POM II - Allergic + Inflammatory Rxn - Exam 1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Type I Hypersensitivity - Allergic
-immediate reaction: lesions arise in seconds to hours and resolves within 24 hours
-urticaria: transient, edematous, red papules and plaques
-angioedema
Acute Urticaria
-eruption lasting <6 weeks
-etiology: often idiopathic (50%)
-40% URI; 9% drugs
-IgE mediated/Histamine driven
-Prognosis - excellent if no re-exposure
Chronic urticaria
-eruption lasting 6+ weeks
-more treatment resistant more aggressive course
-probable IgG1 or IgG3 subclass, anti-IgE antibody
-idiopathic > physical > autoimmune
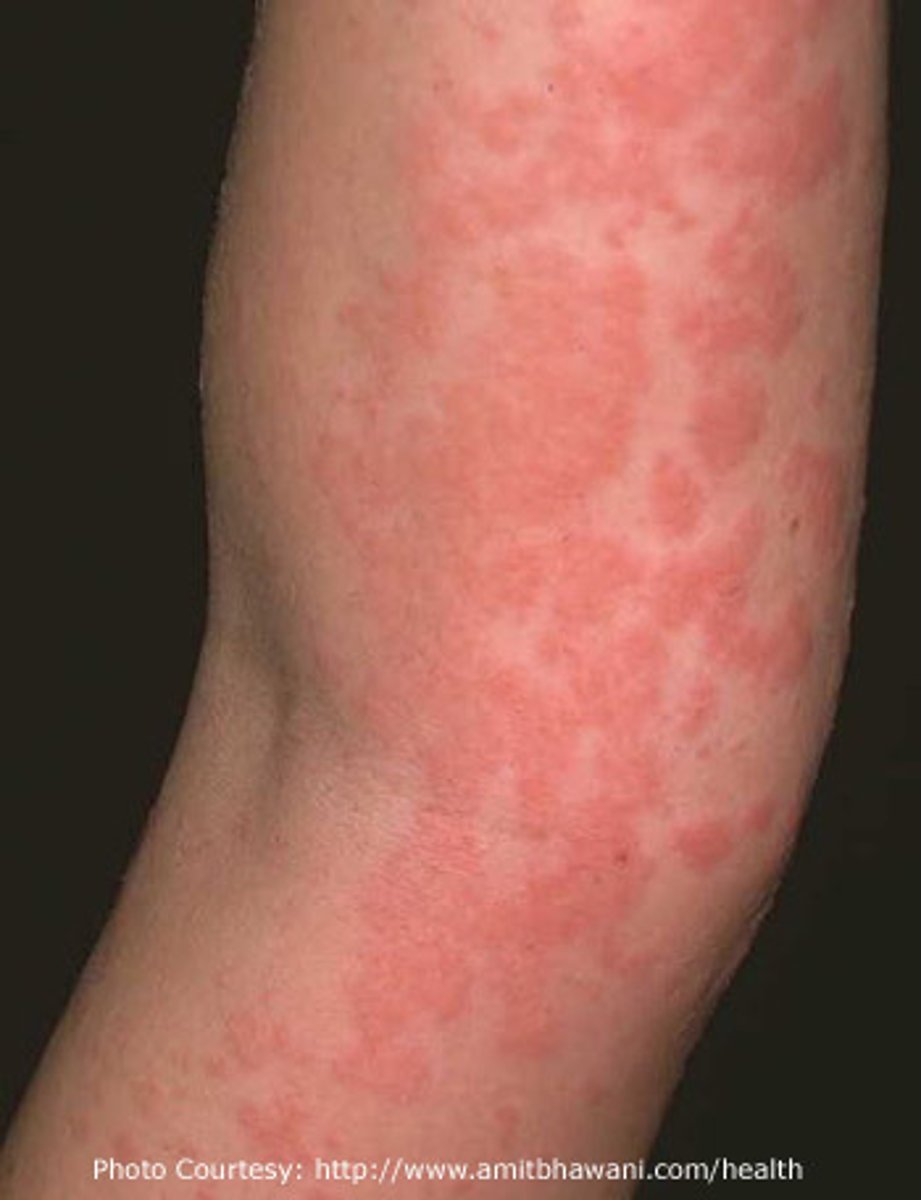
Urticaria
