Ch 19: Advertising, Public Relations, and Sales Promotions
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
What is advertising
a paid form of communication from an identifiable sources about an organization, product, service, or idea designed to persuade the receiver
- most visible form of marketing communications
Steps in Designing and Executing an Advertising Campaign (7 Steps we will go thru)
1. Identify Target Audience
2. Set Advertising Objectives
3. Determine the Advertising Budget
4. Convey the Message
5. Evaluate and Select Media
6. Create Advertisements
7. Assess Impact Using Marketing Metrics
1. Identify Target Audience
- success of an advertising campaign depends on how well advertiser can identify its target audience
- conduct research to identify target audience
- the info is used to set the tone and to select the media
Advertising Plan Def (def in step 2)
- a subsection of the firms overall marketing plan that explicitly analyzes the marketing and advertising situation, identifies the objectives of the advertising campaign, clarifies a specific strategy for accomplishing those objectives, and indicates how the firm can determine whether the campaign was successful
- serves as the yardstick against which advertising success or failure is measured
Pull Strategy (def in step 2)
- A strategy in which the goal is to get consumers to pull the product through the marketing channel by demanding it
Push Strategy (def in step 2)
- A strategy designed to increase demand by motivating sellers- wholesalers, distributers, or salespeople- to highlight the product, rather than the products of competitors, and thereby push the product onto consumers
2. Set Advertising Objectives
- objectives are derived from the overall objectives of the marketing program and clarify the specific goals that the ads are designed to accomplish (objectives are in the Advertising Plan)
- in advertising to customers, the objective is a Pull Strategy (Push Strats also exist)
- Advertising campaigns aim to achieve certian objectives: Inform, Persuade, and Remind customers
- Advertising objectives based on the focus of the ad: Product vs Institutional
2. Set Advertising Objectives: Informative Advertising
- Communication used to create and build awareness, with the ultimate goal of moving (push) through the buying cycle to a purchase
- helps determine early stages of a products life cycle, particularly when consumers have little info abt the specific product or type of product
- Retailers use this type of advertising to tell their customers abt an upcoming sales event or arrival of new merch
2. Set Advertising Objectives: Persuasive Advertising
- When a product has gained a certain amount of brand awareness, firms use persuasive advertising to motivate consumers to take action
- occurs in growth and early maturity stages of the product life cycle, when competition is most intense, and attempts to accelerate the markets acceptance of the product
- in later stages, PA may be used to reposition an established brand by persuading consumers to change their existing perceptions of the advertised product
2. Set Advertising Objectives: Reminder Advertising
- Communication used to remind or prompt repurchases, especially for products that have gained market acceptance and are in the maturity stages of their life cycles
2. Set Advertising Objectives: Product-Focused Advertisements
- Product-Focused Advertisements: Used to inform, persuade, or remind consumers abt a specific product/service
