eye and ear anatomy
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
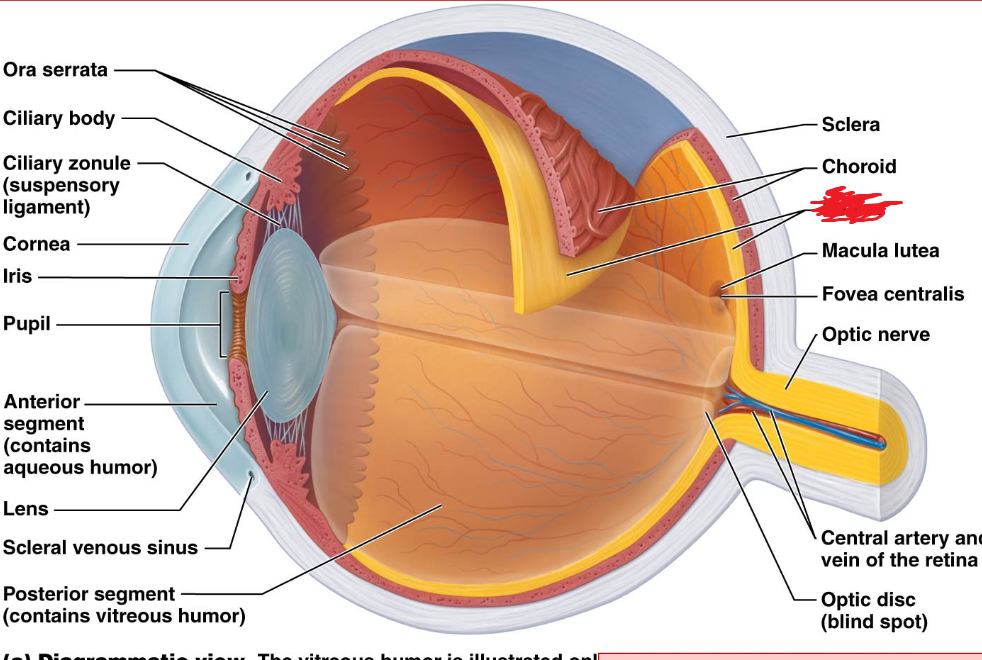
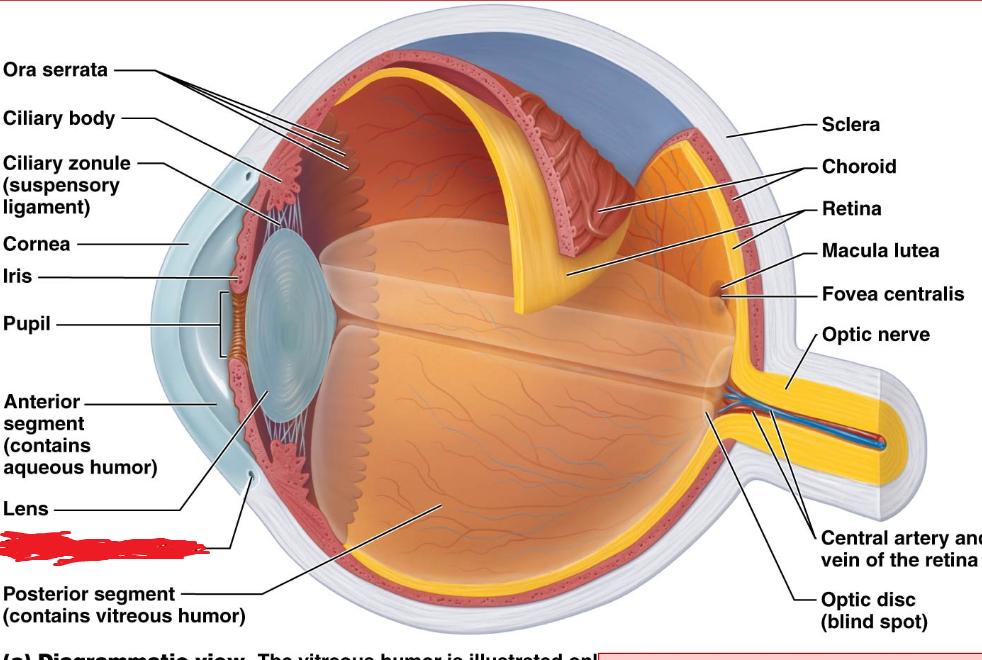
Sclera
Fibrous layer
White part of the eye
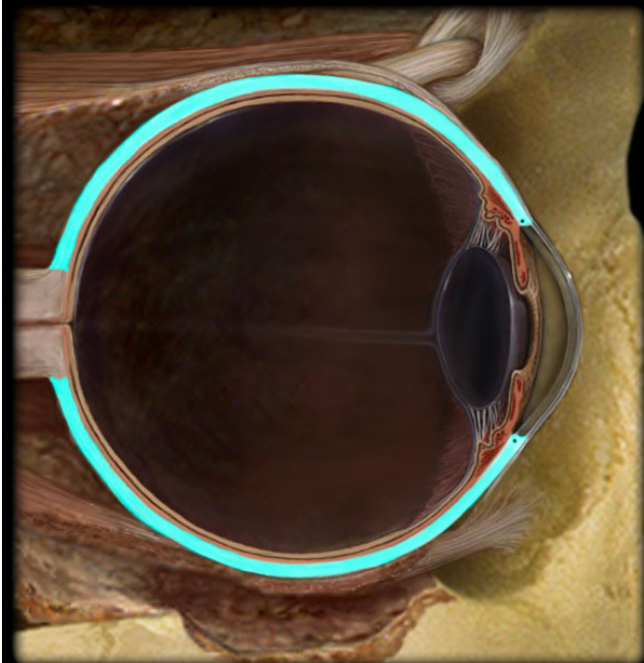
Cornea
Fibrous layer
the transparent layer forming the anterior (front) eye that refracts light as it enters the eye.
Choroid
a highly vascular membrane
Between the retina and the sclera
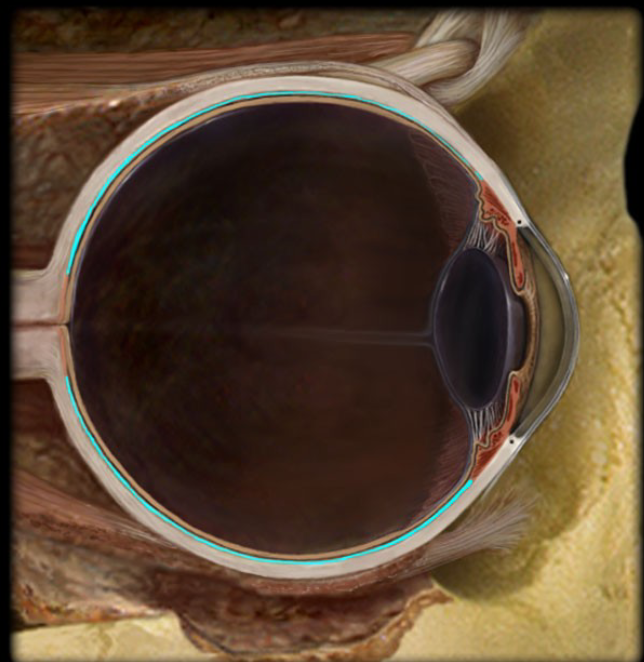
Ciliary Body
Vascular layer
A ring of smooth muscle that alters the shape of the lens to focus light on the retina.
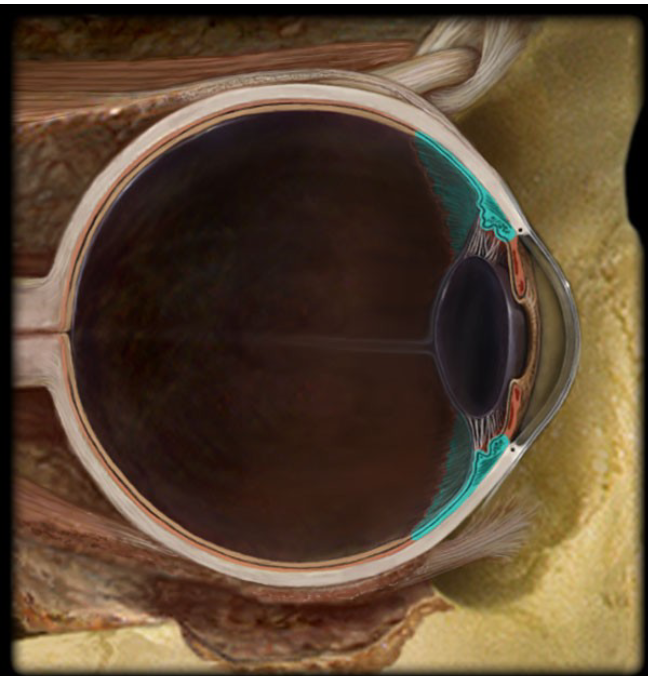
Suspensory ligaments
Vascular layer
Fine threads that connect the ciliary body to the lens; contraction and relaxation of the smooth muscle changes the shape of the lens to focus light on the retina.
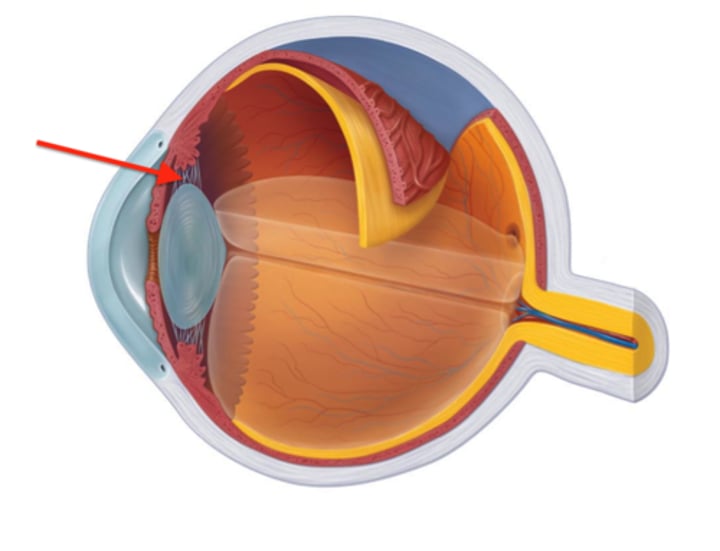
Retina
Iris
Vascular layer
A pigmented ring of smooth muscle cells that surround the pupil and controls the amount of light that enters the eye.
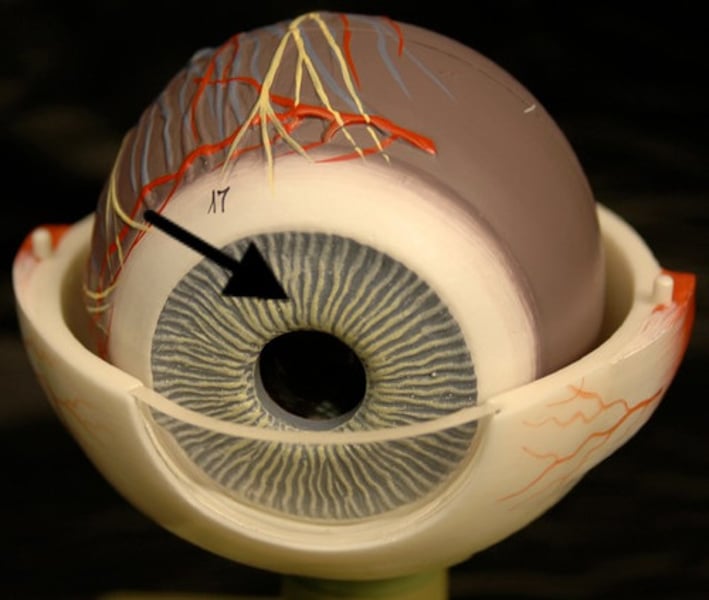
Pupil
Vascular Layer
An opening in the iris through which light enters the eye.