-erythematous, edematous papules or wheals that develop on the skin in response to stimuli
-hives form in response to histamine when blood plasma leaks out of small blood vessels into the skin
-#1 symptom is pruritus
-hallmark: lesions last less than 24 hours
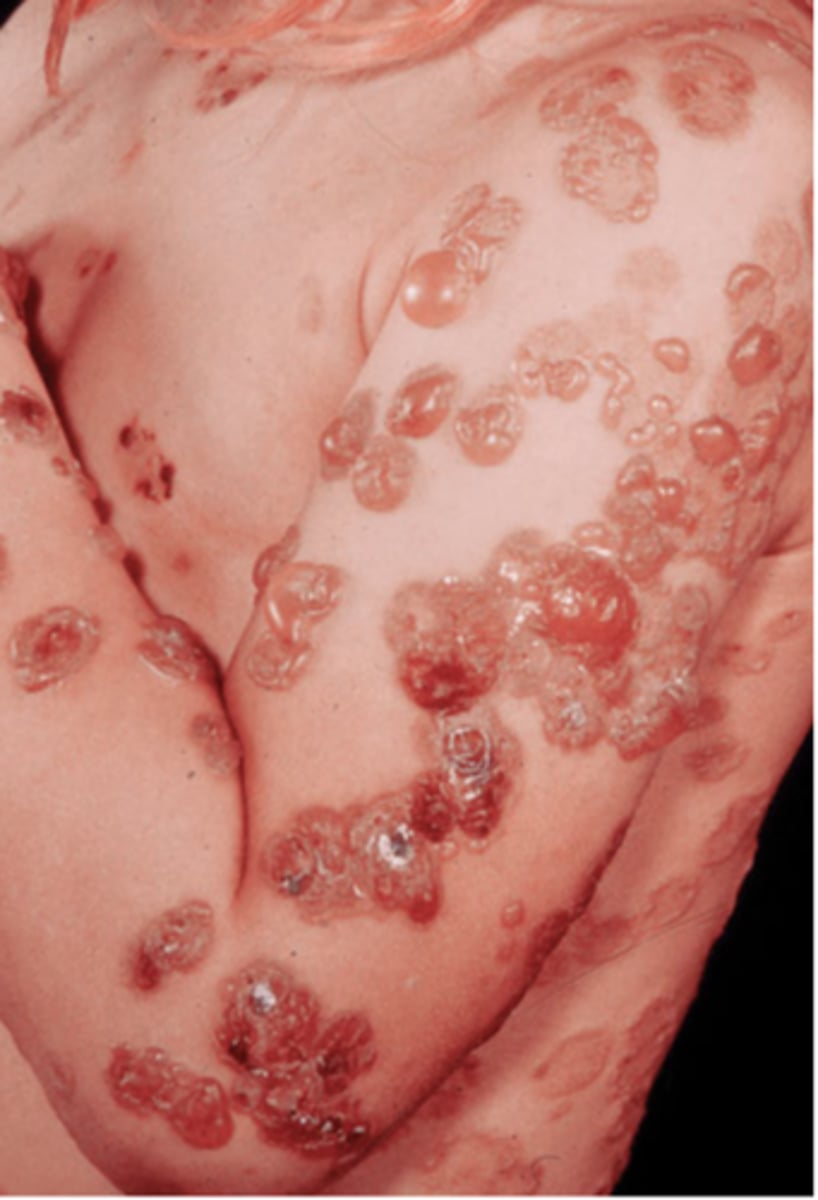
Allergic Urticaria
-food
-environmental
-pets
-inhalants
Chemical urticaria
-drug-induced: NSAIDs, abx common
-stress-induced
Physical Urticaria
-symptomatic dermatographism - mc type of physical
-cold urticaria
-cholinergic
-adrenergic
-contact
-delayed pressure
-solar
-vibratory
-aquagenic
Chronic Urticaria - 5 Is
-ingestants (most common)
-inhalants: dust, feather, pollen
-injectants: drugs, stings, bites
-Infections
-internal disease
Urticaria - Hx
-when did it start?
