Physiology Exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/247
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:30 PM on 3/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
248 Terms
1
New cards
What are the two control systems of the body?
Nervous and endocrine
2
New cards
What does the nervous system communicate through to regulate and control other systems?
Electrochemical impulses
3
New cards
Neuron
Respond to stimuli, conduct electrical activity, release chem. regulators
4
New cards
What are the structural classes of neurons based on?
\# of processes
5
New cards
Unipolar Neuron
1 process; "T"
6
New cards
Bipolar Neuron
2 processes
7
New cards
Multipolar Neuron
Many processes
8
New cards
Parts of the Neuron
Cell body, dendrites, axon, axon hillock (initial segment), axon terminals
9
New cards
What are the functional classes of neurons based on?
Direction of impulse
10
New cards
Interneurons (Association)
Located in CNS (brain) and integrate functions of nervous system
11
New cards
What structural class is an interneuron?
Multipolar
12
New cards
Motor Neuron
Conduct impulses FROM CNS to target organs
13
New cards
What structural class is a motor neuron?
Multipolar
14
New cards
Sensory Neuron
Conduct impulses from sensory receptors TO CNS
15
New cards
Oligodendrocytes
Form myelin sheaths; insulate/cover axon
16
New cards
What do myelin sheaths do?
Speed up conduction of electrical signals along axon
17
New cards
Myelin forming cells are called \_________ in the CNS.
Oligodendrocytes
18
New cards
Myelin forming cells are called \__________ in the PNS.
Schwann cells
19
New cards
What type of cell is a oligodendrocyte?
Glial cell
20
New cards
Neuron Resting Potential
-70 mV
21
New cards
What is the membrane potential established by?
Large negative molecules INSIDE the cell
22
New cards
Ligand Gated Channels
