genetics ospe (not the lap skill) nmu
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms

name this pipetting common error and how to avoid is
loose tip
load the tip with light pressure
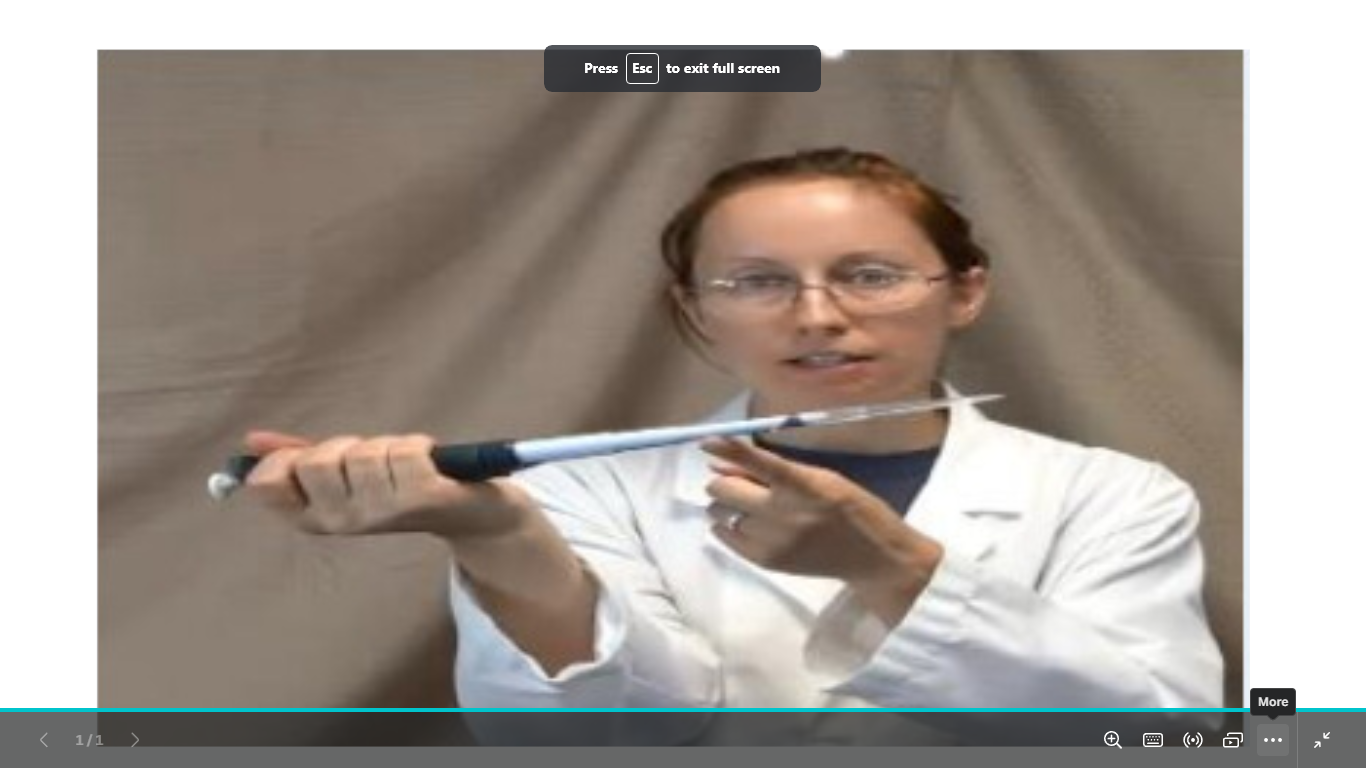
name this pipetting common error and how to avoid is
tilting the pipette
use the pipette vertical for aspiration and (20-45) angle for release only

name this pipetting common error and how to avoid is
quick release of plunger
release the plunger slowly to avoid the inaccurate volume and bubbles
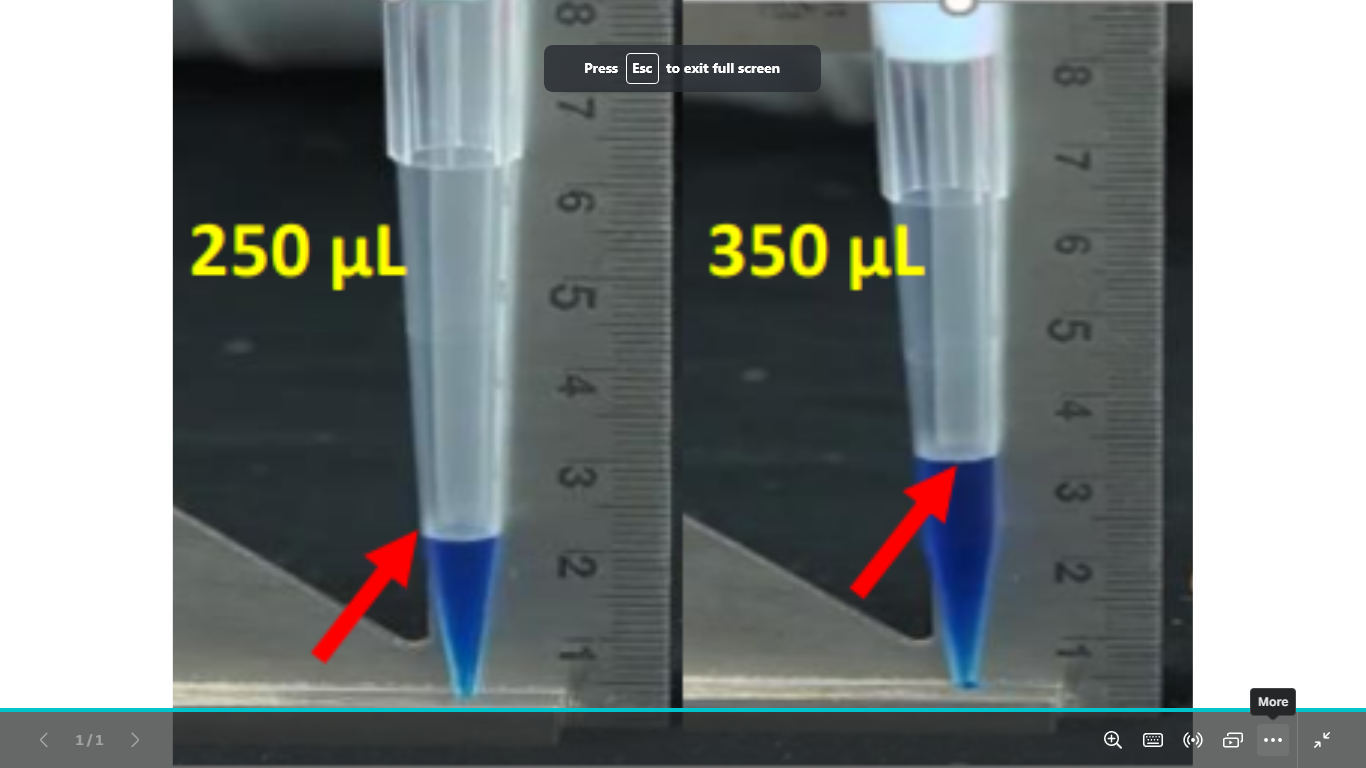

name this pipetting common error and how to avoid is
-the plunger is depressed to the second stop and lead to overaspiration
-the plunger depressed only to the first stop then immersed in the sample to aspirate the required volume
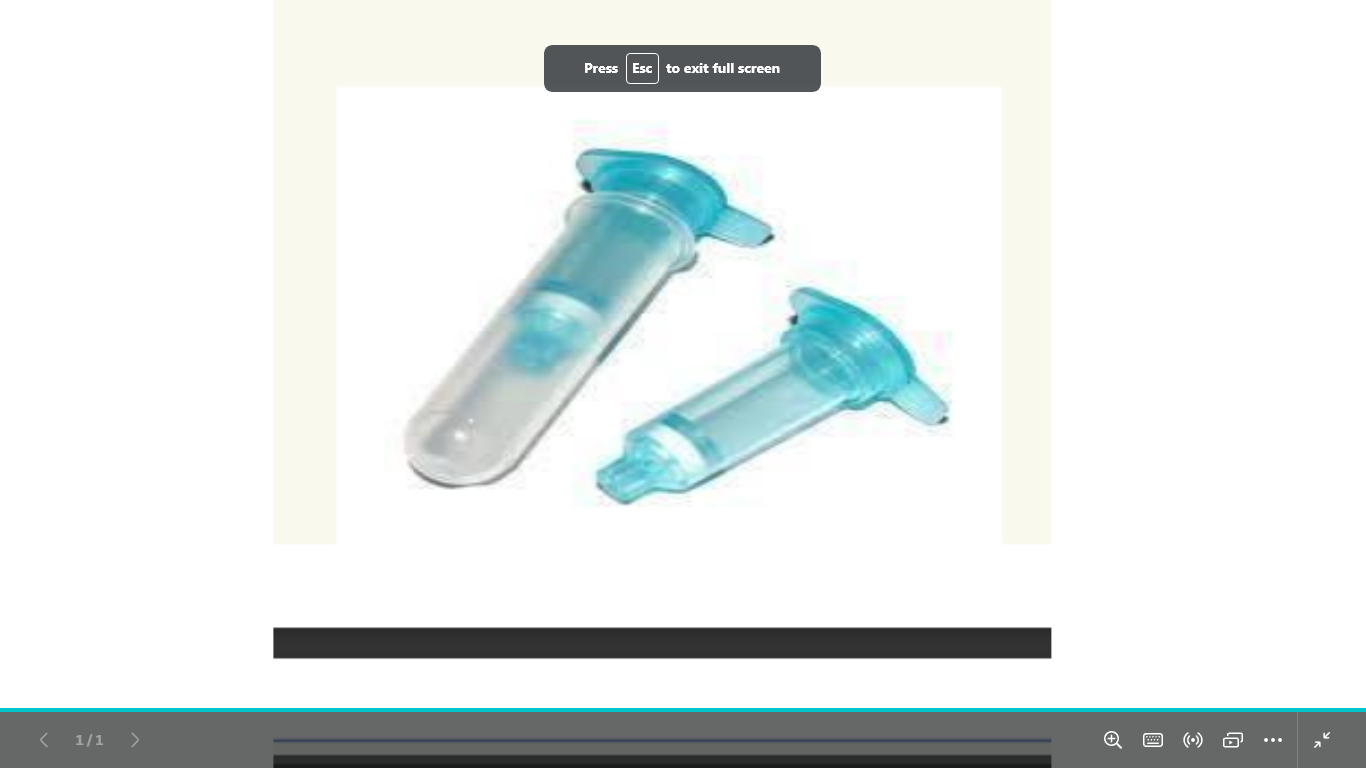
1-identify
2-what is the principle of its work
3-what are they used for
1-spin column