-recent illness
-meds
-travel
-assoc symptoms
-fmhx
-exacerbating factors
-rash that itches or itch that rashes
Urticaria - Tx
-2nd gen antihistamines first line (Certizine, Loratadine, Fexofenadine)
-1st gen antihistamines
-H2 blockers
-leukotriene inhibitors
Angioedema
-histologically deeper variant of urticaria - dermal and subcutaneous swelling
-more diffuse swelling, less pruritus than urticaria
-Mc affected areas include lips, palms, soles, limbs, trunk, and genitals
-rarely, angioedema of the throat, tongue, or lungs can block airway
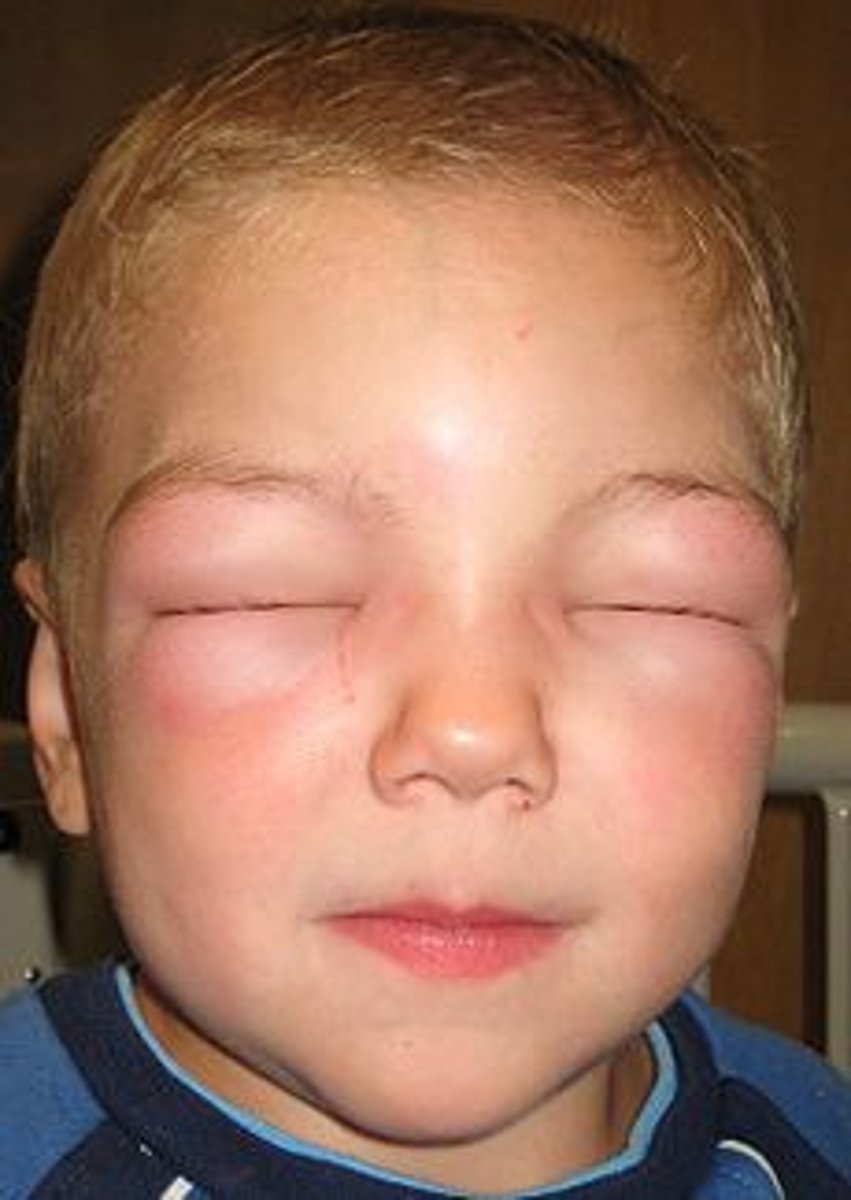
Mast Cell-mediated Angioedema
-associated sx include urticaria, flushing, pruritus, bronchospasm
-begins within minutes of exposure, builds in hours, resolves in 1-2 days
Bradykinin-Induced Angioedema
-no other symptoms
-prolonged course (develops over 24-36 hours, resolves in 4+ days)
-difficult to determine trigger
Angioedema - Tx
-if cause identified, d/c
-laryngeal swelling -- emergent epinephrine
-other long term management --> cyclosporine, omalizumab
Behcet's Syndrome
-recurrent painful oral aphthous ulcers with other systemic manifestations
