Topic 5- Energy changes (copy)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is an exothermic reaction
A reaction which transfers energy to the surroundings
What are examples of exothermic reactions
Combustion, neutralisation and oxidation reactions
What are some uses of exothermic reactions
Hand warmers, self-heating cans of hot chocolate and coffee
What is an endothermic reaction
A reaction which takes in energy from the surroundings eg decomposition reactions
What is a use of endothermic reactions
Cold packs
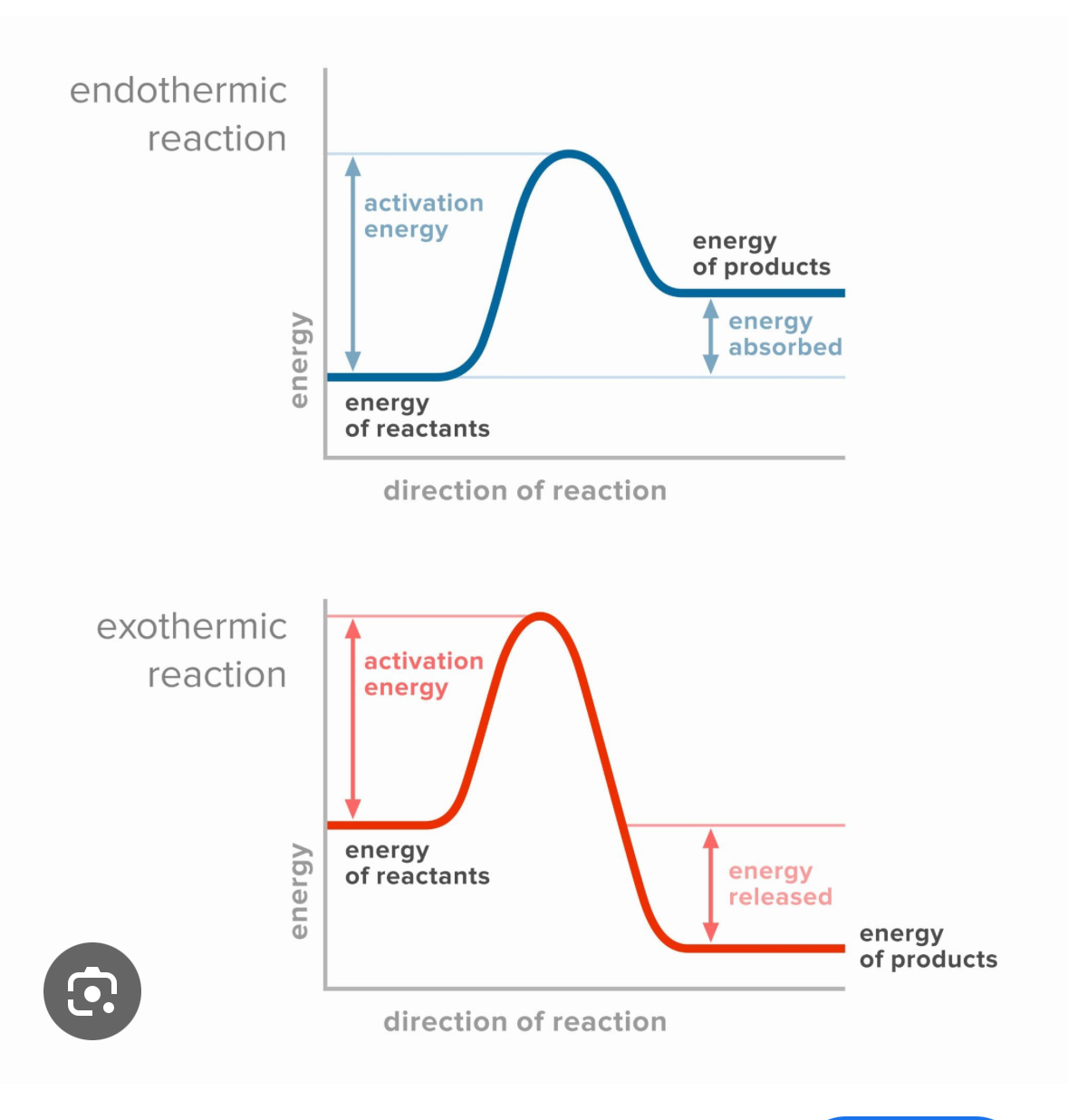
What is a reaction profile
A graph that showed how the energy in a reaction changes as the reaction progresses
How do you find the overall energy change of a reaction profile
Distance between reactants and products
How do you find the activation energy on a reaction profile
Distance between reactants and peak of graph
How do you know if a reaction is exothermic or endothermic on a reaction profile
More energy in reactants than products = exothermic, more energy in products than reactants = endothermic
Why is bond breaking an endothermic process
Energy must be supplied to break existing bonds
Why is bond formation an exothermic process
Energy is released when new bonds are formed
What is the reaction if Bond formation>bond breaking
exothermic reaction
What is the reaction if Bond breaking>bond formation
Endothermic
What is the formula for overall energy change
Energy change = energy of bond breaking - energy of bond making
What is a cell
A system that contains chemicals which react and produce electricity. It contains two different (metal) electrodes in contact with an electrolyte
What is an electrolyte
A liquid that conducts electricity and contains ions which reacts with electrodes
How does a cell work
The chemical reactions between the electrodes and electrolyte set up a charge difference between the electrodes. If electrodes are connected by a wire the charge is able to flow and electricity is produced
Cells can only produce electricity if we use metals with…
…different reactivities
What happens if there’s no difference in reactivity between the two electrodes
The potential difference if the cell will be zero
What does the potential difference of a cell depend on
Identity of the metal electrodes, electrolyte and concentration of ions in electrolyte
Why will there be a low voltage if the concentration of ions in electrolyte is low