2-its a method of nucleic acid extraction that is based on their binding to silica surfaces in the presence of certain salts and under certain ph conditions
3-they are the most common method for dna extraction
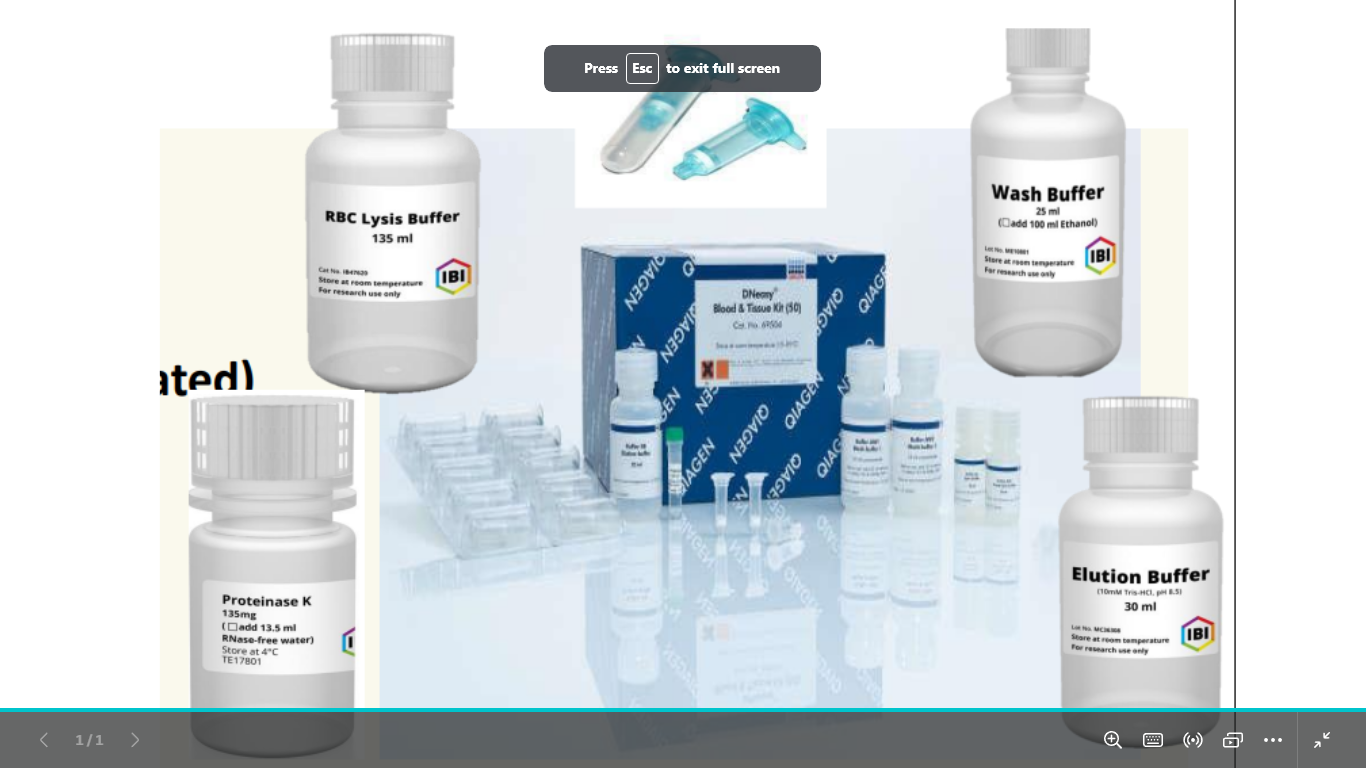
components of dna extraction kit 6
proteinase k
lysis solution
wash buffer 1,2 (conc)
elution buffer
spin columns
collecting tubes
steps of dna extraction 4 عنناوين الخطوات بس
lysis
binding
2 wash steps
elution
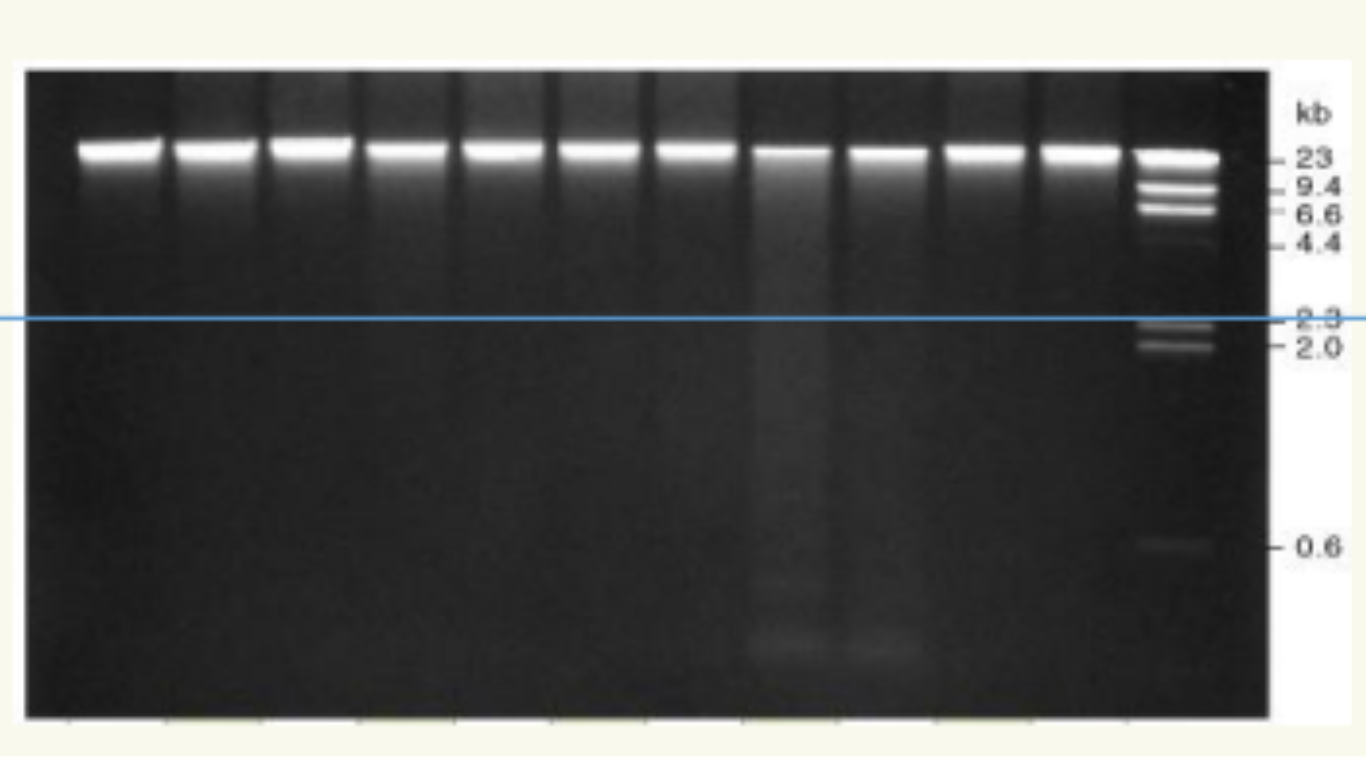
name this
what is it used for in assessment of dna quality
agerose gel electrophoresis
used for checking the quality of extracted dna
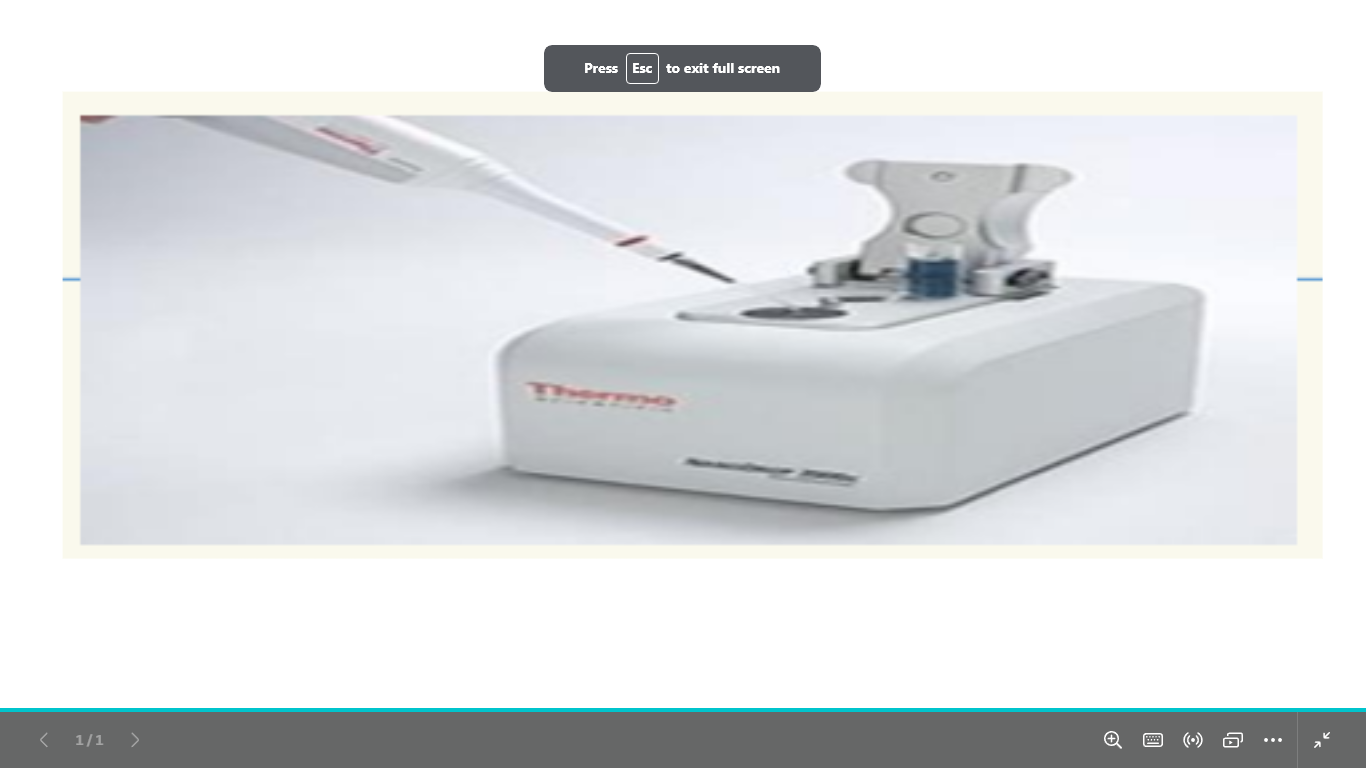
name this
what is it used for in assessment of dna quantity
uv spectrophotometry (nanodrop)
assessment of dna quantity
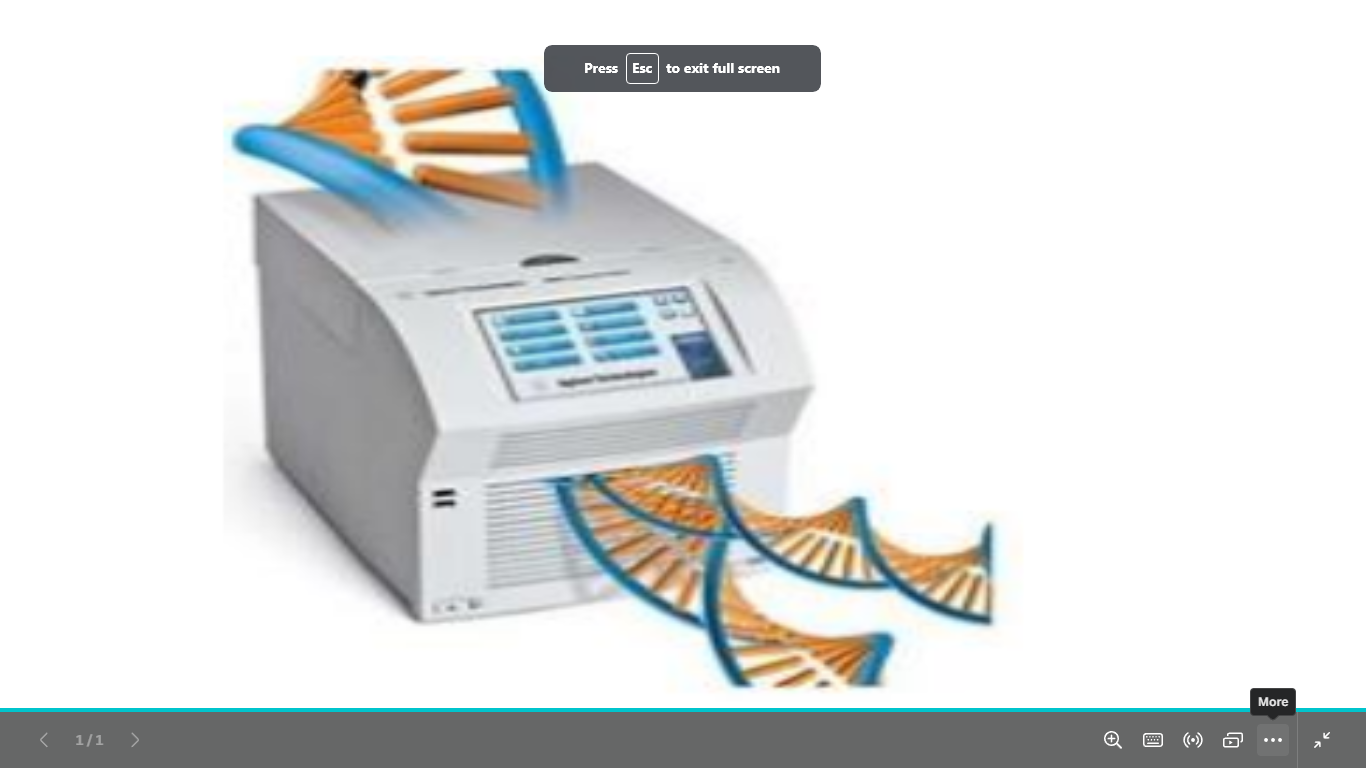
name the dna amplification technique and
descripe it
PCR
In vitro laboratory technique for rapidly producing millions to billions of copies of a specific segment of DNA
in vitro يعني في تيوب
