OCR Computer Science 1.1 Systems Architecture
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Basic computer system model
Input, Processing, Output and optional storage
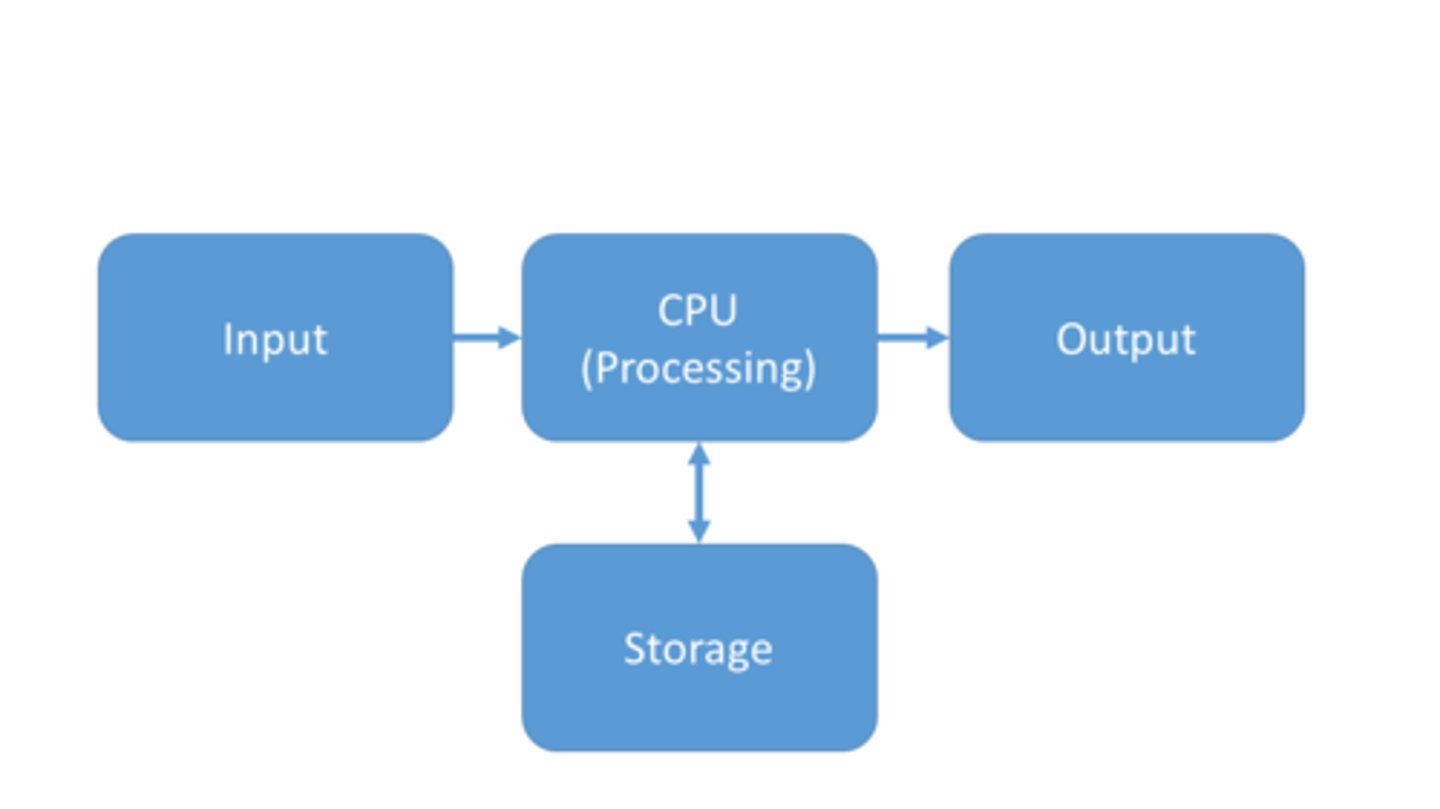
CPU
Central Processing Unit
Input device
A device used to enter information into a computer.
Output device
any device that presents data from the computer
Storage device
a piece of computer equipment on which information can be stored.
Central Processing Unit
the part of a computer that decodes and executes instructions and manages the rest of the hardware.
Von Neumann Architecture
Instructions are fetched, decoded and executed one at a time.
Instructions and data are held together in the same memory space.
Bus
The paths, or lines, on the motherboard on which data, instructions, and electrical power move from component to component.
Address Bus
carries addresses from the processor to memory and input/output devices.
Data Bus
sends data between the processor, memory and input/output devices.
Control Bus
carries signals to coordinate all the computer activities.
CU
Control Unit. Coordinates all the activities taking place inside the CPU.
Control Unit functions
1. controls the execution of instructions in the correct sequence.
2. decodes the instructions.
3. regulates and controls processor timing using regular pulses from the system clock.
4. sends and receives control signals to and from other devices within the computer.
ALU
Arithmetic Logic Unit. Carries out all mathematical and logical operations.
Arithmetic Logic Unit functions
1. Logical Operations: AND, OR and NOT.
2. Shift Operations: The bits in a binary number can be shifted to the left or the right a number of times.
3. Arithmetic Operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
Special Purpose registers
special very fast memory locations within the CPU with specific purposes in the process of executing instructions.
MAR
Memory Address Register
MDR
Memory Data Register
PC
Program Counter
ACC
Accumulator
Memory Data Register (MDR)
Holds the data fetched from or to be written to memory.
Memory Address Register (MAR)
Holds the address of data ready for use by the MDR, or the address of an instruction passed from the PC.
Program Counter (PC)
The register that contains the address of the next instruction to be executed
Accumulator (ACC)
Holds the result of calculations.
FDE Cycle
Fetch Decode Execute Cycle. The CPU uses the FDE cycle to carry out the program instructions.
Fetch
1. The address A of the next instruction to be executed is copied from the PC to the MAR
2. The PC is incremented so it points at the next instruction to be fetched. Simultaneously, the instruction held in location A is then copied into the MDR.
3. The contents of the MDR are copied to the CIR.
Decode
The CU decodes the instruction in the CIR to see what is to be done next.
Execute
The instruction is executed.
Cache
Memory in the processor providing fast access to frequently used instructions and data.
Factors affecting the speed of the CPU
1. Clock Speed
2. Number of Cores
3. Cache Size
Embedded System
A computer system within a larger mechanical
or electrical system designed for a
specialist purpose.