2. Set Advertising Objectives: Institutional Advertisements
- Institutional Advertisements: Promotes a company, corporation, business, institution, or organization; Not intended to sell a p/s
- Public Service Advertising is a category of Institutional Advertisements
2. Set Advertising Objectives: Institutional Advertisements (PSA)
- Public Service Advertising (PSA):
--- Category of Institutional Advertising
--- a form of Social Marketing
--- focuses on public welfare and is sponsored by nonprofit institutions, civic groups, religious organizations, trade associations, or political groups
--- like inst and prod focused advertisements it informs, persuades, or reminds consumers, but the focus is the betterment of society
--- broadcasters donate free airtime to them under Federal Communication Commission rules
--- usually creative and stylistically appealing
2. Set Advertising Objectives: Institutional Advertisements (Social Marketing)
- the application of marketing principles to a social issue to bring abt attitudinal and behavioral change among the general public or specific population segment
3. Determine the Advertising Budget
1. firms must consider the role that adverting plays in their attempt to meet their overall promotional objectives
2. Advertising expenditures vary over the course of the product life cycle
3. the nature of the market and the product influence the size of advertising budgets
- the nature of the market also determines the amount of money spend on advertising
--- less money is spend on advertising in B2B than B2C
--- Personal selling is more important in B2B markets
4. Convey the Message
- marketers determine what they want to convey abt the p/s
1. firm determines the key message it wants to communicate to the target audience
2. firm decides what appeal would most effectively convey the message
- these steps must be considered simultaneously
4. Convey the Message: The Message
- provides the target audience with reasons to respond in a desired way
- communicate the p/s problem solving ability in a clear, compelling fashion
- p/s solve problems, whether real/perceived
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): a strategy of differentiating a product by communicating its unique attributes in the entire advertising campaign (snapshot of entire campaign)
- the selling proposition must be unique to brand and meaningful to customer; be sustainable overtime
4. Convey the Message: The Appeal
- Advertisers use diff appeals to portray their p/s and persuade consumers to purchase them, though advertising terns to combine the types of appeals into 2 categories: Informational Appeals and Emotional Appeals
4. Convey the Message: The Appeal: Informational Appeals
- help consumers make purchase decisions by offering factual info that encourages consumers to evaluate the brand favorability on the basis of the key benefits it provides
4. Convey the Message: The Appeal: Emotional Appeals
- aims to satisfy consumers' emotional desires rather than their utilitarian needs
- the key successful emotional appeal is the use of emotion to create a bond btwn the consumer and the brand
- the most common types: Fear/Safety, Humor, Happiness, Love/Sex, Comfort, and Nostalgia and Community
5. Evaluate and Select Media
- Media Planning: Process of evaluating and selecting the Media Mix
- Media Mix: the combo of the media used and the frequency of advertising in each medium- that will deliver a clear, consistent, compelling message to the intended audience