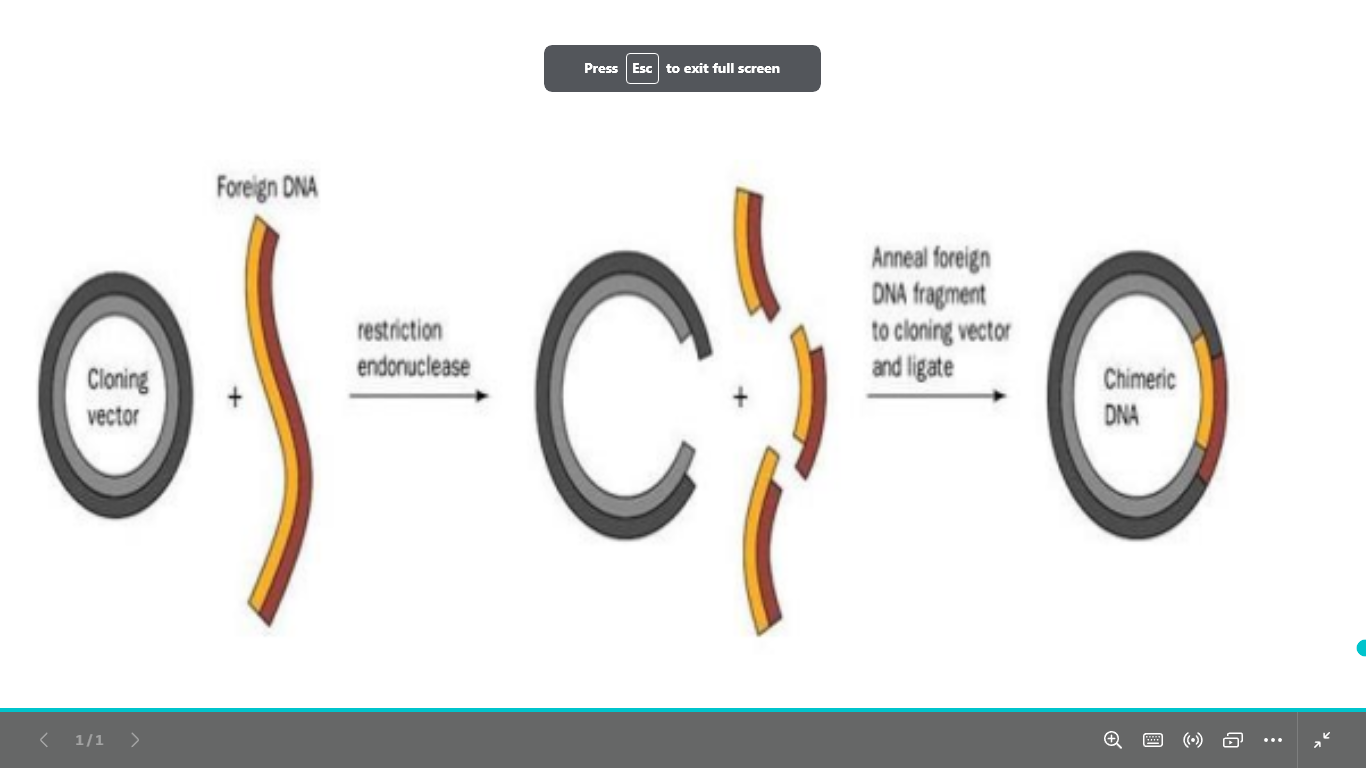
name the dna amplification technique and
descripe it
cloning of dna
Producing many copies of a gene (DNA segment) in vivo for example, by replicating it in a culture of bacteria
in vivo يعني في كائن حي
pcr reaction components
1) Target DNA
2) Pair of Primers
3) dNTP
4) A Thermostable DNA Polymerase (Taq polymerase)
5) Buffer solution
مش لاقي صوره للسؤال دا بس سهل يجي ومعاه سؤال تاني ب صوره احد ال components وهما في الطريق في باقي الكروت
3 steps of a single PCR cycle
1- denaturation (95)
2-annealing (55)
3-extension (72)
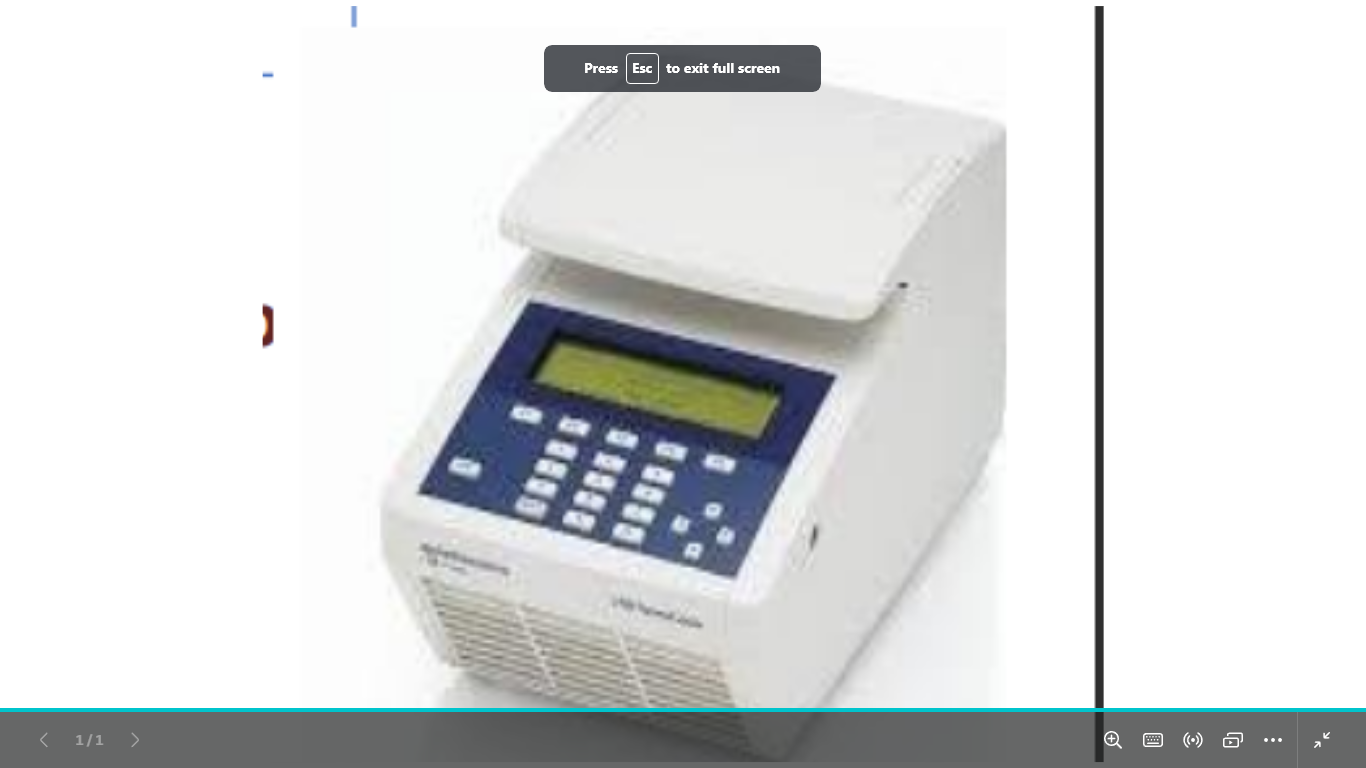

identify
thermal cycler
where the PCR is done
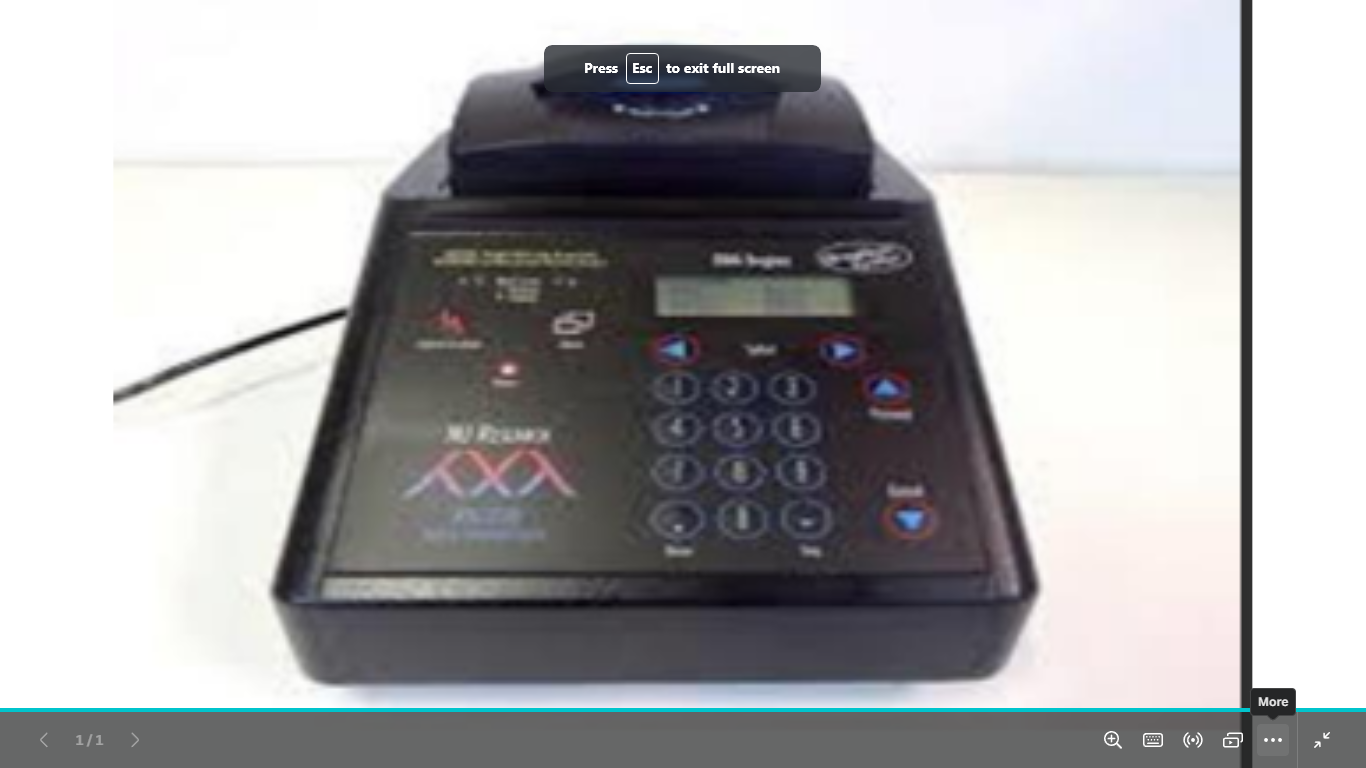

identify
thermal cycler
where the PCR is done
after 20-30 cycles of PCR how many copies are made
millions / billions of copies are formed
After amplification, why the PCR product is analyzed using agarose gel
electrophoresis
to check the size of the DNA fragments produced.