Opening in response to BINDING of chemical ligand to its RECEPTORS
23
New cards
Voltage Gated Channels
Protein channel when stimulated DEPOLARIZES (AP) membrane to threshold
24
New cards
What are voltage gated channels specific to?
Ions (Na+, K+)
25
New cards
Mechanical Gated Channel
Open when physical deformation to membrane occurs
26
New cards
Voltage-Gated K+ Channels
Slower to open and close
27
New cards
What membrane potential do voltage-gated K+ channels open at?
+30 mV
28
New cards
What membrane potential do BOTH voltage-gated K+ and voltage-gated Na+ channels CLOSE at?
-70 mV
29
New cards
What membrane potential doe voltage-gated Na+ channels open at?
-70 mV
30
New cards
Voltage-Gated Na+ Channels
Respond faster at threshold (-55 mmV)
31
New cards
Threshold
Approximate value (-55 mV) need for an action potential to occur
32
New cards
Strength of stimulus affects \_________ of AP and may recruit more neurons to have AP
Frequency
33
New cards
Action Potential
All or nothing electrical event in a single cell where membrane potential quickly becomes positive then returns to resting potential
34
New cards
Depolarization (AP)
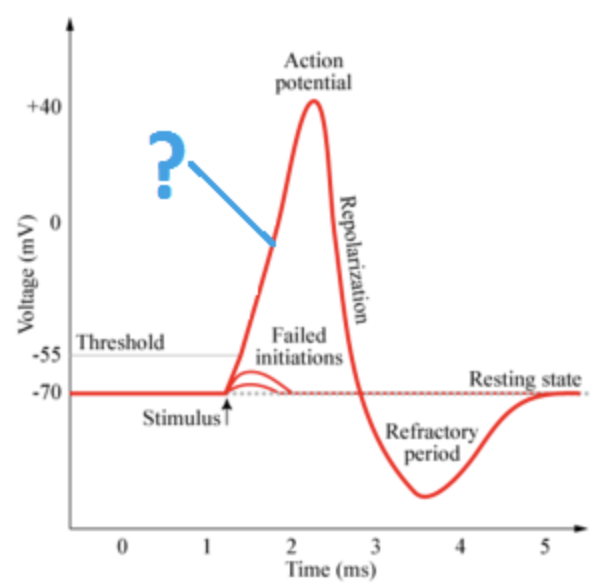
35
New cards
Overshoot (AP)
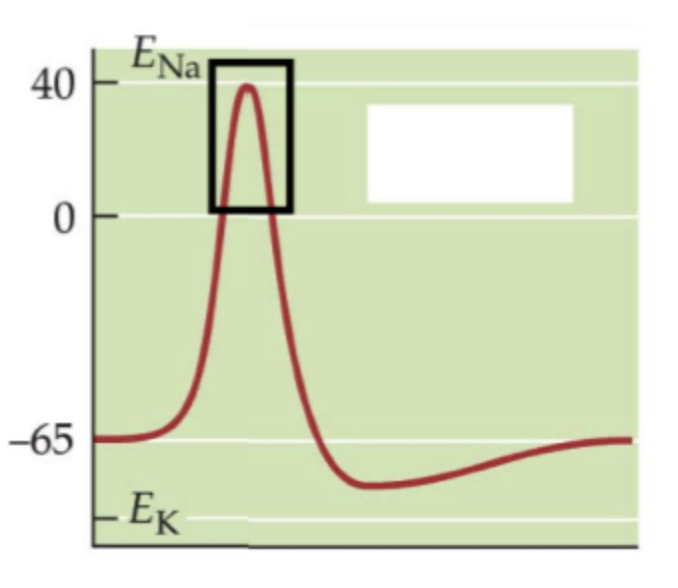
36
New cards
Repolarization (AP)
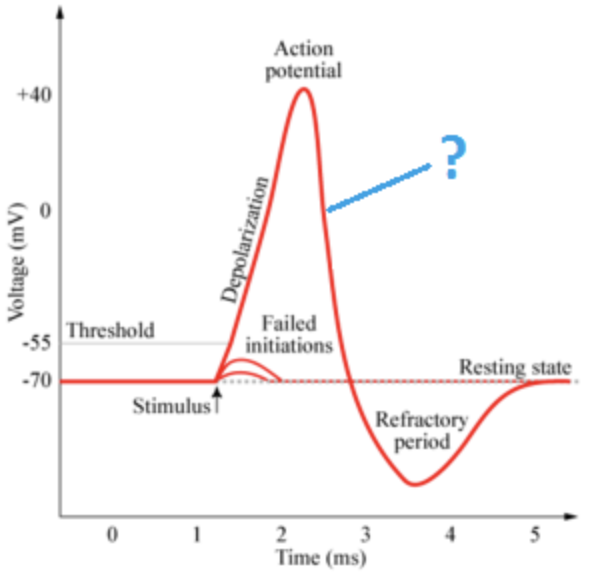
37
New cards
What letter is hyperpolarization (AP)?
D
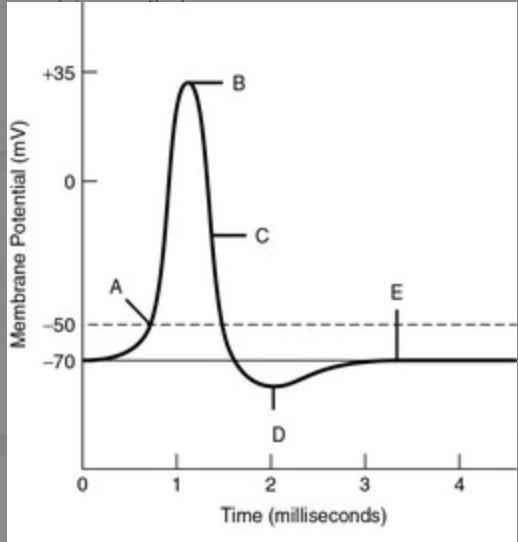
38
New cards
Resting Potential (AP)
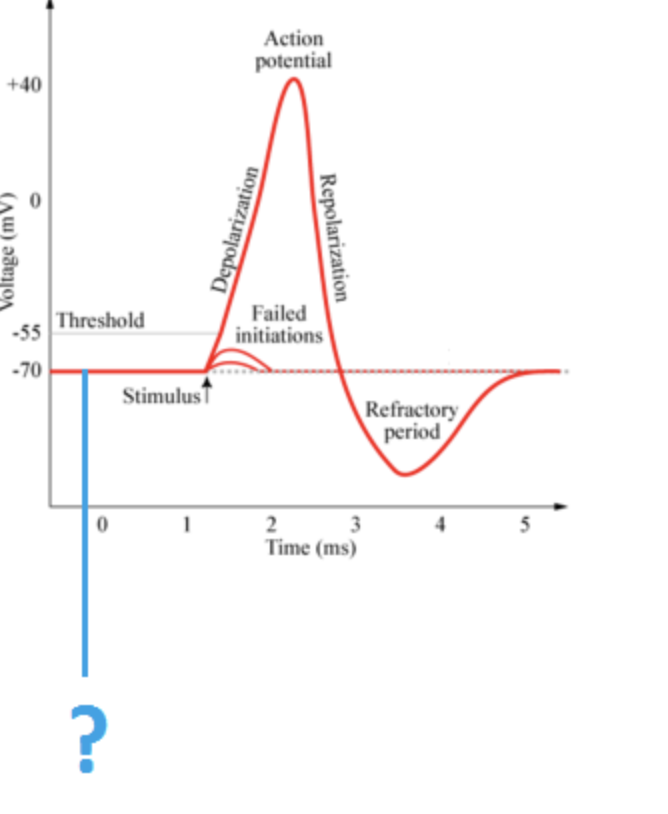
39
New cards
Stimulus of Action Potentials
Receptors (sensory)
40
New cards
Where on the neuron does the action potential take place?
Axon hillock/initial segment
41
New cards
How does an action potential happen?
Na+ in, K+ out
42
New cards
Absolute Refractory Period
Second stimulus will NOT produce an action potential
43
New cards
What causes absolute refractory periods?
