Veterinary Parasitology Chapter 9 - Acanthocephalans
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study material for Chapter 9 of Diagnostic Parasitology for Veterinary Technicians. For class BIO225 at MWCC.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Acanthocephalans are also called what?
Thorny-headed worms
Acanthocephalans mostly affect which species?
Fish and aquatic birds
True or false: Acanthocephalans are endoparasites
True
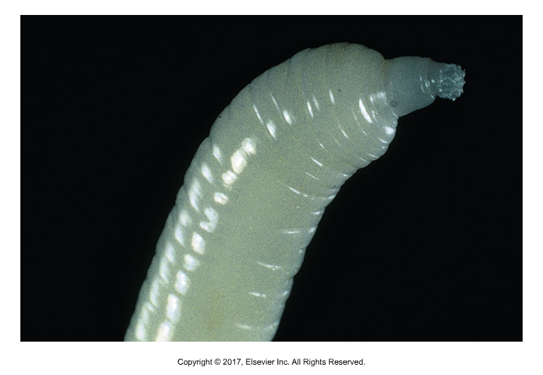
What shape are Acanthocephalans?
Long and cylindrical, tapered on both ends
True or false: Acanthocephalans are dioecious
True
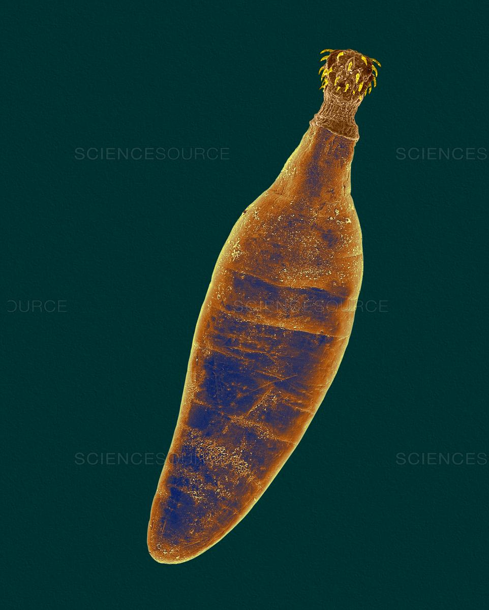
Acanthocephalans have a retractable proboscis on anterior end covered in what? And why?
Spines, for attachment
What do Acanthocephalans use to absorb their nutrients through?
Tegument (skin)
How many eggs can a female worm make per day?
250,000
Ancanthocephalans life cycle
Eggs released in host feces
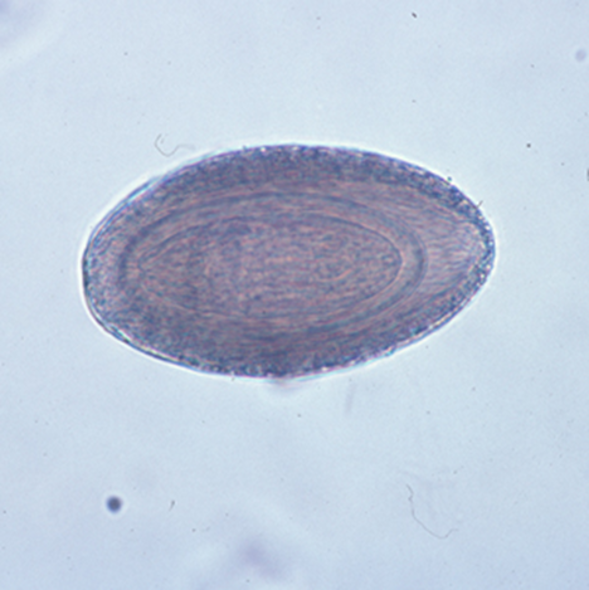
Spindle shaped egg with 3 layers
Egg contains larva acanthor
Intermediate host: arthropod
Acanthor hatches into ancanthella then cystoacanth with inverted proboscis
Definitive host ingests arthropod, adult pushes out proboscis and attaches to intestine wall
Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceus
Definitive host: Pig
Intermediate host: Dung beetle
Not zoonotic
Can perforate the intestine leading to peritonitis and even death.
Males average 10cm, Females 35cm but can grow as long as 70cm
Eggs are 3 layered, 2nd layer is brown and pitted, found on fecal float
Can look like Ascaris suum at necropsy, but is attached to wall, not free living

Oncicola canis
Definitive host: Dog
Adult in small intestine
Intermediate host: Dung beetle
Cause of infection: Ingestion of dung beetle
Tiny, only 14mm long
Can also cause perforation
Egg found in fecal float