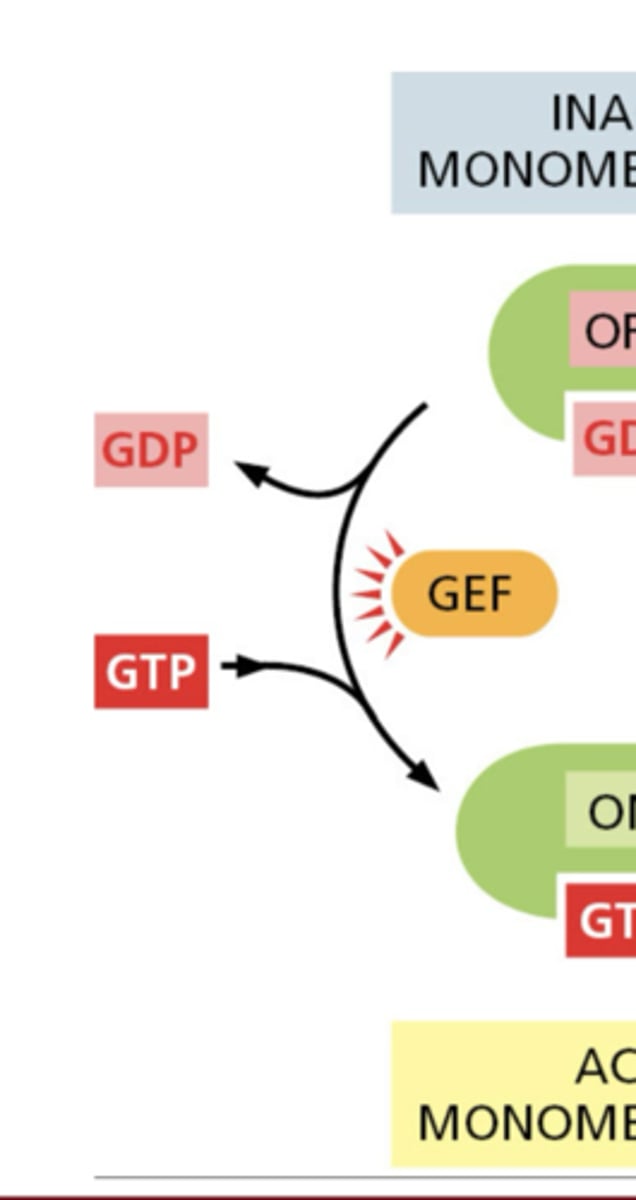
What do GEFs (guanine nucleotide exchange factors) do?
activate GTPases by stimulating GDP release and GTP binding
Why does GTP binding occur quickly?
cytosolic GTP concentration is ~10x greater than GDP
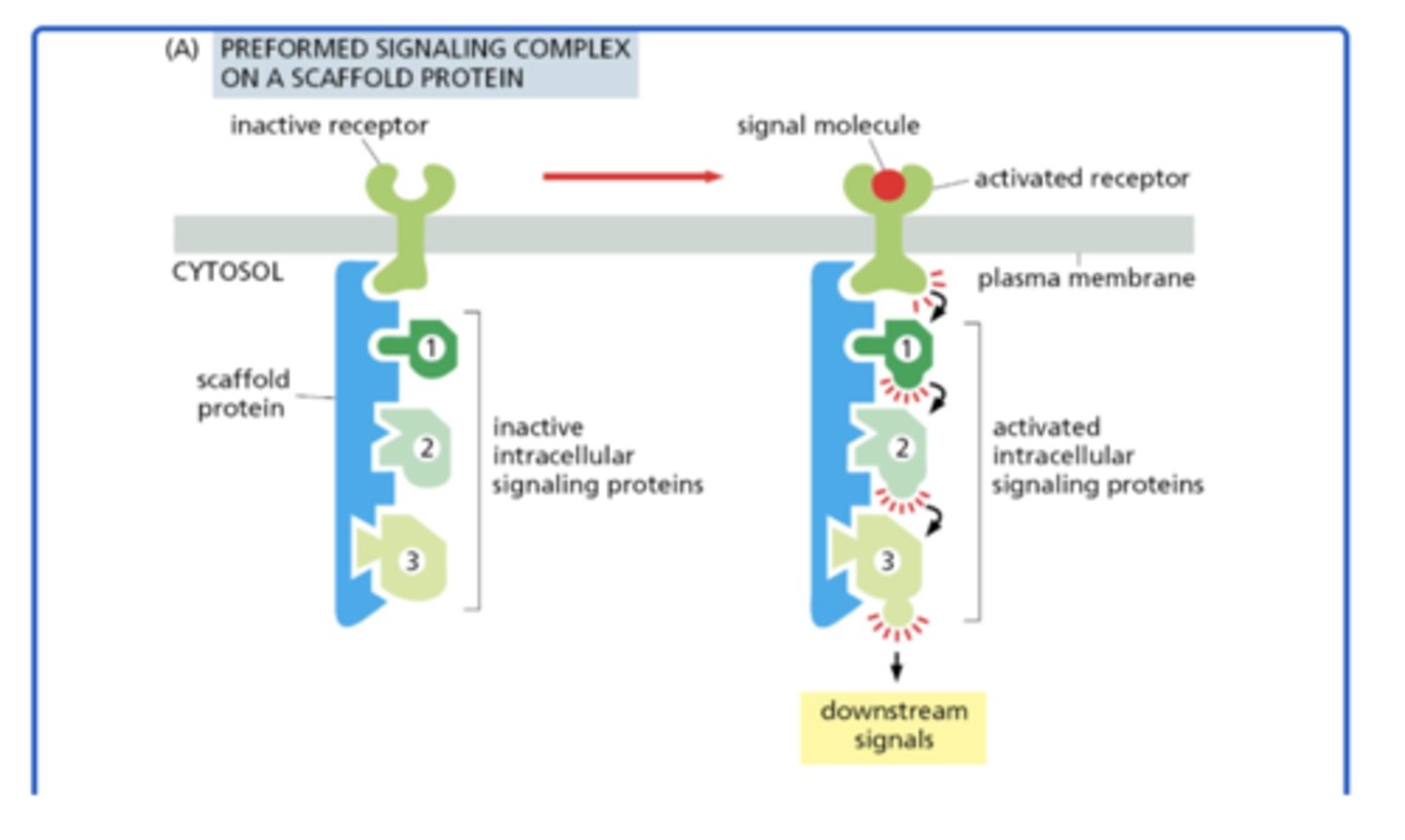
How can intracellular signaling complexes form via scaffold proteins?
