Unit 1 Part 2 APPsych Study Set
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
The brainstem
oldest region of the brain, necessary for survival
Medulla (part of brainstem)
controls functions that occur w/out conscious thought
heart rate
breathing
blood pressure
UNCONSCIOUS SURVIVAL FUNCTIONS
Reticular Activating System (reticular formation)
network of nerves - vital in survival functions:
attention
arousal
alertness
being aware something has come into your environment in order to survive threats
SURVIVAL FUNCTIONS
cerebrum
contains the left & right cerebral hemispheres
Cerebral Cortex
thin layer of neural cells that cover the cerebral hemispheres
responsible for most of the sophisticated INFORMATION PROCESSING of the brain
contains the Limbic system along w/ the cerebrum
Cerebellum
cereBELLum- BALANCE & equilibrium
coordinates sequences of movement
ex: walking
supports NON-VERBAL learning and skill learning
occurs without conscious awareness
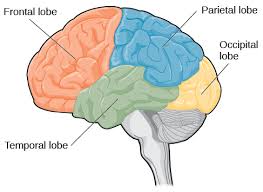
a hemispheres subdivisions of the cortex (4 lobes)
frontal
parietal
occipital
temporal
besides the 4 lobes the cerebrum & cerebral cortex also include:
the limbic system and corpus callosum
parts of limbic system
thalamus
hypothalamus
hippocampus
amygdala
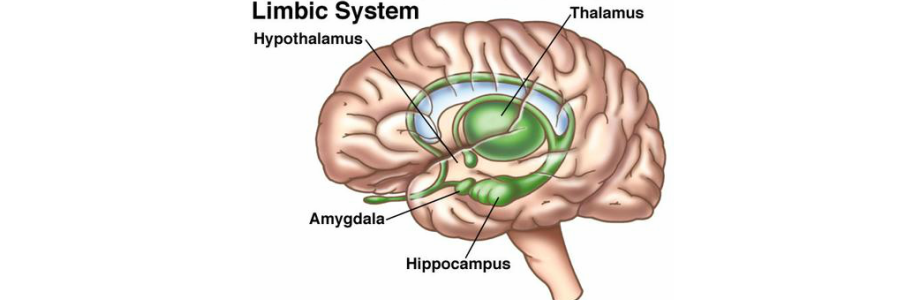
thalamus
“sensory switchboard”
incoming sensory info (except smell) is received & sorted/processed here before being sent to the cortex for further interpretation
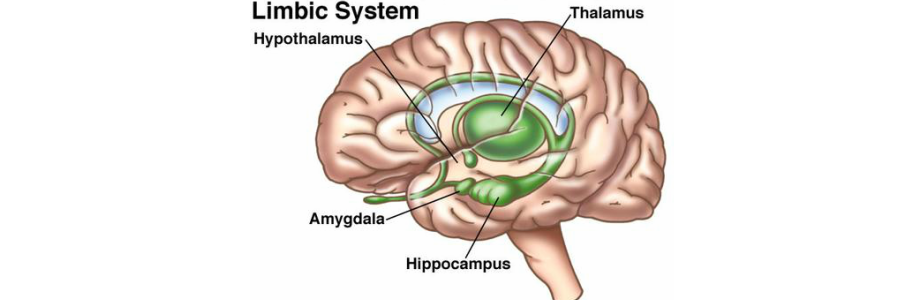
hypothalamus
FIGHT or FLIGHT response
HUNGER motivation
directs activities that help as maintain homeostasis
controls endocrine system
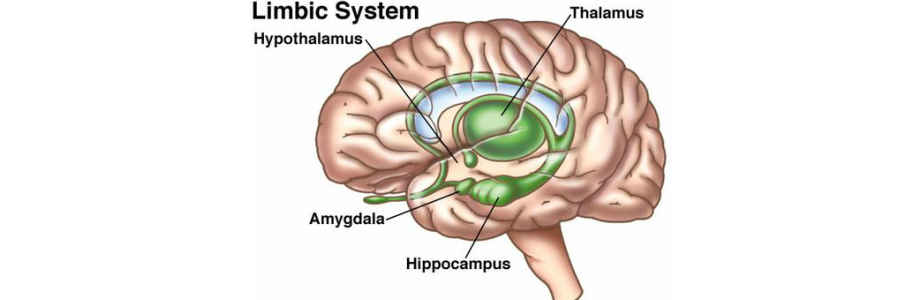
amygdala
linked to emotions
3 A’s
Anger Aggression, Afraid (aka fear)
helps ingrain highly emotional memories
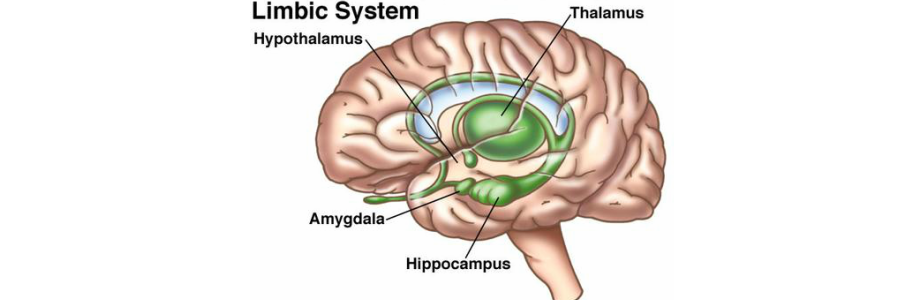
hippocampus
converts short term memory into long term memory
creates, processes, and retrieves memories of facts and events but DOES NOT store them
dysfunction associated w/ Alzheimer’s
losing hippocampus due to surgery or injury will lose their ability to form NEW memories
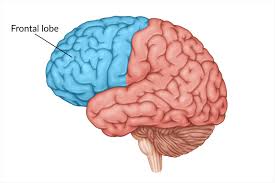
frontal lobes
prefrontal cortex