7 applications of PCR
1- detection of infectious agents
2-forensic medicine (طب شرعي يعني)
3-prenatal genetic diagnosis of diseases والجنين في بطن امه يعني
4-detection of genetic polymorphism
5-tissue typing (to test for compatibility before organ transplant)
6-gene therapy
7-study of evolution
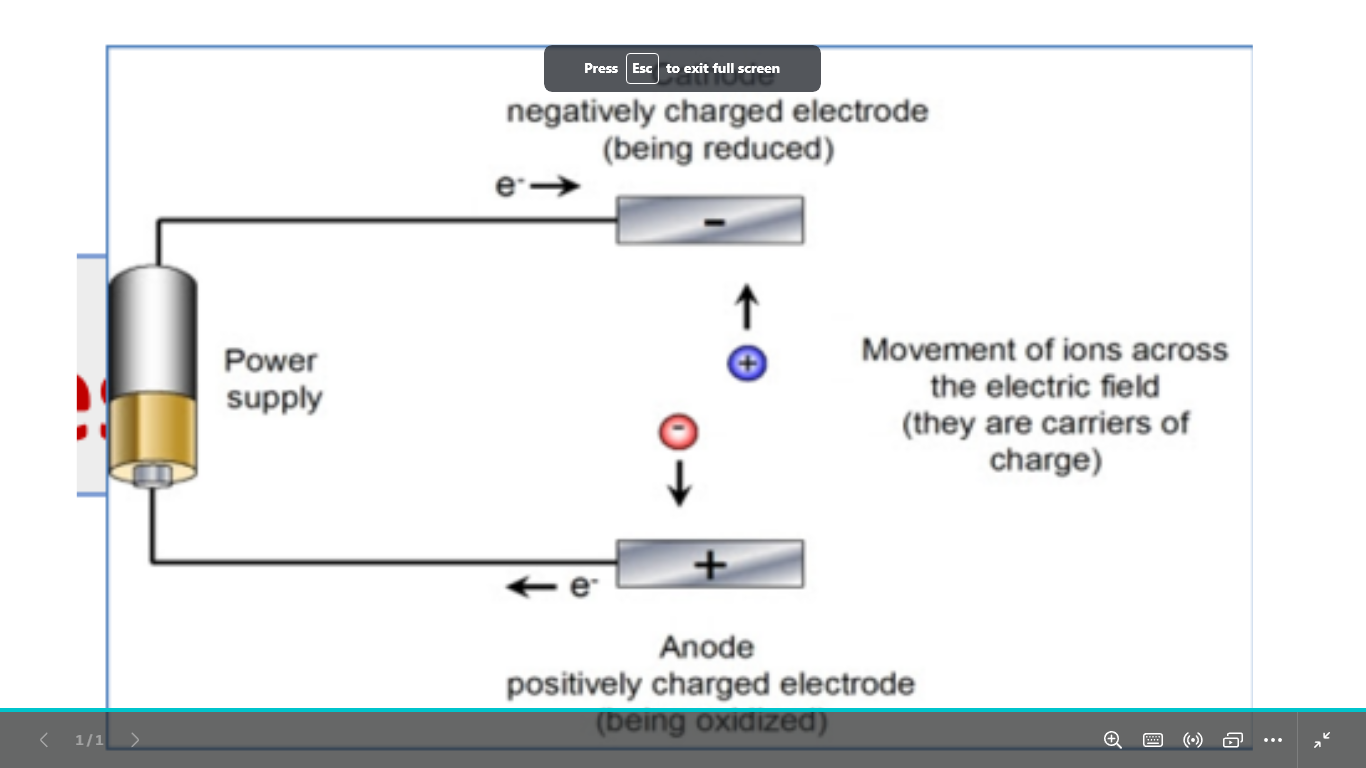
name the process
define it
what is it used to
this technique depends on what ?(سؤال مهم )
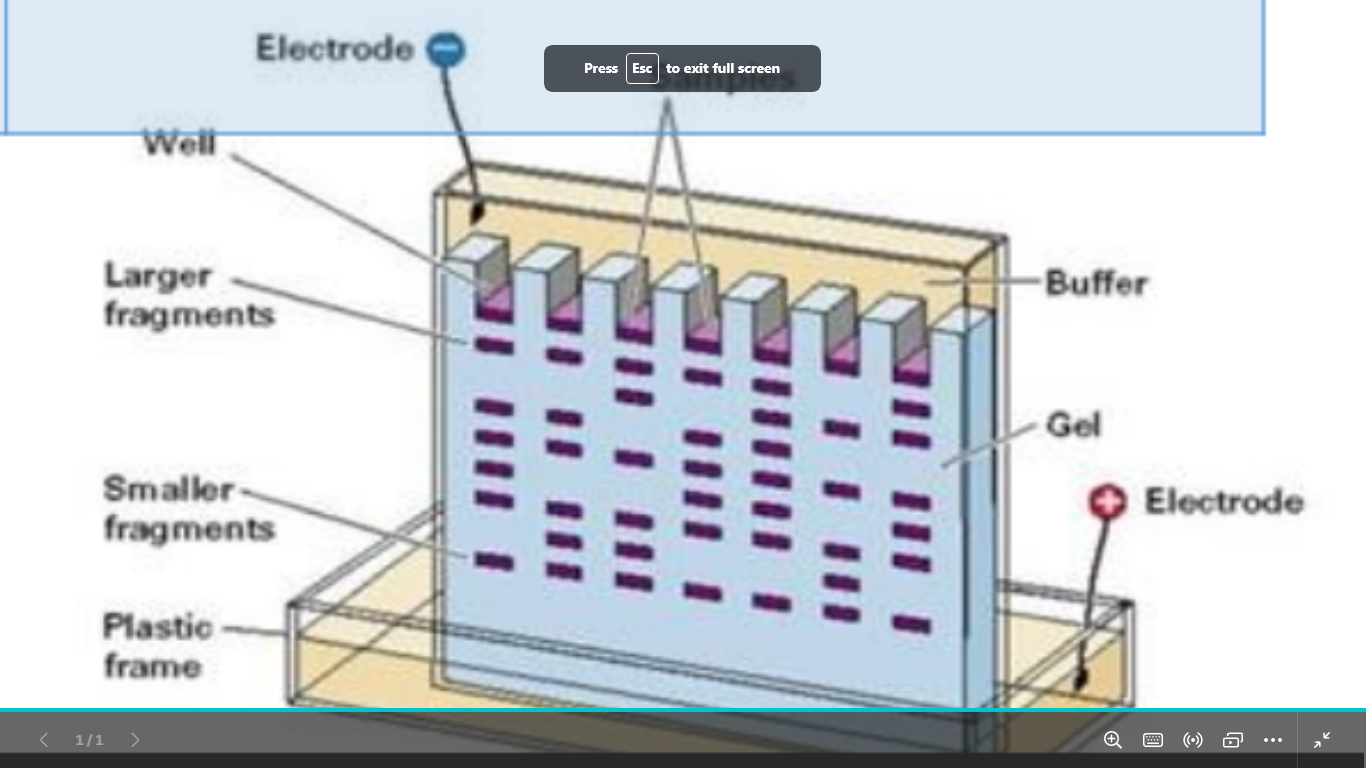
electrophoresis
its the movement of charged particles under the influence of an electric field cations moves toward cathode anions move towards anode
used to identify and separate biomolecules : nucleic acids or proteins
based on charge and size (lighter molecules move more distance)
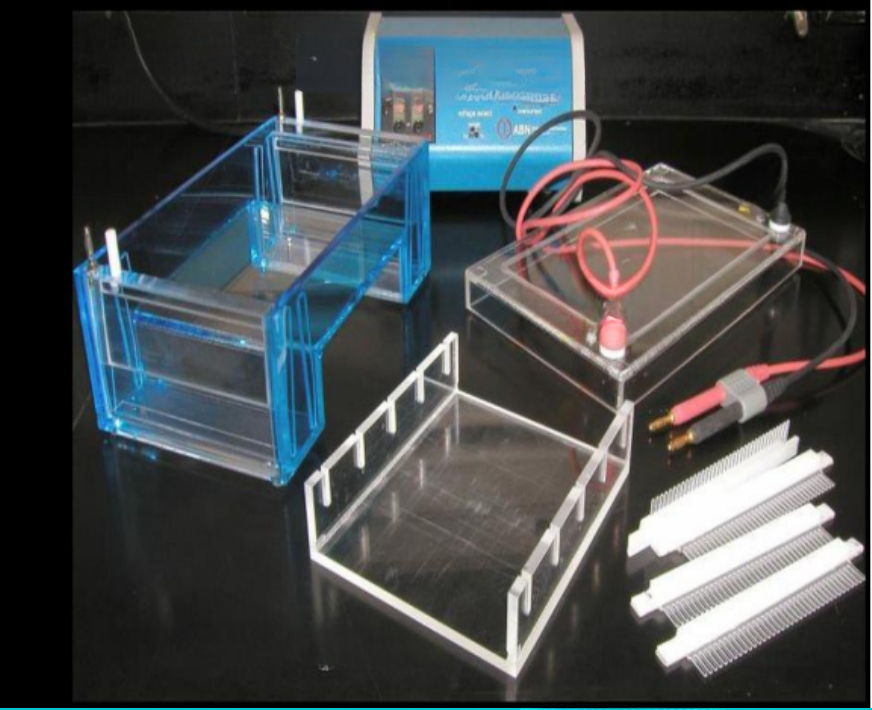
electrophoresis apparatus is formed of what parts
power supply
electric leads
casting tray
gel tank
gel combs
cover
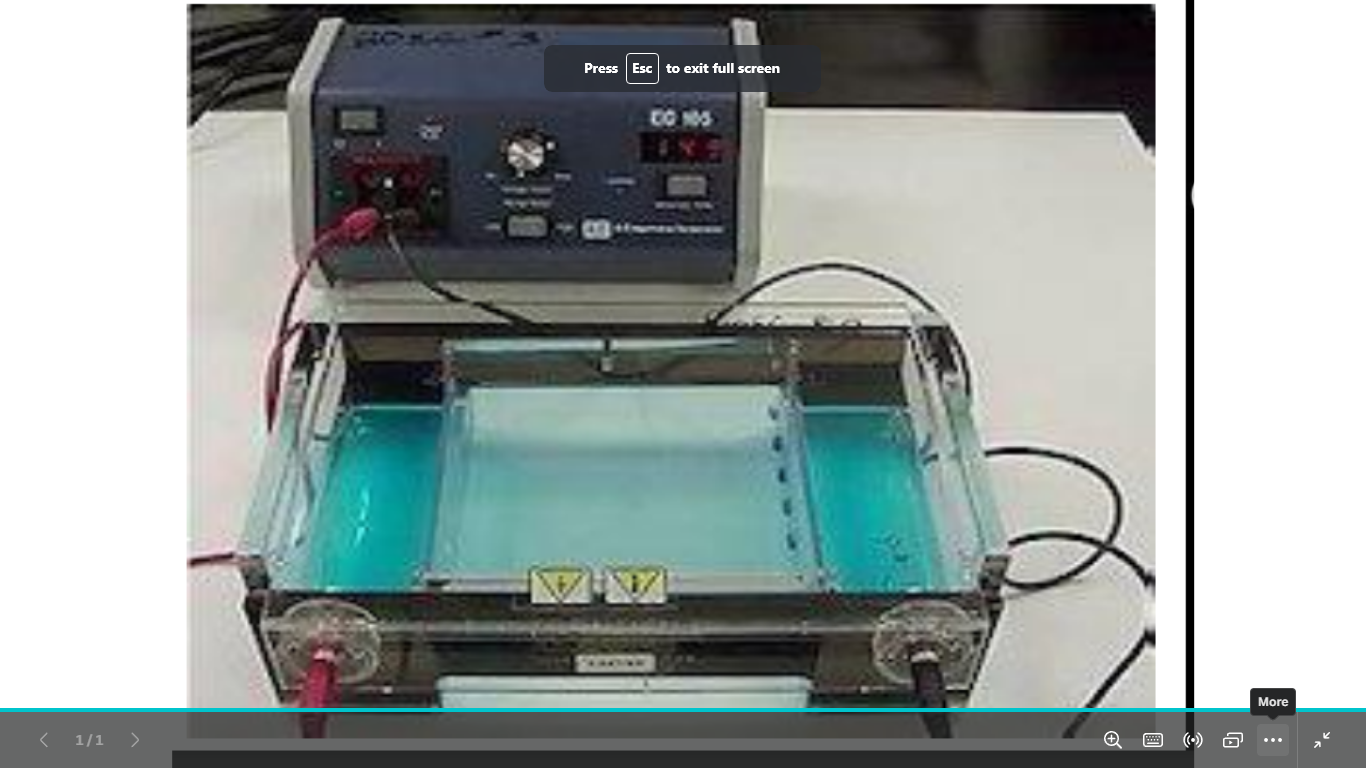

identify
anad what are the types
electrophoresis apparatus
types of dna gel electrophoresis
1)agarose gel electrophoresis
2)polycrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE)

identify
and mention its properties 3
utilize what ?
placing ?
separates what ?
agarose gel electrophoresis
utilize agarose powder
horizontal
separate chains of larger size
identify
and mention its properties 3
utilize what ?
placing ?
separates what ?
polyrylamide gel electrophoresis
utilize polyacylamide
vertical
separates short chains of dna thtat differ in length by only one nucleotide !! so its very efficient in separation
2 properties of agerose that make it appropriate for electrophoresis
1-liquid when hot and solidifies on cooling
2-agarose is porous allowing for the movemnt of dna and it resembles a sponge with holes
مش لاقي صوره مناسبه بس جا محتوي سلايد كامل!