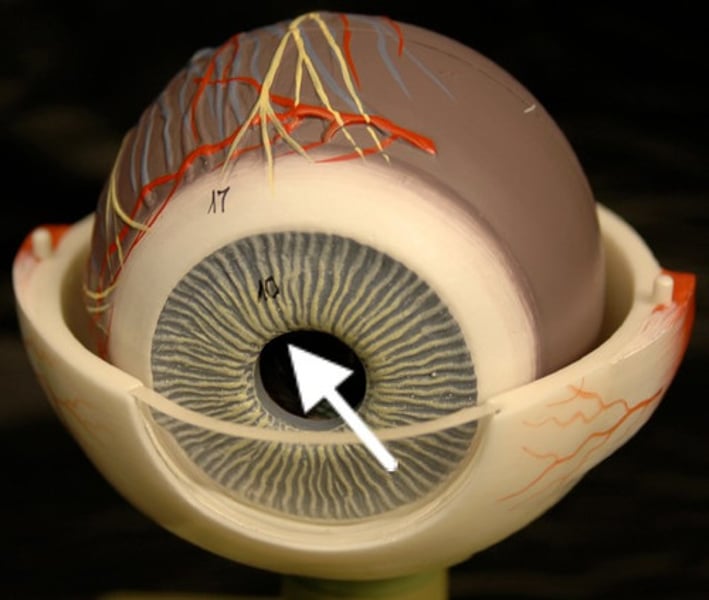
Lense
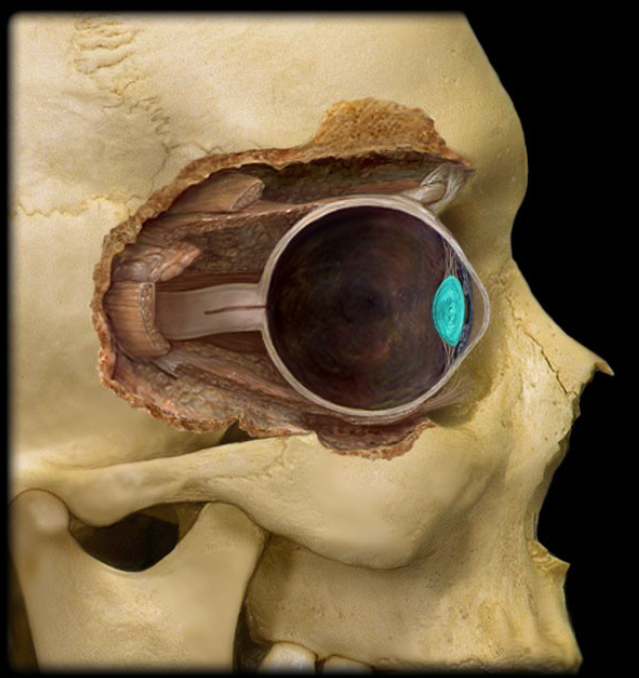
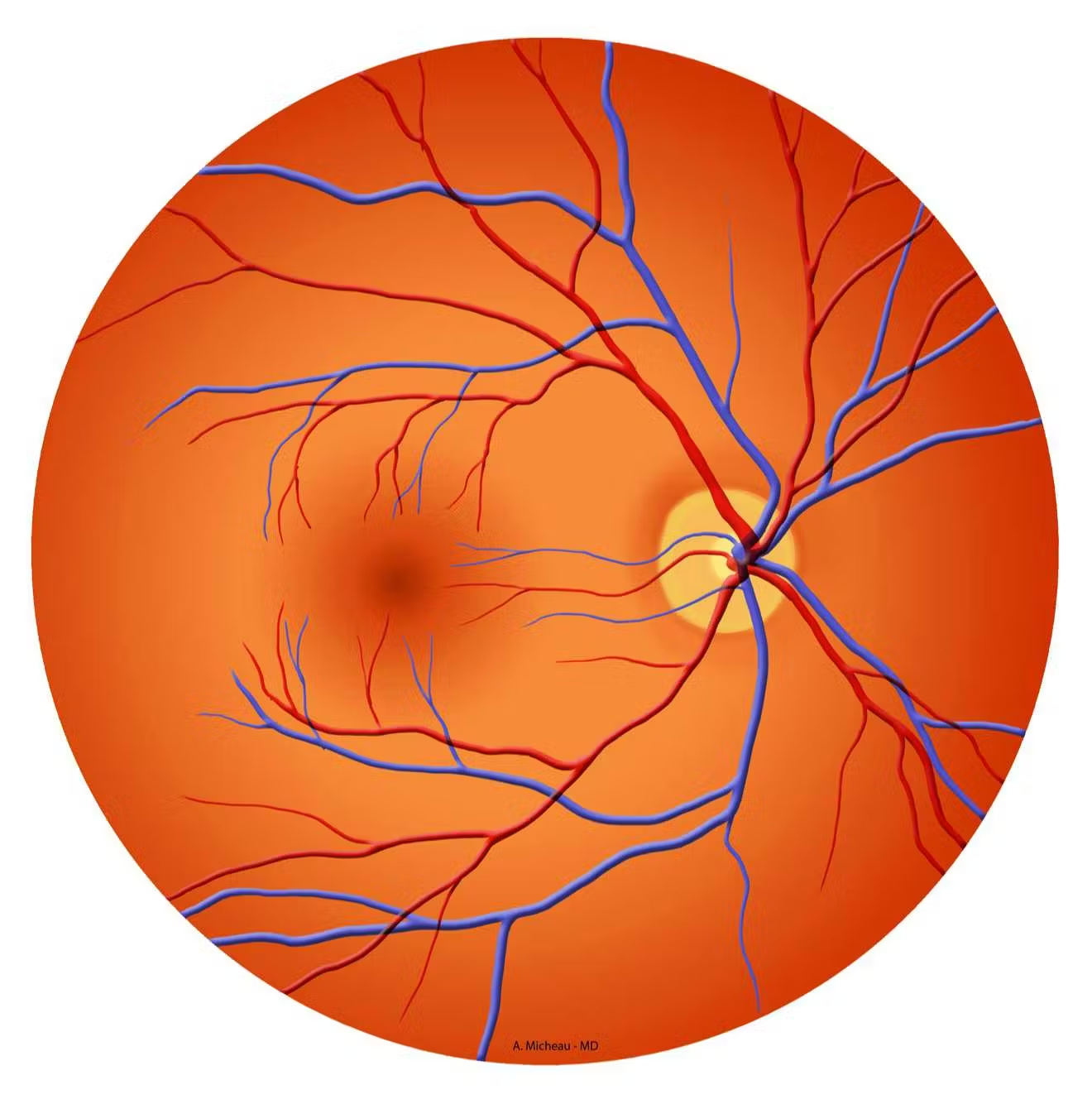
fovea centralis
Neural Layer (retina)
An area of the retina with the highest density of cones that produces high acuity vision.
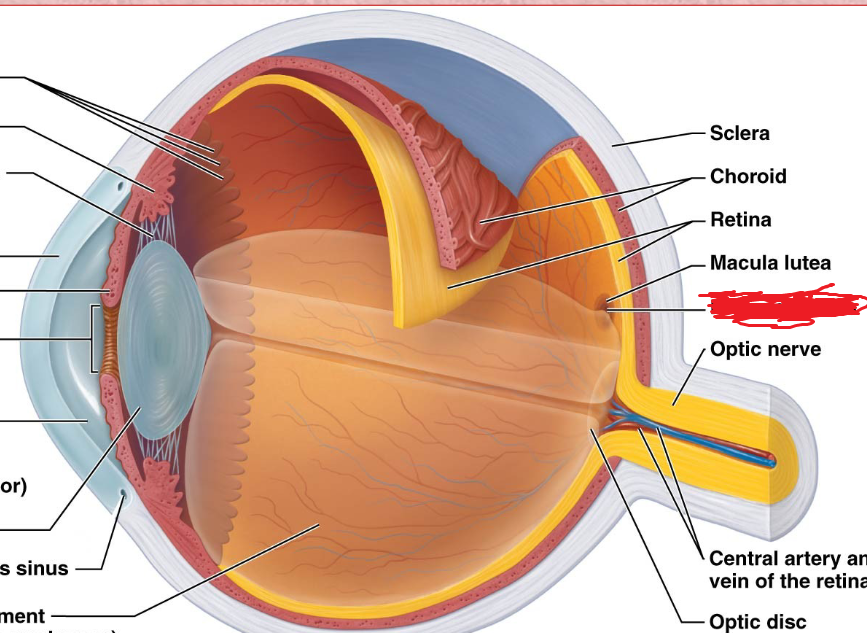
macula lutea
Neural Layer (retina)
center of the retina, where photoreceptors are conctrated; appears as a yellow spot on retina
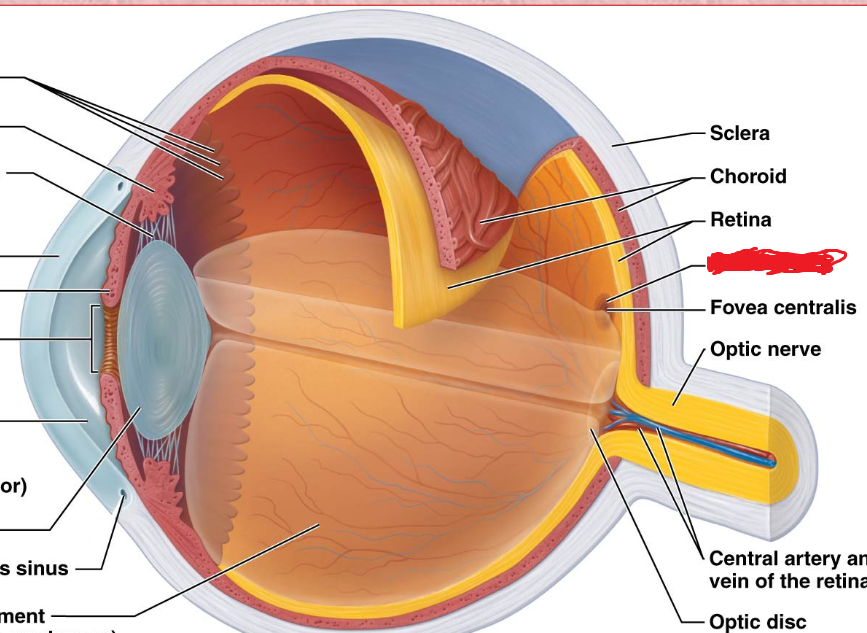
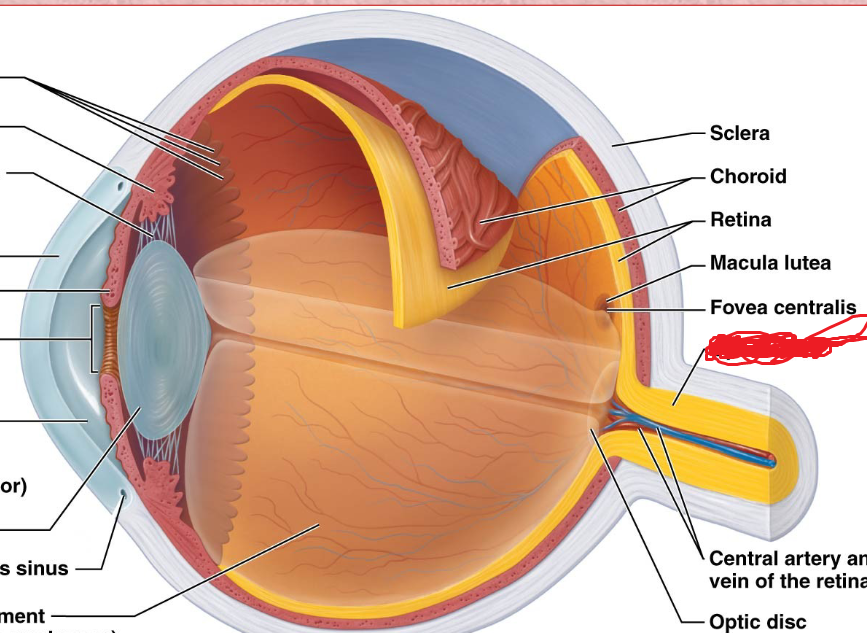
optic disc
Neural Layer (retina)
Blind spot
does not contain any photoreceptors
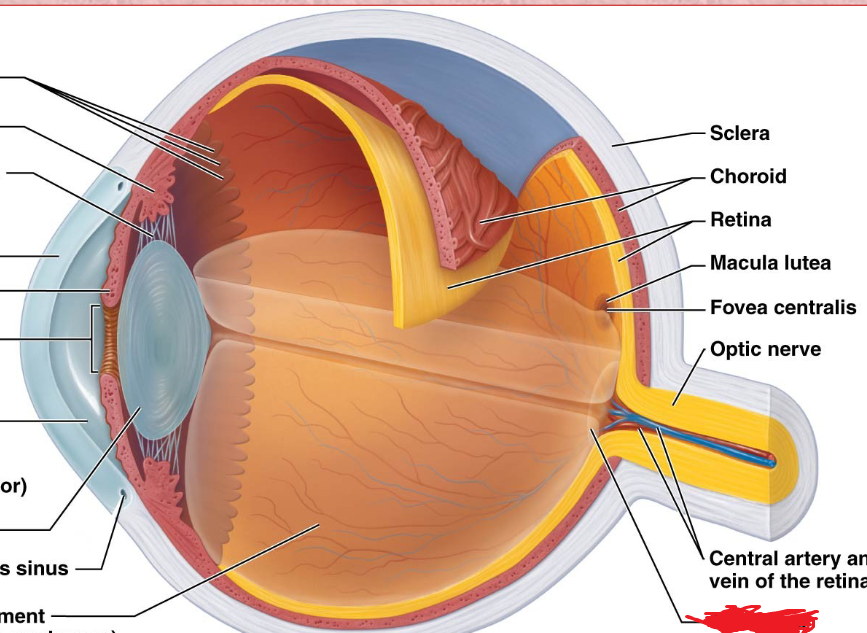
Optic Nerve
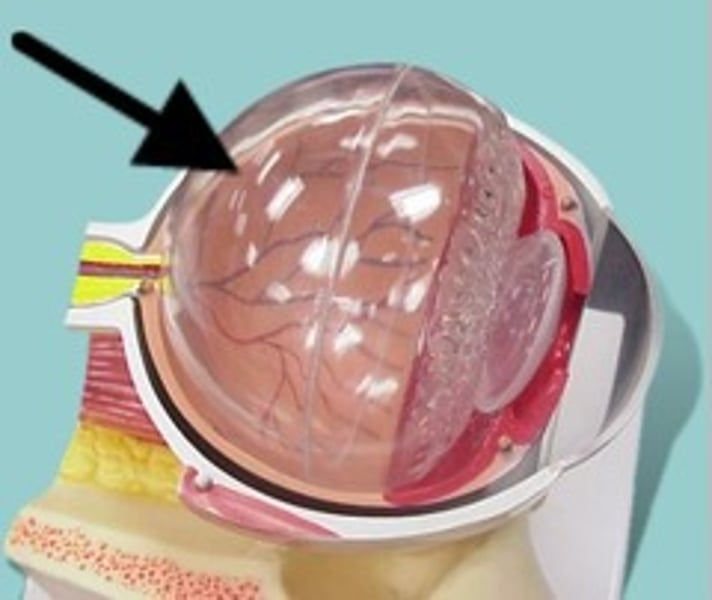
vitreous humor
Thick fluid located in the posterioir cavity of the eyeball.