Na+ channels are inactivated
44
New cards
Relative Refractory Period
Second action potential can happen ONLY IF stimulus strength is GREATER than usual
45
New cards
Why can relative refractory periods occur?
Some K+ channels still open
46
New cards
Action Potential Conduction
1. Depolarization of 1st AP is a stimulus for new AP
2. Each AP is separate; REGENERATED
3. Positive feedback of Na+ allows AP to travel without decrease
47
New cards
Myelinated Neurons
Myelin prevents Na+/K+ from moving through membrane
48
New cards
Saltatory Conduction
AP jumps node to node
49
New cards
What can synapses use to pass info?
Chemical and electrical stimuli
50
New cards
Synapse
Junction where impulses are transmitted form neurons and PNS
51
New cards
Presynaptic
Conducting signal TOWARDS synapse
52
New cards
Postsynaptic
Conducting signal AWAY from synapse
53
New cards
SNARE Complex
Proteins loosely dock vesicles
54
New cards
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP)
Opening Na+ or Ca2+ channels result in a graded depolarization
55
New cards
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential (IPSP)
Opening K+ or Cl- channels results in graded hyperpolarization
56
New cards
Does an IPSP increase or decrease likelihood of an action potential?
Decrease
57
New cards
Graded Potential
Summation and lack of refractory period; amplitude decreases as signal moves toward axon hillock
58
New cards
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Neurotransmitter; increased arousal, enhanced cognition
59
New cards
What is ACh involved in?
Muscle action, memory
60
New cards
Dopamine
Neurotransmitter; increased pleasure, suppressed appetite
61
New cards
What is dopamine involved in?
Mood, sleep, learning
62
New cards
Norepinephrine (NE)
Neurotransmitter; increased arousal, suppressed appetite
63
New cards
What is norepinephrine involved in?
Heart, intestines, alertness
64
New cards
Nicotinic ACh Receptors
Binding of 2 acetylcholine molecules opens a channel
65
New cards
Agonist of Nicotinic ACh Receptor
Nicotine
66
New cards
Antagonist of Nicotinic ACh Receptor
Curare
67
New cards
Muscarinic ACh Receptor
Binding at receptor opens ion channels using a G-protein
68
New cards
Monoamines (Neurotransmitter)
Synthesized from amino acids
69
New cards
Sensory Neurons
Receive sensory stimuli and produce nerve impulse
70
New cards
Modalities
Types of senses arise from different receptors
71
New cards
Mechanoreceptor
Mechanical deformation
72
New cards
Thermoreceptor
Heat/cold
73
New cards
Photoreceptor
Light
74
New cards
Chemoreceptor
Chemical composition
75
New cards
Nociceptor
Pain
76
New cards
Cortical Association Areas
Where perception occurs along with emotional/varying factors that will affect perception
77
New cards
Factors that Affect Perception
Receptor adaptation, emotions/experiences, lack of receptors, damaged neural pathways, drugs, mental illness, not all stimuli give conscious sensation
78
New cards
Phasic Receptors
Respond quickly but adjust
79
New cards
Tonic Receptors
Maintain response to simulus
80
New cards
Coding Potentials
Stimulus strength and adaptation
81
New cards
Rods
Responds to LOW levels of light
82
New cards
Cones
* Respond to BRIGHT light signals
* Red, blue, green
* Red, blue, green
83
New cards
Glutamate
Neurotransmitter; increased learning, enhanced memory
84
New cards
What is glutamate involved in?
Memory and learning
85
New cards
Where do the optic nerves meet?
Optic chiasm
86
New cards
Tympanic Membrane
Air molecules push against it at same frequency as sound wave
87
New cards
What do pressures and movement of tympanic membrane indicate?
Pitch and volume
88
New cards
Bones of Ear
Malleus, incus, stapes
89
New cards
What do the three bones of the ear do?
Transduce sound by amplifying it through middle ear to oval window
90
New cards
Photoreceptors and bipolar cells only undergo \____________, they lack the \_______________ that mediate action potentials.
Graded responses; voltage-gated channels
91
New cards
Glutamate (Organ of Corti)
Binds and causes action potentials in neurons making up vestibulocochlear nerve
92
New cards
Stereocilia
Bent back and forth as sound waves vibrate
93
New cards
Organ of Corti Receptor Cells
Hair cells (mechanoreceptors)
94
New cards
Is fluid in the ear positive or negative?
Positive; more K+
95
New cards
Neural Pathway in Hearing
Vestibulocochlear nerve -\> brainstem (medulla oblongata) -\> thalamus (director) -\> auditory cortex
96
New cards
Chemical binding to specific CHEMORECEPTORS are responsible for the \_____________
Detection of taste and smell
97
New cards
Microvilli
Increase surface area; come into contact with chemicals
98
New cards
Where are taste buds located?
In bumps on tongue called papillae
99
New cards
Salt Taste
Sodium ions
100
New cards
Sour Taste
High acid (H+ ions)