APES Midterm Final yay! (study guide + warm ups + jeopardy for the multiple choice)
1/200
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
201 Terms
What is an example of positive feedback with respect to climate change and the melting of permafrost? Hint: CH4 (methane) is stored in frozen permafrost.
The carbon that is being released to the atmosphere in the form of methane
A change in a system can either be increased or decreased by what?
any amount of heat
What are all the 'hidden costs' associated with a car?
The cost of gas, and repairs, the degradation it does to the environment
People living in ______ (not a country) often degrade forest and soil resources, negatively impacting the environment.
poverty
What event led to the exponential growth of the human population?
The deaths of the old and the boost of babies.
List 4 examples of the degradation/destruction of natural capital.
Rapid urbanization, excessive water extraction and unsustainable aquaculture
__________ growth starts off slowly, but after only a few doublings, grows rapidly.
population
List 4 ways humans can avoid suffering from the 'nature deficit disorder'.
Direct exposure to nature, put away electronics, go for a walk and talk to a friend.
Define anthropogenic.
originating in human activity
Sketch a line graph (x and y axis) and indicate which has the dependent and which has the independent variable.
independent = x-axis and dependent = y-axis
define energy
Power from the utilization of physical or chemical resources, especially to prove light and heat to work machines.
What's the difference between a positive and negative feedback loop?
Positive feedback loops enhance or amplify changes and negative feedback tends to dampen or buffer changes
List 4 characteristics of crude oil.
Black, thick, gooey, destructive.
Explain the process of fracking. Drill down into the earth before a high pressure water mixture is directed at the rock to release the gas inside.
Drill down into the earth before a high pressure water mixture is directed at the rock to release the gas inside
If ________ costs of the use of coal were included in the price, the use would most likely ______.
hidden, stop
What method of storing radioactive nuclear waste do most scientists and engineers agree is the safest and cheapest?
Geological repositories/ deep underground
MATH: How do you calculate the number of half-lives and how to calculate the years.
a(1/2)^n
n= number of lives
a = original amount
List the major parts of a nuclear reactor used to create electricity and describe what each does.
There's the fuel, moderator, control reds and blades, coolant, pressure vessel or pressure tubes, steam generator and containment. The reactor separates the fissionable nu dealer material. The moderator slows the speed of the neutrons. The coolant is used to carry the heat produced by the fission reaction to an external boiler and turbine, where it is turned into electricity. Control rods control the fission rate of the nuclear fuel by adjusting the number of slow neutrons present to keep the rate of the chain reaction at a safe level. A reactor has to withstand high temperatures and pressures and must protect operating personnel from the radiation.
True or False: Coal can be blamed for the depletion of the ozone layer.
true
MATH: how do you calculate a percentage change?
difference between old & new values, divided by old value
ex: old=$400, new=$500
% change = (500-400)/400 x 100 = %25 increase
ex: grace bought shares of a stock at $35 per share on January 1st. On February 1st, the stock was worth $45.50. by what percentage did her share value increase?
45.50-85 = $10.50
10.50/85 = 0.3 x 100 = 30%
List 4 hidden costs of gasoline
hurts the environment, air pollutants, asthma, death
List 4 ways of saving energy in the transportation sector. Hint: saving energy would also benefit the environment.
Keep car tuned, make sure the tires are properly inflated, don't store unneeded things in your trunk and choose energy conserving oils
What device converts solar energy directly into electricity?
Photovoltaic cells
Which countries lead the world in terms of geothermal electricity production?
The US, Indonesia, Philippines, Turkey and New Zealand
List 4 commonly used biofuels
Ethanol and biodiesel, methanol and palm oil
For each increase of 1 on the Richter scale, ___ times more energy (magnitude) is released.
32
Which of the following materials combined with topsoil would allow for the fastest percolation rate?
a. silt heavy soil
b. clay heavy soil
c. sand heavy soil
c. sand heavy soil
What are the 3 types of plate boundaries?
Convergent, Divergent, Transform
Which plate boundary destroys the Earth's crust?
convergent
Which plate boundary creates a new crust
divergent
List characteristics of mineral resources.