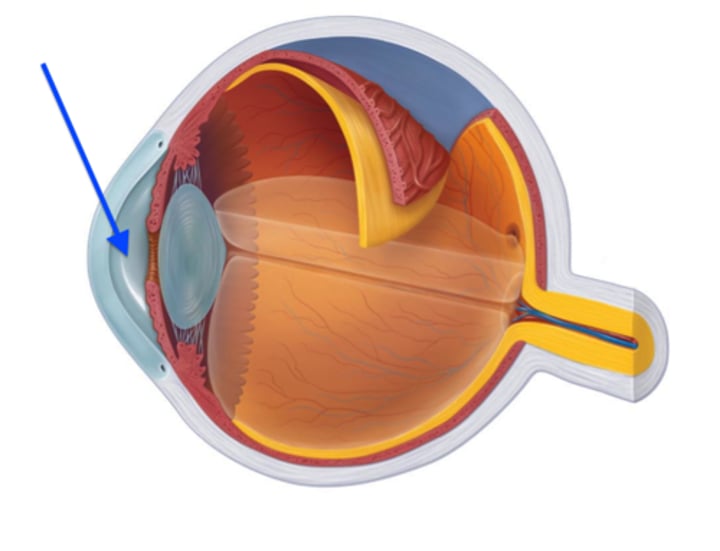
anterior chamber
Anterior Cavity
located behind the cornea and in front of the iris
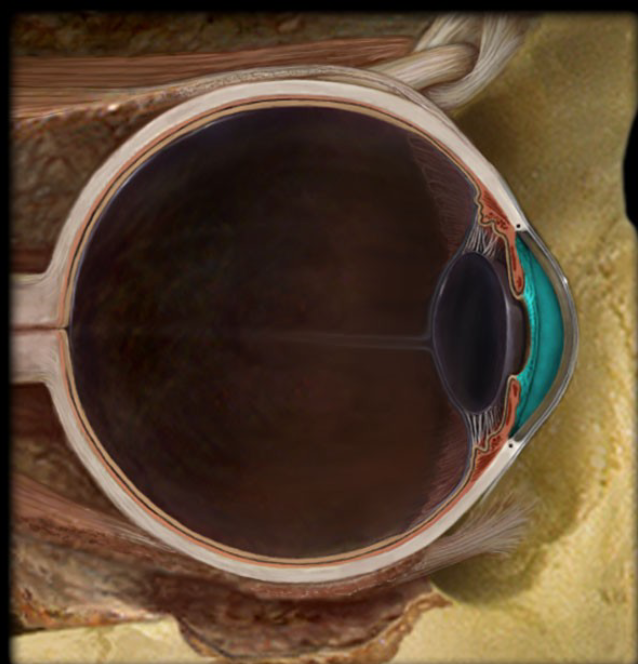
posterior chamber
Anterior Cavity
located posterior to the lens, filled with vitreous humor
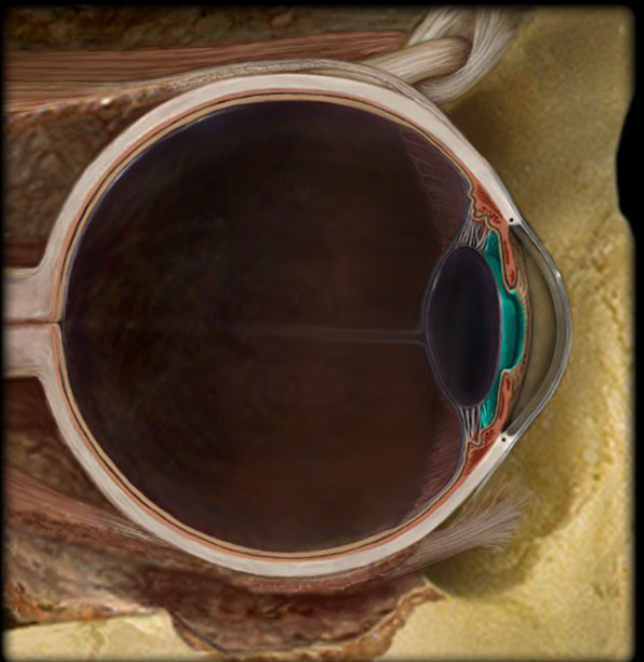
aqueous humor
Watery fluid that fills te anterior cavity of the eyeball
Sclera Venous Sinus
Arteriole/Venule
Auricle
Outer ear
also known as pinna
Consists of elastic cartilage covered with skin
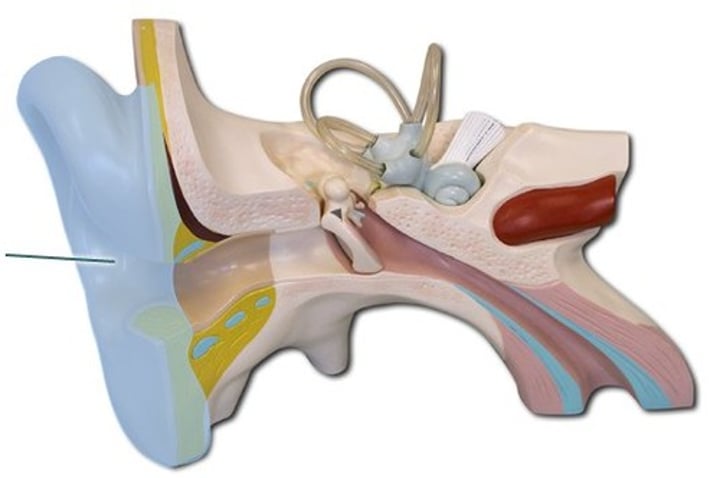
Auditory Canal
Outer ear
transmits sound waves from the pinna to the tympanic membrane of the middle ear
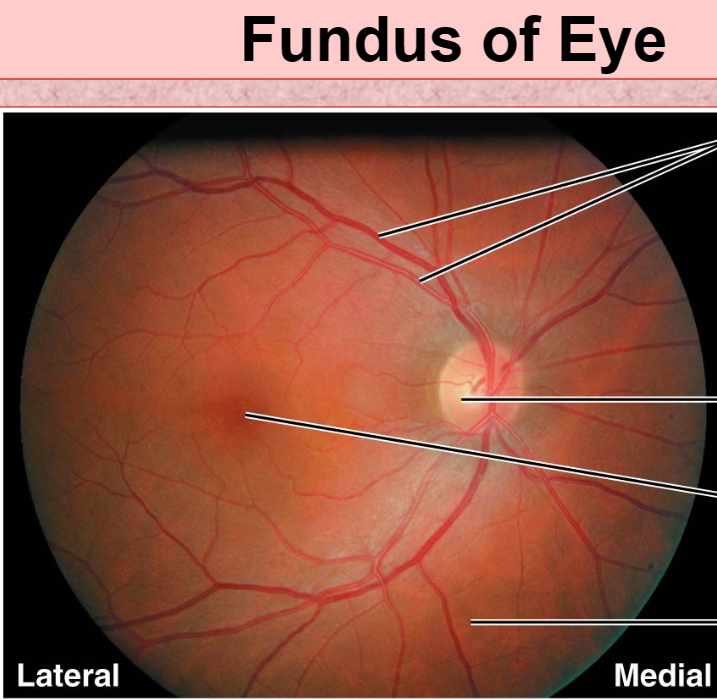
Fundus
Inside back surface of eye
Conjunctiva
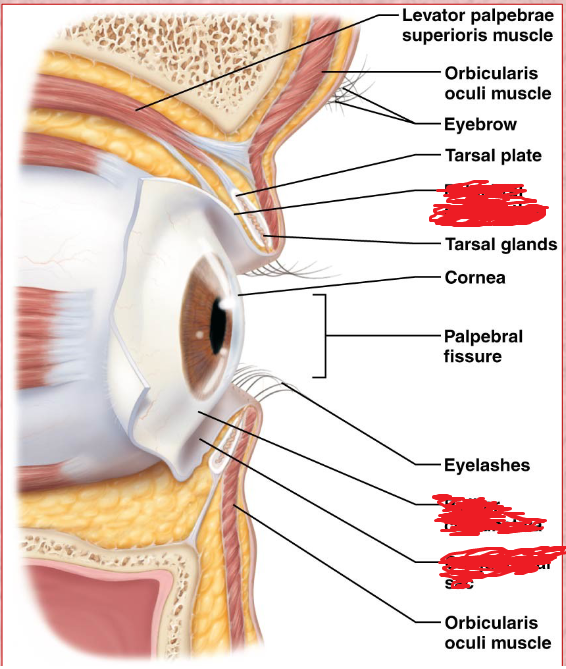
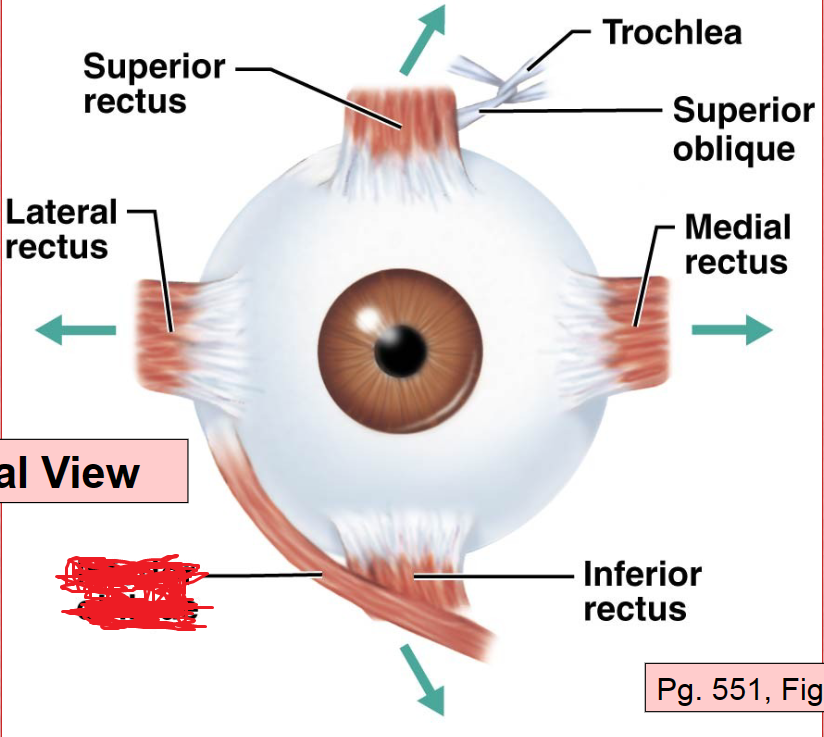
