Stimulus Identification
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What 3 factors affect stimulus identification?
Clarity = how easily detectable is the stimuli
Intensity = how obvious is the stimuli
Modality = where is the stimuli coming from (e.g. exteroception, introception, proprioception)
What is exteroception?
Stimulus from outside the body (e.g. vision, audio)
What is interoception?
Stimulus from within the body
What is proprioception?
Stimulus derived from orientation and movement (e.g. muscle spindles, joint receptors)
How long is reaction time for visual stimuli?
100 to 180ms
How long is reaction time for auditory stimuli?
85 to 100ms
How long is reaction time for tactile stimuli?
120 to 150ms
What are cones in the eye used for?
High resolution and colour
Concentrated in the fovea
4.5 million of them
What are rods in the eye used for?
Detect light
Poor for high resolution
90 million of them
What is binocular vision and what degrees is the field of view?
The 2 eye balls vision is combined into the binocular vision. This improves the field of view
120-180 degrees
What is ventral/focal stream of information?
Detects what information is sent and identifies it
Uses the central visual field
This is conscious processing
What is dorsal/ambient stream of information?
Detects where things are and how they’re moving
Uses central and peripheral visual field
This is non-conscious processing
What is optical flow?
As the light hits the eye, it creates patterns on the retina. If movement occurs (by either us or an object/opposition) the pattern of light moves across the back of the eye
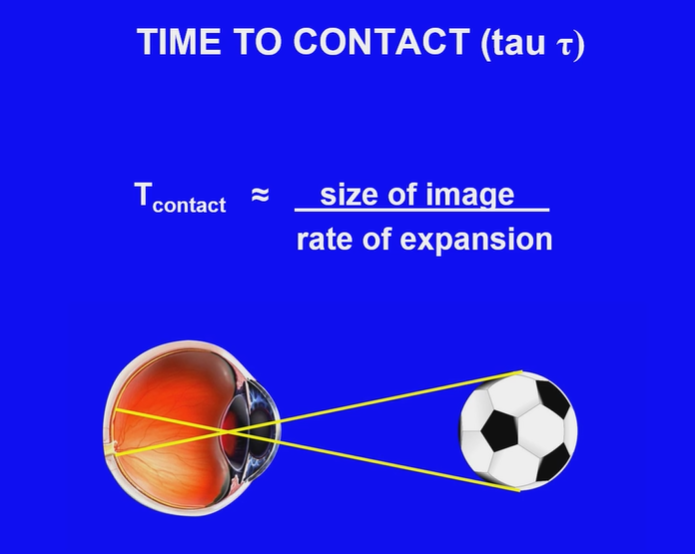
What is the equation for time to contact?
Size of image / Rate of expansion
What did Scott et al study on long jumpers show us?
A study on elite long jumpers found that they were able to accurately correct their run up to the board. The novices also followed the same pattern, but had a larger standard deviation
This process is a fundamental strategy which is naturally occurring when trying to achieve a target
Training can help to improve this accuracy
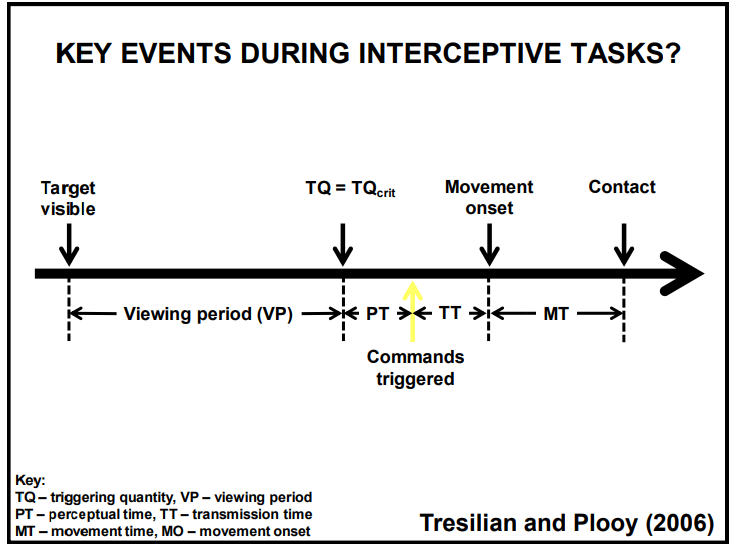
What is a trigger quantity?
The cue an athlete uses to know when to act (e.g. how fast the ball is moving)
What is perceptual time?
The brains estimation of how much time is left (e.g. ball is 0.5 seconds away)
What is transmission time?
Time taken for nervous system to process cue and send signal to muscle
What is movement onset?