- Media Buy: the actual purchase of airtime or print pages; the largest expense in an advertising budget
- To categorize the types of media we use a dichotomy: Mass and Niche Media
5. Evaluate and Select Media: Mass and Niche Media
- Mass Media: Channels that are ideal for reaching large numbers of anonymous audience members; include national newspapers, magazines, radio, and television
- Niche Media: Channels that are focused and generally used to reach narrow segments, often with unique demographic characteristics or interests; Specialty tv channels (HGTV) and specialty magazines (Real Simple) are examples
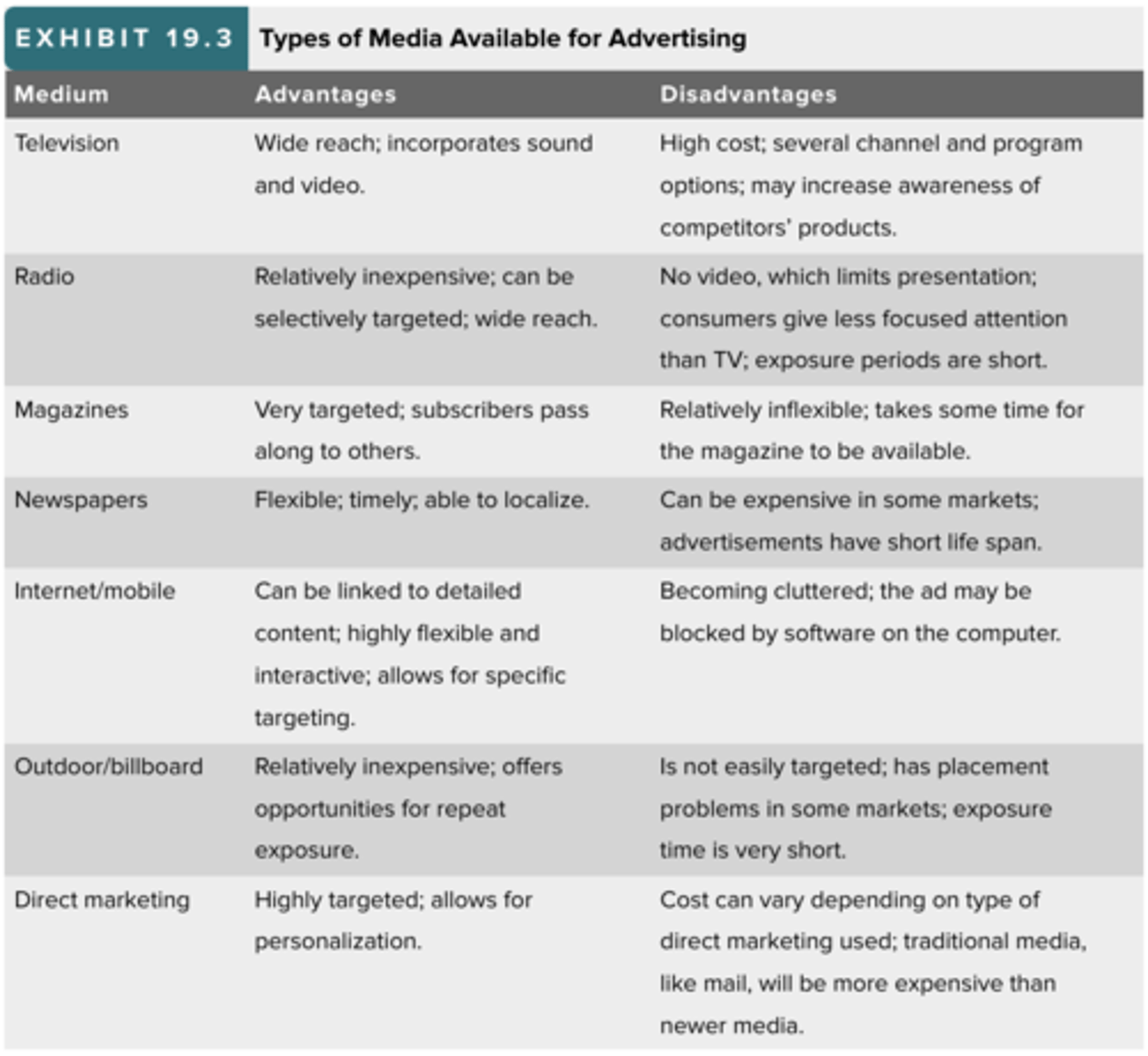
5. Evaluate and Select Data: Choosing the Right Medium (types of media available for advertising)
television, radio, magazines, newspapers, internet/mobile, outdoor/billboard, direct marketing
5. Evaluate and Select Data: Determining the Advertising Schedule
- Advertising Schedule: the specification of the timing and duration of advertising
- Three types: Continuous Schedule. Flighting, and Pulsing
5. Evaluate and Select Data: Determining the Advertising Schedule (Continuous Schedule)
- Runs steadily throughout the yr and therefore is suited to products and services that are consumed continually at relatively steady rates and that req a steady level of persuasive and/or reminder advertising
- ex. P&G advertises its tide brand continuously
5. Evaluate and Select Data: Determining the Advertising Schedule (Flighting)
- and advertising schedule implemented in spurts, with periods of heavy advertising followed by periods of heavy advertising followed by periods of no advertising. This pattern generally functions for products whose demand fluctuates, such as suntan lotion, which manufacturers may heavily advertise in the months leading up and during summer
5. Evaluate and Select Data: Determining the Advertising Schedule (Pulsing)
- combines the continuous and flighting schedules by maintaining a base level of advertising but increasing advertising intensity during certain periods
- ex. airlines, hotels and car rental companies might continuously advertise to ensure brand awareness but might increase the advertising in spikes during certain low-demand periods
6. Create Advertisements
- message and appeal translated into actual words and images
- the type of medium determines the execution style
- creativity plays a major role
- creativity should not overshadow the message
- execution style must match the medium and objectives
- remain consistent across styles-Integrated Marketing
6. Create Advertisements: Headline and Subhead
- Headline: large type in an ad that is designed to draw attention
- Subhead: smaller headline, provides more info abt what you are selling
- both should be short, use simple words, and include the primary benefits of the p/s, the name of the brand, and an interest-provoking idea
- should contain and action verb and give enough info for learning even if the headline is only read
6. Create Advertisements: Body Copy and Brand Elements
- Body Copy: main text portion of the ad; used to build interest generated by the visual and headlines, explains in more depth what the headline and subheads introduced, arouses desire for the product, and provides enough info to move the target consumer to action
- Brand Elements: characteristics that identify the sponsor of a specific ad; logo and a unique selling proposition
7. Assess Impact Using Marketing Metrics
The effectiveness of an advertising campaign must be assessed before, during, and after the campaign has run.