Superior Rectus Muscle
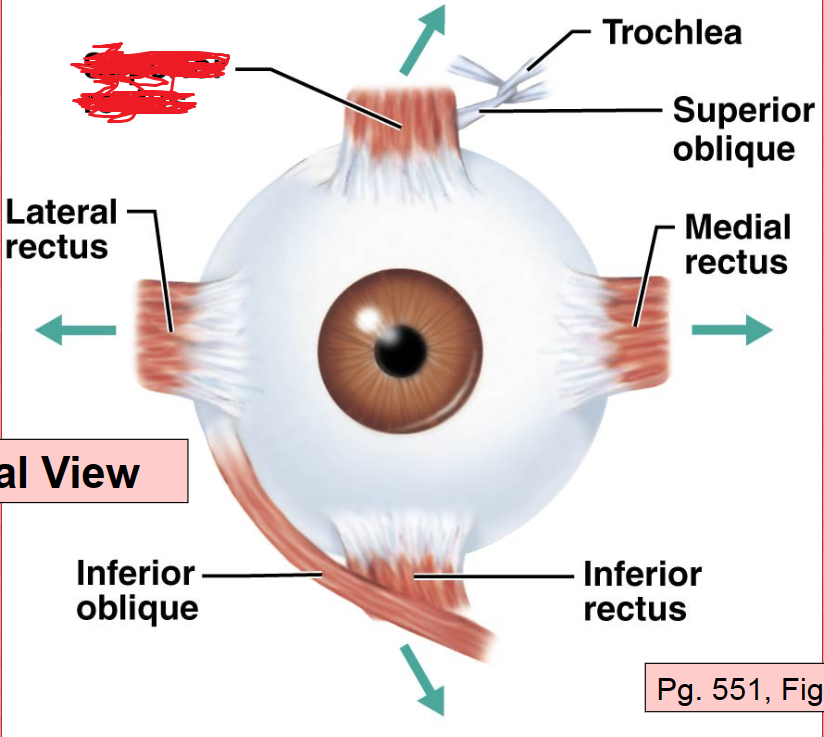
Lateral Rectus Muscle
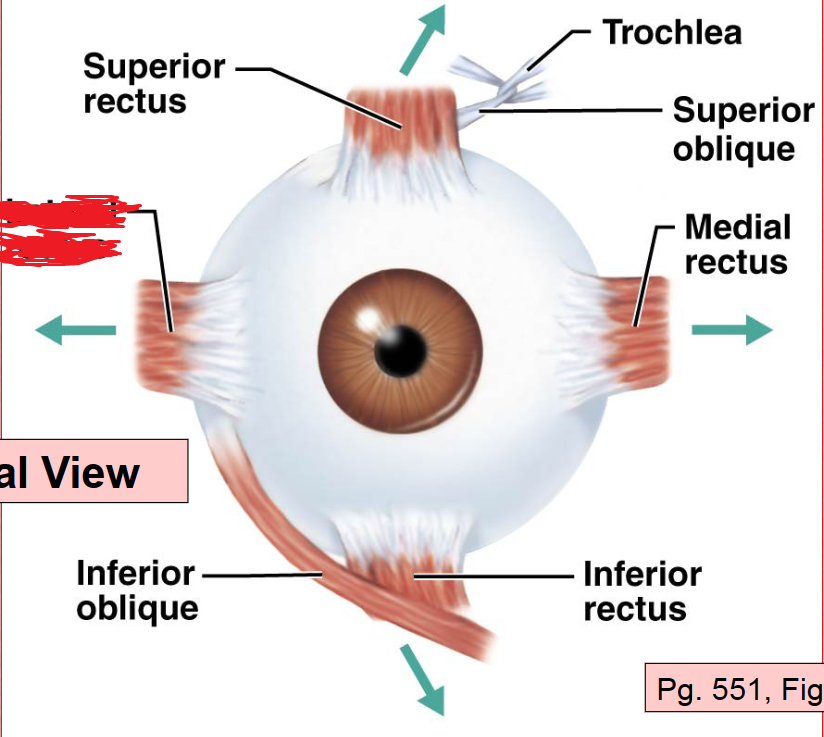
Inferior Rectus Muscle
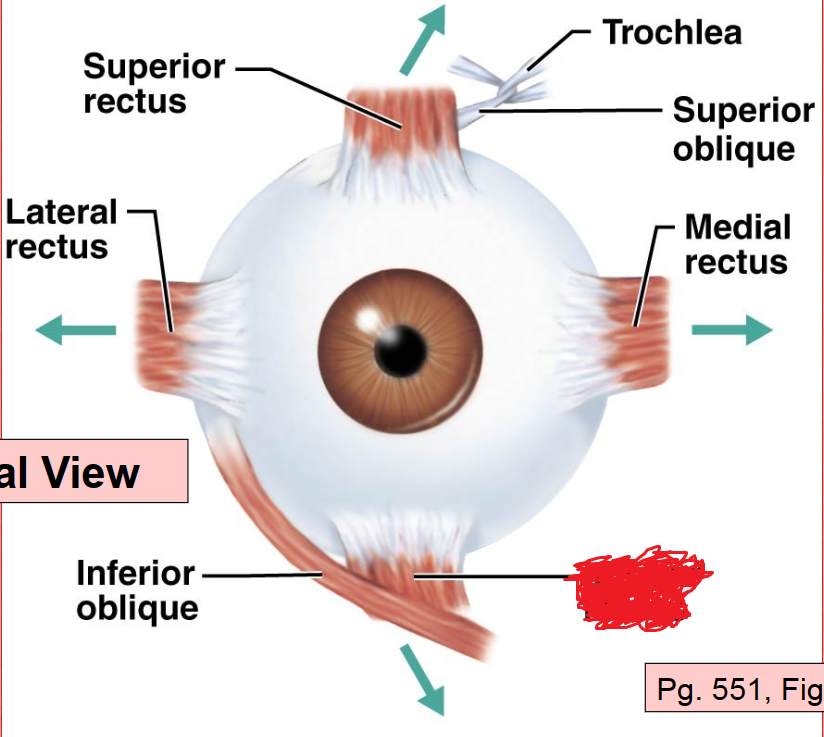
Medial Rectus Muscle
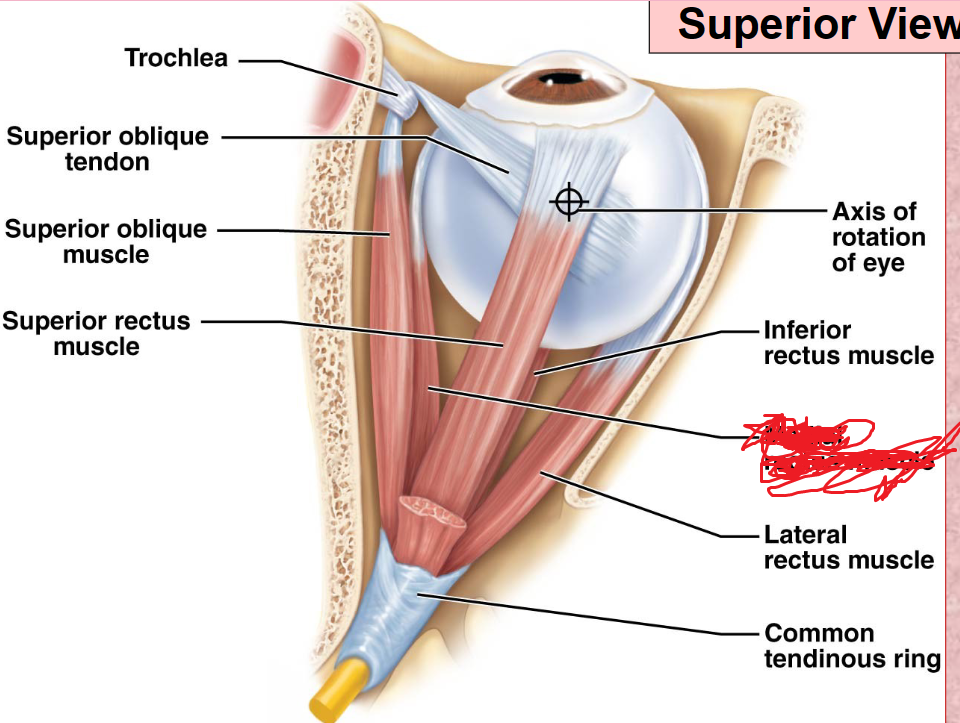
Superior Oblique Muscle
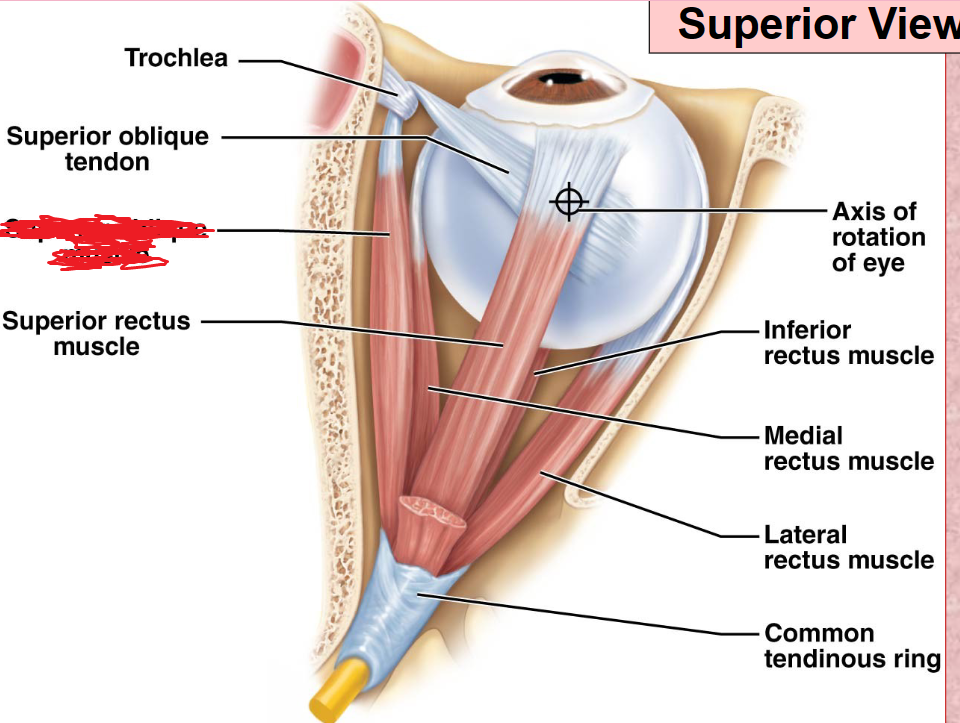
Inferior Oblique Muscle
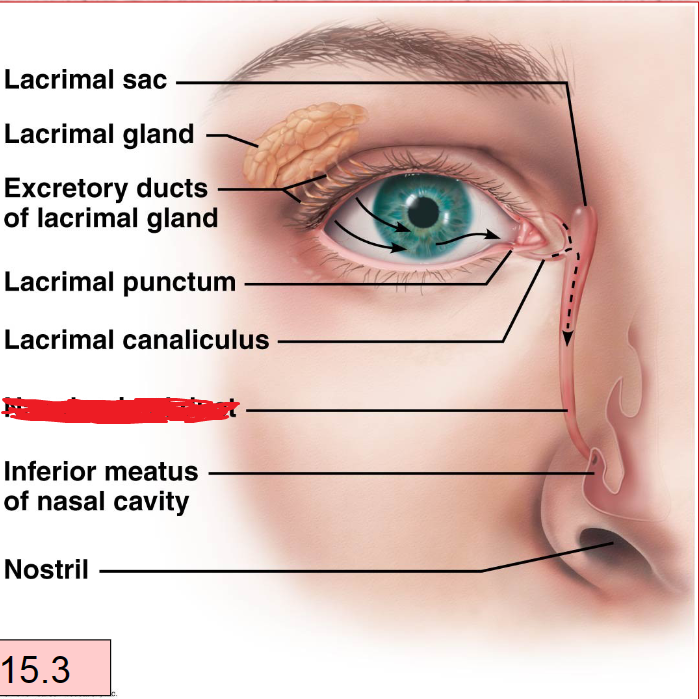
Lacrimal Apparatus
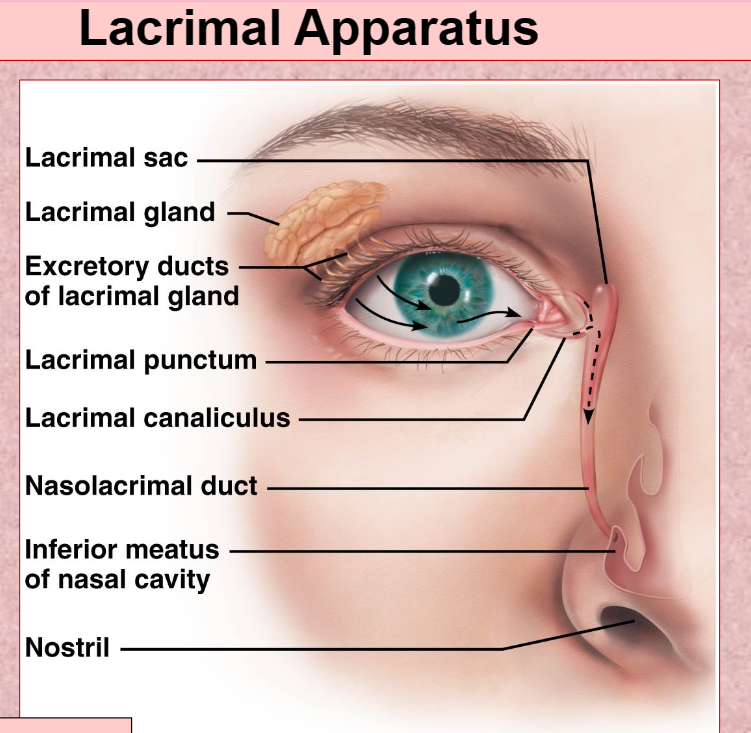
lacrimal Gland With Duct
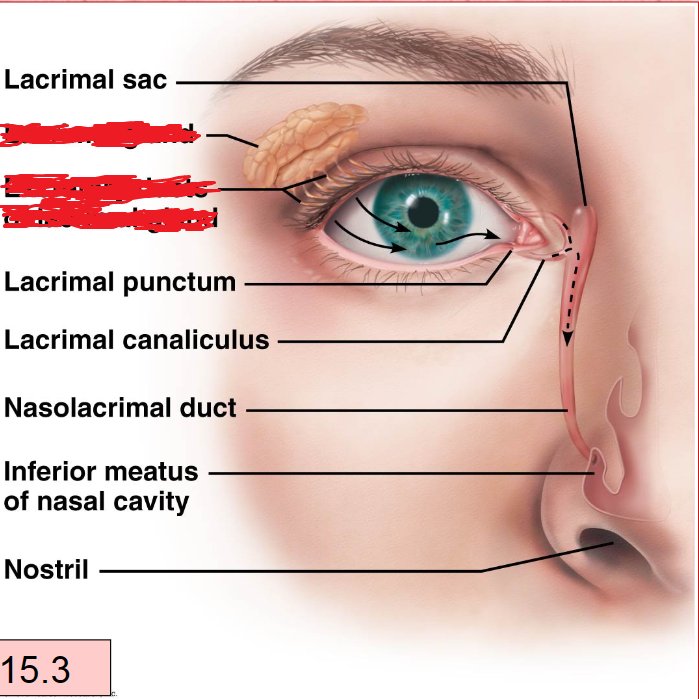
Lacrimal Canaliculi
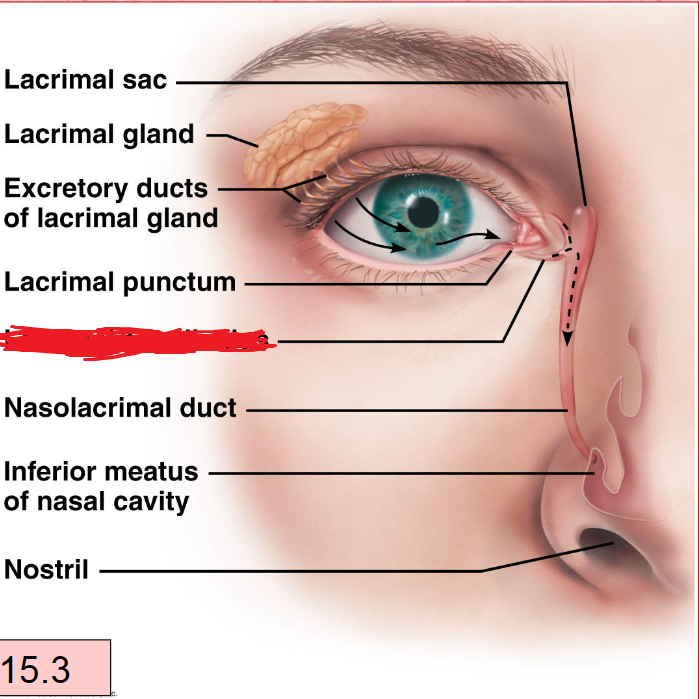
Lacrimal Sac
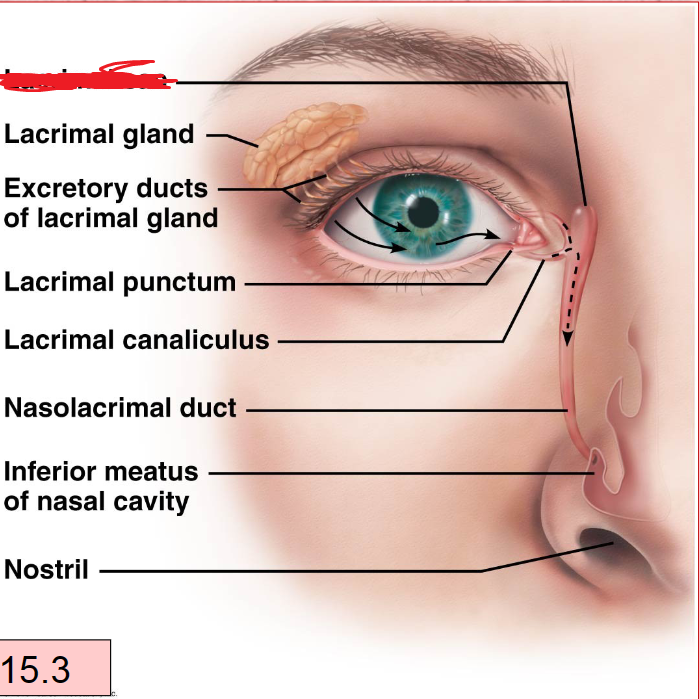
Nasolacrimal Duct
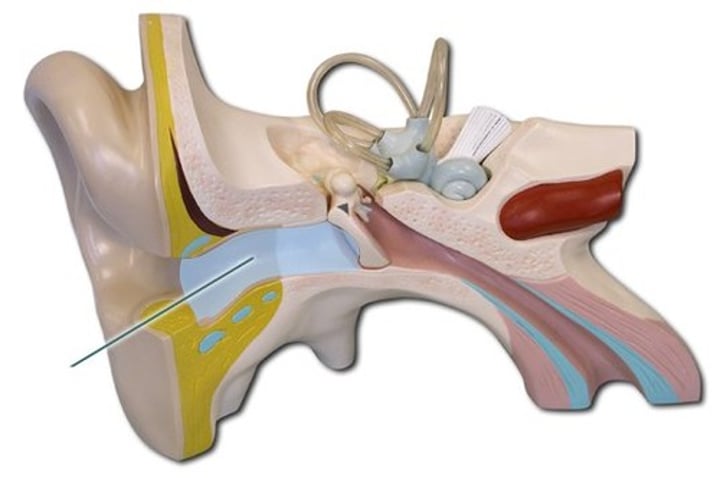
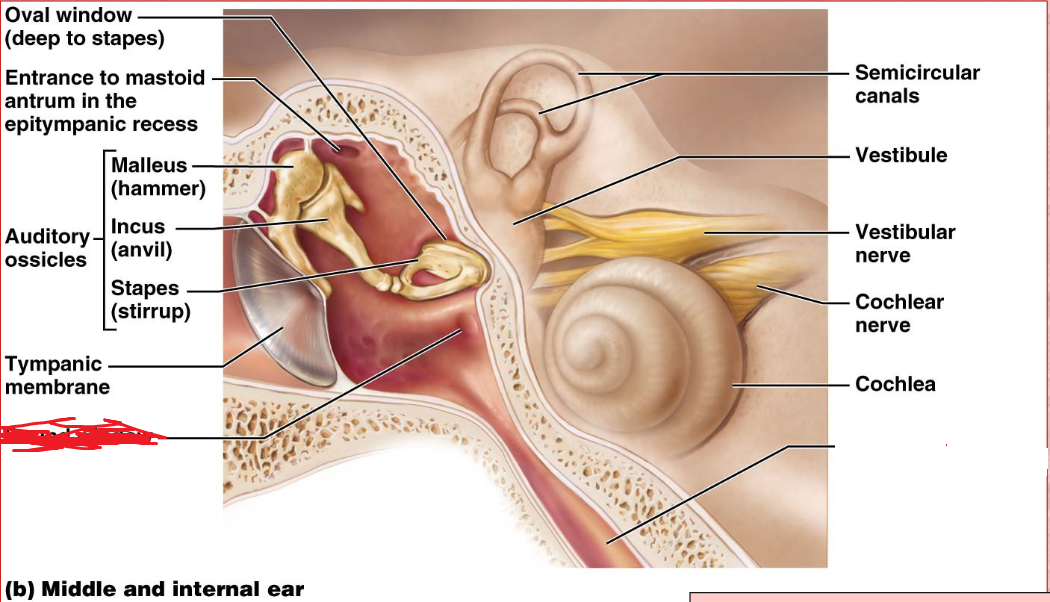
Tympanic membrane
Outer ear
The membrane that separates the external auditory canal from the middle ear.
