7.Coordination, Response & Homeostasis
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
What is the nervous system?
A system that coordinates and regulates body responses to stimuli
Name the two parts of the human nervous system
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
What does the central nervous system consist of?
Brain and spinal cord
What does the peripheral nervous system consist of?
All nerves outside the CNS
What is a nerve impulse?
An electrical signal that travels along neurones
What is a neurone?
A specialised nerve cell
What is a nerve?
A bundle of neurones
Name the three types of neurone
Sensory relay motor
What is the function of sensory neurones?
Carry impulses from receptors to the CNS
What is the function of relay neurones?
Connect sensory and motor neurones in the CNS
What is the function of motor neurones?
Carry impulses from the CNS to effectors
What is an effector?
A muscle or gland that produces a response
What is an axon?
A long fibre that carries nerve impulses
Why are neurones long?
To reduce time taken for impulses to travel
What is the role of myelin sheath?
Insulates the axon and speeds up impulse transmission
What are nodes of Ranvier?
Gaps in the myelin sheath where impulses jump
What are dendrites?
Extensions that receive impulses from other neurones
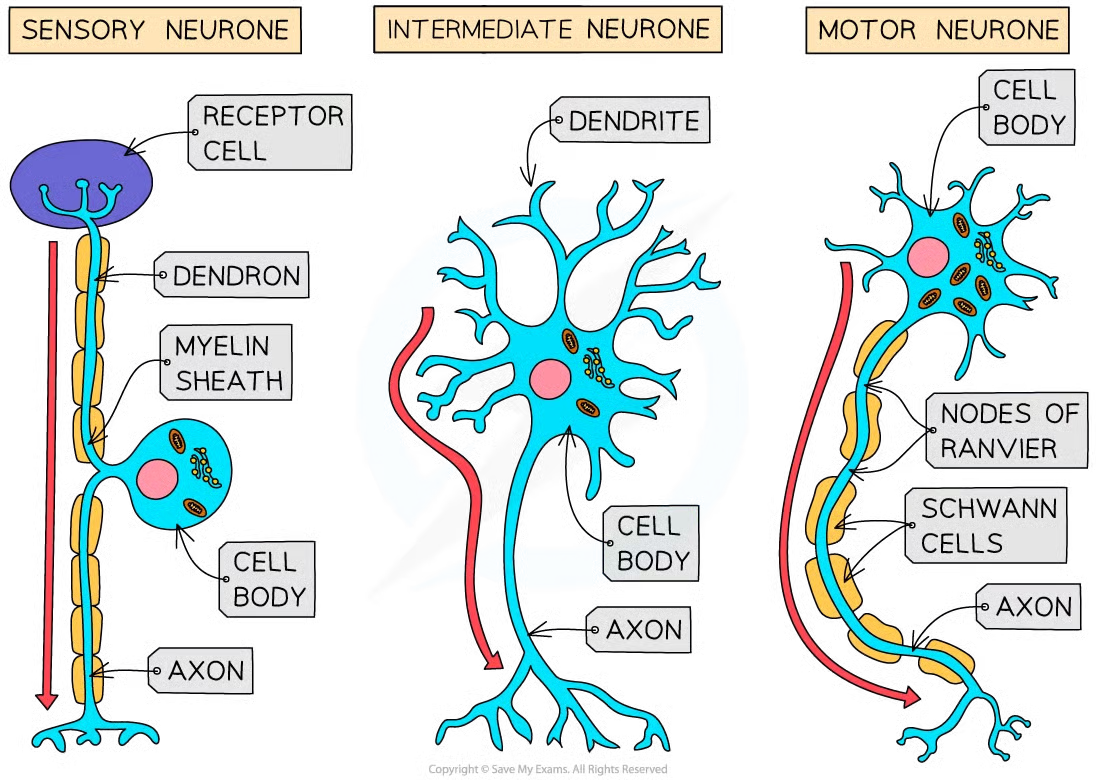
Describe a sensory neurone
Long with cell body in the middle
Describe a relay neurone
Short with many dendrites
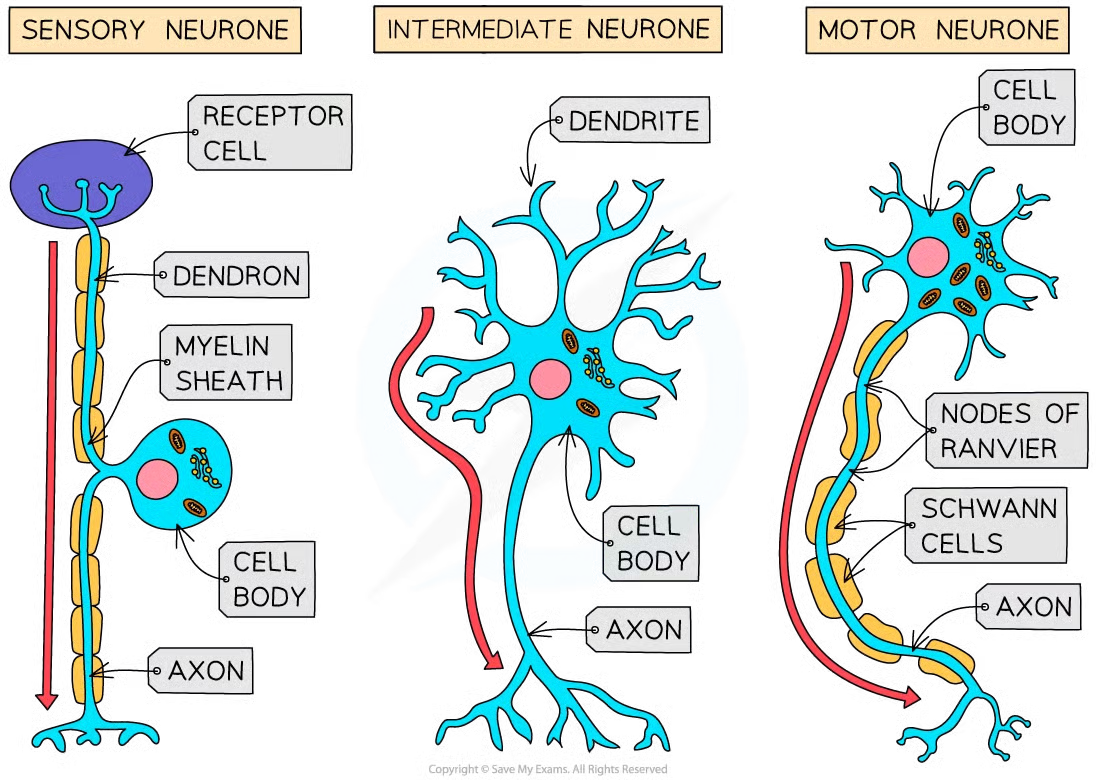
Describe a motor neurone
Long with large cell body at one end
What is a voluntary response?
A conscious response controlled by the brain
Give an example of a voluntary response
Picking up a cup
What is a reflex response?
An automatic rapid response not involving the brain
Why are reflexes fast?
They bypass the brain
State one advantage of reflex responses
Minimises damage to the body
Define a stimulus
A change in the environment
Define a response
An action produced by an effector
What is a reflex arc?
The pathway followed by a nerve impulse in a reflex
List the stages of a reflex arc
Receptor sensory neurone relay neurone motor neurone effector
Where is the coordinator in a reflex?
Spinal cord
What is a receptor?
A group of specialised cells detecting stimuli
What happens at the effector in a reflex?
A muscle contracts or gland secretes
What is a synapse?
A junction between two neurones
Why do neurones not touch?
To control direction of impulses
What is a neurotransmitter?
A chemical messenger released at a synapse
How is an impulse transmitted across a synapse?