-vasculitis involving all types of blood vessels
-autoimmune/autoinflammatory
-genetic link
-clinical dx
Behcet's Syndrome Incidence
-Turkey (up to 420 cases per 100,000) but more rare in the US
-young adults
Behcet's Syndrome - Tx
-symptom management (steroids, sucralfate)
-lesion treatment/prevention (colchicine)
-immunologics for severe disease
Erythema Multiforme
-type IV hypersensitivity reaction usually triggered by infections, most commonly HSV
-HSV 1 > HSV2, young males usually
-clinical dx
-minor: mild or no mucosal involvement
-major: mucosal involvement
-usually acute and self-limited
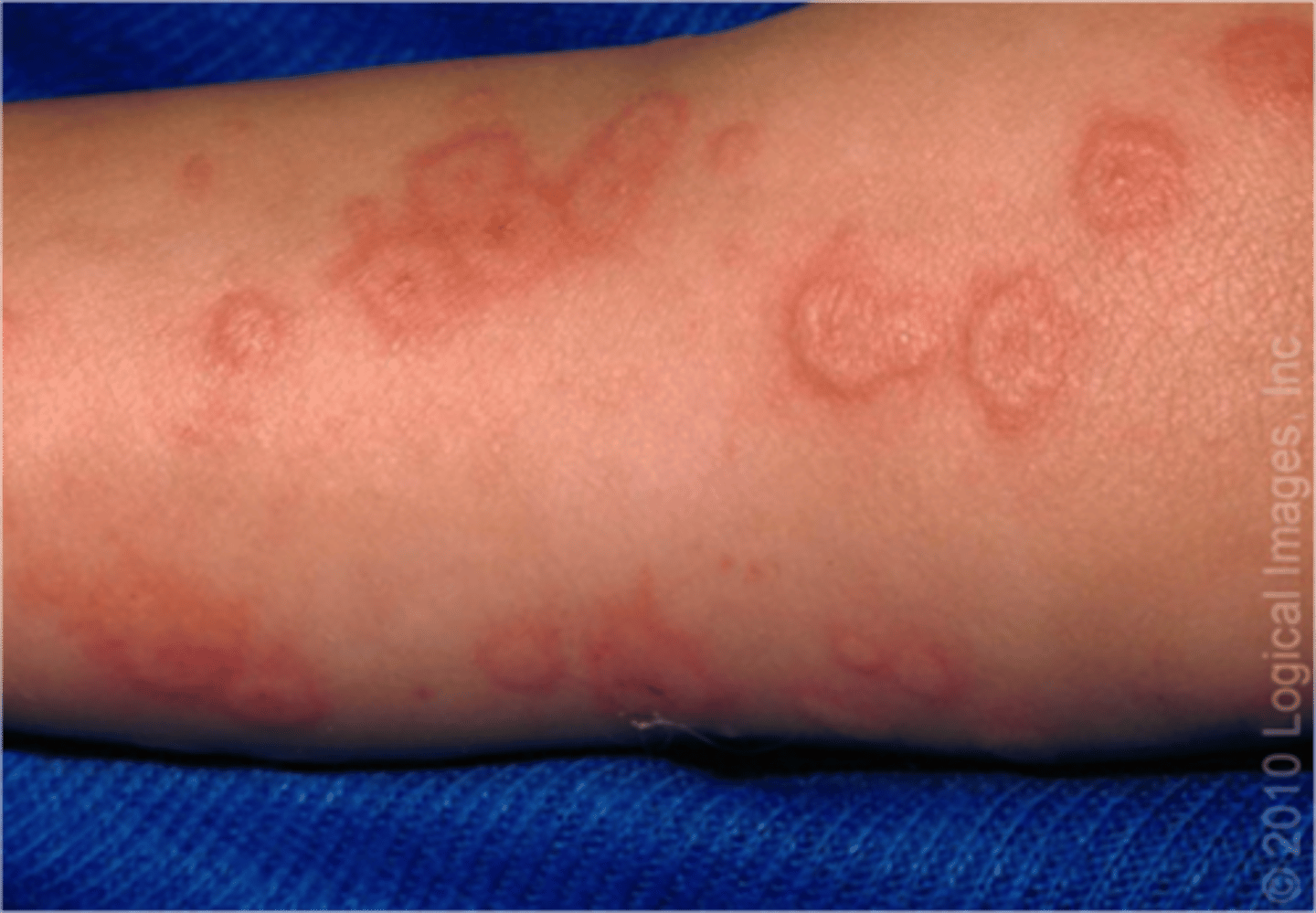
Erythema Multiforme - Lesion
-sharp margin, regular round shape, three concentric color zone
-center: dark red with blister or crust
-2nd ring: paler pink, raised due to edema
-outermost ring: bright red
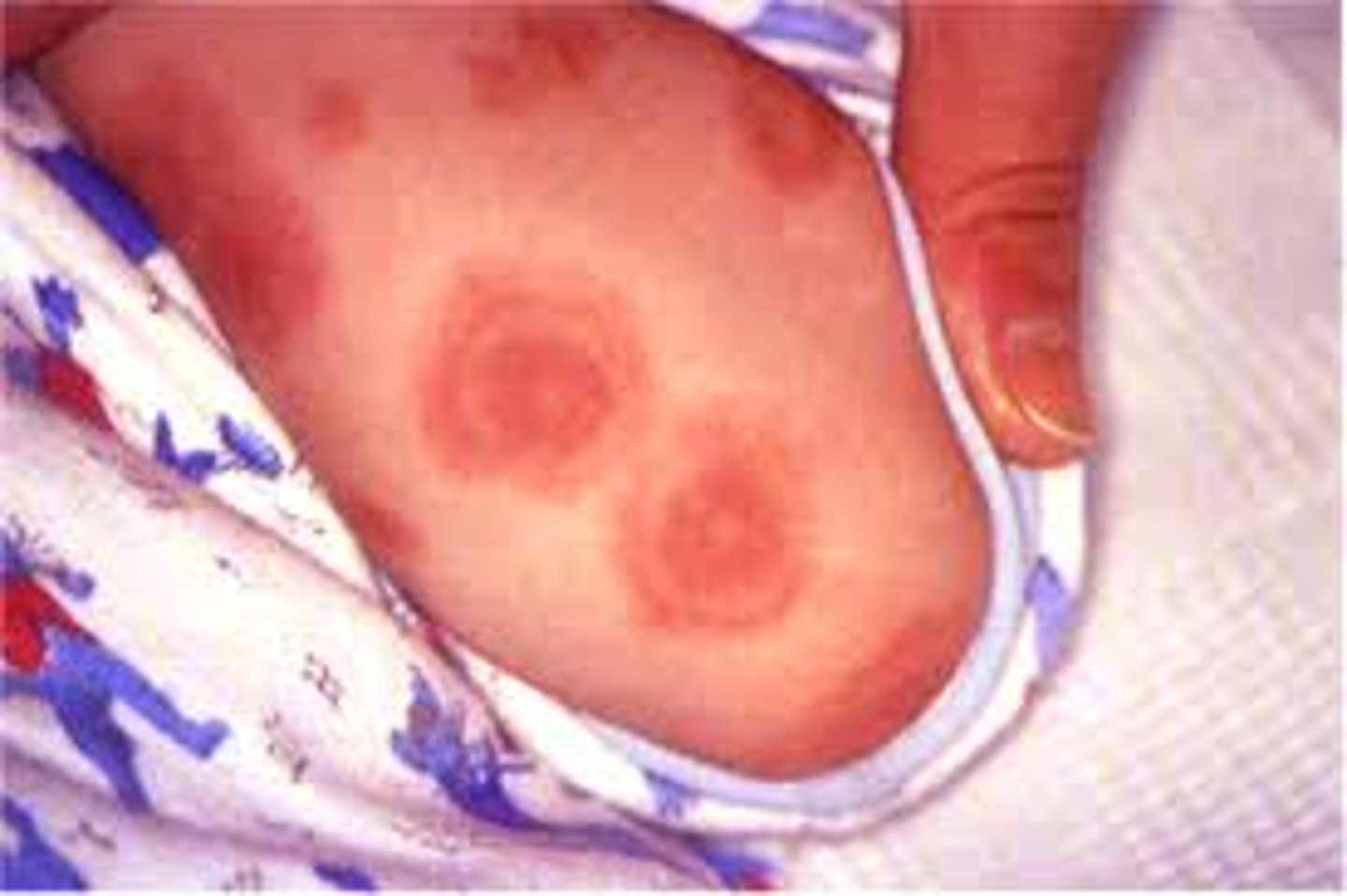
Erythema Multiforme Major
-same lesions as EM-minor + mucosal involvement
-can affect eyes, anus, genital, and GI tract
-oral mucosa is most affected (lips, inside cheeks, tongue)
Erythema Multiforme - Tx
-treat primary infxn
-supportive: antihistamine, topical CCS, mouth washes