Vibrates when struck by sound waves and transmits the vibrations to auditory ossicles.
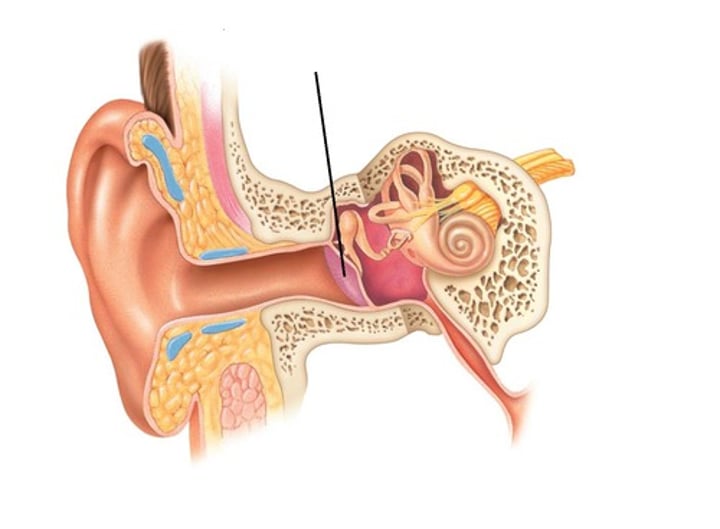
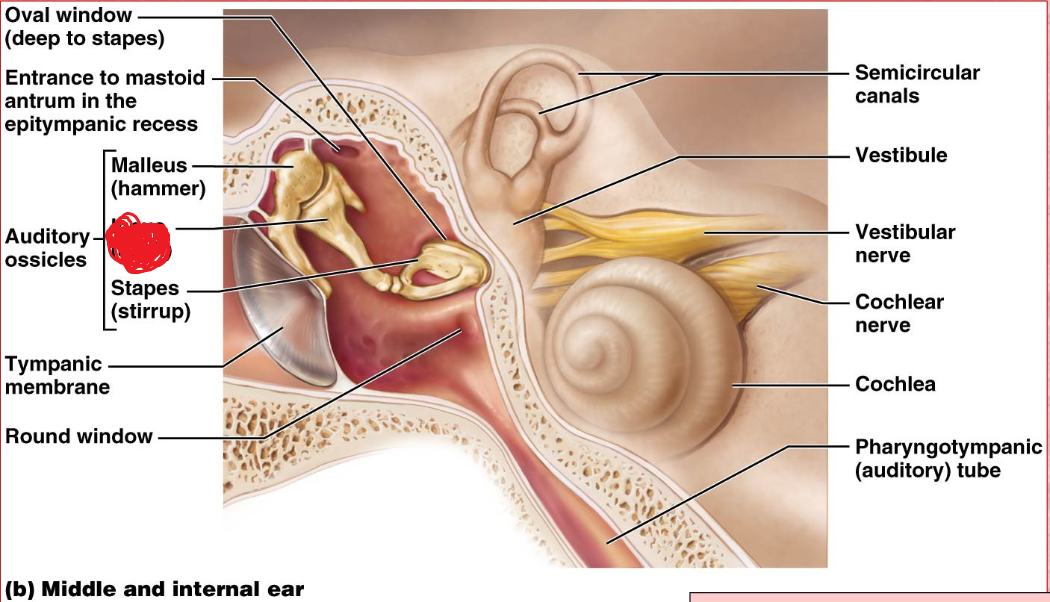
pharyngotympanic tube
middle ear
The passageway that connexts the middle ear and the nasopharynx
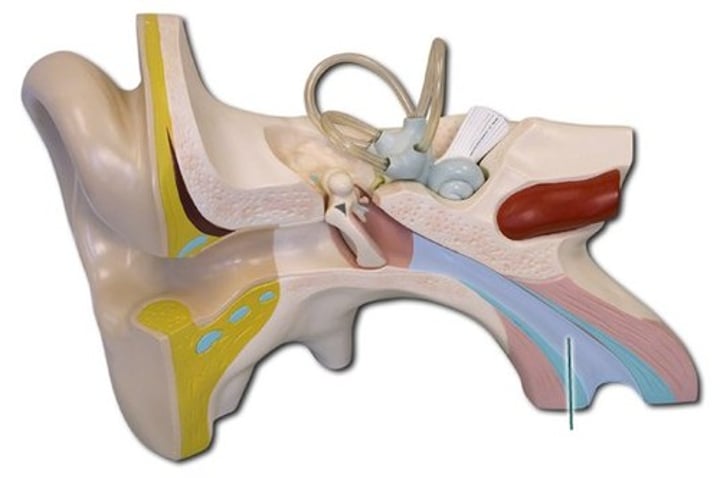
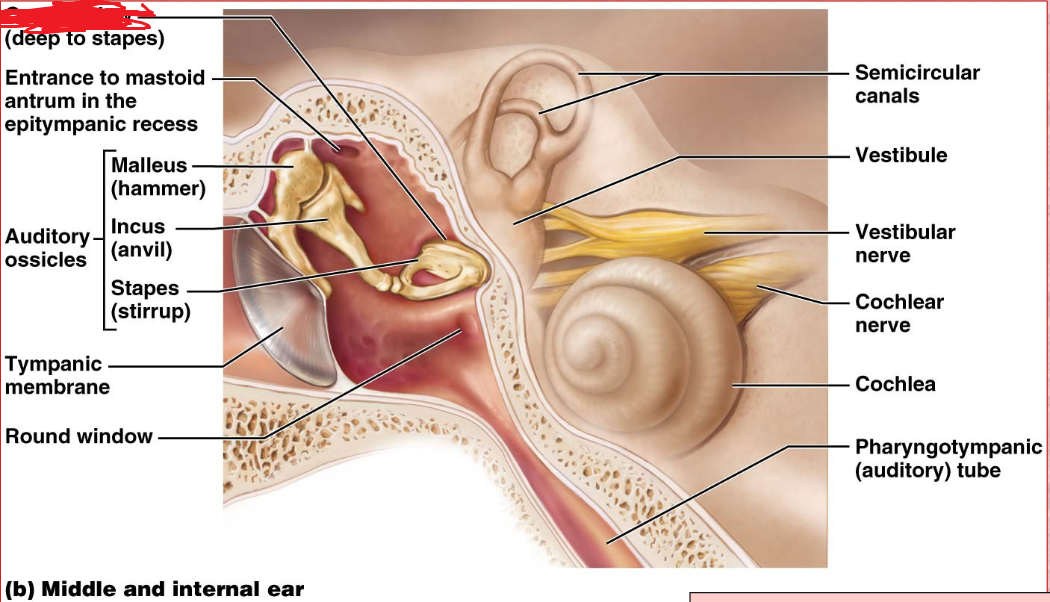
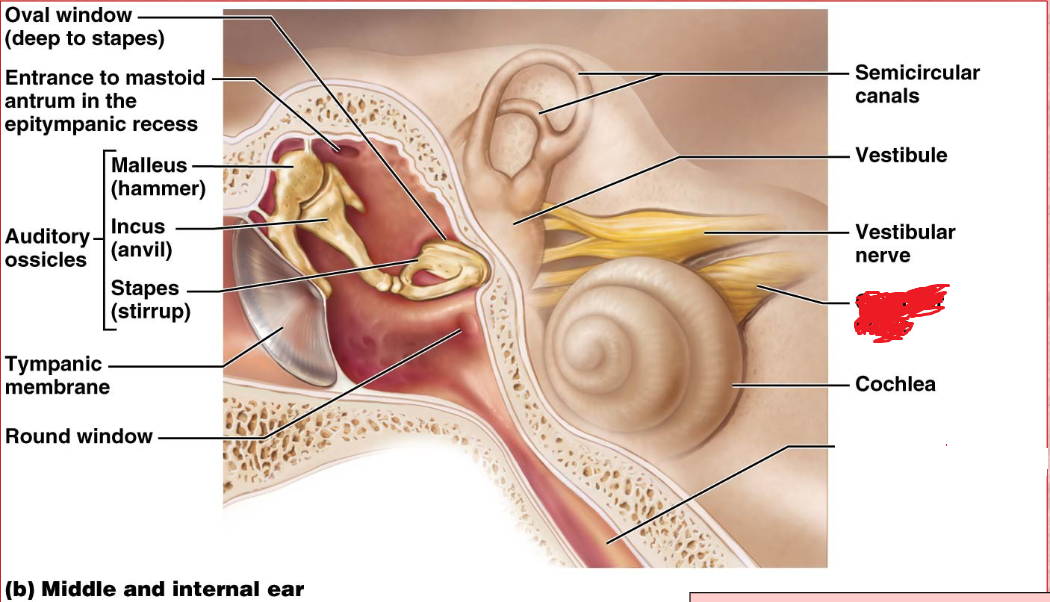
Ossicles
Middle ear
A chain of 3 bones (malleus, incus, and stapes) that connect the tympanic membrane to the oval window.
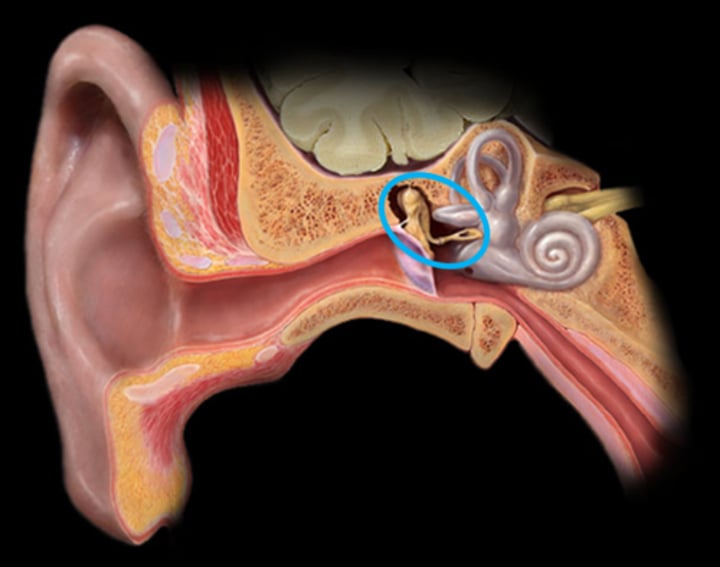
Malles
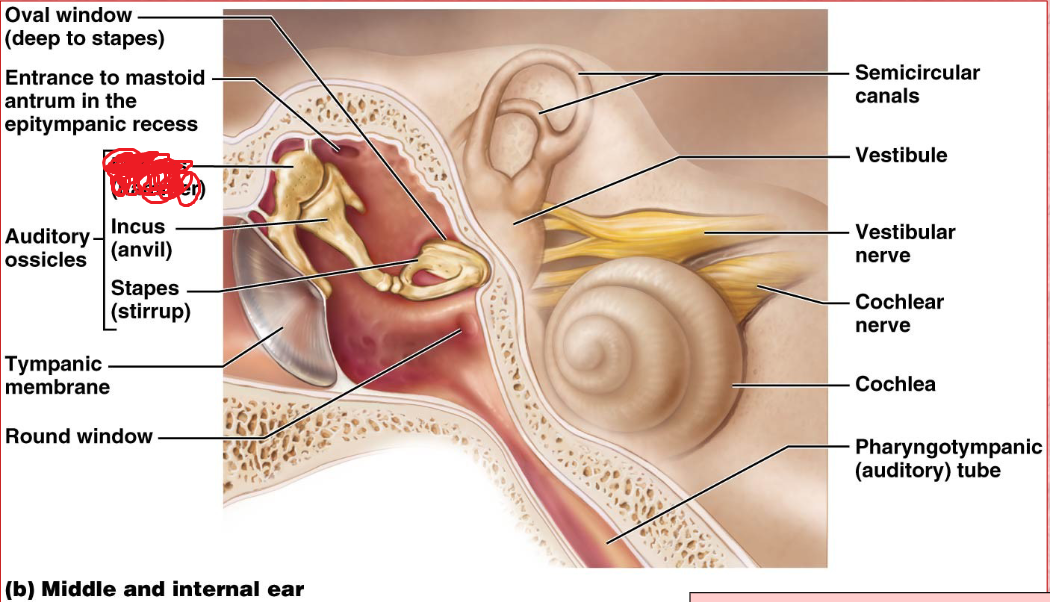
Incus
Stapes
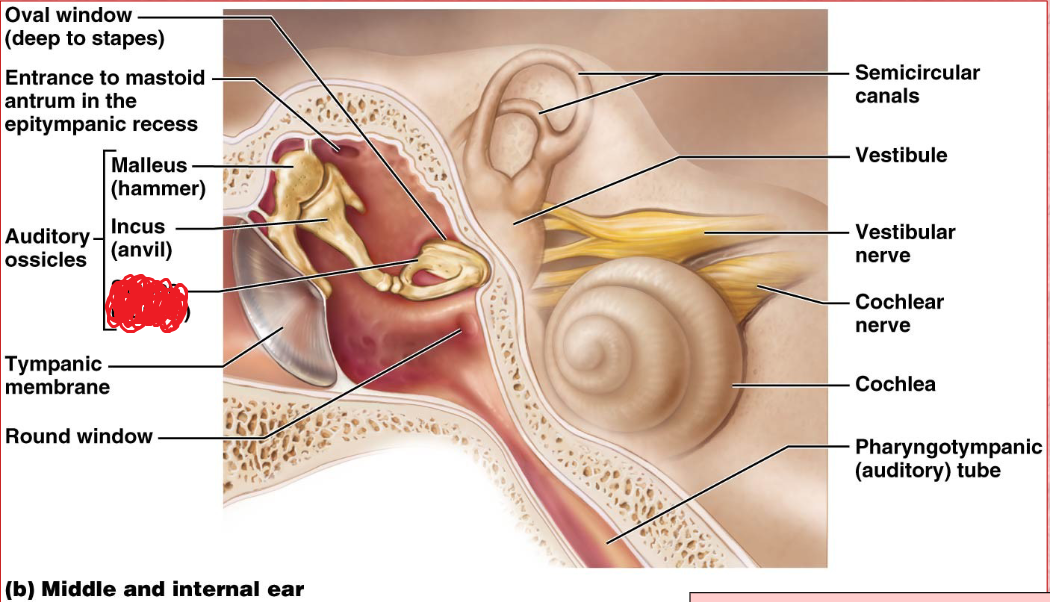
oval window
middle ear
Boundary between air filled middle ear and fluid filled inner ear.