They are nonrenewable, definite chemical composition, and material comes from inorganic processes
MATH: how do you identify a soil type based on percentages of sand, silt, and clay?
use the percentage triangle
draw a line following each of the percentages
identify soil type where the lines meet
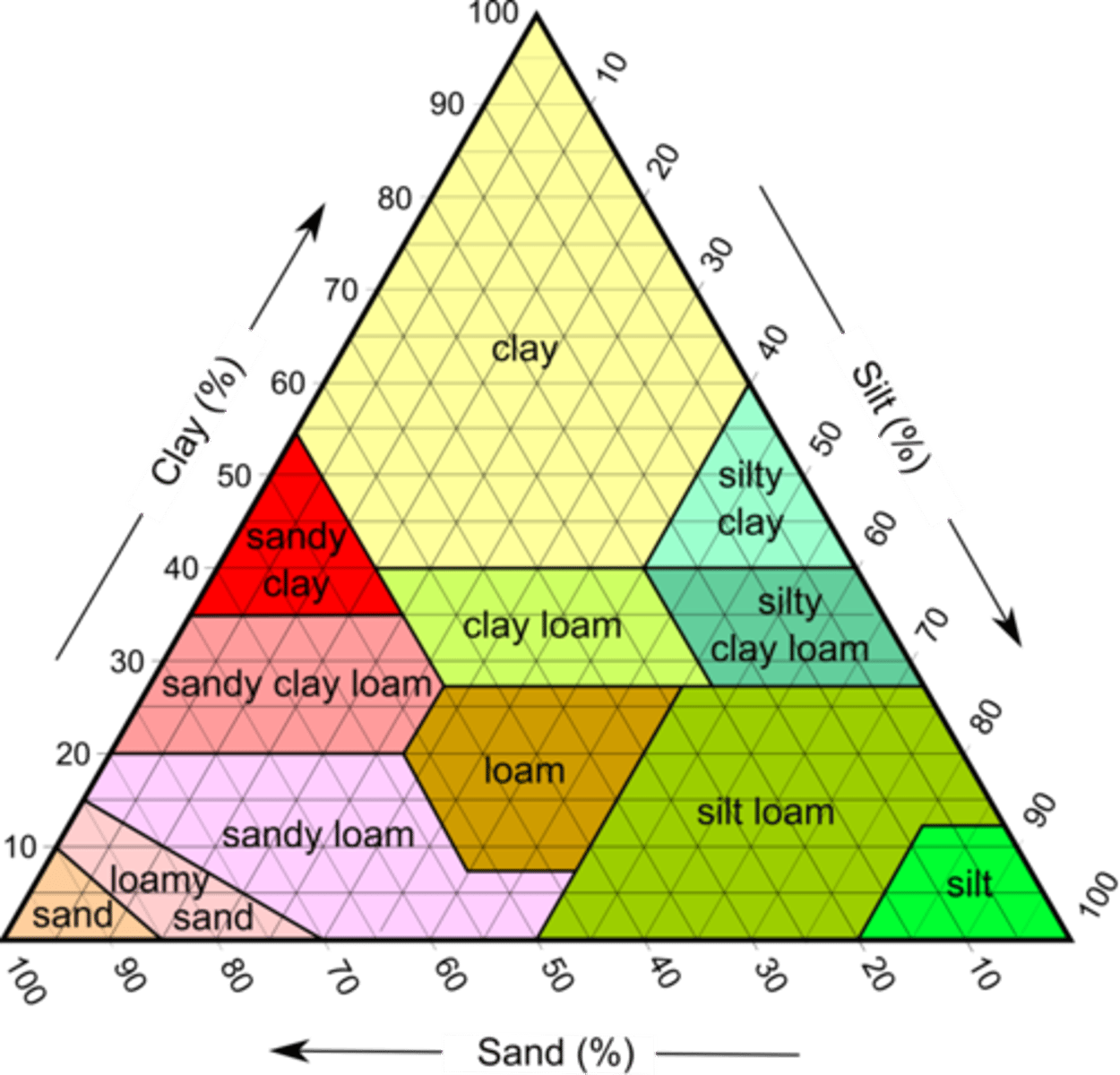
True or False: Mineral resources are always economically worth mining.