motor cortex
association areas
Broca’s area (left side only)
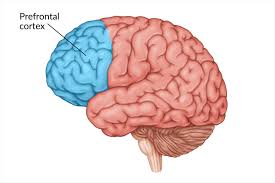
prefrontal cortex (in frontal lobes)
involved in cognitive functions
thinking, planning, decision making, impulse control
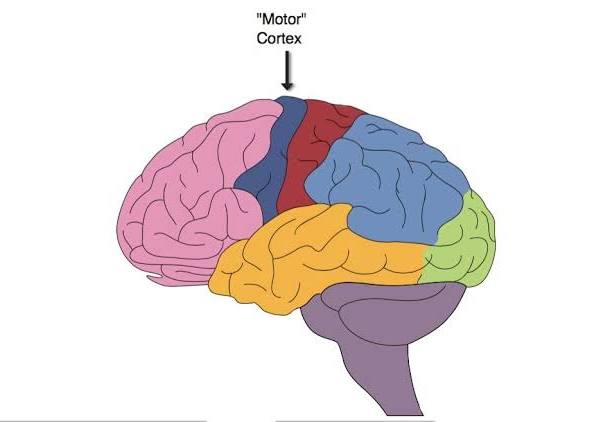
motor cortex (in frontal lobes)
involved in initiating voluntary movement
contralateral hemispheric organization
LH- controls movement on the right side of body
RH- controls movement on the left side of body
areas of the body that make precise movements get more tissue from this cortex in the brain devoted to them
ex: fingers or lips
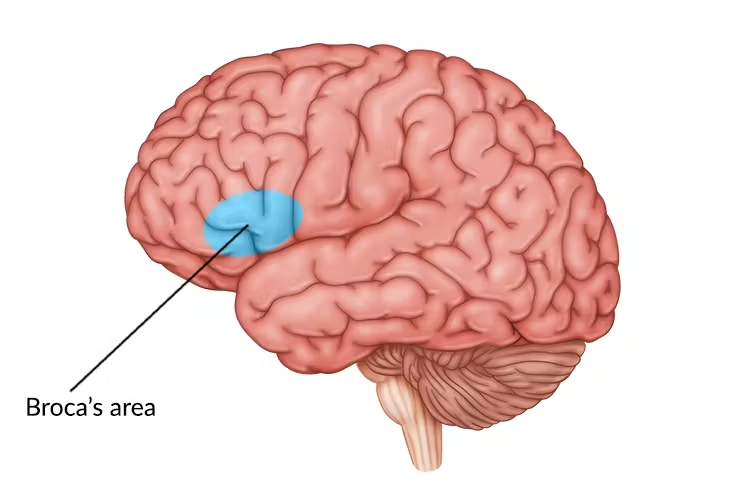
Broca’s Area (left frontal lobe only)
involved in expressing and producing speech
damage can lead to Broca’s aphasia which is the inability to produce speech
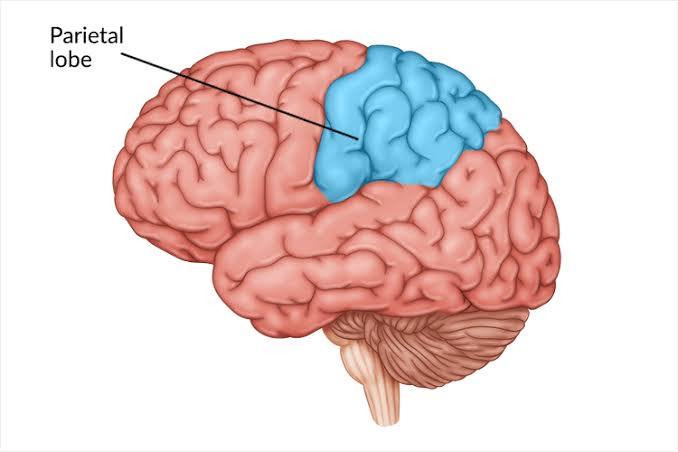
parietal lobes
somatosensory cortex
somatosensory cortex (in parietal lobes)
represents sense of touch
more sensitive parts of the body have more tissue devoted to them on this strip
ex: fingers and lips
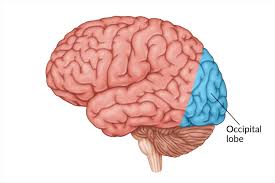
Occipital Lobes
primary visual cortex
primary visual cortex (in occipital lobes)
visual processing
damage to the Occipital lobe can cause blindness despite the fact that there may be no damage to the eyes
due to the interpretation process being lost
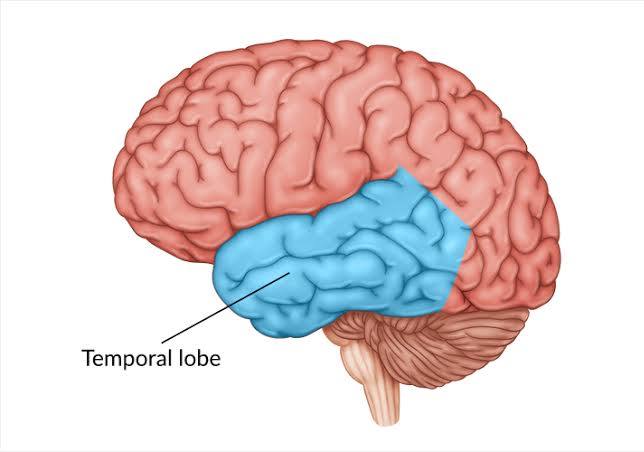
temporal lobes
primary auditory cortex, aka hearing
LEFT temporal lobe contains Wernicke’s area
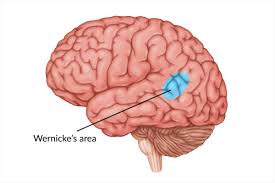
Wernicke’s Area (in left temporal lobe)
involved with understanding and comprehending language
Damage can lead to Wernicke’s aphasia which is the inability to comprehend or understand speech
parietal lobes contains
somatosensory cortex
association areas
occipital lobes contains
primary visual cortex
association areas
temporal lobes contain
auditory cortex
association areas
wernicke’s area (left side only)
case studies for studying the brain
for a long time, scientists would observe cases of accidental brain damage in order to understand the brain better
Lesions
scientists can learn about the brain by observing the effect on brain function when brain tissue is destroyed