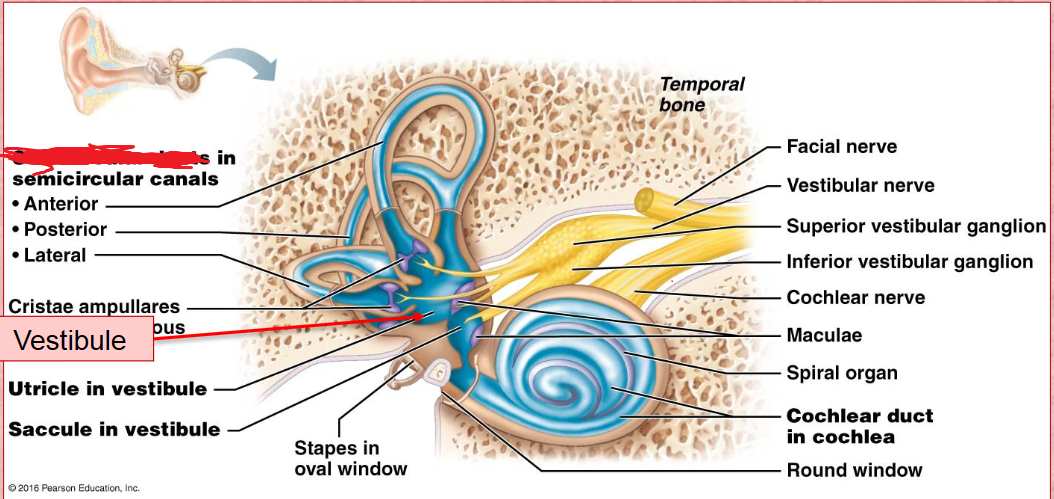
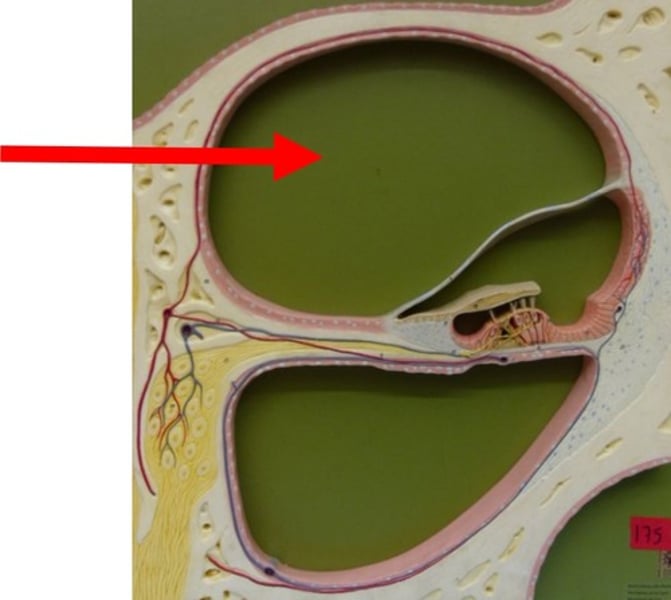
Vestibule
inner ear
Its wall contains the membraous oval window.
Houses two portions of the membranous labyrith filled with endolymph, the utricle and saccule.
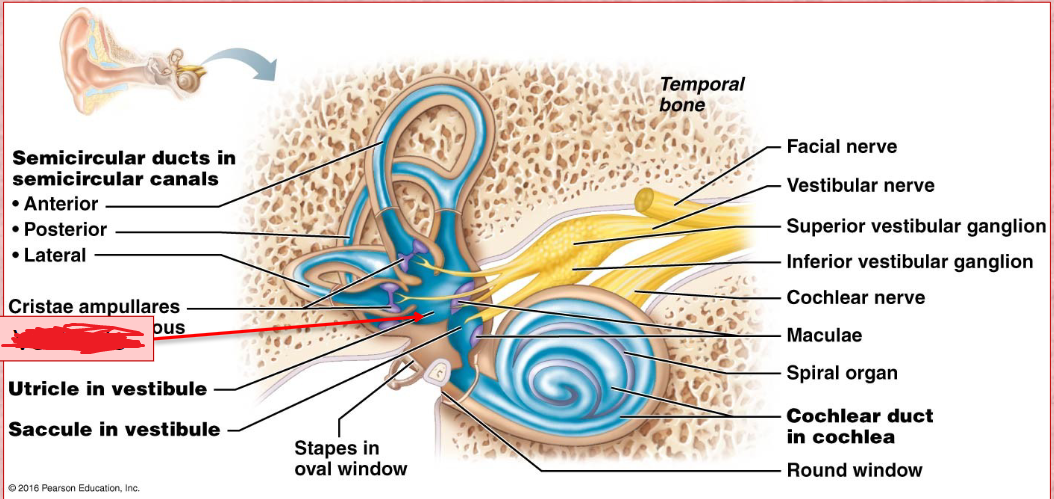
Semicircular Duct
Vestibular Nerve
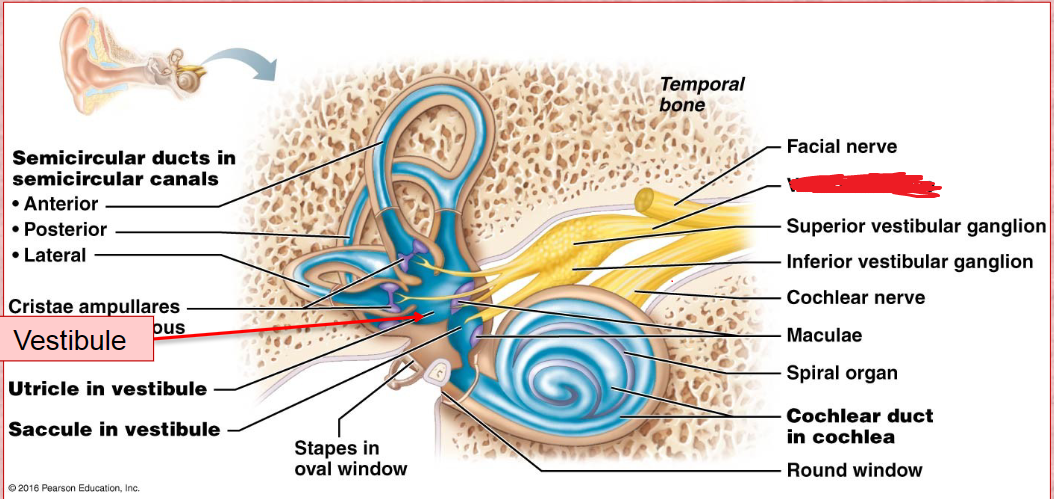
vestibulocochlear nerve
Stem connecting the cochlear and vestibuli nerve
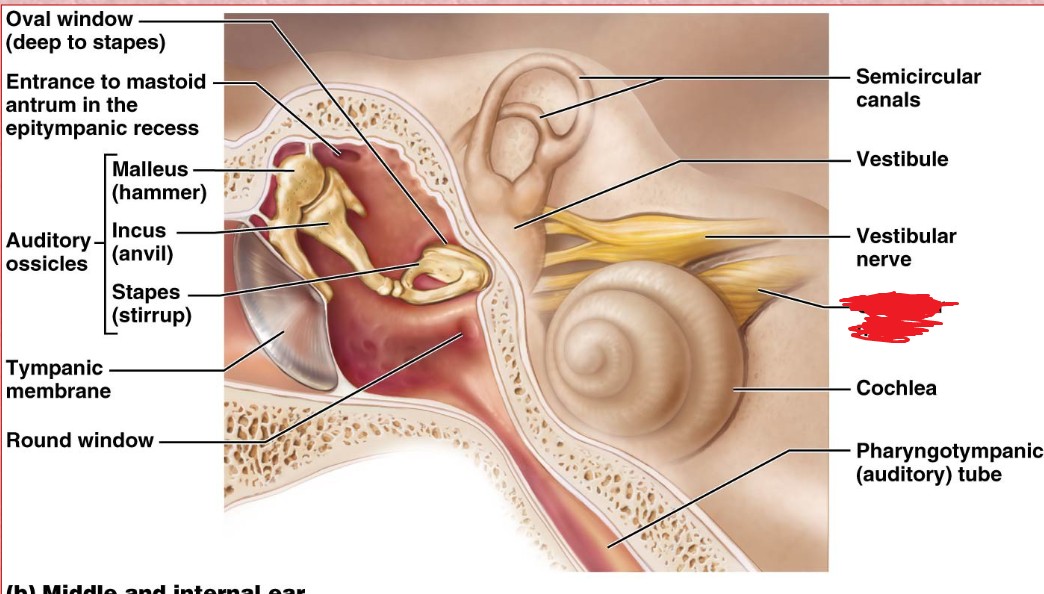
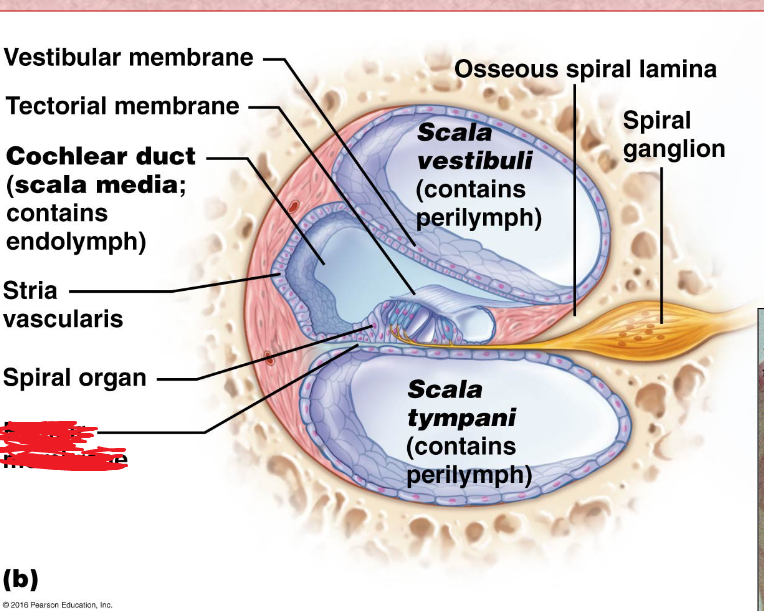
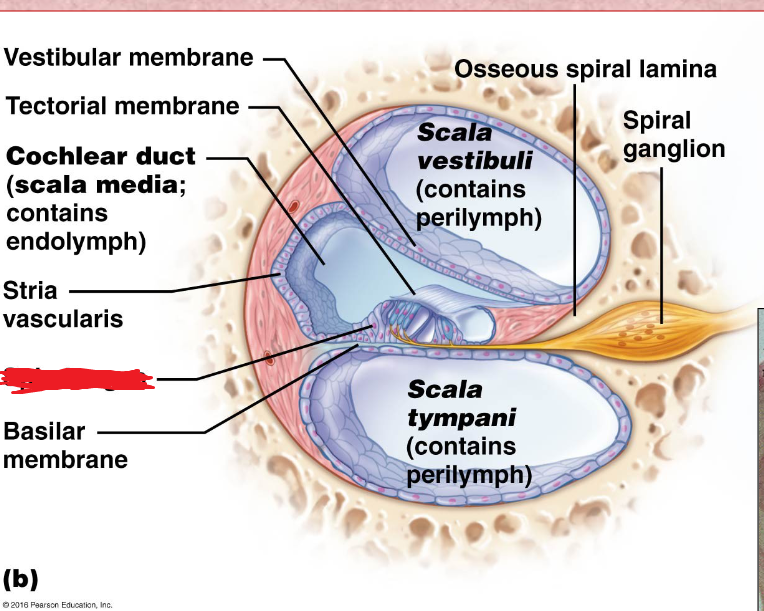
Cochlea
Inner ear
A coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear through which sound waves trigger nerve impulses
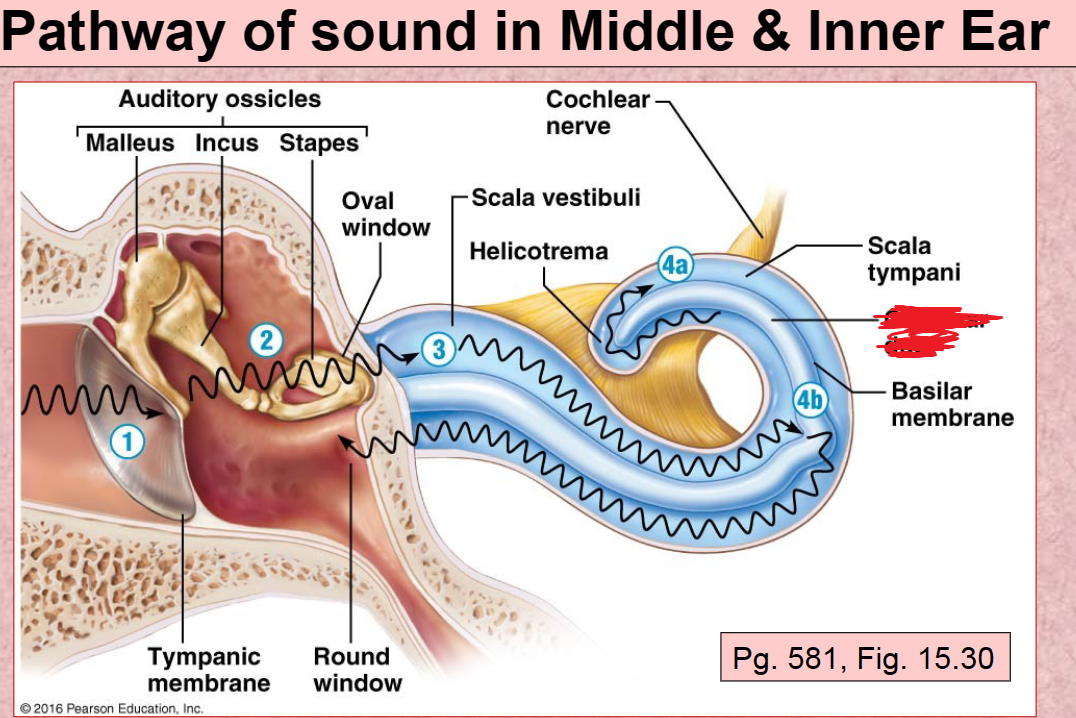
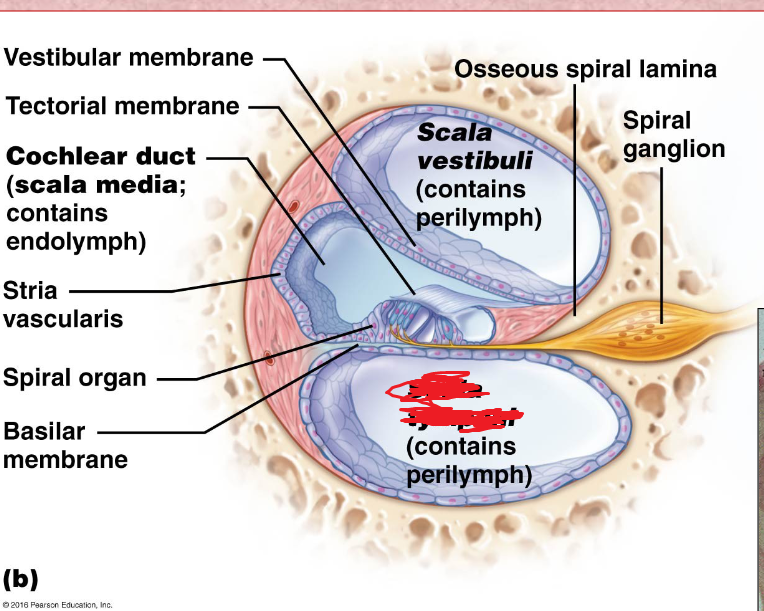
Cochlear duct
located in between the tympanic duct and the vestibular duct
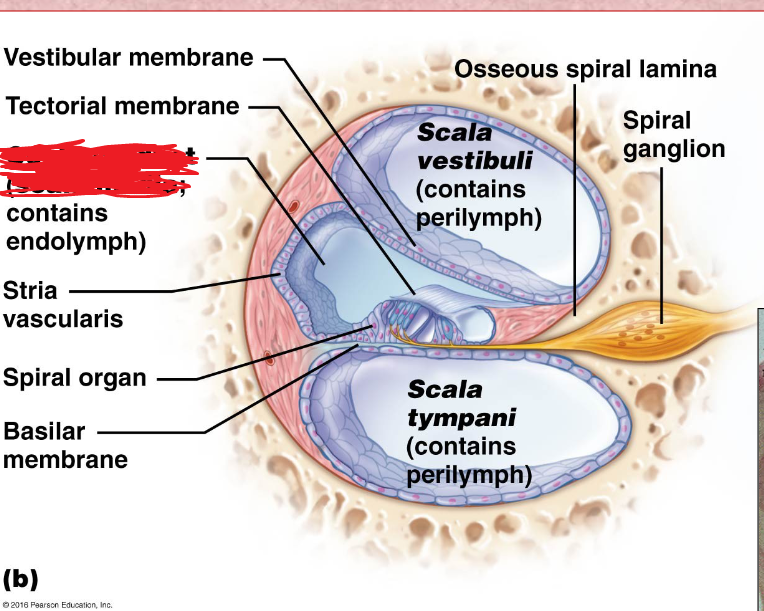
Scala Vestibuli
the upper bony passage of the cochlea.