- three stages: Pretesting, Tracking, and Posttesting
- Measuring sales can be hard bc of the many influences other than advertising on consumer choices, purchase behavior, and attitudes
--- the influences include the level of competitors' advertising, econ conditions in the target market, sociocultural changes, in-store merch availability, and even weather; advertisers need to identify these and isolate those of the particular advertising campaign
7. Assess Impact Using Marketing Metrics: Pretesting
- assessments performed before an ad campaign is implemented to ensure that the various elements are working in an integrated fashion and doing what they are intended to do
7. Assess Impact Using Marketing Metrics: Tracking
- included monitoring key indicators such as daily or weekly sales volume while the advertisement is running to shed light on any problems with the message or the medium
7. Assess Impact Using Marketing Metrics: Posttesting
- the evaluation of the campaign's impact after it has ben implemented
- assess the sales and/or communication impact of the advertisement or campaign
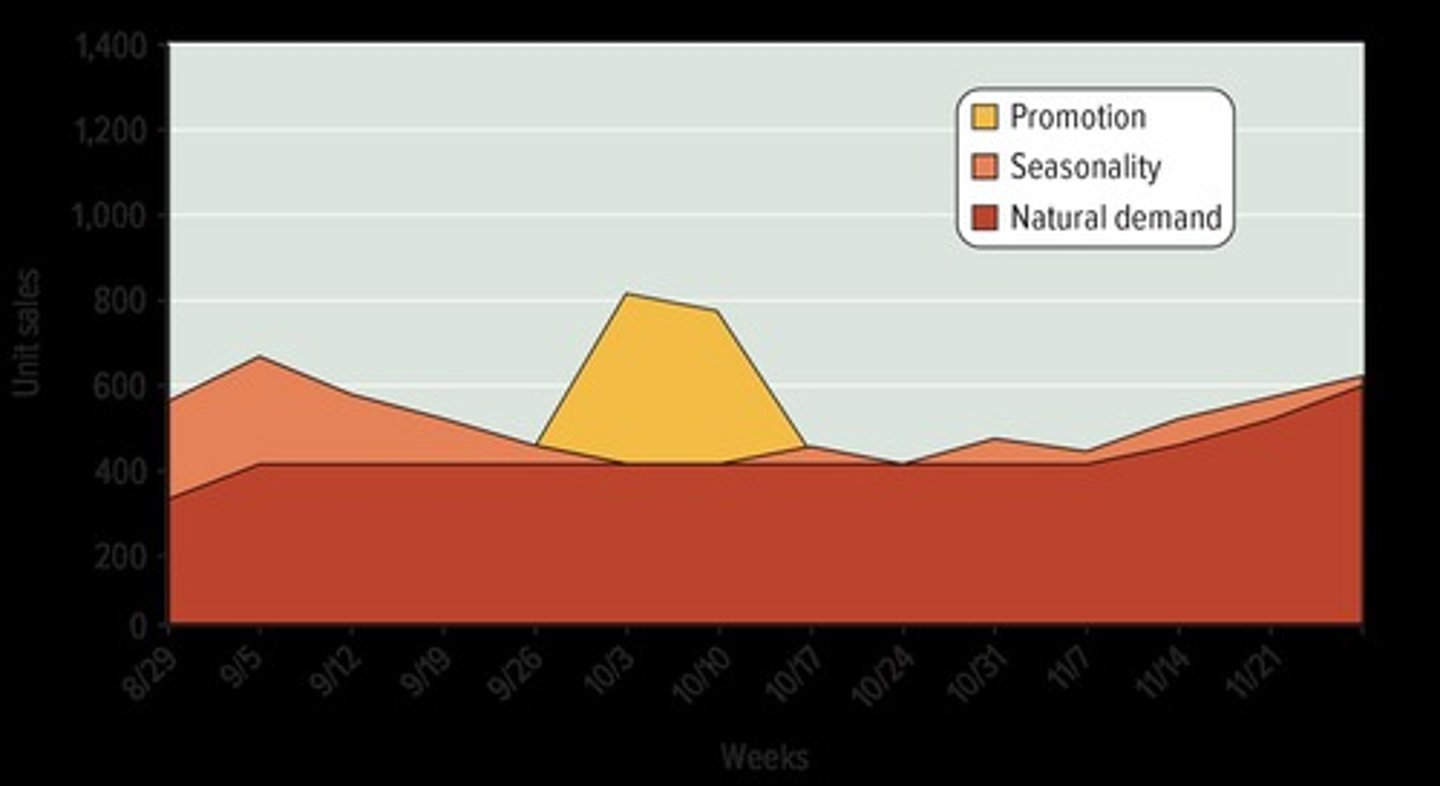