what is that blue thing and why its used and what type of electrophoresis is this(سؤال مهم )
a coloured loading dye (bromophenol blue) is mixed to dna sample to
Color and increase sample weight/density to help sample loading
Track the DNA migration (color)
dna bands can be visualized by staining with dyes like ?
and what happens then ?
خد بالك فرق كبير بين ال loading dye وال visualization dye
ethidium bromide
it intercalates between the nitrogenous bases of dna and allows visualization of dna bands under ultraviolet light

what does this indicates in the electrophoresis apparatus
it means that electrodes are connecteed,plugged in and that current is flowing
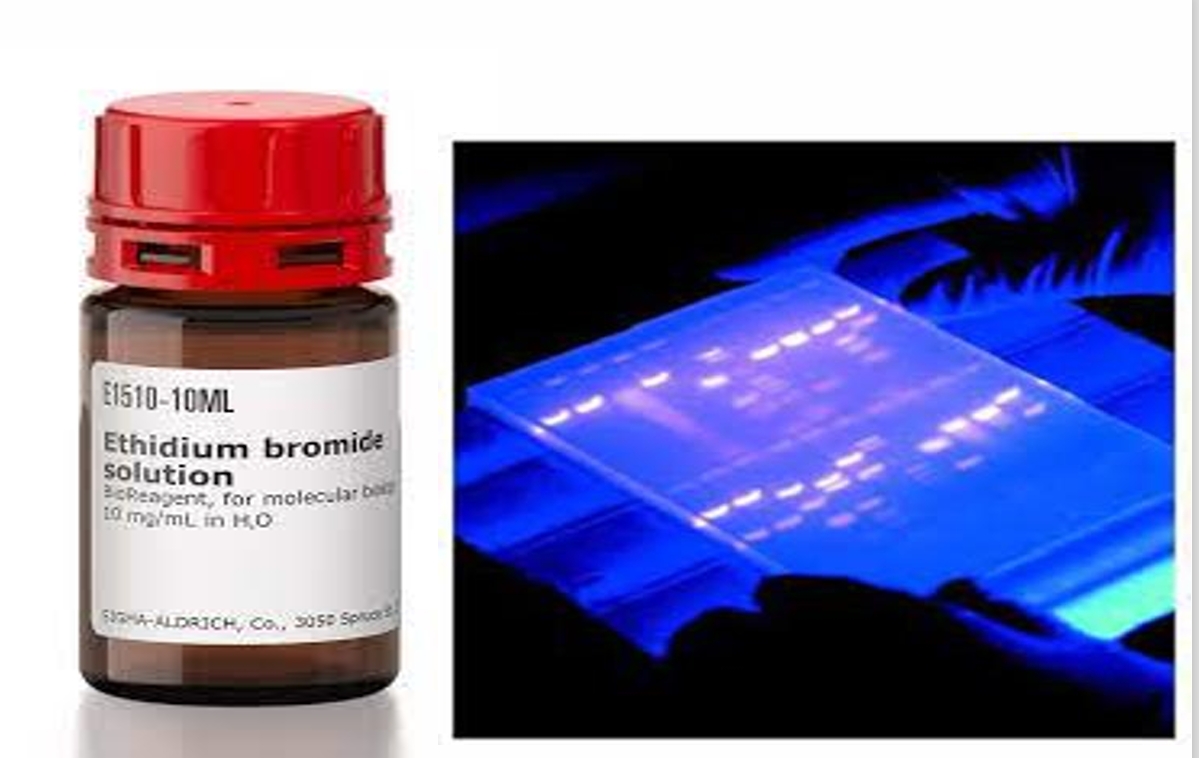

identify this solution and its uses
ethidium bromide dye
visualized DNA bands by intercalating between the nitrogenous bases of DNA
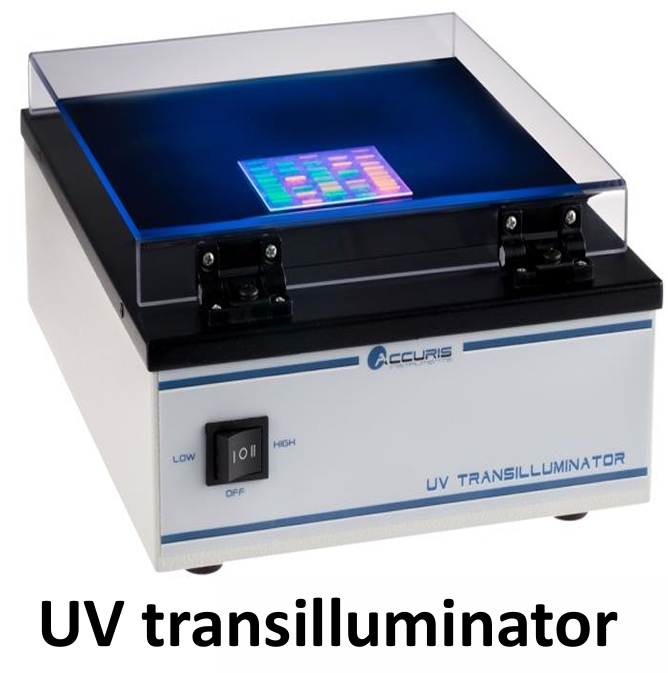

Identify the device and its uses
UV transilluminator
Visualization of DNA bands under ultraviolet light

what is this
and why it is applied
dna ladder its a solution of dna molecules of different lengths used in agarise or acrylamide gel electrophoresis
its applied as a reference to estemate the size of an unknown dna molecule by comparing them to the closest fragment in the ladder
what is karyotype used to ?
in which stage is karyotyping captured