Basilar Membrane
a membrane in the cochlea that bears the organ of Corti.
Spiral organ
Tectorial membrane
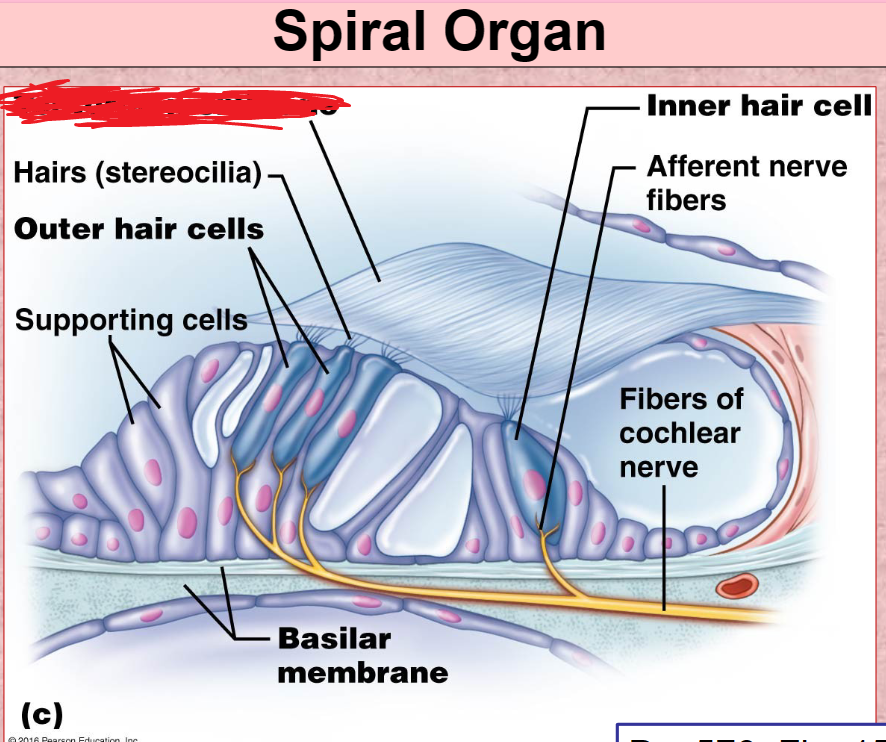
Hair Cells
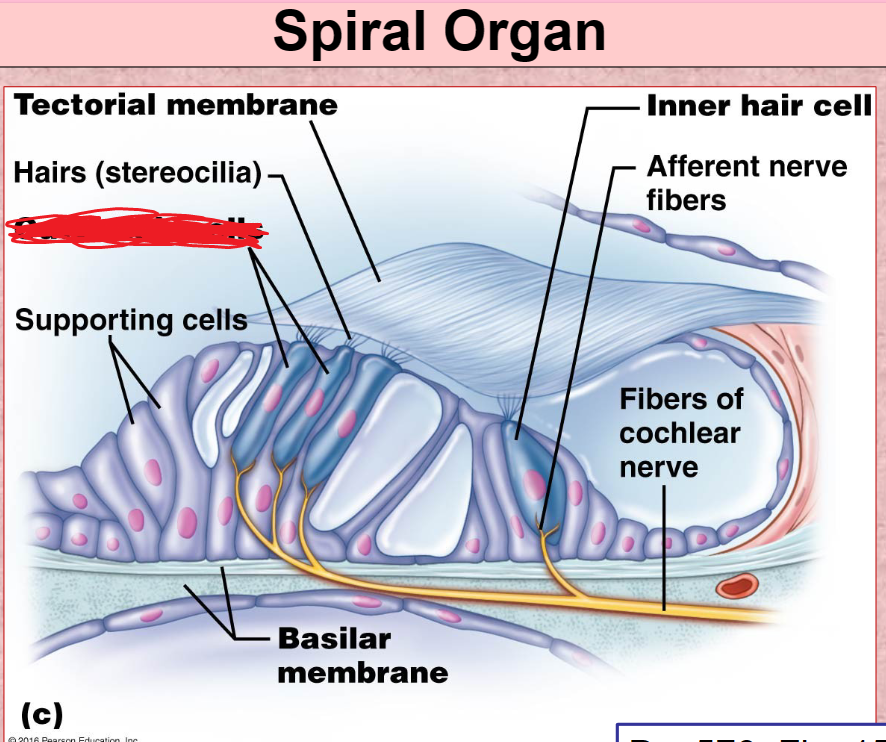
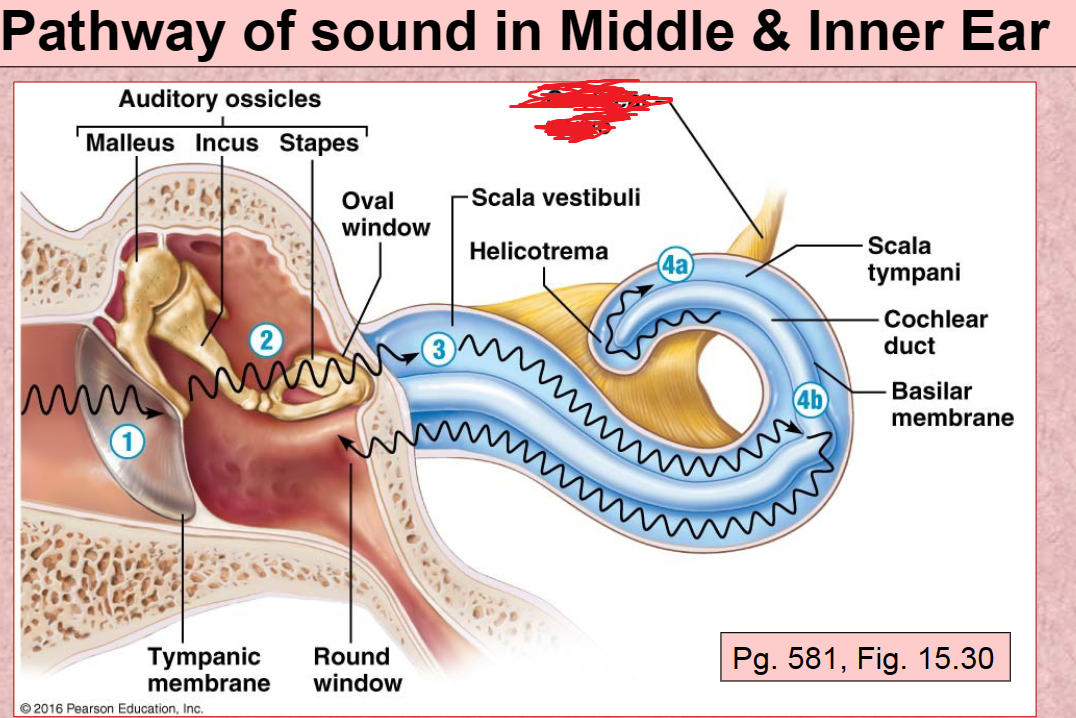
Cochlear nerve
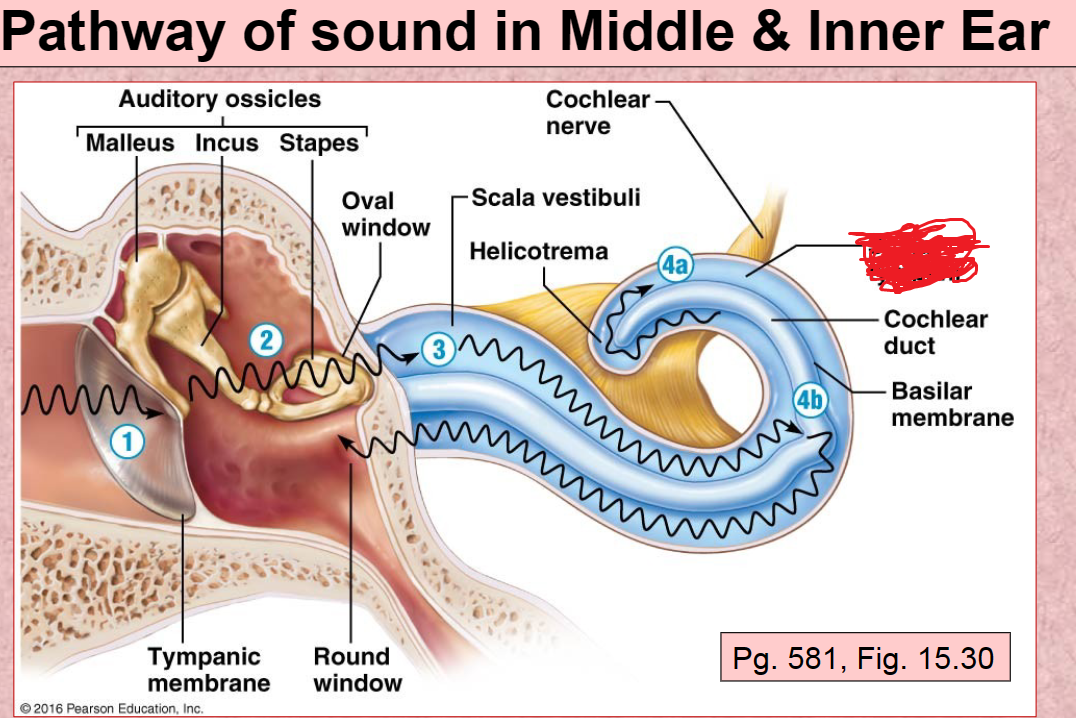
Scala Tympani
Round Window
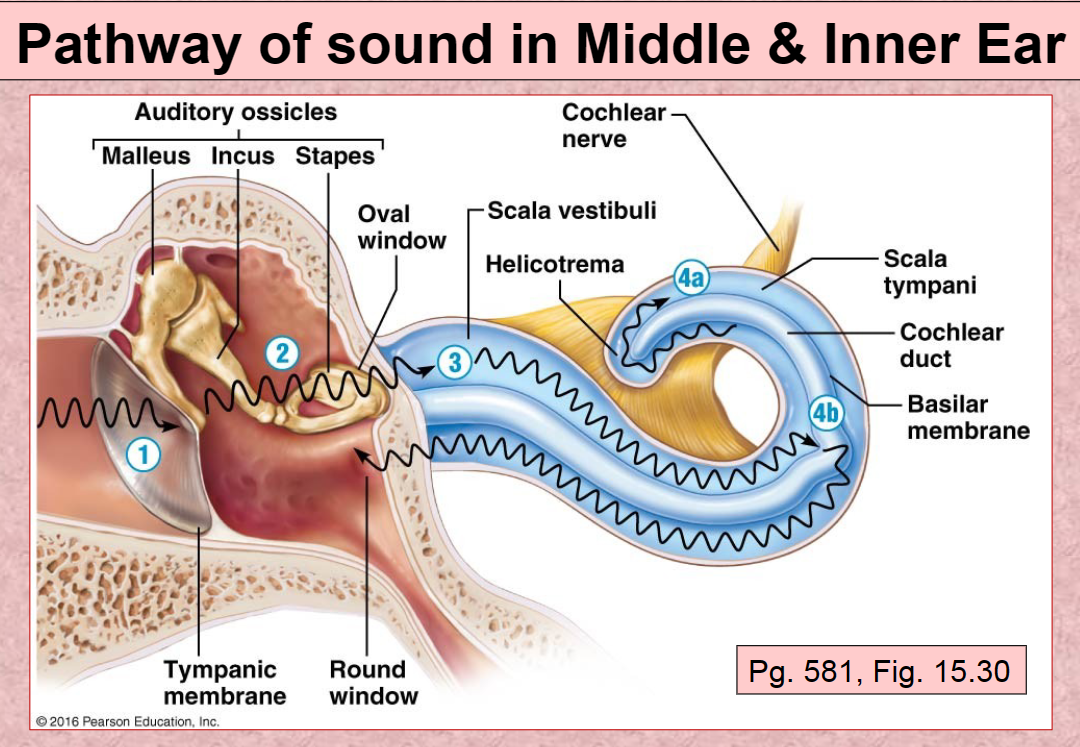
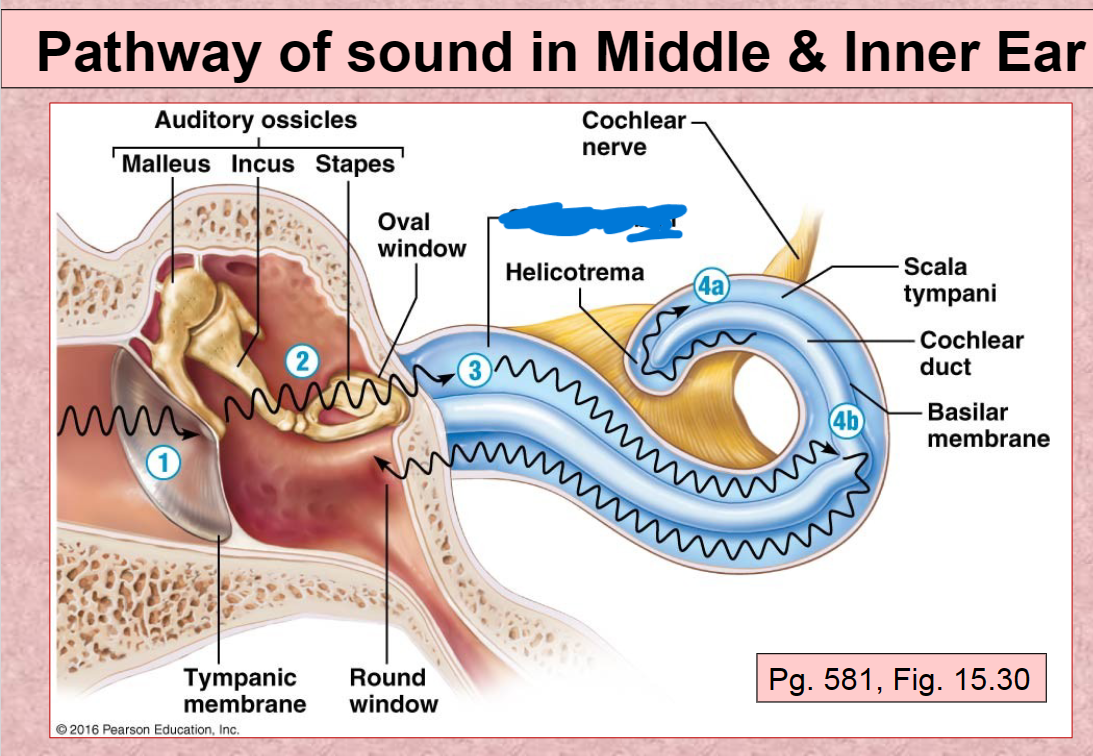
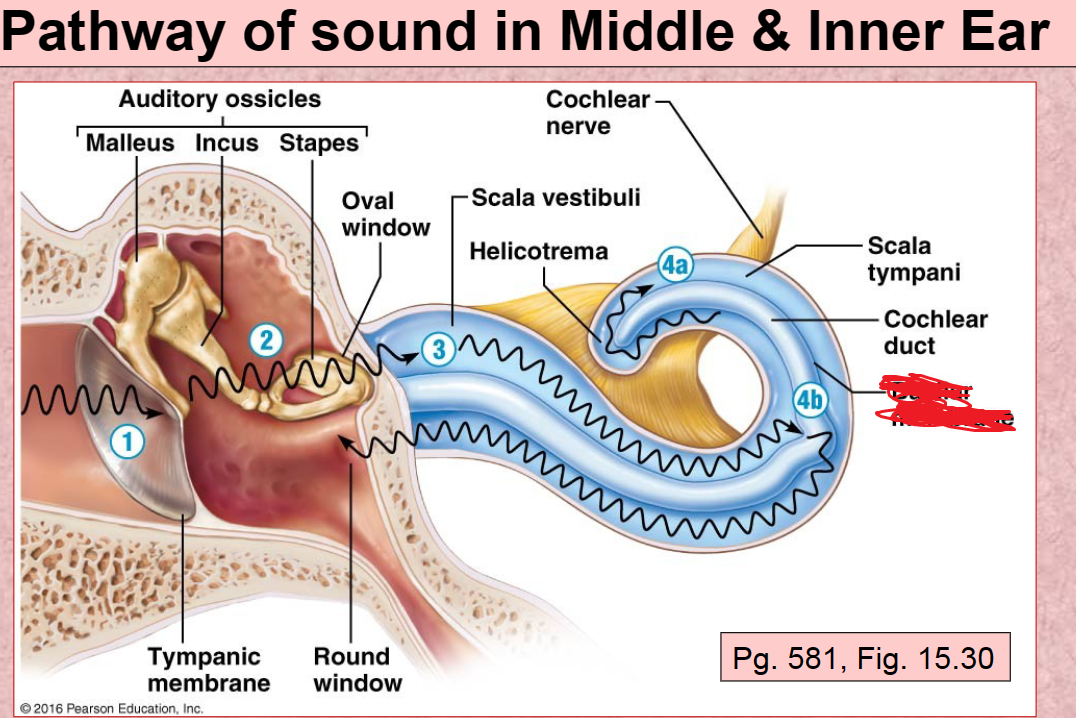