preformed on a large scaffold protein, which holds receptors and signaling proteins together even before activation
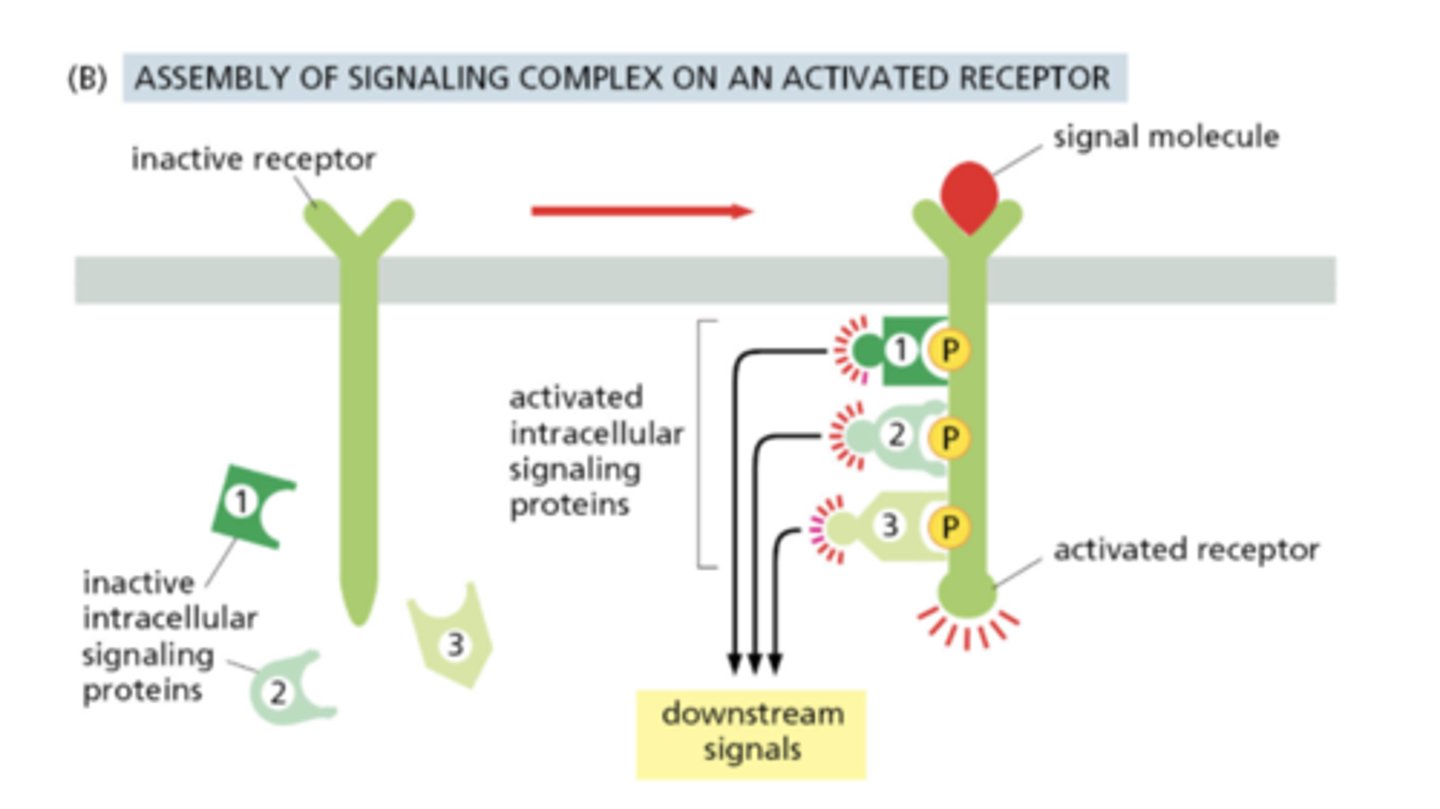
How can intracellular signaling complexes assemble on an activated receptor?