It describes the number & appearance of chromosomes under light microscope
In metaphase stage
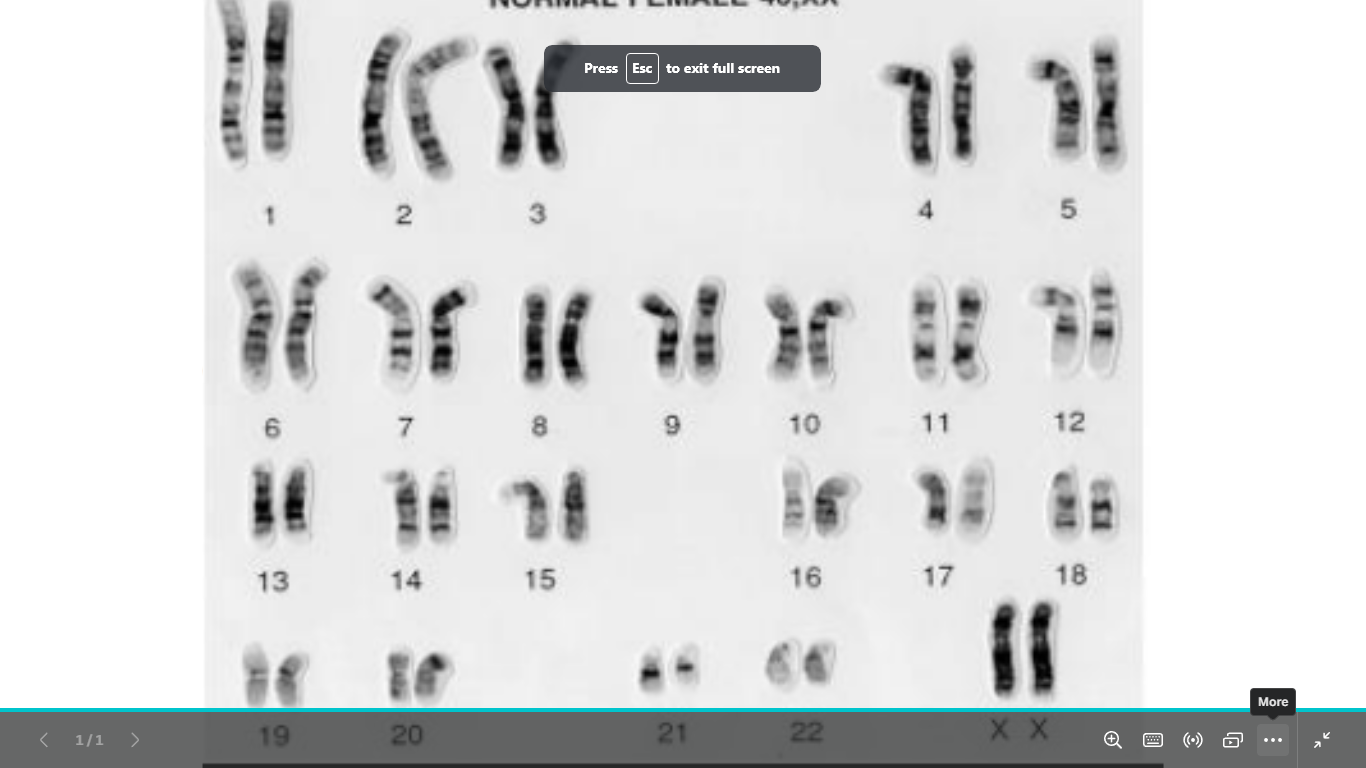
identify and write it
normal female karyotype
46,xx
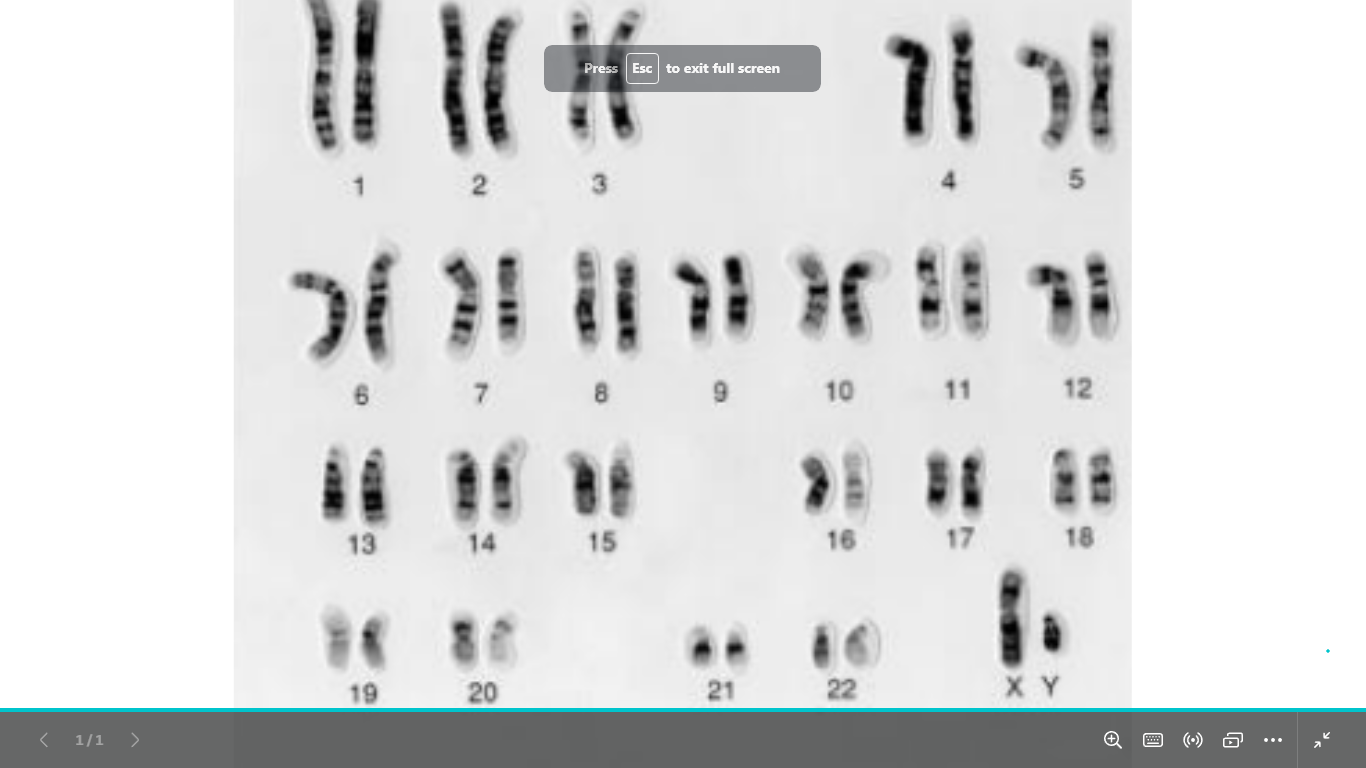
identify and write it
normal male karyotype
46,xy
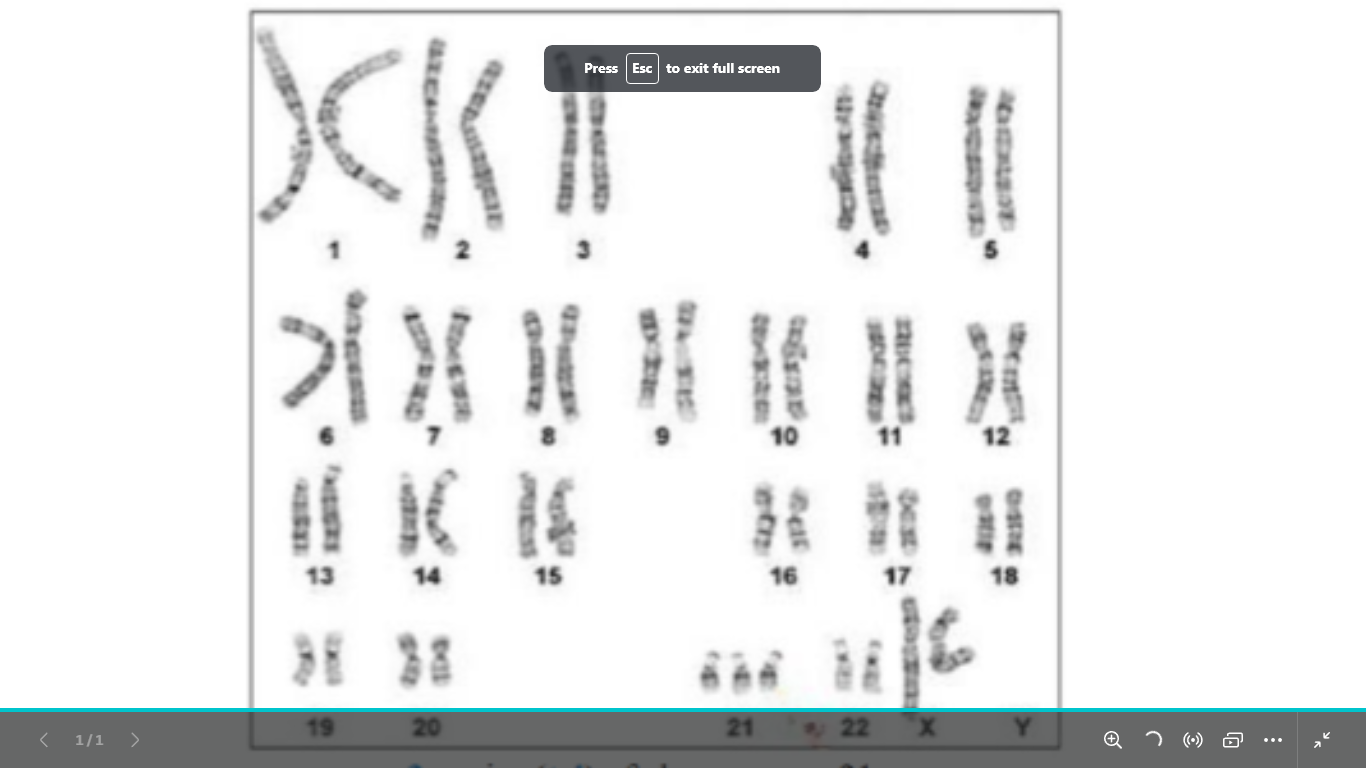
type of chromosomal abnormality
and write it
and what is its name
numerical chromosomal abnormality
trisomy of chromosome 21 (male or female)
the picture example 47,xx+21
the male with down syndrome karyotype
47,xy+21
down syndrome

type of chromosomal abnormality
gender
syndrome name
karyotype
caused by ?
abnormality in sex chromosome
female
turner syndrome
45,X0
caused by missinf of one X chromosome in females
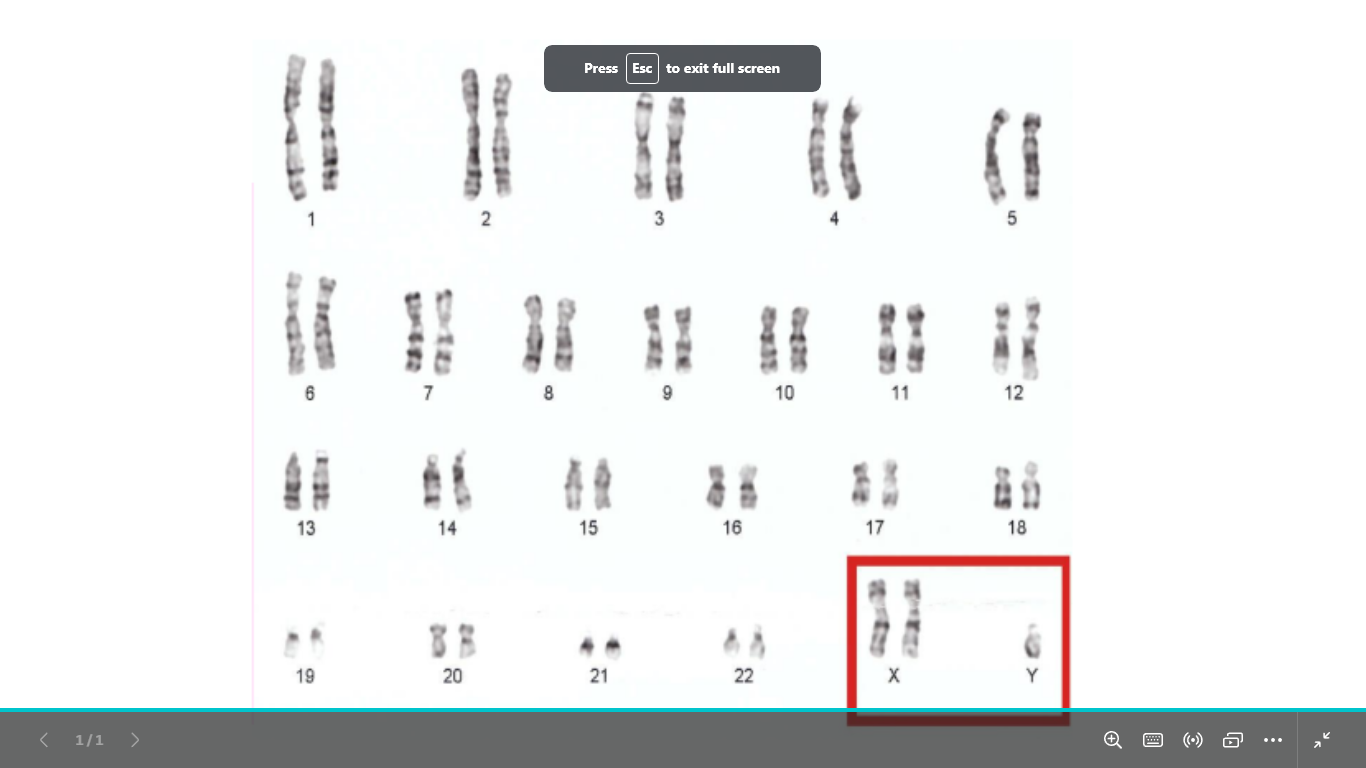
type of chromosomal abnormality
gender
syndrome name
karyotype
caused by ?
common ?
abnormality in sex chromosomes
male
klienfelter syndrome
47,xxy (male)
caused by an extra x chromosome (XXY)
its the most common chromosomal abnormality in males
Why karyotyping is Performed? Indications of karyotyping
1. Detection of chromosomal abnormalities
2. Gender determination (Identify the sex of a person)
3. Find out the cause of baby's birth defect or disability
4. Find out the cause of infertility
5. Identify genetic problems
Types of Samples used for Karyotyping
1. A blood sample
2. Amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling procedures
3. Bone marrow or tissue sample collections
where is karyotype captured ?
and is stained by what ?
سؤال مهم
is arrested at metaphase by (colchicine)
By Giemsa stain then photographed
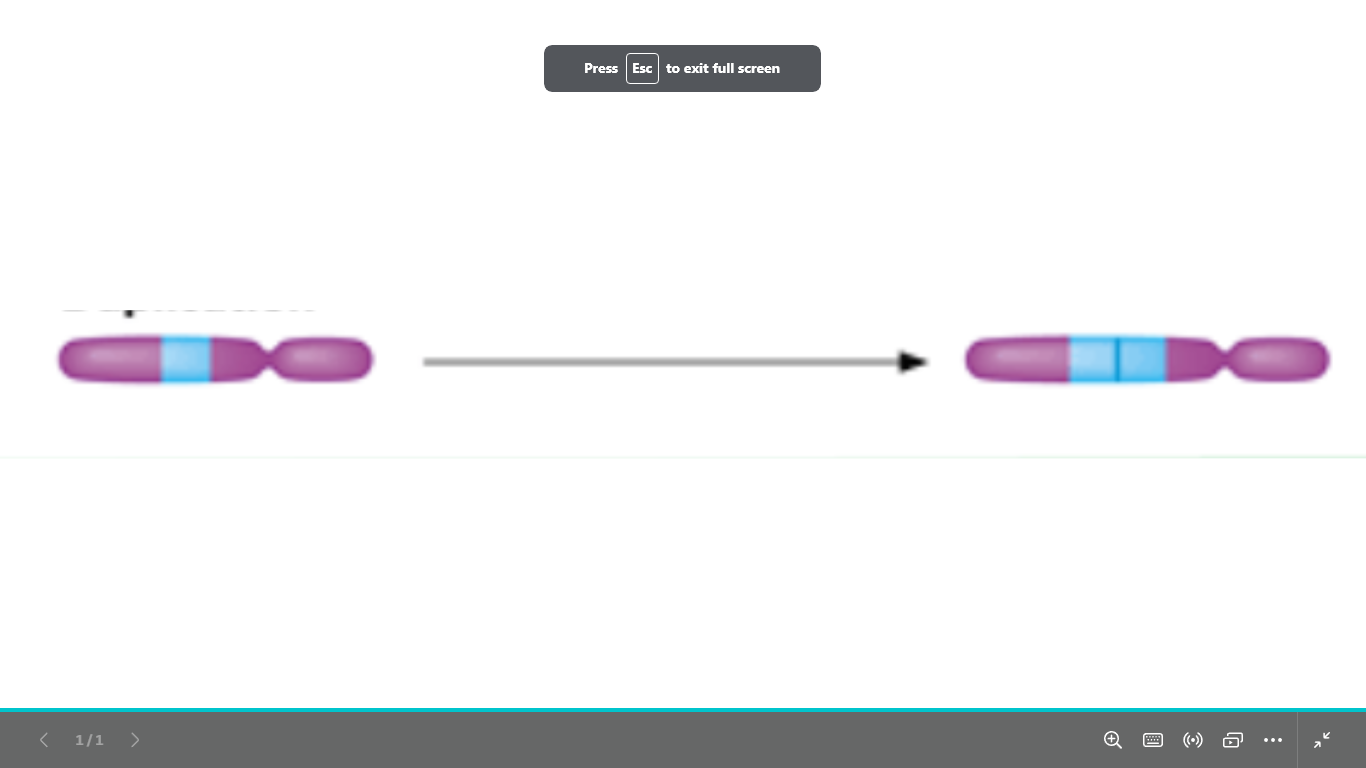
what type of chromosomal abnormality is
structural chromosomal abnormality
duplication
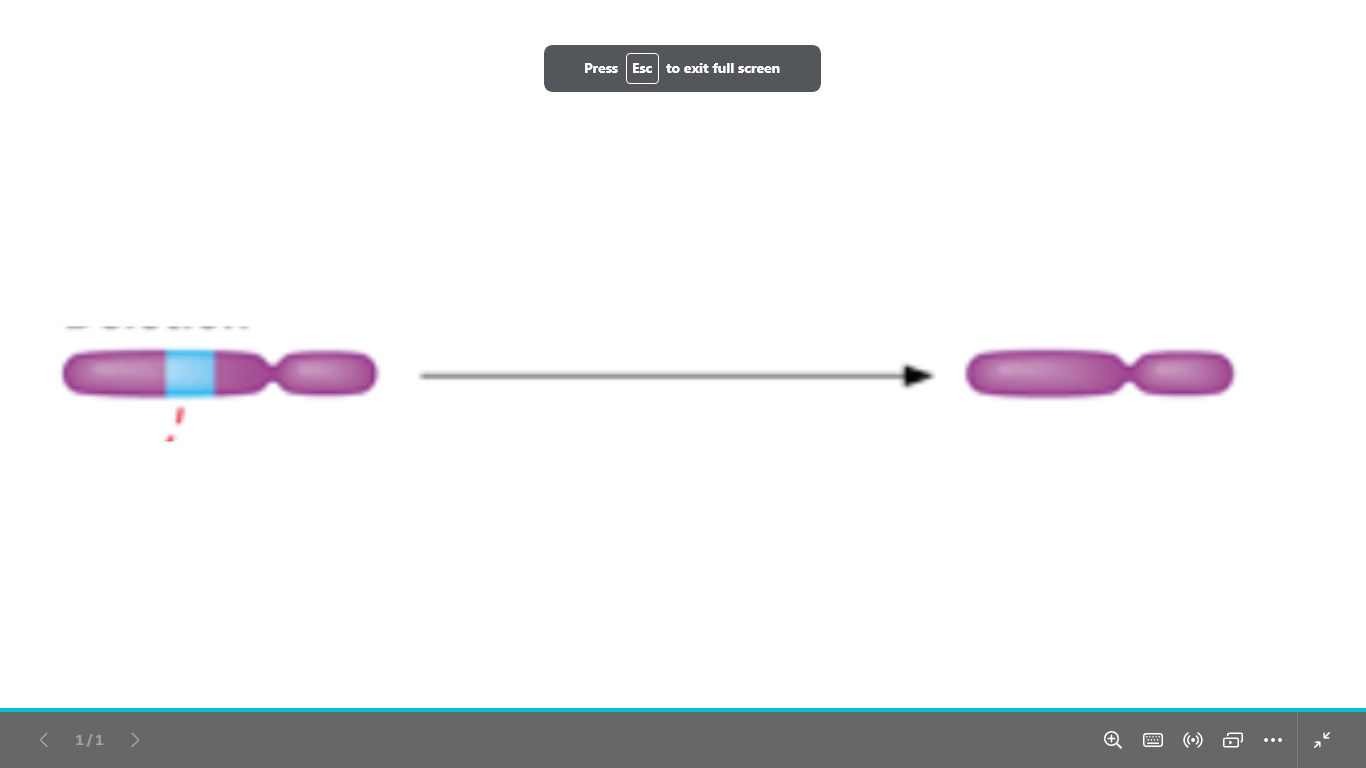
what type of chromosomal abnormality is
structural chromosomal abnormality
deletion
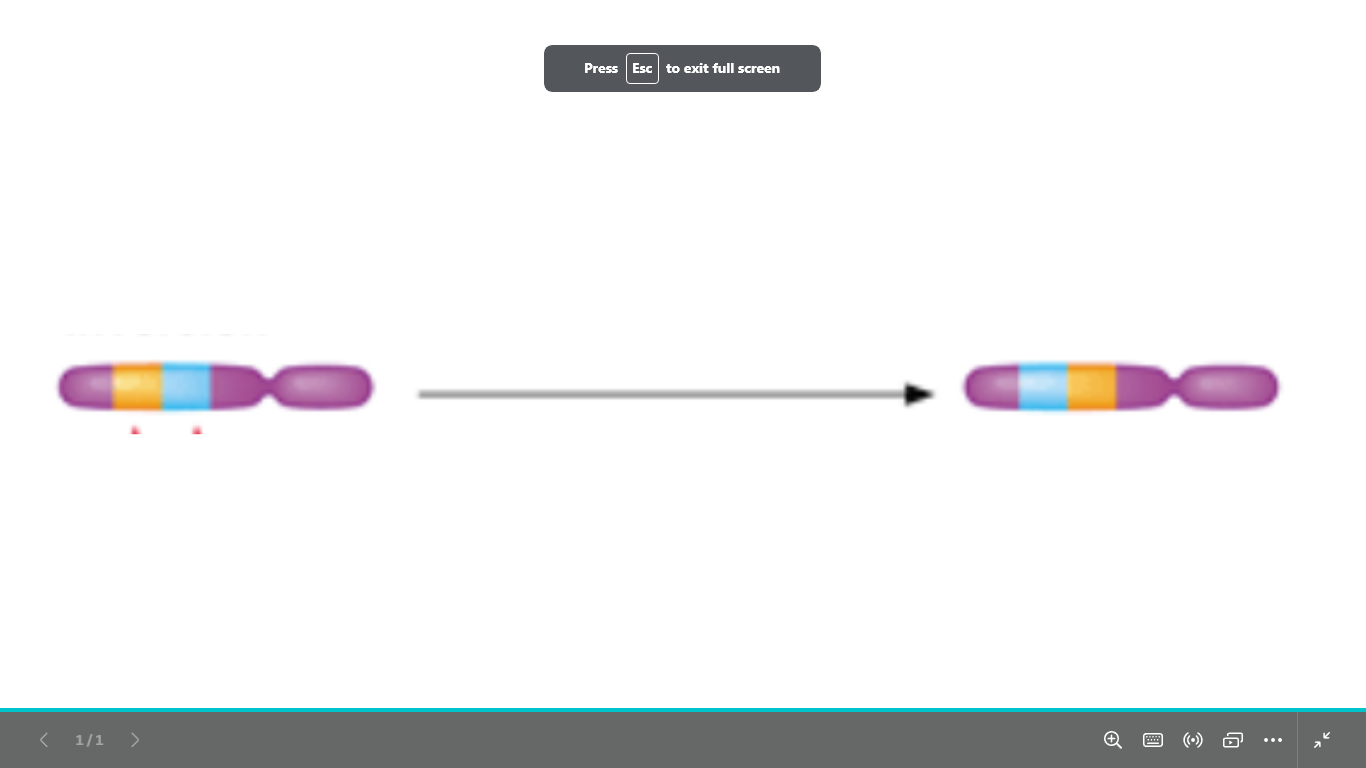
what type of chromosomal abnormality is
structural chromosomal abnormality
inversion
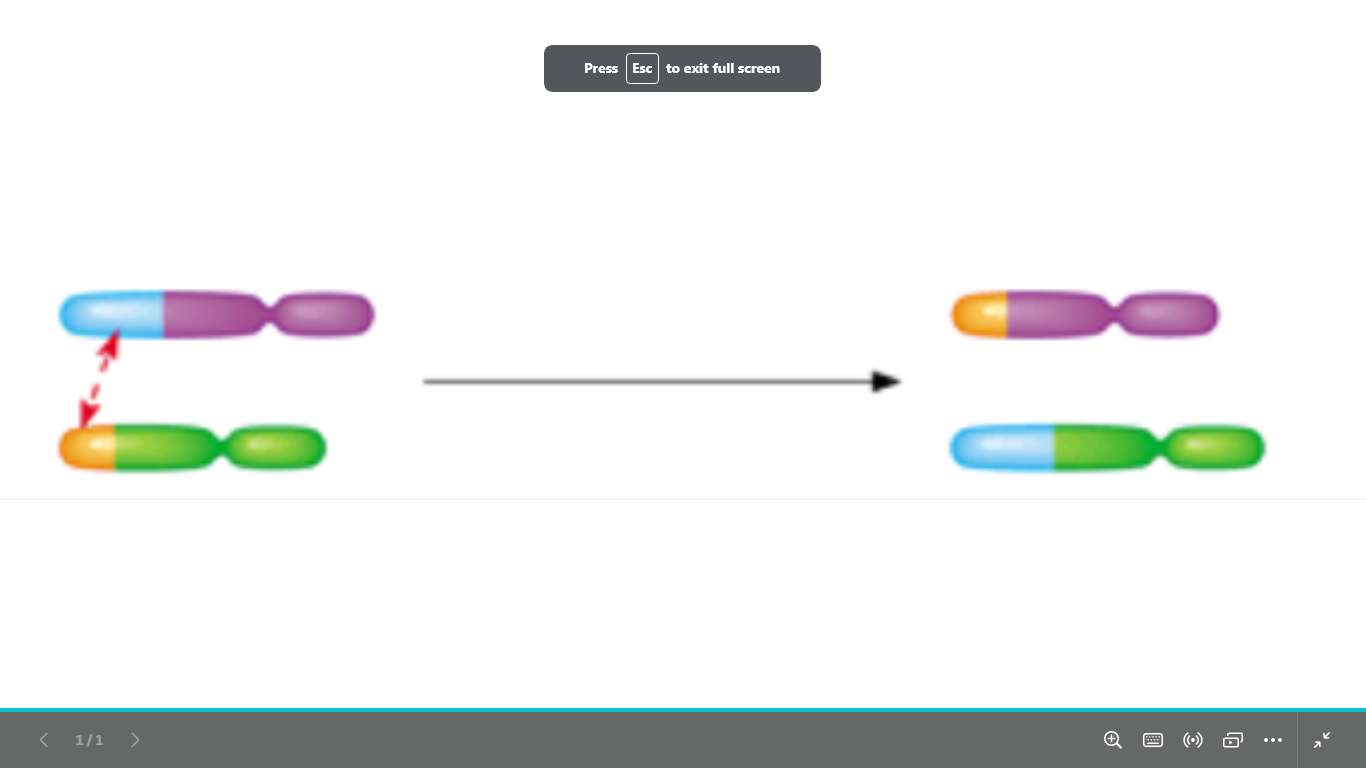
what type of chromosomal abnormality is this
structural chromosomal abnormality
translocation
lysis step needs what and what happens in it
need lysis solution and what happen is lysis of cellular and nuclear membrane so the nuclear content are released
مش مهم صوره
binding step needs what and what happens in it
needs the spin column and what happens is binding of dna to silica gel membrane
2 wash steps need what and what happens in them
need the 1,2 wash buffer what happen is the removal of protein and any impurities or contaminants
elution step needs what and what happens in it
needs elution buffer and what happen is the release of dna from the membrane so pure dna is formed