-recurrent: continuous oral acyclovir or valacyclovir for 6 months
-usually resolves w/o scarring over 2 weeks to 1 month
Erythema Nodosum
-painful nodules without ulceration on anterior lower legs
-lasts 6 weeks, can recur; may be preceded by fever, malaise, arthralgia
-incidence: women 10x more than men
Erythema Nodosum - Etiology
-idiopathic
-infection
-sarcoidosis
-IBD
-Pregnancy
-OCPs
Erythema Nodosum - Tx
-NSAIDs and elevation for pain and swelling
-corticosteroids, dapsone, colchicine, hydroxychloroquine
Graft vs Host Disease
-donated bone marrow or stem cells view recipient's body as foreign and attack it
-rash: raised or discolored thickening or tightening of skin; burning sensation; palms/soles of feet, often on trunk and extremities
-can also present with hepatic or GI sx
GHD incidence
1/3 to 2/3 of all allogeneic transplant recipients
GHD prognosis
can be fatal if untreated, resolves within 5 years with treatment
GHD - tx
-depends on affected body system and symptom severity
-immunosuppressants, steroids
Hypersensitivity Vasculitis
-predominantly small vessel disease without systemic vasculitis
-palpable purpura on lower extremities
-induration, necrosis, ulceration, ecchymosis, haloing, and confluence can occur
-benign, undetermined origin
Hypersensitivity Vasculitis
-incidence: 38-55 per million, equal about gender and ages
-prognosis good, but may decrease if systemic disease present
-dx: skin biopsy, further workup if suspect systemic vasculitis or underlying disease
Hypersensitivity Vasculitis - Tx
-identify and control triggers, compression stockings, elevation, bed rest
-topical or oral steroids, colchicine, dapsone, immunosuppressants may be considered
Anaphylaxis
-severe, life-threatening allergic rxn within seconds to minutes of exposure
-sx: skin rxn, hypotension, airway constriction, NVD, dizziness/fainting
-mc drugs: NSAIDs, beta lactams (amoxicillin)
Drug-Induced Hypersensitivity Syndrome
-rare, autoimmune
-ranges from mild pruritus to life-threatening skin/mucosal loss
-blanket term for SJS, TEN, DRESS, Drug-induced lupus
-usually 1-3 weeks after first ingestion of meds
Epidermal Necrolysis
-extensive necrosis and detachment of the epidermis (sloughing)
-mucous membrane involvement
SJS
if a patient has <10% of their body surface area involved, do they have SJS or TEN?