False
List 4 environmental hazards associated with surface mining.
the soil, reduce fertility, pollute water and drain water reserves
List 4 advantages of recycling aluminum cans.
Saves energy, time, money and natural resources
List as many methods involved in integrated pest management as you can.
Biological, fumigation, field burning, heat treatment
MATH: how do you do a productivity math problem. You are given the GPP and NPP and will have to calculate the biomass lost through respiration.
ex: imagine we run an experiment on the algae Cladaphora Glometra. we place equal amounts of algae into a light bottle and a dark (covered) bottle. we measure the dissolved oxygen in both bottles and find it as 10/mg/L. we let both bottles sit for a week. in one week, the light bottle has dissolved oxygen value of 11mg/L and the dark bottle has a value of 5mg/L.
Calculate the amount of respiration, the NPP and GPP for the species of algae.
light=gnl= NPP -> 11mg/L - 10mg/L/week = 1mg/L/week
dark=respiration -> 10mg/L- 5mg/L/week
NPP=GPP-respiration
1mg/L = GPP-5mg/L
6mg/L= GPP
NPP = 1mg/L/week
GPP = 6mg/L/week
respiration = 5mg/L/week
The major goal of industrialized agriculture is to increase crop _____.
Yield
Define salinization.
The process by which water soluble salts accumulate in the soil
Define waterlogging
Saturate with water, or make something water logged
List 4 methods that could be used to reduce/reverse desertification.
-Plant more trees
-Improve the quality of the soil
-reduce soil erosion
-Reintroduce selected species
How much energy from a lower trophic level gets transferred to the consumer? ____ This means that approximately ____ is lost as heat.
10%, 90%
List all of the major gasses in the troposphere that absorb long-wave infrared radiation contributing to the greenhouse effect.
water vapor, carbon dioxide and methane
What are the 2 reactants for photosynthesis?
carbon dioxide and water
What are the 2 products for photosynthesis?
glucose and oxygen
What provides the energy for the reaction of photosynthesis?
sunlight
Which of the nutrients spends no time in the atmosphere within the N cycle, P cycle, or C cycles?
the p cycle (phosphorus)
Which process found within all nutrient cycles must happen in order to 'recycle' the elements for future use? Hint: many of the organisms who do this are microscopic.
biochemical cycle
What's the difference between a biotic component and an abiotic component in an ecosystem?
Biotic factors are living things within an ecosystem, like plants and animals. Where the abiotic are non living components like water and soil
If polar regions become warmer due to climate change, what might organisms who live in warmer regions currently do in the future?
they may go extinct or some may adapt to their new environment, but it's most likely they will go extinct because they need the cold to survive, migrate
What is the main human activity/human related activity causing species to become endangered and extinct?
unsustainable hunting and harvesting, we have to much meat
Which type of diversity allows organisms to adapt to and survive environmental changes?
natural selection
What is the importance of species richness?
it will stabilize the ecosystem more
If a species is found over a large geographic region and can feed on many different things, it is categorized as a (check one) specialist or ______.
generalist
Earth's biodiversity is determined by a balance of what two things?
speciation and extinction
List the most important reason for the elephants as a keystone species in the African Savanna. Hint: think of the most important producer for the food webs there.
the balance the natural ecosystems, for example they trample forests and dense grasslands, which makes room for smaller species to coexist
Define the greenhouse effect.
when the sun's warmth is trapped in a planets lower atmosphere
What phenomenon is caused by the rotation of the Earth that deflects the atmosphere in different directions in the N and S hemispheres?
the Coriolis effect
What is the biggest reason tropical regions get more rain than other regions?
the sun's radiation is strongest near the equator. More evaperation = more rain
Define the rainshadow effect.
the side of a mountain where the precipitation is noticeably less than on the windward side, and because the moisture bearing air mass loses most of its moisture on the inward side before reaching the lee side
Why are the soils in temperate deciduous forests so rich in nutrients?
because the trees shed their leaves each fall and the leaves decay which leaves nutrients that is absorbed by the soil
True or False: the location of mountain ranges and the shapes of continents have the largest influence on global air circulation patterns (wind currents).