The moment the body starts to move (the arm starts to lift to catch the ball)
Explain the key events of an interceptive task
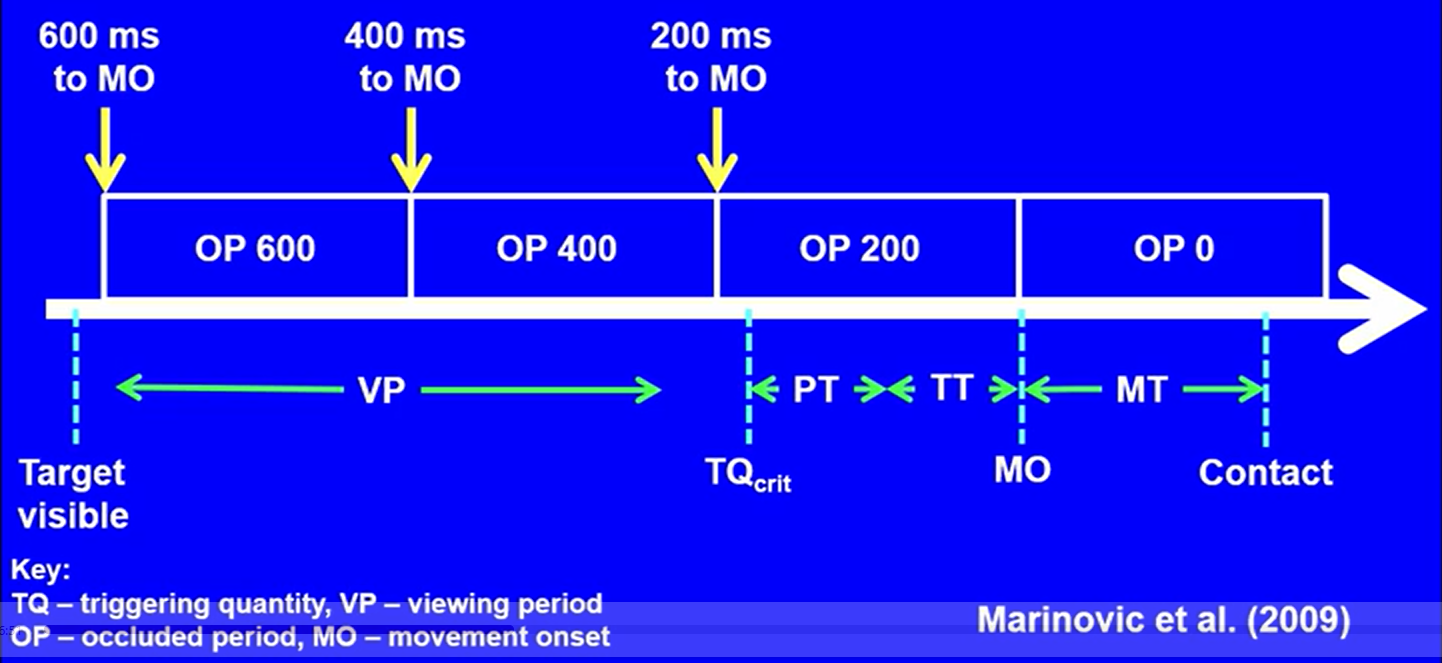
What is temporal error?
Difference between time athlete acts and the ideal time they should have acted to be successful
What happens to temporal error if information is occluded earlier?
Temporal error increases because the movement is still being programmed and adjusted
The brain relies on sensory information to plan and correct the movement over time
What does the optical height theory state?
Uses the equation of vertical height / horizontal height and assumes a parabolic flight
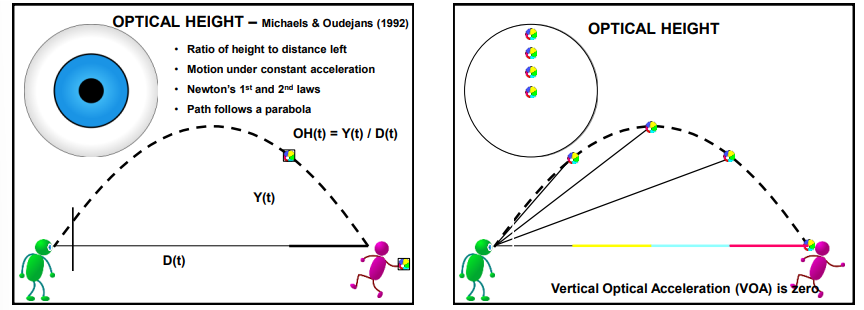
What occurs if the optical height gaps change?
Gap gets smaller = athlete must run forward to keep vertical optical acceleration at 0
Gap gets bigger = athlete must run backwards to keep vertical optical acceleration at 0
What are the issues with the optical height theory?
Trajectory of an object is rarely parabolic
Athlete won’t always have constant acceleration
Plane of view is based on a fixed head position
What is gaze angle?
The angle between
The horizontal line from the observer’s eyes
The line to the moving object (e.g., a ball)
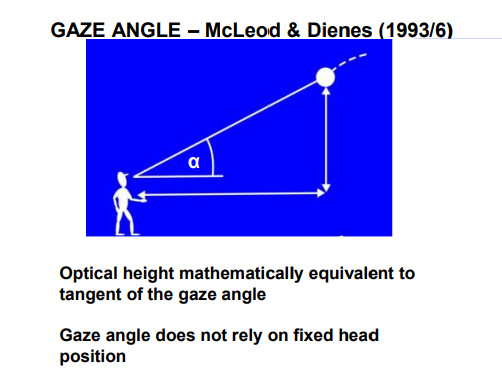
If the 2nd derivative of tan a is negative what should an athlete do?
Speed up (ball is falling in front of them)
If the 2nd derivative of tan a is positive what should an athlete do?
Slow down