1st Pathway of Sound vibration in ear
Tympanic membrane
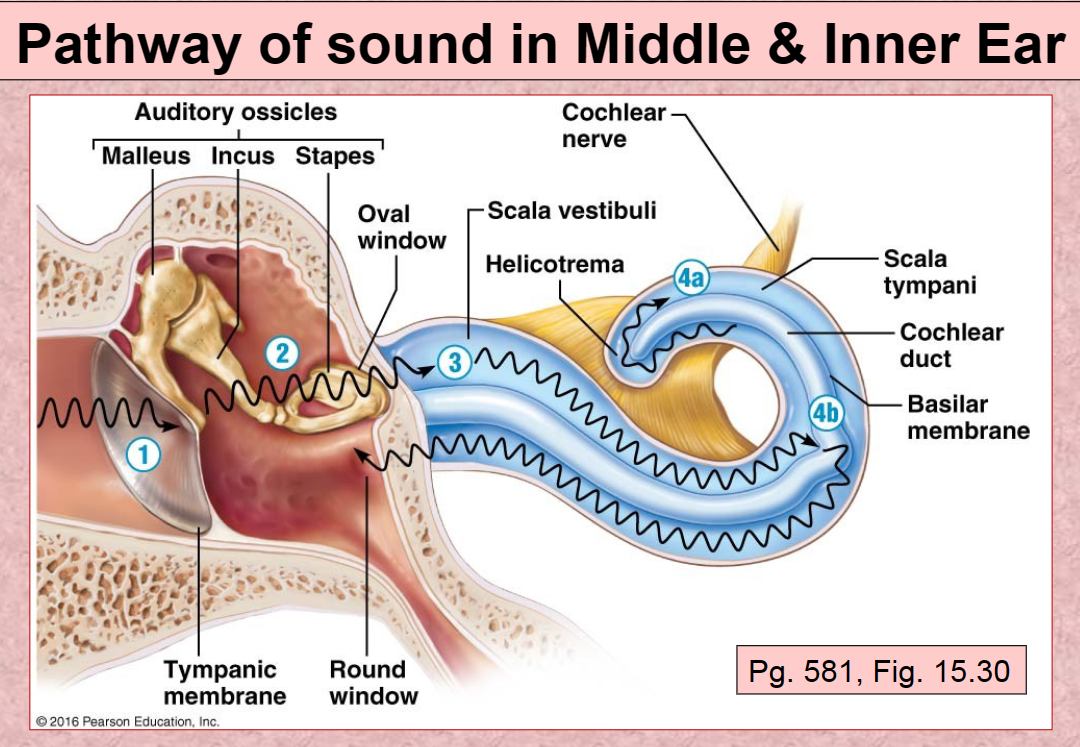
2nd Pathway of sound in ear
Auditory ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes)
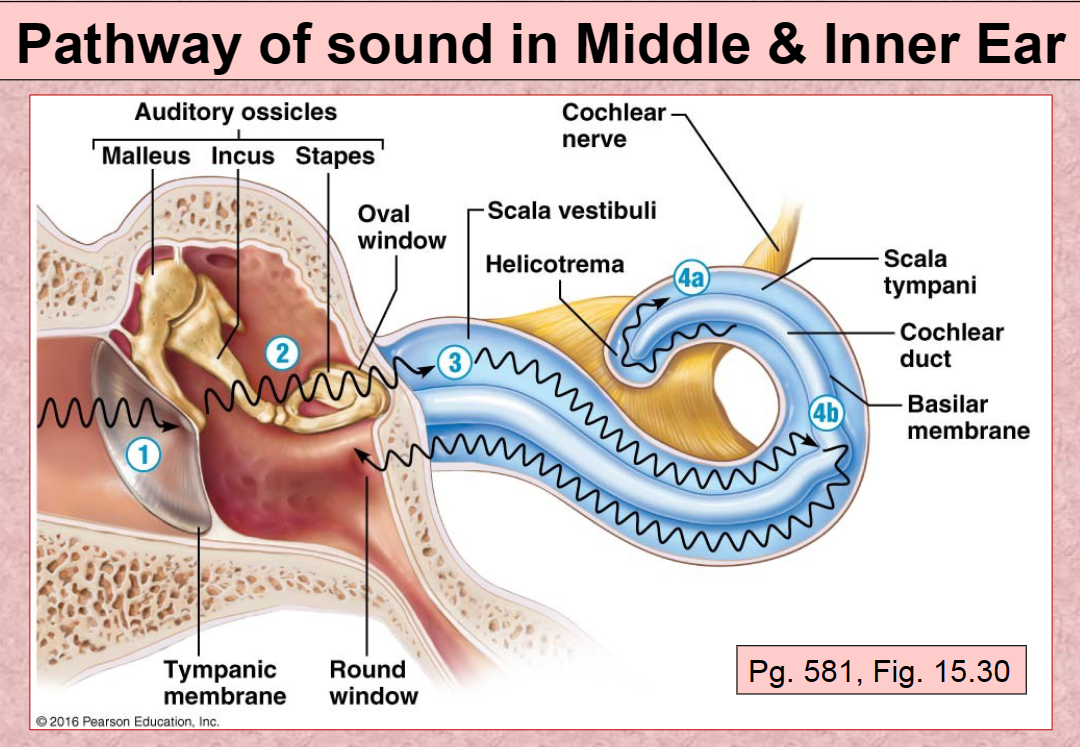
3rd Pathway of sound in ear
Scala Vestibuli
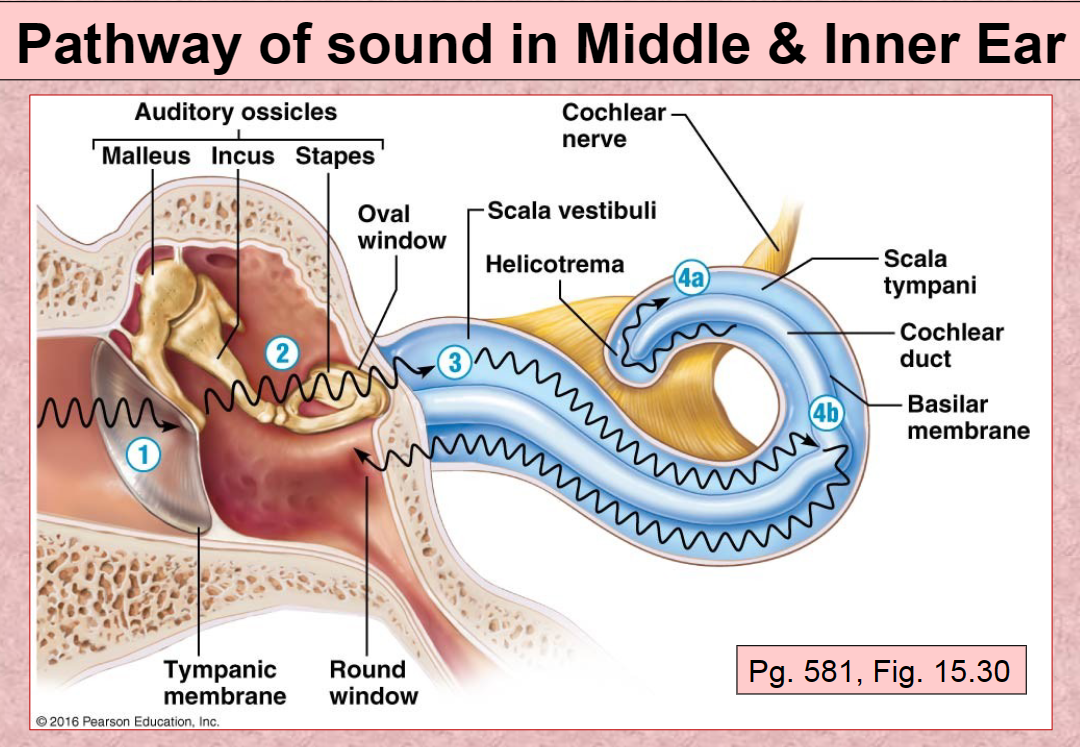
4th (A) Pathway of sound in ear
Scala Tympani
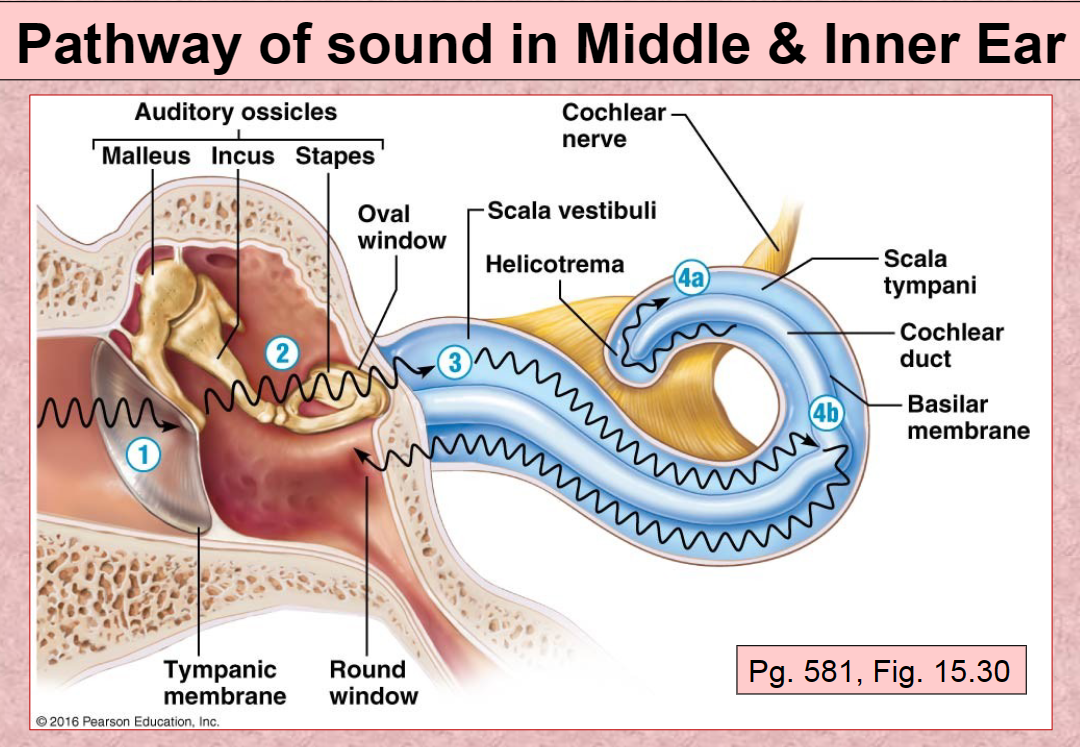
4th (B) Pathway of sound in ear
Basilar membrane