movement of charged particle direction
cations move towards cathode
anions move towards anode
cathod anode cation aniion charge respectively
cathode negative
anode positive
cation positive ion
anion negative ion
اللي قريبين في الاسم مختلفين في التشارج فا بيروح ل بعض
dna charge and ion name and where does it migrate and what is the colour of the wire that it migrate towards
dna is negatively charged
so its name is an anion and it will migrate to the anode to the positive red wire
agerose gel properties 2
liquid when hot and solidifies on cooling
its porous allowing movement of dna
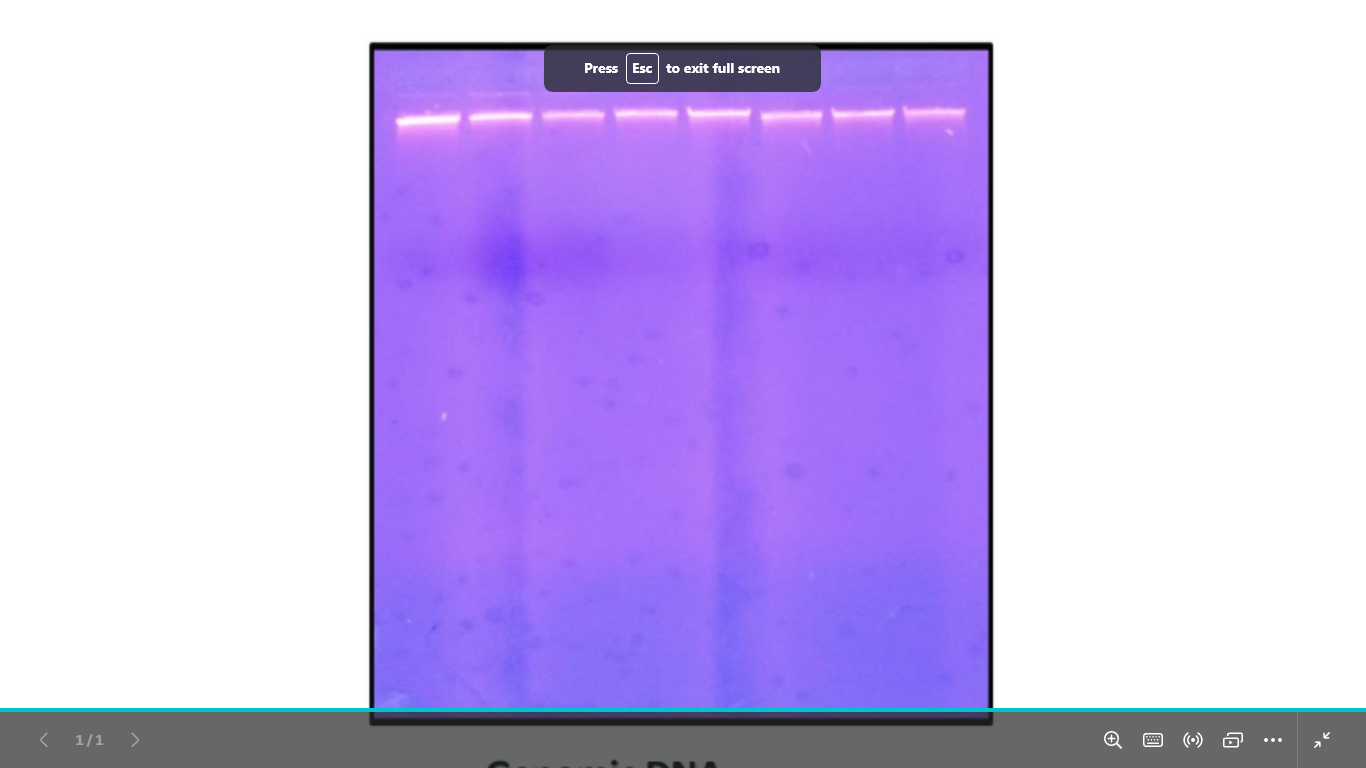
what is this dna (visualization)
genomic dna
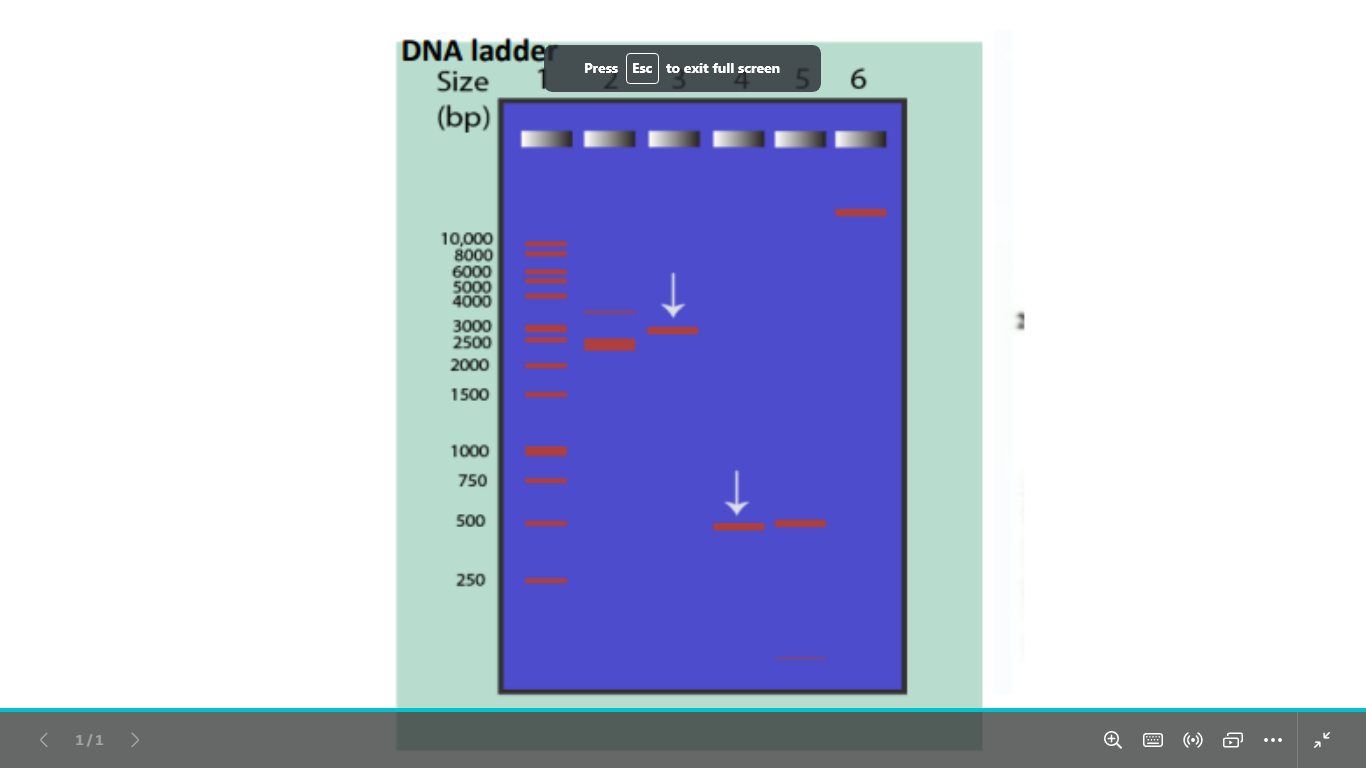
what is this dna (visualization)
PCR product
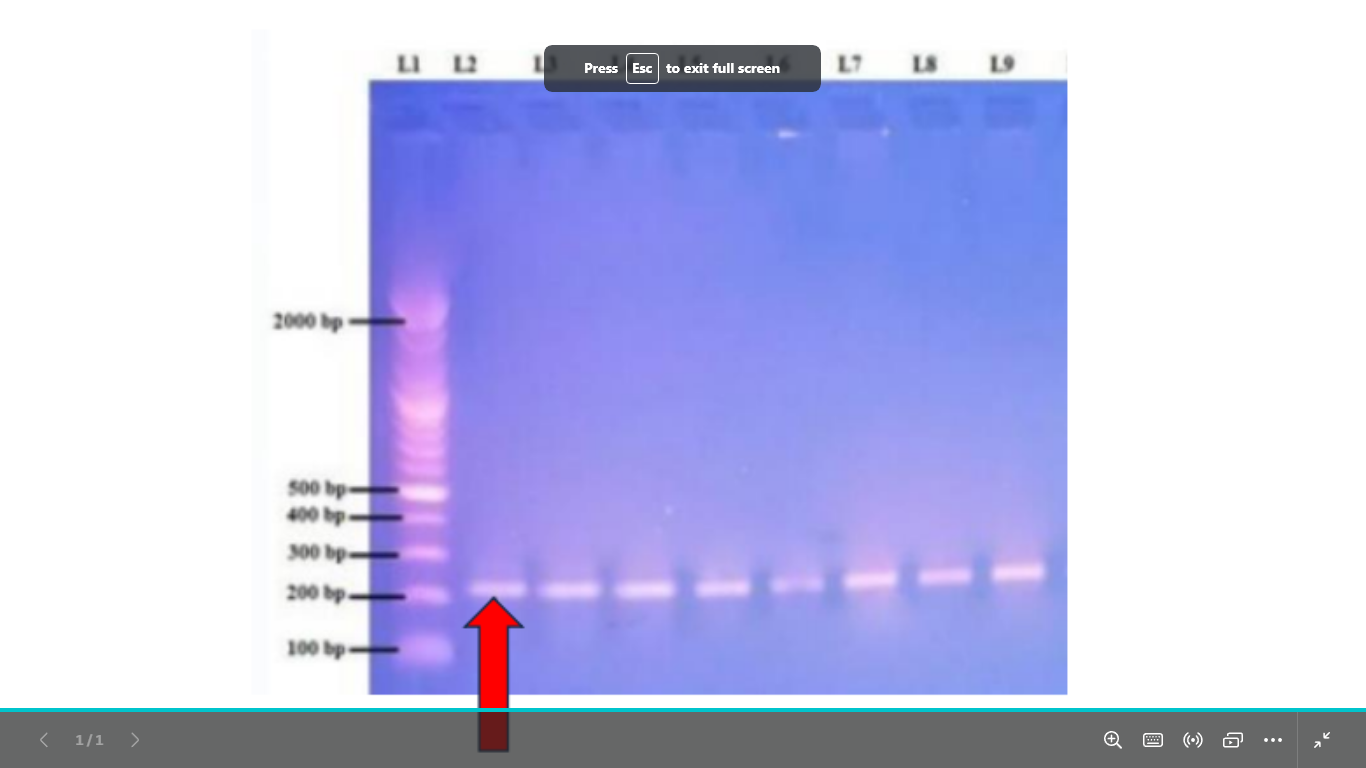
what is this dna (visualization)
PCR product
how is karyotyping done (extracting cellular dna)
cells are captured during metaphase stage in mitosis by colchicine the chromosomes are highly condensed and arranged at the cell equator
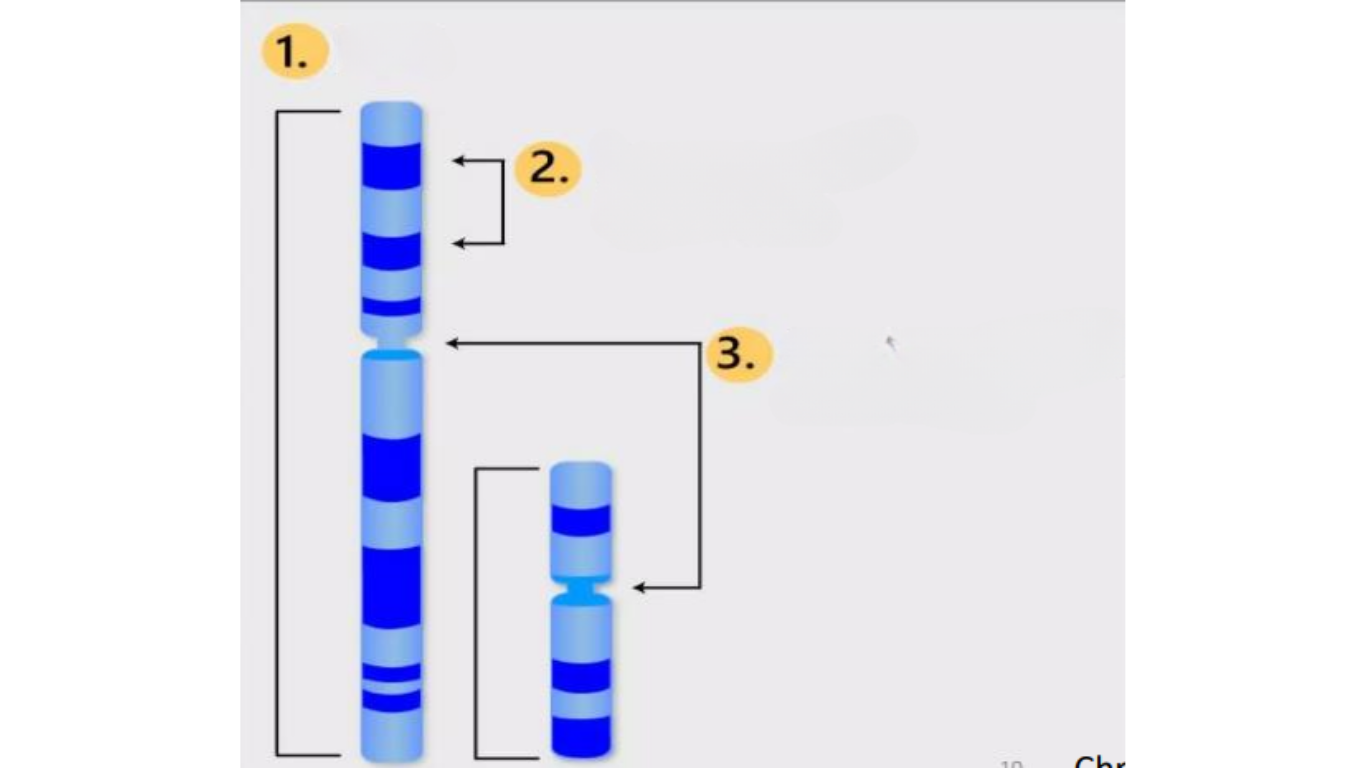
the 3 key features to identify chromosomes
1 size
2 banding pattern
3 centromere position
why karyotyping is formed 5
detection of genetic abnormality
gender determination
find out the cause of baby birth defect or disability
find out the cause of infertility
help identify genetic problems