7. Assess Impact Using Marketing Metrics: Evaluating effectiveness of advertising with sales volume and time series analysis
- for freq purchased goods in the maturity stage of the product life cycle, sales volume offers a good indicator for advertising effectiveness
- bc their sales are relatively stable, and if we assume that the other elements of the marketing mix and the environment have not changed, we can attribute changes in sales volume to changes in advertising
- using time series analysis, sales data from the past are used to forecast the future
- basic trend (red), seasonal influences (orange), and the Lift (additional sales caused by advertising) (yellow). In this case the lift caused by the advertising is substantial
- for goods in other stages of the product life cycle, sales data offers only one of the indicators that marketers need to examine to determine advertising effectiveness
(may not be on test) Regulatory and Ethical Issues in Advertising
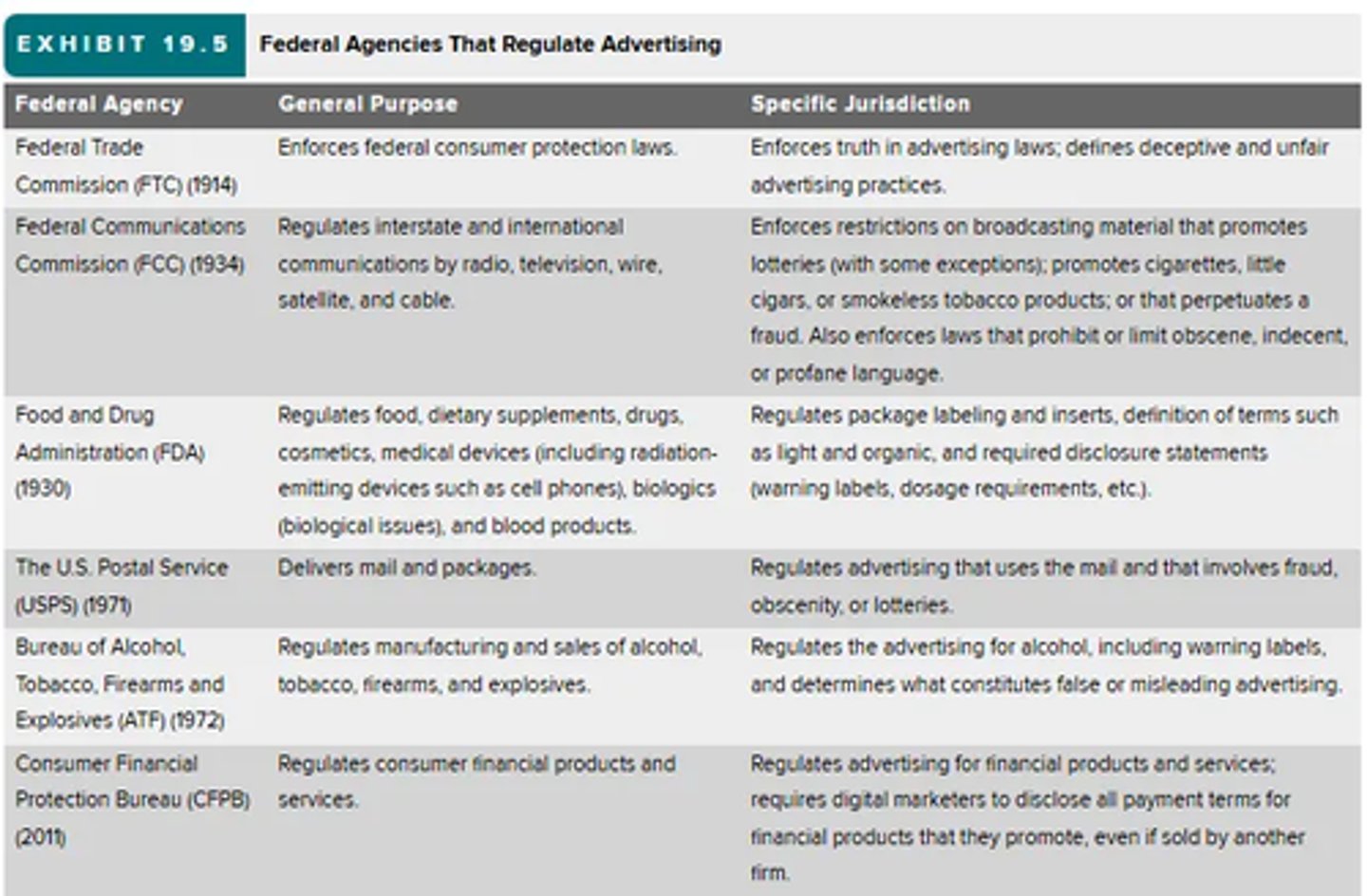
- in the U.S., the regulation of advertising involves a complex mix of formal laws and informal restrictions designed to protect consumers from deceptive practices