After ligand binding and receptor autophosphorylation, intracellular signaling proteins transiently dock to the receptor
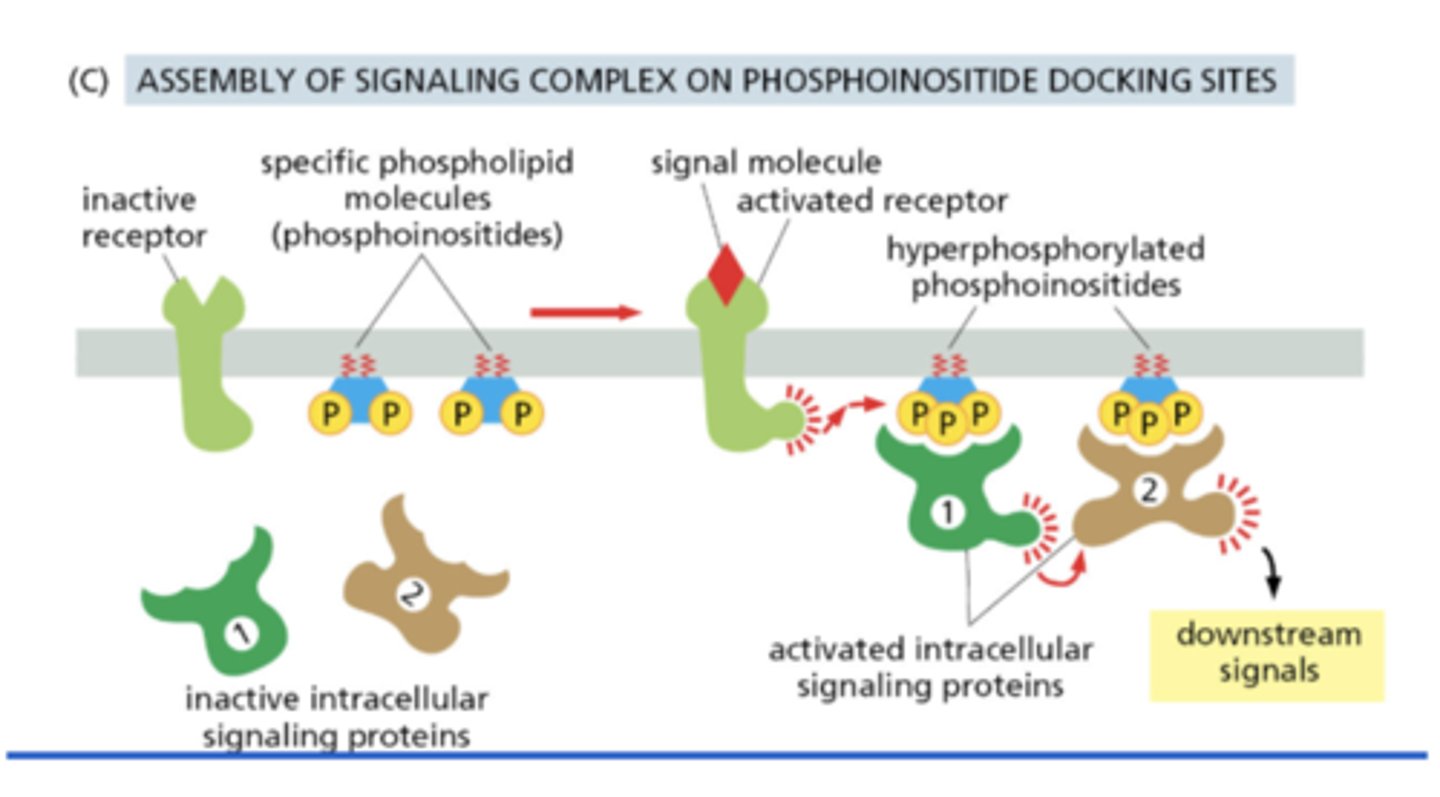
How can intracellular signaling complexes form on phosphoinositides?
receptor activation increases phosphoinositide phosphorylation in the plasma membrane, which then serves as docking sites for signaling proteins
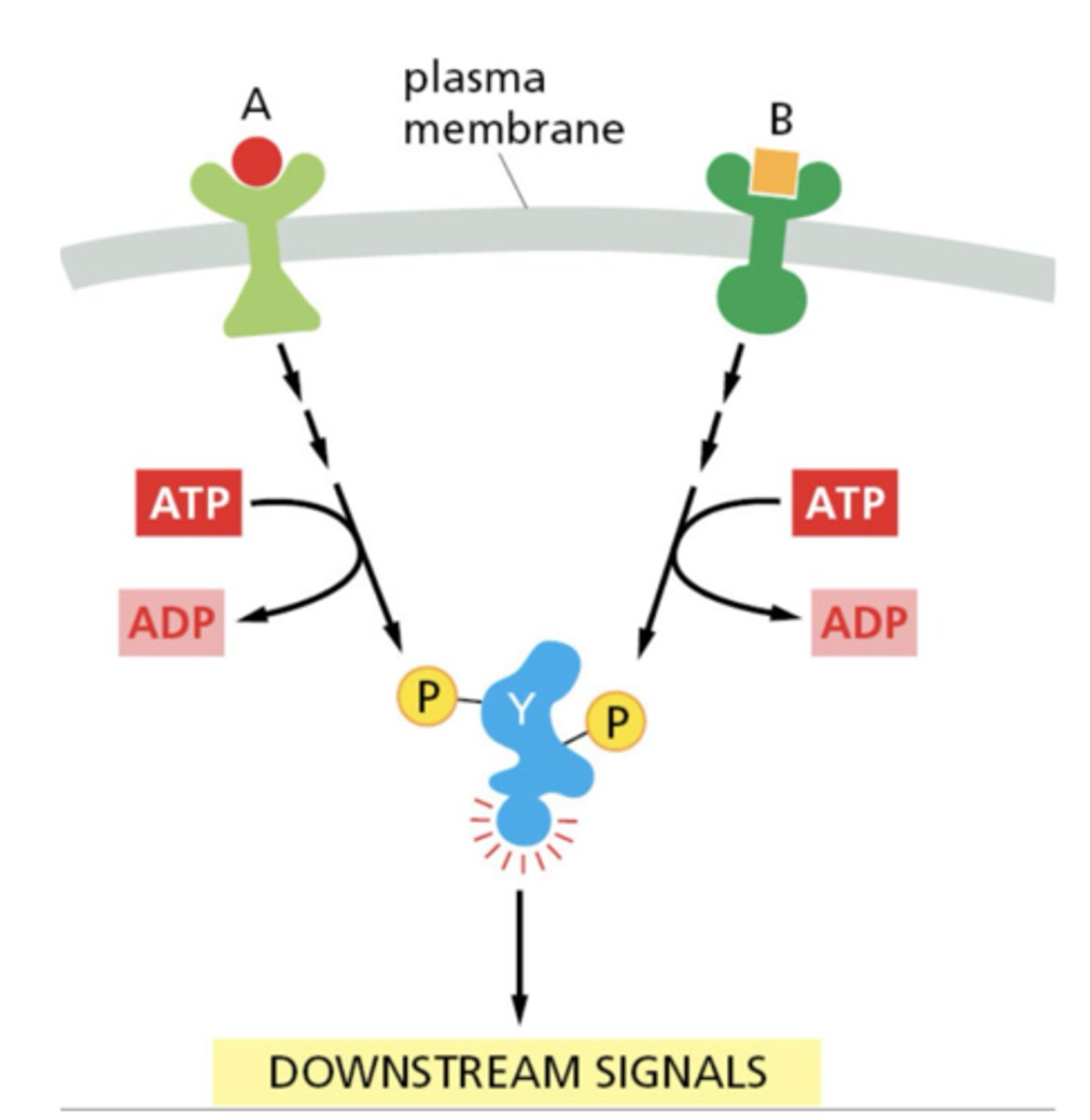
How do signals integrate?