False
True or False: terrestrial habitat loss is a human threat to marine ecosystems.
False
List as many ecosystem services coral reefs provide as you can.
They protect coastlines from erosion, provide a source of food and homes and help with water purification. They also create tourism and recreation
What are the biggest causes of pollution in Chesapeake Bay
Huge amounts of nitrogen and phosphorus which comes from fertilizers, wastewater and also air pollution and runoff from cities and farms, and overfishing
What are the 4 distinct zones in large lakes
littoral, limnetie, profundal and benthic
List 3 characteristics of a euphotic lake
Topmost layer, net primary production and sunlight
What's the biggest reason for ocean acidification?
the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere which dissolves in the ocean
If a population overshoots the ecosystem's carrying capacity, what will begin to happen? Hint: carrying capacity is the greatest population that an ecosystem's resources can support
resources will become scarce and water will be an issue, poverty will increase and malnutrition and hunger will worsen
When different species use a resource in different locations, different times of the day, and different times of the year, it is called what?
resource partitioning
True or False: Camouflage is used by both predators and prey to increase their rate of survival.
true
Define mutualism
The ecological interaction between two or more species where each species has a net benefit
Define commensalism
a long-term biological interaction in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed
define parisitism
a relationship between the two living species in which one organism is benefited at the expense of the other
_______ succession begins on bare rock, where _______ succession begins with existing soil.
primary, secondary
True or False: Exponential growth of a population is common when there is a high amount of intraspecific competition.
false
What would an age structure diagram look like for a country with a declining population, an increasing population, and a stabilized population?
the first one would be small at the top and bigger at the bottom, the second one would be small at the bottom, the second one would be small at the bottom and bigger at the top and the third one would look the same throughout the years
What will likely happen to a population that has more young people than old people? What about more old people than young people?
with more young people, the economy will be better and there will be more kids being brought into the world and with an older population, the economy would slow and there would be very few families bringing children into this world
MATH: how do you calculate doubling/halving time given a growth rate (both + and -)?
doubling time = 70/annual growth rate (%)
ex: if a country were doubling its population every 85 years, what would its growth rate be?
DT = 70/r
85 = 70/r
r = 70/85 = 2%
MATH: how do you calculate the growth rate given births, deaths, immigration, and emigration?
Hint: don't forget to multiply by 100 to get it into a %
((births + immigration)-(deaths + emigration)/total population)x 100
True or False: the number of elderly will influence current birth and fertility rates?
false
List 4 things that could decrease the total fertility rates in a population.
marriage, reduction of age in marriage, subfertility and timing of births
Which industrialized nations are facing a declining population this century?
China
after what event did the human population begin growing exponentially?
industrial revolution
what 2 compounds are pulled out of the air for photosynthesis?
Water (g) and CO2
nutrients are considered 'non-living'. What scientific word describes this?
abiotic
which nutrient cycle does not have a part in the atmosphere (gas phase)?
phosphorus
True or False: development of renewable energy sources is an example of natural capital degradation
false
what type of population growth stats off slowly but quickly grows to very large numbers?
exponential
True or False: reading about being outside in nature can help people suffering from nature deficit disorders.
False
What process is important to the C, N, and P cycles?
Decomposition
_______ _______ enables life on earth to adapt and deal with changes to the environment.
genetic diversity
the balance b between speciation and extinction determines the earth's ______.
biodiversity
species that are common over large geographic ranges and can feed on a variety of foods are considered to be _____.
generalists
the greater the sustainability, the greater the species ______.
richness
______ is the ability to do work.
energy
Feedback can either increase or decrease a change in a ________.
system
A ________ feedback loop is one where the result increases the process to occur again.
positive
why do temperate deciduous forests have such nutrient-rich soils?
yearly leaf dropping
the deflection of the atmosphere due yo the spin/rotation of Earth is called the ______ ______.
Coriolis effect