As the ions in the electrolyte react, their concentration will slowly decrease and so will the voltage of the cell
What is a battery/ how is it formed
A battery contains two or more cells connected in series to produce a greater voltage
Why can a cell only produce electricity for a certain period of time
Eventually the chemicals in the cell run out and the reaction stops
Why are alkaline batteries non rechargeable
The reactants in batteries run out so no more electricity is produced; reaction is irreversible
Why can you recharge rechargeable batteries
Reaction can be reversed when we apply an electrical current.
What is a fuel cell
A type of electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel and oxygen into electrical energy that can be used to power things
What happens in a hydrogen oxygen fuel cell
Hydrogen and oxygen react together to form water
What is often used as the electrolyte in a hydrogen oxygen fuel cell
Potassium hydroxide
What is used as the electrodes in a hydrogen oxygen fuel cell
Porous carbon with a catalyst
What happens at the anode (negative electrode) in hydrogen oxygen fuel cells
Hydrogen loses electrons to produce H+ ions, this is oxidation. H+ ions in the electrolyte move to the cathode (positive electrode)
What happens at the cathode (positive electrode) in hydrogen oxygen fuel cells
Oxygen gains electrons from the cathode and reacts with H+ ions in the electrolyte to make water, this is reduction
What is the electric current in a hydrogen oxygen fuel cell
The flow of electrons through an external circuit from the anode to the cathode
What is the overall reaction in hydrogen oxygen fuel cell
Redox
What is the half equation at the anode
H2 —> 2H+ + 2e-
What is the half equation at the cathode
O2 + 4H+ + 4e- —> 2H2O
What are the pros of hydrogen oxygen fuel cells
Fuel cell vehicles don’t produce as many pollutants as other fuels, only require hydrogen and oxygen, last longer than batteries, less polluting to dispose of
What are the cons of hydrogen oxygen fuel cells
Hydrogen is a gas so takes up more space to store than fossil fuels or batteries, hydrogen is explosive when mixed with air making it difficult to store safely, making hydrogen fuel requires energy which usually comes from fossil fuels
high cost, the lack of a widespread hydrogen refueling infrastructure, and challenges with hydrogen production and storage