Different signals can converge on the same pathway
- sometimes both signals are required for full activation
Example of slow responses to signals.
gene transcription, new protein synthesis
Example of fast responses to signals.
protein modification (e.g., phosphorylation), immediate functional change
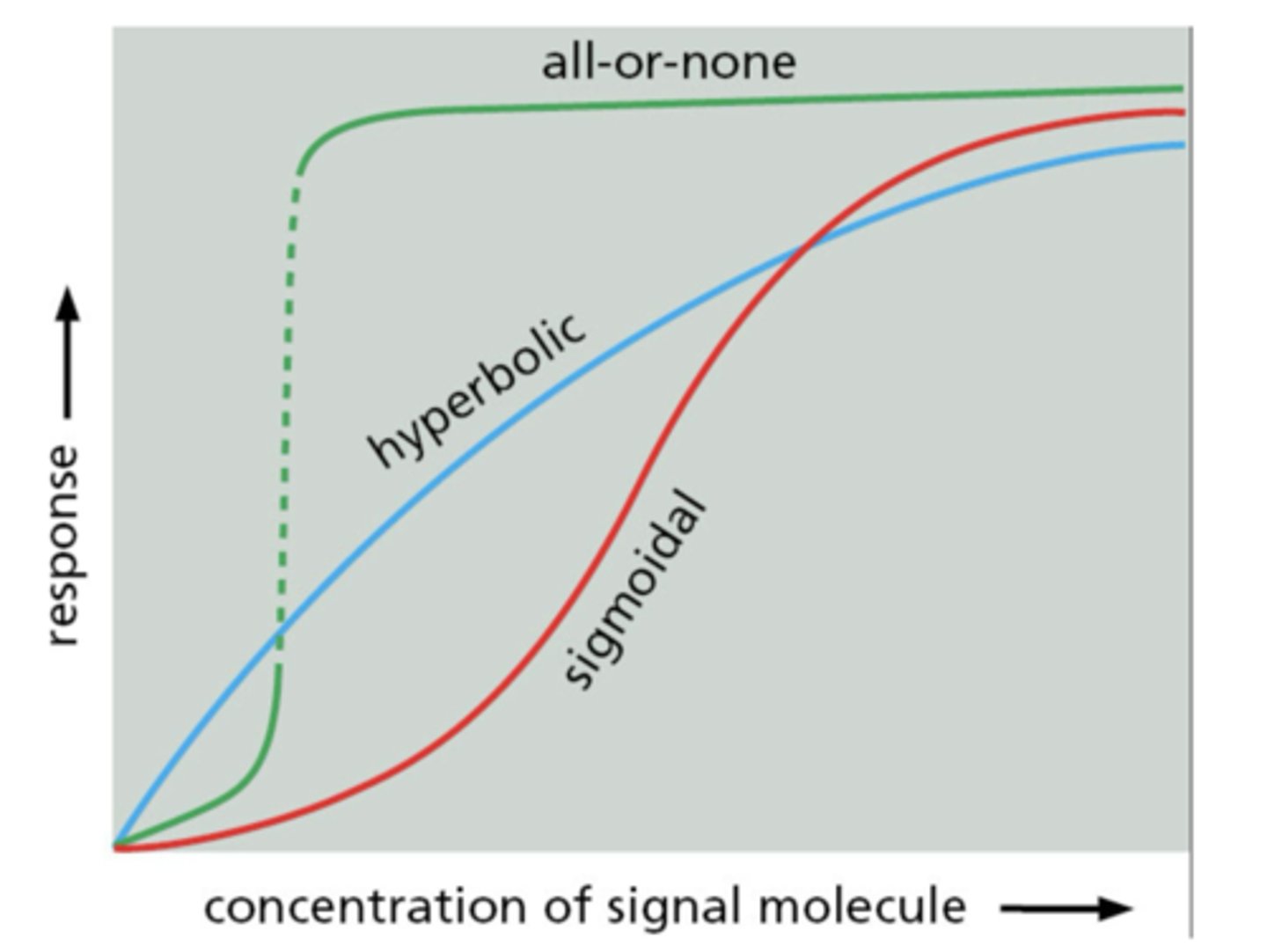