this tissue destruction is a lesion
these may occur due to disease, trauma, during surgery, or experimentally
Electroencephalogram/EEG (type of brain scan)
measures brain’s electrical activity
the electrodes that is put on the scalp look for normal/abnormal brain wave patterns to diagnose or treat certain conditions
help diagnose sleep disorders
functional MRI/fMRI (type of brain scan)
can detect BOTH structure and function
measures oxygen and blood flow to brain regions
used ONLY to look at the brain
can be used to understand the parts of a patients brain that become active & inactive during various tasks
pathways that use the contra lateral hemispheric organization
motor and sensory pathways
corpus callosum
bundle of fibers that connect the two hemispheres
hemispheric specialization aka lateralization
tendency for 1 hemisphere to excel at a certain skill compared to the other side
understood using split brain research
left hemispheric specialization
language
analysis
calculations
right hemispheric specialization
spatial abilities
facial recognition
right visual field
right side of each eyes VF
its info goes to the LH
left visual field
left side of each eye’s VF
its info goes to RH
Visual field diagram
RVF LVF
LHemi RHemi
RHand LHand
neuroplasticity
the brains ability to change by building new pathways based on experience or reorganizing after damage
especially in childhood
some damage is permanent though
neurons of a severed brain and spinal cord cannot regenerate
sometimes it can reorganize and functions that were once under the control of a removed or damaged part of the brain can be taken up by a working part of the brain
neurogenisis
process by which a brain area that has been deprived of its typical sensory input begins to process new inputs from different sensory modalities
dual processing
processing more information than we are consciously aware of
things are processed on either a “high road” or “low road” in our brain
circadian rhythm
internal biological clock, regular body rhythms like temp and sleep/wake cycle that occur on a 24h cycle
Sleep stages
NREM sleep
stage 1
stage 2
stage 3
REM sleep
the cycle repeats about every 90-120 min