TEN
if a patient has >30% of their body surface area involved, do they have SJS or TEN?
Stevens Johnson Syndrome
-severe immune-mediated cutaneous drug reaction
-<10% BSA epidermal detachment
-prominent mucosal involvement
-prodrome: fever, malaise, ST, then painful rash
-common triggers: sulfonamides, anticonvulsants, allopurinol
-treat like burn patient
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
-same disease as SJS, but more extensive
-most commonly drug-induced: sulfonamides, allopurinol
->30% BSA epidermal detachment
-positive Nikolsky sign
-burn unit or ICU, 30-50% mortality
TEN tx
-outcome depends on quality of care and rapidity with which tx is initiated
-stop offending drug
-admission to burn unit/supportive care
-IVIG 0.2 g/kg/day to 2 g/kg/day for 1-5 days
Sunburn
-genetic component
-prevention!!!
-can affect all skin tones
-risk factor for skin cancer
-mild erythema --> highly painful erythema with edema, vesiculation, blistering
Sunburn - Tx
-OTC calamine lotion, aloe
-cool compresses
-NSAIDs
-mild soap/water
Drug-Induced Photosensitivity
-considered an adverse drug reaction
-common offenders: tetracyclines, HCTZ, sulfonamides, metformin, FQs, NSAIDs, amiodarone, retinoids
-onset within minutes to hours of sun exposure, limited to exposed skin
-vesicles or bullae may form, UVA radiation
Drug-Induced Photosensitivity - Tx
-DC offending agent if possible
-sun protection
-treat as sunburn
Solar Lentigo
-well-circumscribed 1- to 3-cm brown macules
-localized proliferation of melanocytes and accumulation of melanin due to chronic sun exposure
-eval for suspicion of malignancy
Solar Lentigo - tx
-cryotherapy
-laser
-minimize sun exposure
-sunscreen
Dermatoheliosis
-skin changes induced by chronic UVA and UVB exposure
-aka photoaging
-can be prevented by sunscreen, protective outerwear
-if present, monitor for skin cancer
-tretinoin is best treatment
Immunobullous Disease
-caused by associated with specific autoantibodies that bind to epithelium resulting in tissue separation/blistering
-pemphigus, bullous pemphigoid, linear IgA disease, dermatitis herpetiformis
Pemphigus Vulgaris
-rare autoimmune blistering d/o of skin and mucous membranes
-fragile bullae, rupture easily
-etiology: DRUGS, systemic malignancy, and trauma
Pemphigus Vulgaris - Dx
-direct (punch biopsy)
-indirect (serum)
-immunofluorescence
Pemphigus Vulgaris - Tx
-d/c offending drug
-corticosteroids/immunosuppressants
Bullous Pemphigoid
-autoimmune blistering d/o
-presents as intact tense blisters/bullae
-type II hypersensitivity rxn
-rarely affects mucosal skin, most common older pts
Bullous Pemphigoid - Biopsy
shave for hematoxylin and eosin stain + punch for direct immunofluorescene
Bullous Pemphigoid - Tx
-topical steroids
-systemic prednisone or steroid sparing immunosuppressants
-antibiotics (tetracyclines or erythromycin)
Dermatitis Herpetiformis
-autoimmune from gluten sensitivity
-associated with celiac, avg age 30s-40s
-subepidermal deposition of IgA and neutrophilic dermal infiltrates in superficial dermis
-very pruritic inflammatory papules and vesicles on forearms, knees, scalp, buttocks
-eliminate dietary gluten, dapsone
Linear IgA Disease
-rare autoimmune blistering disease
-idiopathic or drug induced
-IgA antibodies bound to basement membrane zone
-humoral and cellular immune responses involved
-skin and/or mucosal membrane lesions: tense pemphigus-like vesicles and bullae
-tx: dapsone and topical corticosteroids