Hyperbolic response to signal concentration
gradual plateau at saturation
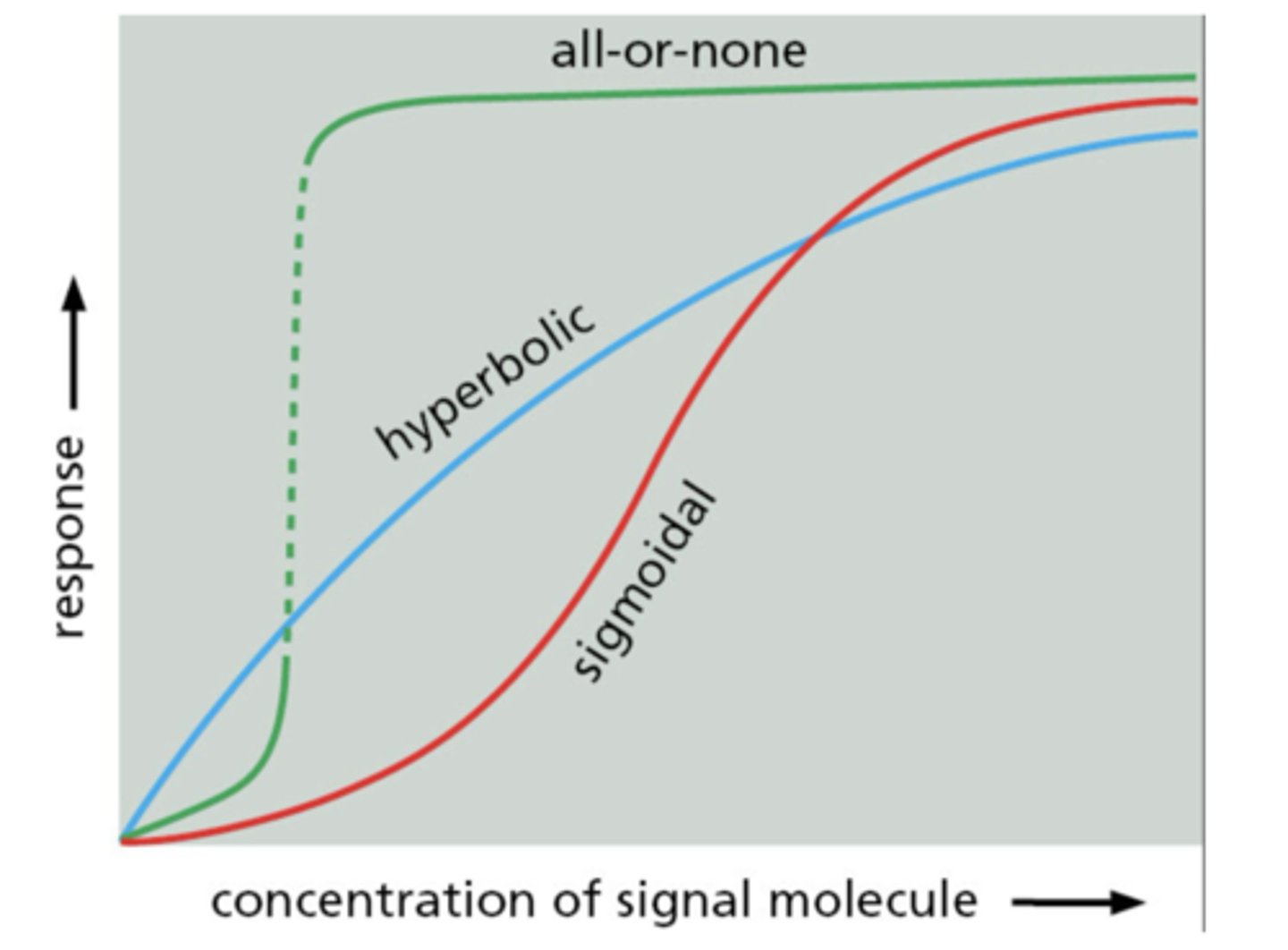
Sigmoidal response to signal concentration
steep response at intermediate concentration
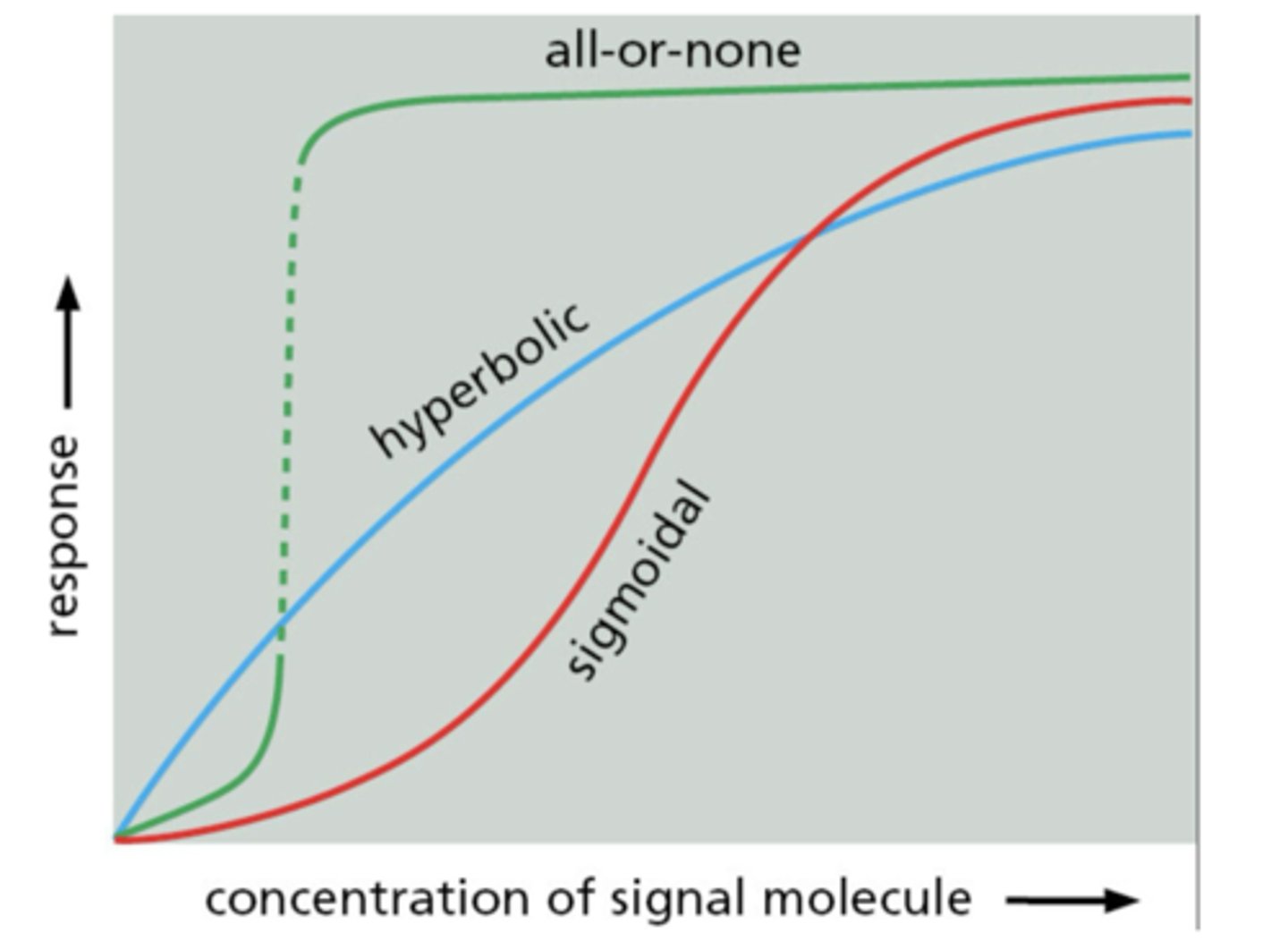
All-or-none response to signal concentration
abrupt switch from low to high response
Why must fats be transported in the body?