NREM
distinct EEG patterns
amount decreases as night goes on
stage 1 aka NREM 1
beginning of cycle for a few minutes
lightest stage
hypnagogic sensations
hypnagogic sensations
images resembling hallucination, or sensations of falling, floating weightlessly
stage 2 aka NREM 2
typically lasts about 20 min
clearly asleep then
stage 3 aka NREM 3
aka body sleep or slow-wave sleep
typically lasts for about 30 min
deep sleep hard to awaken
hormones are released into bloodstream
essential for good health, w/out you are at a greater risk of illness
REM sleep
heart rate rises
breathing becomes rapid or irregular
eyes dart in momentary bursts- indicating dreams
arousal of genitals
muscles relax, essentially paralysis
sometimes called paradoxical sleep
cant move, but has high brain activity
increases over the course of the night
what affects our sleep patterns?
age
genetics
cultural, social, economic influences
light exposure
restoration theory
sleep restores our physiological functions during NREM
sleep restores our mental processes during REM
needed because our bodies wear out during the day
memory consolidation theory
NREM 3 consolidates memories by strengthening neural connections of things we’ve learned
sleep reactivates experiences stored in the hippocampus & moves them to permanent storage elsewhere in the cortex
sleep deprivation affects our…
brain
heart
immune system
joints
muscles
gain of weight
insomnia
ongoing difficulty falling/staying asleep
affects 1 in 5 adults
chronic tiredness, increase risk of depression, hypertension, and more
narcolepsy
sudden attacks of overwhelming sleepiness
affects 1-2000 adults
risk of falling asleep at dangerous moments
sleep apnea
stopping breathing repeatedly while sleeping causing one to constantly wake up
affects 1-20 adults
fatigue, depression, and association w/ obesity
sleepwalking
repeated episodes of complex motor behavior such as walking while asleep
occurs in stage 3
1-15 in 100 people in the general pop.
no serious concerns
won’t remember the next morning
REM sleep behavior disorder
acting our dreams while asleep
vocalizing dreams
risk of accidental injury to self or sleep partner