By diffusion of neurotransmitters
Why do impulses travel in one direction across synapses?
Neurotransmitters are released from presynaptic neurone only
What happens to neurotransmitters after transmission?
They are destroyed
Why do drugs affect synapses?
Because synapses use chemicals
What are receptors?
Cells that detect stimuli
What do sense organs contain?
Groups of receptors
What happens when a receptor is stimulated?
An electrical impulse is generated
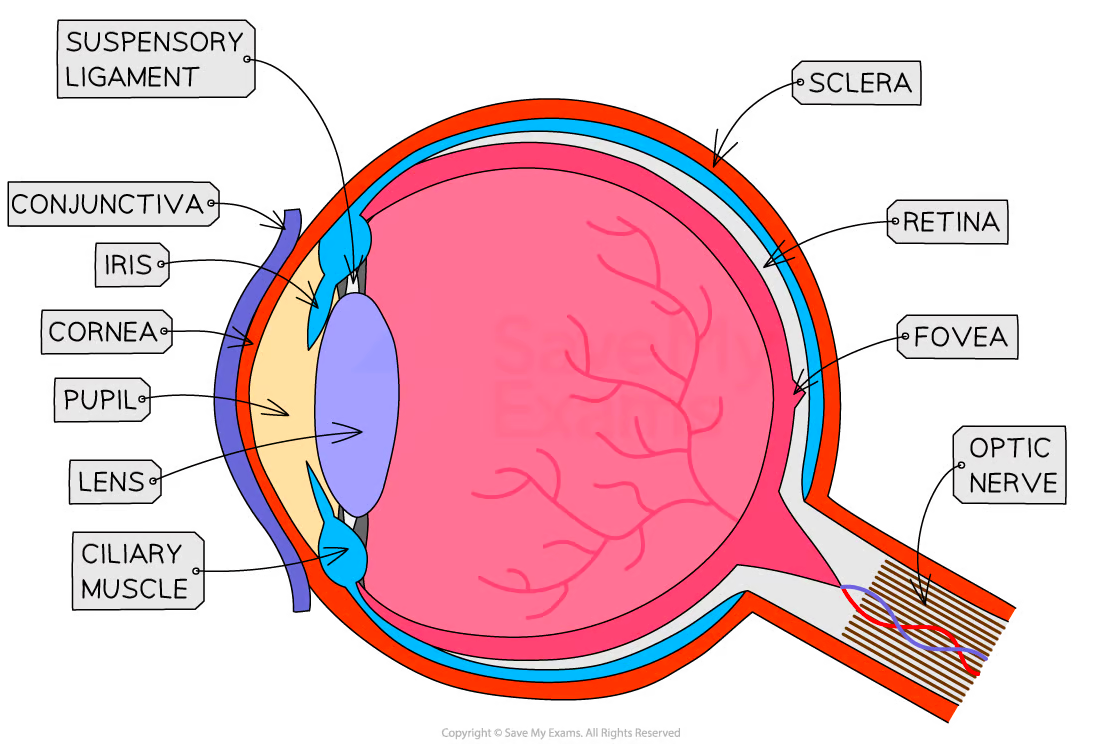