Fat absorbed from the diet and lipids synthesized in the liver must move between tissues for utilization and storage
Why are lipoproteins necessary?
Because lipids are insoluble in water, they must be packaged with proteins into water-soluble lipoproteins
When are fats primarily used for calories?
During periods of negative caloric intake
Which lipoprotein transports triglycerides from the intestine?
Chylomicrons (intestine → tissues)
Which lipoprotein transports triglycerides from the liver?
VLDL (liver → tissues)
In what form are lipids mobilized from adipose tissue?
As free fatty acids (FFAs) bound to serum albumin
How are free fatty acids removed from the blood?
Very rapidly, by tissue uptake and oxidation
What happens after fatty acids dissociate from albumin?
They bind to a membrane fatty acid transport protein and enter cells for metabolism
What are the main components of lipoproteins?
Apoproteins, phospholipids, cholesterol, and triacylglycerol
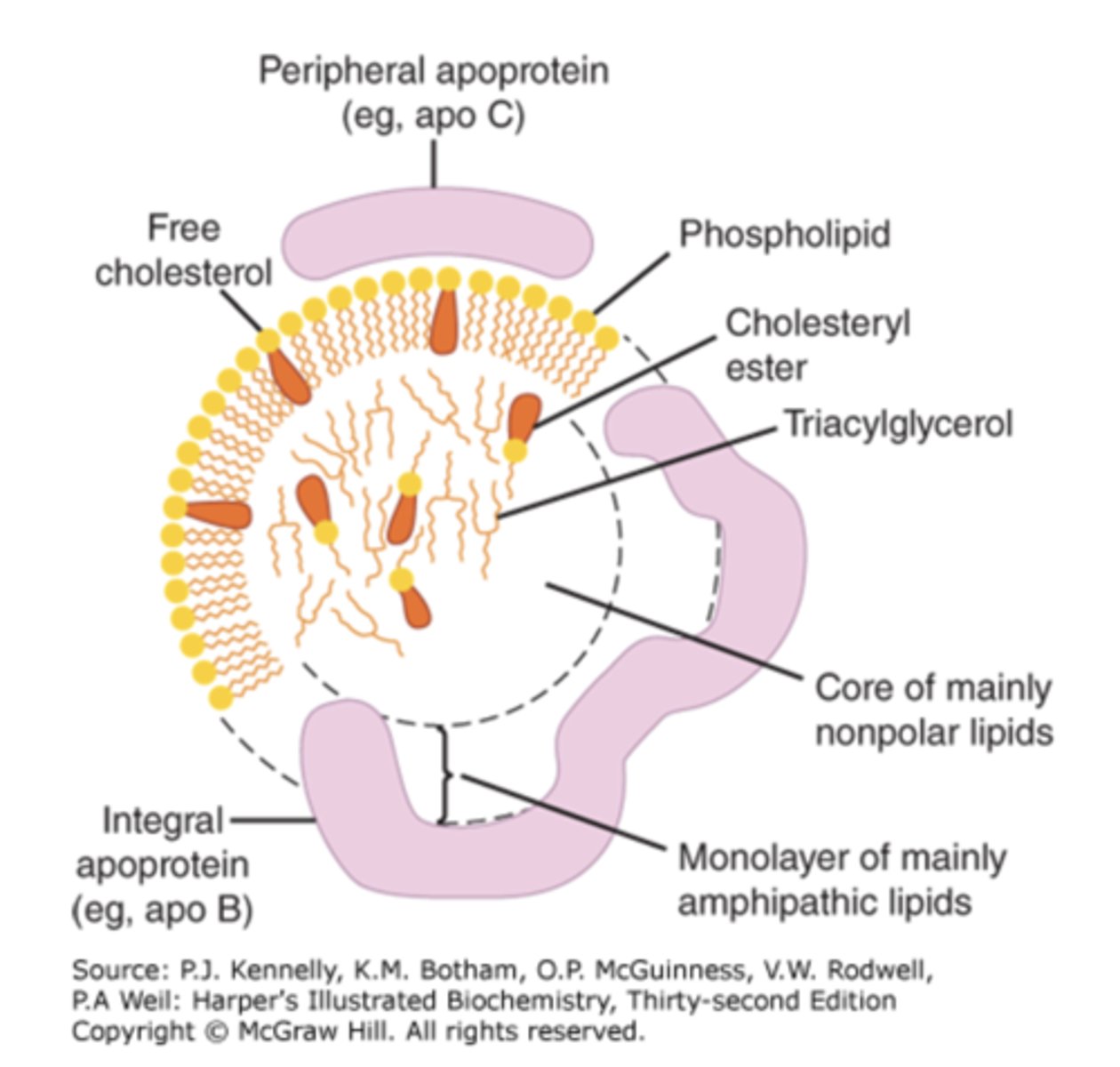
What are apolipoproteins, and how are they abbreviated?