- Primary federal agencies that regulate advertising activities: Federal Trade Commission (FTC), Federal Communications Commission (FCC), Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
- Others that regulate advertising to some degree: Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives (ATF), and the U.S> Postal Service (USPS)
(may not be on test) Regulatory and Ethical Issues in Advertising: Federal Agencies that Regulate Advertising Image
(may not be on test) Regulatory and Ethical Issues in Advertising: FTC
- primary enforcement agency for most mass media advertising, although it cooperates with other agencies to investigate an enforce regulations on particular advertising practices
Regulatory and Ethical Issues in Advertising: Puffery
- the legal exaggeration of praise, stopping just short of deception, lavished on a product
- hard to discern what is legal and illegal with this
- the less specific the claim, the less likely it might be considered deceptive
- acceptable as long as consumers know that the firm is stretching the truth thru exaggeration
Public Relations (PR)
- the organizational function that manages the firm's communications to achieve a variety of objectives, including building and maintaining a positive image, handling or heading off unfavorable stories or events, and maintaining positive relationships with the media
- supports other promotional efforts by generating free media attention and general goodwill
- consumers view media coverage generated thru PR as more credible and objective that any other aspects of an Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC) program bc the firm does not buy the space in print media or time on radio or television
Public Relations (PR): Cause-Related Marketing
- commercial activity in which businesses and charities form a partnership to market an image, a product, or a service for their mutual benefit; a type of promotional campaign
Public Relations (PR): Event Sponsorship
- occurs when corporations support various activities (financially or otherwise), usually in the cultural or sports entertainment sectors
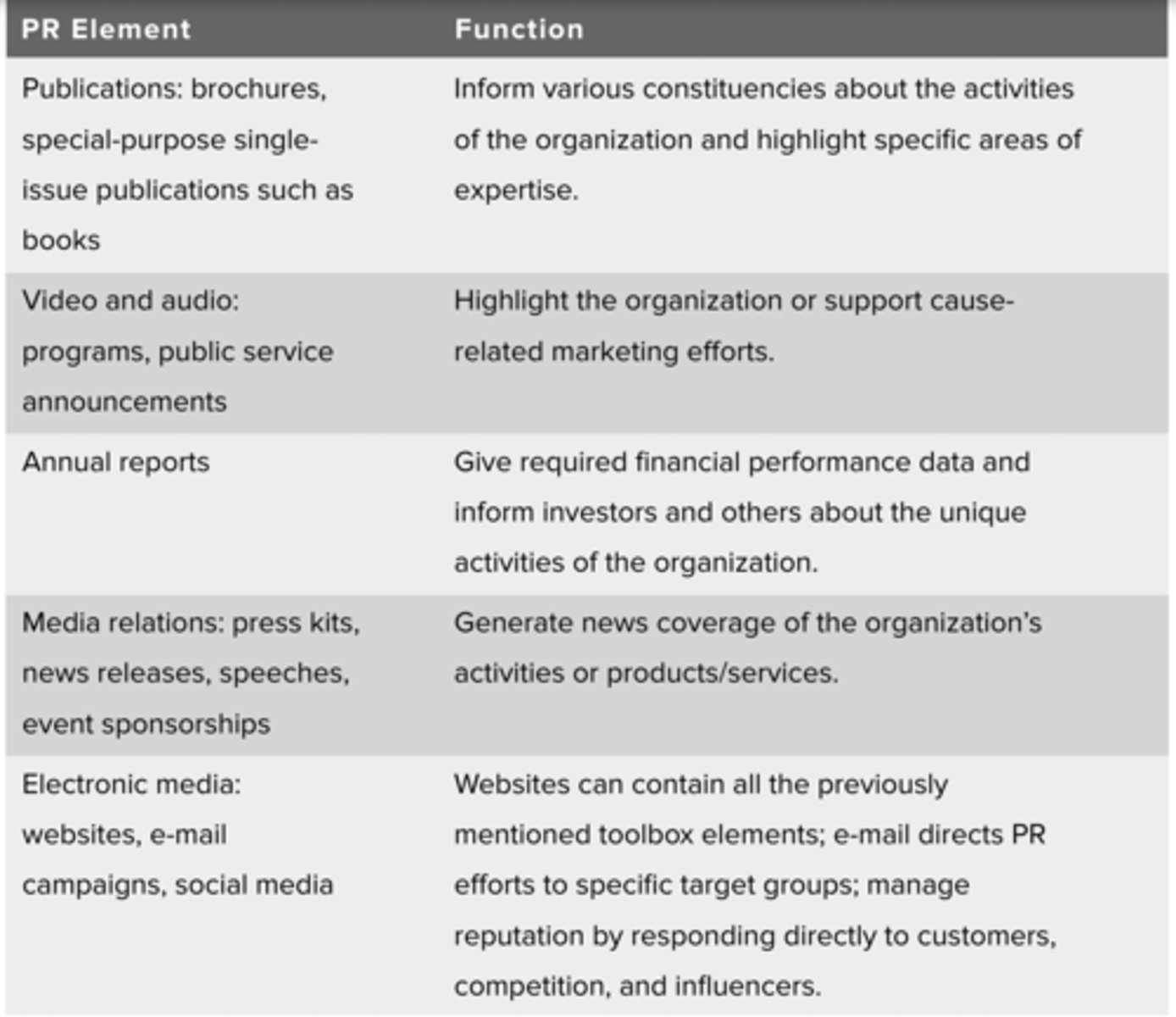
Public Relations (PR): Elements of a Public Relations Toolkit (she did go over this)
print, broadcast, internet, and out of home
Sales Promotions
- Special incentives or excitement-building programs that encourage the purchase of a product or service, such as coupons, rebates, contests, free samples, and point-of-purchase displays.