Name the main parts of the eye
Cornea iris lens retina optic nerve
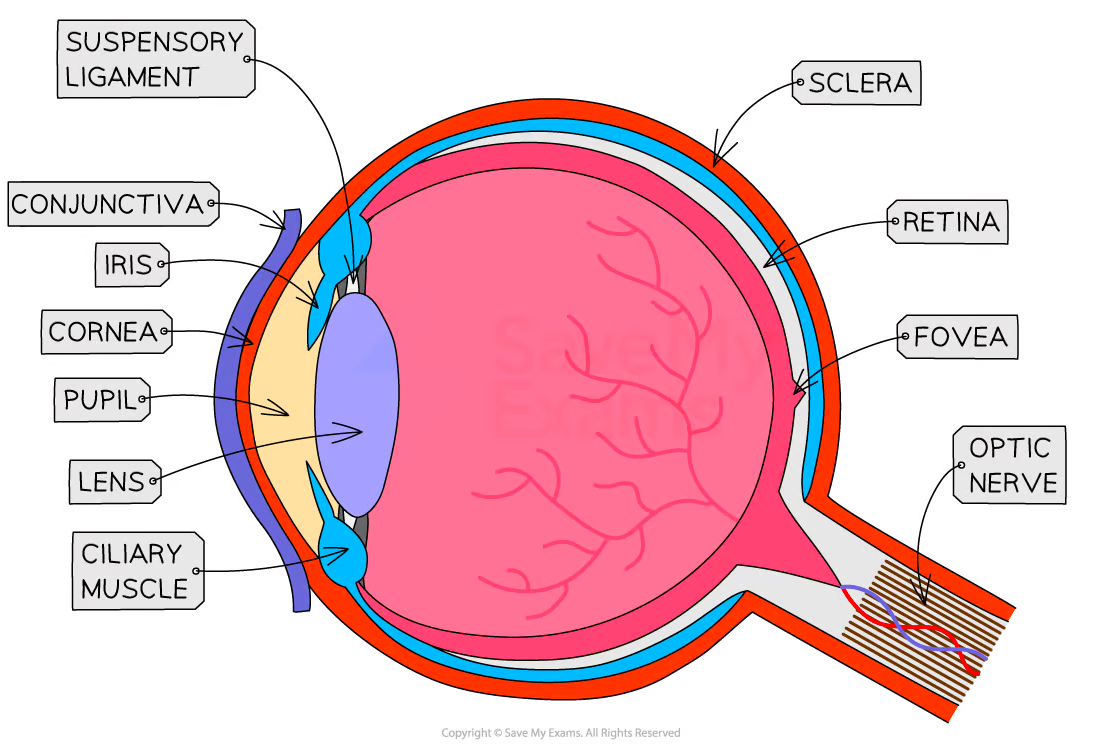
What is the function of the cornea?
Refracts light
What is the function of the iris?
Controls pupil size
What is the function of the lens?
Focuses light onto the retina
What is the function of the retina?
Contains light receptors
What is the function of the optic nerve?
Carries impulses to the brain
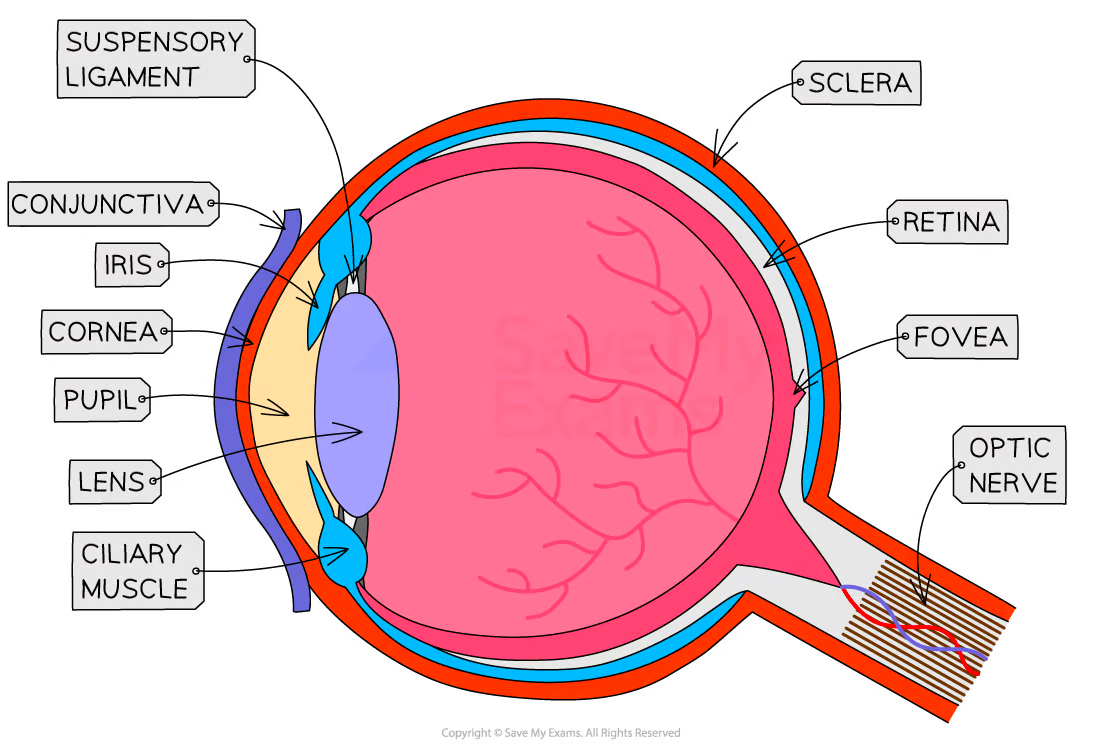
What is the fovea?