Proteins that bind lipids (cholesterol, fatty acids) to form lipoproteins
- abbreviated as apo
Where are chylomicrons formed?
In intestinal cells
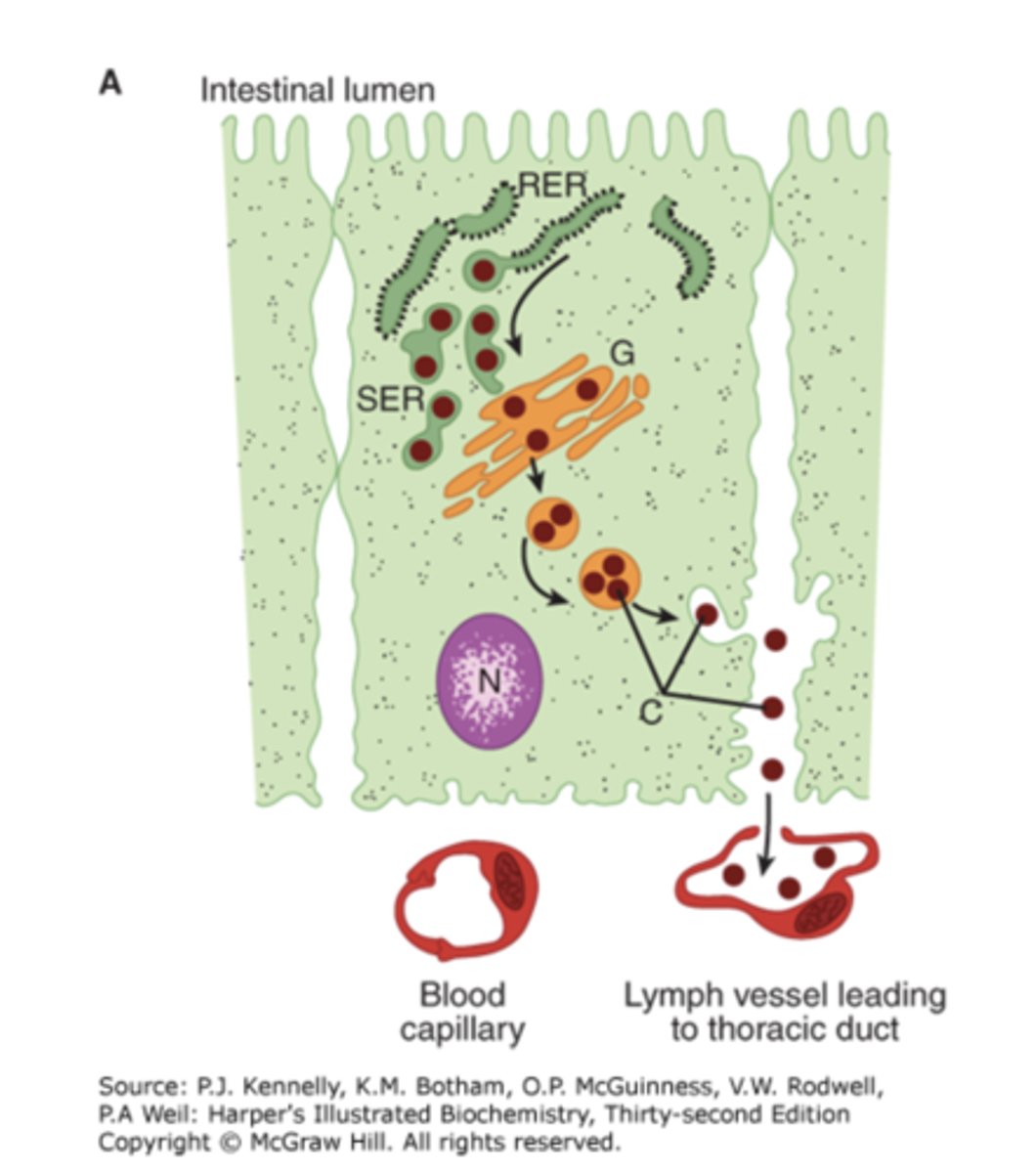
Which organelle synthesizes apolipoproteins?
Rough ER
Where are lipids incorporated into chylomicrons?
In the smooth ER, along with triacylglycerol, cholesterol, and phospholipids
How are chylomicrons modified in the Golgi?
By the addition of carbohydrate residues
How are chylomicrons secreted?
By reverse pinocytosis into the circulation
Where are VLDLs formed?