- can be targeted at end user or channel members
- can be either push or pull strats
Types of Sales Promotions (went over this)
Coupons, Deals, Premiums, Contests, Sweepstakes, Samples, Loyalty Programs, Point-of-Purchase Displays, Rebates, Product Placement
Types of Sales Promotions: Coupons
- Coupons: offer a discount on the price of specific items when the items are purchased
- used to simulate demand and are issued by manufacturers and retailers
- some retailers link coupons to their loyalty programs
- might contain info abt the customer who used it
- low redemption rates and inexpensive tool, but using customer data to create a more targeted promotions has resulted in higher redemption rates, increasing their expense
- adv: stimulates demand (stimmy mummy) and allows for direct tracking of sales
- disadv: low redemption rates and high cost
Types of Sales Promotions: Deals
- type of short-term price reduction that can take several forms, such as a featured price, a price lower than the regular price; a certain percentage "more free" offer contained in larger packaging; a BOGO offer, or limited time discount
- also is a special financing arrangement such as reduced percentage interest rates or extended repayment terms
- encourage customers to try a product bc its less risk and less cost
- adv: encourages trial and reduces customer risk
- disadv: may reduce perception of value
Types of Sales Promotions: Premiums
- offers an item for a free or at a bargain price to reward some type of behavior, such as buying, sampling, or testing
- builds goodwill among consumers, who often perceive high value in them
- can be distributed in the product packaging (toy in cereal), placed visibly on package (coupon on cheerios box), handed out in tore, or delivered in mail
- effective if consistent with brand's message and image and highly desirable to the target market
- adv: buids goodwill and inc perception of value
- disadv: consumers buy for premium not product and has to be carefully managed
Types of Sales Promotions: Contests
- brand-sponsored competition that requires some form of skill or effort
- like a social media competition
- adv: inc consumer involvement and generates excitement
- disadv: requires creativity and must be monitored
Types of Sales Promotions: Sweepstakes
- oh my gosh i just won the Danimals Sweepstakes
- offers prizes based on a chance drawing of entrants' names
- do not require entrant to complete a task other than buying a ticket or filling out a form
- encourage current consumers to consume more if the sweepstakes from appears inside the packaging or with the product
- sometimes no purchase is necessary to enter
- adv: inc involvement with the product
- disadv: sales often decline when its over
Types of Sales Promotions: Samples
- offers potential customers the opportunity to try a product or service before they make a buying decision
- distributing samples is the most costly sales promotion tools but also one of the most effective
- adv: encourages trial and offer direct involvement
- disadv: high cost to the firm
Types of Sales Promotions: Loyalty Programs
- specifically designed to retain customers by offering premiums or other incentives to customers who make multiple purchases over time
- encourage customers to increase their engagement and purchases from a given firm
- growing more popular and tired to long-term CRM systems
- carefully managed bc they can be costly
- adv: creates loyalty and encourages repurchase
- disadv: high cost to the firm
Types of Sales Promotions: Point-of-Purchase Displays
- merch displays located at the point of purchase, such as at the checkout counter in a supermarket
- most valuable real estate is at the POP bc they inc product visibility and encourage trial
- adv: provides high visibility and encourages brand trial
- disadv: difficult to get a good location in the store and costly to the firm
Types of Sales Promotions: Rebates
- type of price reduction in which a portion of the purchase price is returned by the seller to the buyer in the form of cash
- online or mail in
- attract customers and stimulate sales, but they may not have to pay off all the rebates offered bc some customers don't bother to redeem them
- adv: stimulates demand and inc value perception
- disadv: easily copied by competitors and may just advance future sales
Types of Sales Promotions: Product Placement
- pay to have product included in narrative situations, such as in a scene in a movie or tv
- increase viability of products
- adv: displays products non traditionally and demonstrates product use
- disadv: firm often has little control over display and product can be overshadowed
Using Sales Promotion Tools
- use care in sales promotions, especially when lowering price
- may stock up on lower prices items, which shifts sales and leads to short run benefits at the expense of long term sales stability
- create value for customers and firm
- the role of sales promotion has been to generate short term results while the goal of advertising was to generate long term results