Area of retina with many cones
What is the pupil reflex?
Control of pupil size in response to light
What happens to the pupil in dim light?
It dilates
What happens to the pupil in bright light?
It constricts
What muscles control the pupil?
Circular and radial muscles
What does antagonistic mean?
Muscles working in opposition
What happens to iris muscles in dim light?
Radial contract circular relax
What happens to iris muscles in bright light?
Circular muscles contract radial muscles relax in bright light
Define accommodation
Adjustment of lens shape to focus light
What happens to the lens for near objects?
Becomes thicker
What happens to the lens for distant objects?
Becomes thinner
What do ciliary muscles do when viewing near objects?
Contract
What happens to suspensory ligaments when viewing near objects?
Loosen
What are rod cells?
Receptors sensitive to low light
What are cone cells?
Receptors sensitive to colour
Where are cone cells concentrated?
Fovea
Where are rod cells found?
Throughout the retina except blind spot
What is a hormone?
A chemical messenger transported in the blood
What system produces hormones?
Endocrine system
Why do endocrine glands have good blood supply?
To transport hormones quickly
What is a target organ?
Organ affected by a hormone
How does the liver affect hormones?
Breaks down excess hormones
State one difference between nervous and hormonal control
Nervous is fast hormonal is slow
What is homeostasis?
Maintenance of a constant internal environment
Give one example of a controlled condition
Body temperature
What is negative feedback?
A system that returns conditions to a set point
What happens when blood glucose rises?
Insulin is released
What does insulin do?
Converts glucose to glycogen
What happens when blood glucose falls?
Glucagon is released
What does glucagon do?
Converts glycogen to glucose
Where are insulin and glucagon produced?
Pancreas
What is glycogen?
Stored form of glucose
What is adrenaline?
Fight or flight hormone
Where is adrenaline produced?
Adrenal glands
Give one effect of adrenaline
Increased heart rate
Why does adrenaline increase blood glucose?
To provide energy for muscles
Define Type 1 diabetes
Inability to produce insulin
How is Type 1 diabetes treated?
Insulin injections
State one symptom of diabetes
Extreme thirst
Why must diabetics monitor blood glucose?
To control insulin dosage
What is temperature regulation?
Control of body temperature
What is the normal human body temperature?
37 degrees Celsius
Why is temperature regulation important?
Enzymes denature at high temperatures
Name three skin structures involved in temperature control
Sweat glands capillaries hairs
What happens when the body is too hot?
Sweating vasodilation
What happens when the body is too cold?
Shivering vasoconstriction
Define vasodilation
Widening of blood vessels
Define vasoconstriction
Narrowing of blood vessels
What is the effect of vasodilation?
Increased heat loss
What is the effect of vasoconstriction?
Reduced heat loss
What is a tropism?
A growth response to a stimulus
What is phototropism?
Response to light