In the liver (hepatocytes)
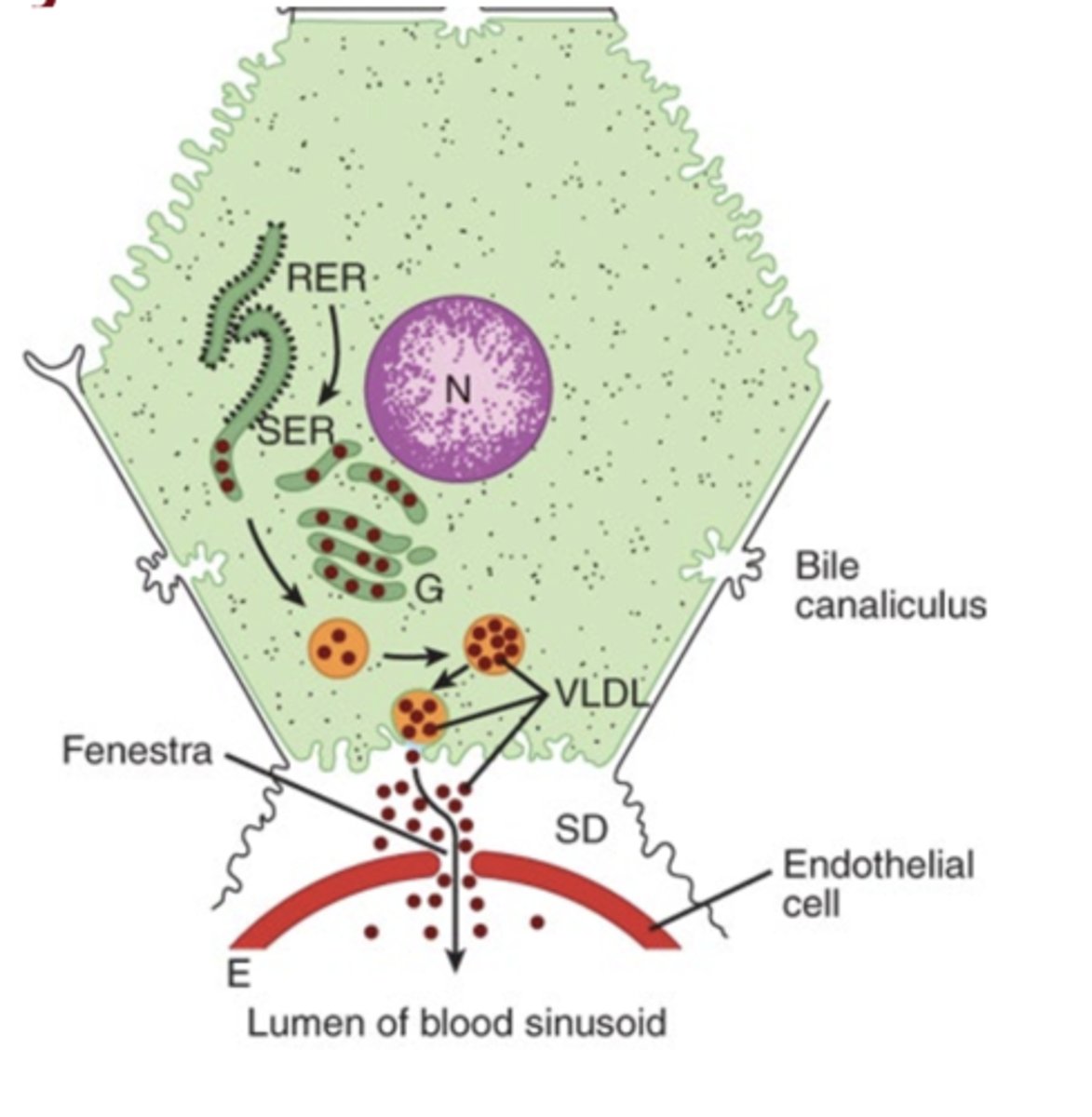
What is the main role of VLDLs?
To export triacylglycerol from the liver to extrahepatic tissues
What apoprotein remains a structural component of VLDL?
Apo B
How quickly are chylomicrons cleared from circulation?
Clearance is rapid
Where are fatty acids from chylomicrons delivered?
To adipose tissue, heart, and muscle (≈80%)
Which enzyme hydrolyzes chylomicron triacylglycerols?
Lipoprotein lipase, producing free fatty acids (FFA) and glycerol
What happens to the released fatty acids?
They are transported into tissues for metabolism
What do chylomicron remnants contain?
Some triacylglycerol (TG) and cholesterol
How are remnants cleared from circulation?
Taken up by the liver via the LDL receptor
What must happen before triacylglycerols can be catabolized?
They must be hydrolyzed by lipases into fatty acids and glycerol
Where are VLDL receptors expressed, and what is their function?
On adipocytes
- they bring VLDL close to lipoprotein lipase
What happens when lipoprotein lipase acts on VLDL?
Triacylglycerol is hydrolyzed, releasing FFA and glycerol
What does VLDL become after lipase action?
LDL, which primarily carries cholesterol
How is LDL taken up into cells?
Via the LDL receptor, found in hepatocytes and on cells of the arterial wall
Where is HDL synthesized?
In the liver
Which apoproteins does HDL carry?
Apo C and Apo E
Why are Apo C and Apo E important?
They are required for the metabolism of chylomicrons and VLDL
What is the major role of HDL?
reverse cholesterol transport
- removal of cholesterol from tissues and return to the liver
Which receptor allows hepatic uptake of HDL and cholesterol?
SR-B1 receptor
How is cholesterol eliminated from the body?
Through the liver in bile
What happens to HDL after delivering cholesterol?
It is reformed and re-released to provide Apo C and Apo E to chylomicrons and VLDL
Where is TAG stored, and what processes does it continuously undergo?
Stored in adipose tissue and undergoes continuous lipolysis and reesterification
What determines plasma FFA concentration?
The balance between lipolysis and reesterification
How is glycerol for TG synthesis made in adipocytes?
From glucose
Which enzyme hydrolyzes adipose TG into FFA + glycerol?
Hormone-sensitive lipase
How is hormone-sensitive lipase different from lipoprotein lipase?
Hormone-sensitive lipase acts on intracellular TG; lipoprotein lipase hydrolyzes plasma TG from lipoproteins
What happens to FFAs after lipolysis inside adipose tissue?
They can be reconverted to acyl-CoA and reesterified with glycerol-3-phosphate to reform TG
What happens if lipolysis exceeds reesterification?
Excess FFAs accumulate, diffuse into plasma, bind albumin, and increase plasma FFA concentration
How are FFA levels in adipocytes regulated?
By hormones that control the rates of lipolysis and reesterification
Which two hormones are highlighted as regulators of lipolysis?
Insulin and thyroid hormone
What key factors affect cholesterol balance in cells?
1. LDL
2. LDL receptors
3. Cholesterol and cholesterol esters
4. ACAT (acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase)
What are the major elements of cholesterol transport?
- cholesterol synthesis
- cholesterol & cholesterol esters
- LDL and LDL receptors
- HDL and LCAT
- bile acids
resulting in overall cholesterol balance
What are the structural features of fatty acids?
- carboxyl group at one end
- hydrocarbon chain of variable length
- can be saturated (no double bonds) or unsaturated (one or more double bonds, causing kinks)
