Knee and Femur Image Critique and Pathology
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Trauma and Non Trauma AP Knee
•Evidence of proper collimation and the presence of a side marker placed clear of the anatomy of interest
•Knee fully extended if patient’s condition permits
•Entire knee without rotation
•Femoral condyles symmetric and tibia intercondylar eminence centered
•Slight superimposition of the fibular head if the tibia is normal
•Patella completely superimposed on the femur
•Open femorotibial joint space, with interspaces of equal width on both sides if the knee is normal
•Bony trabecular detail and surrounding soft tissues
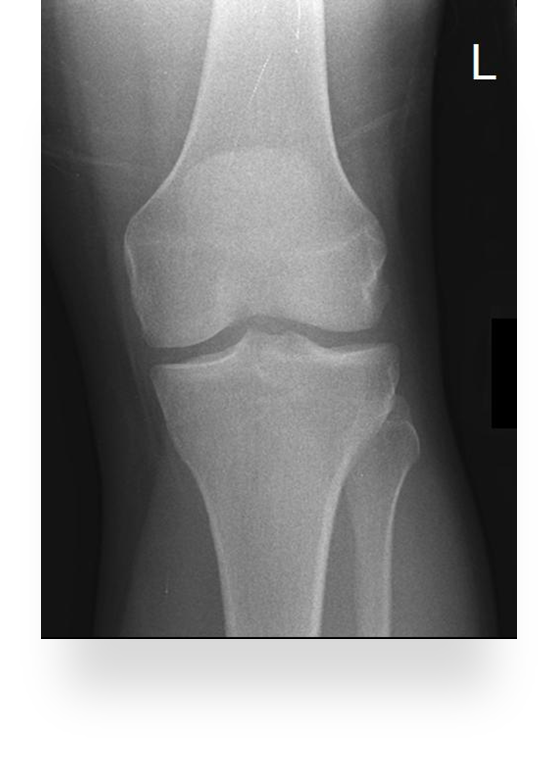
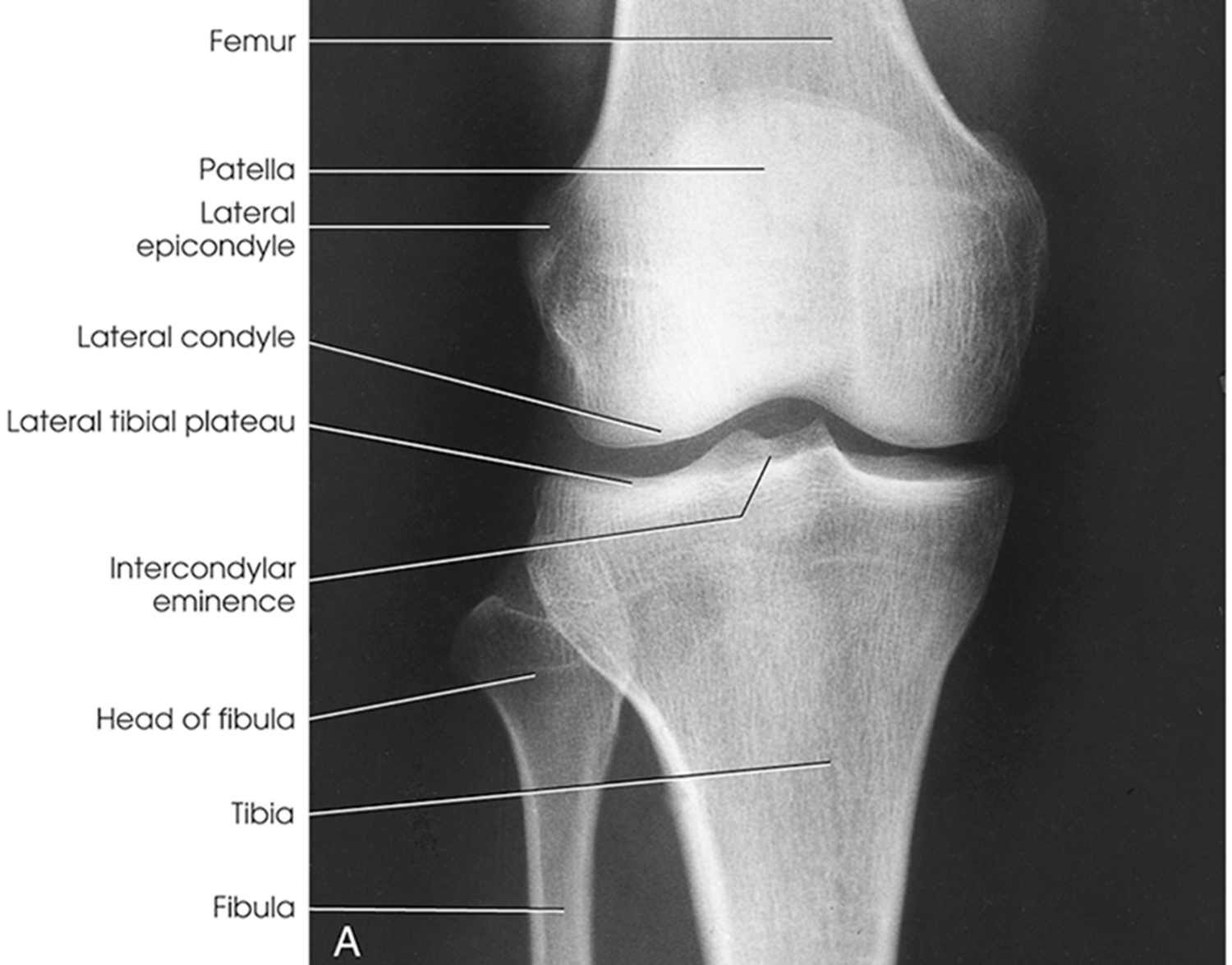
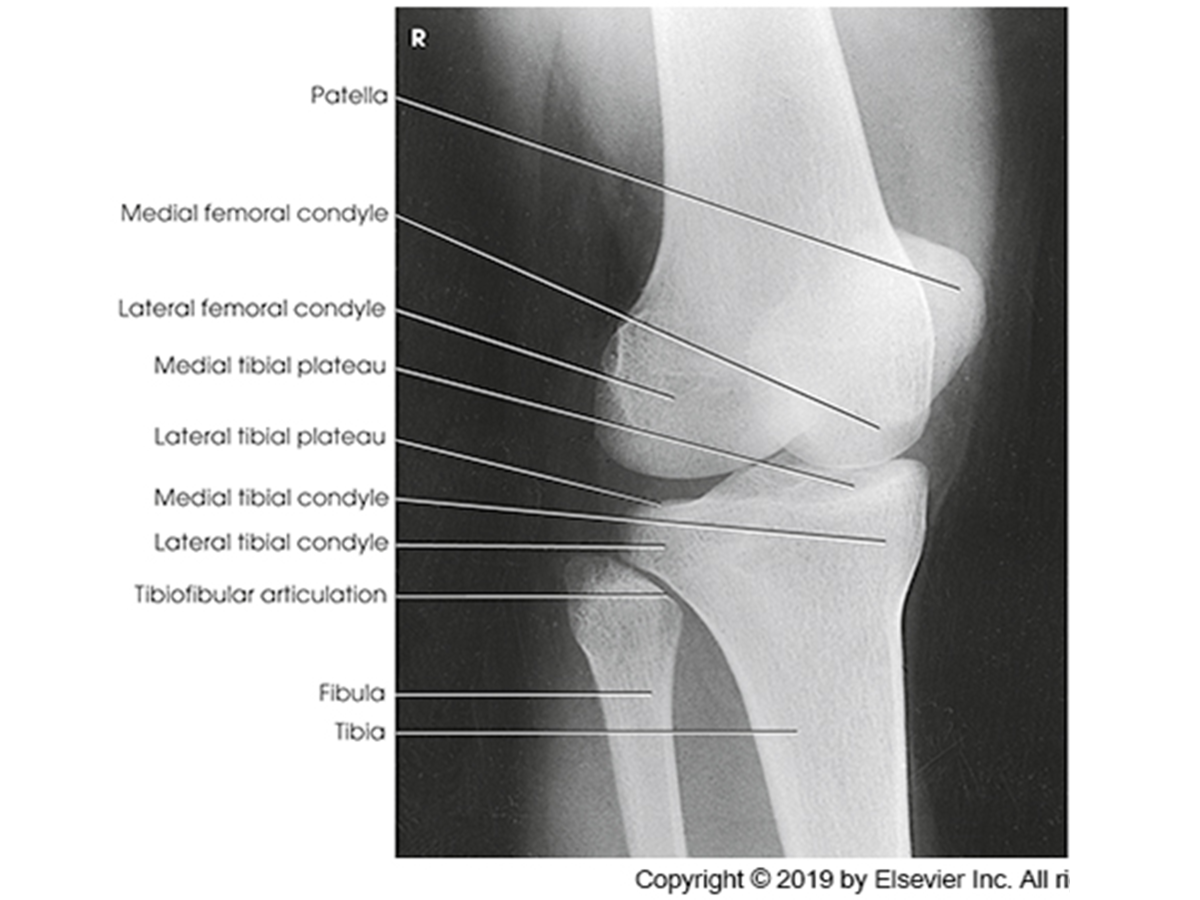
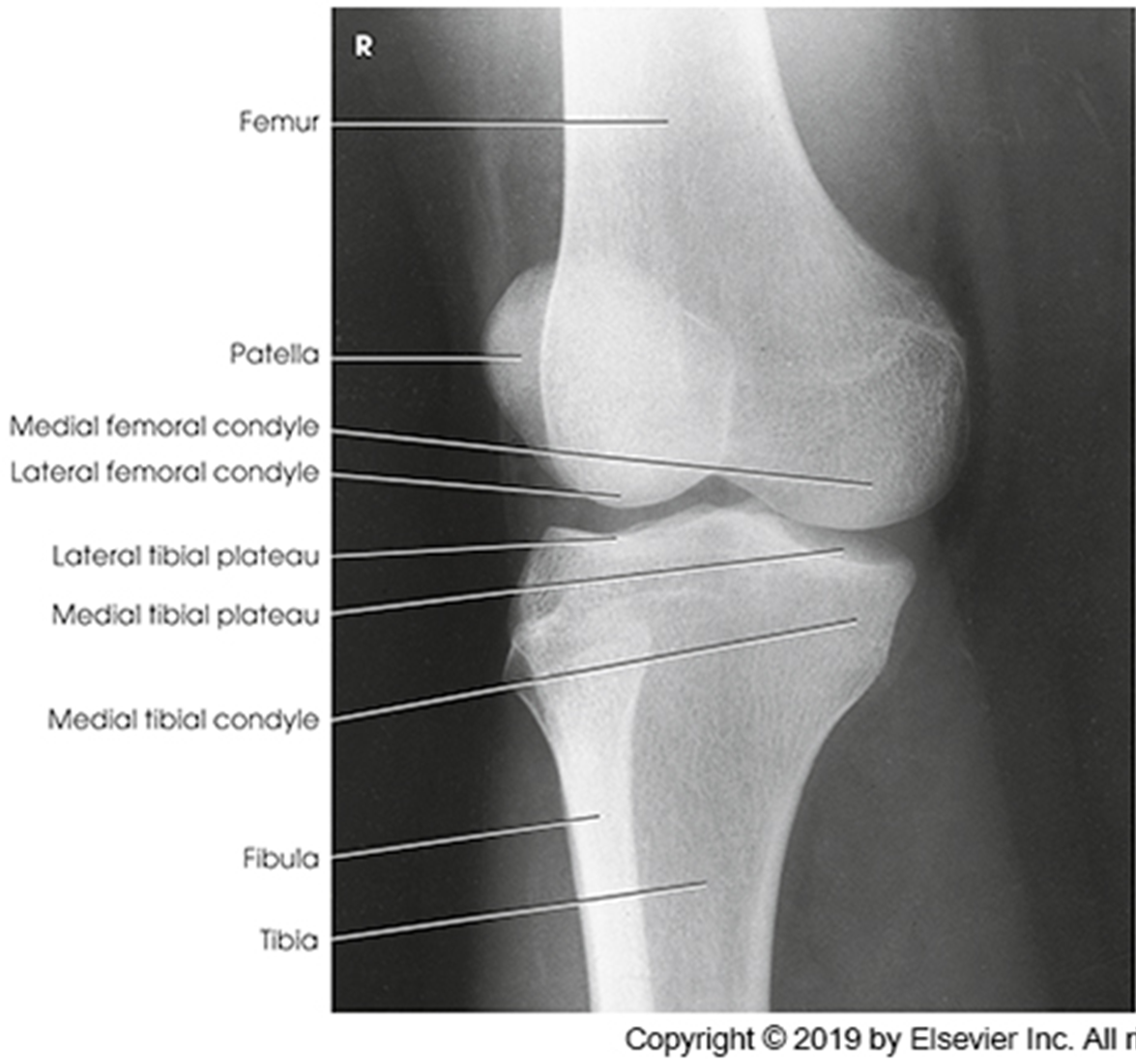
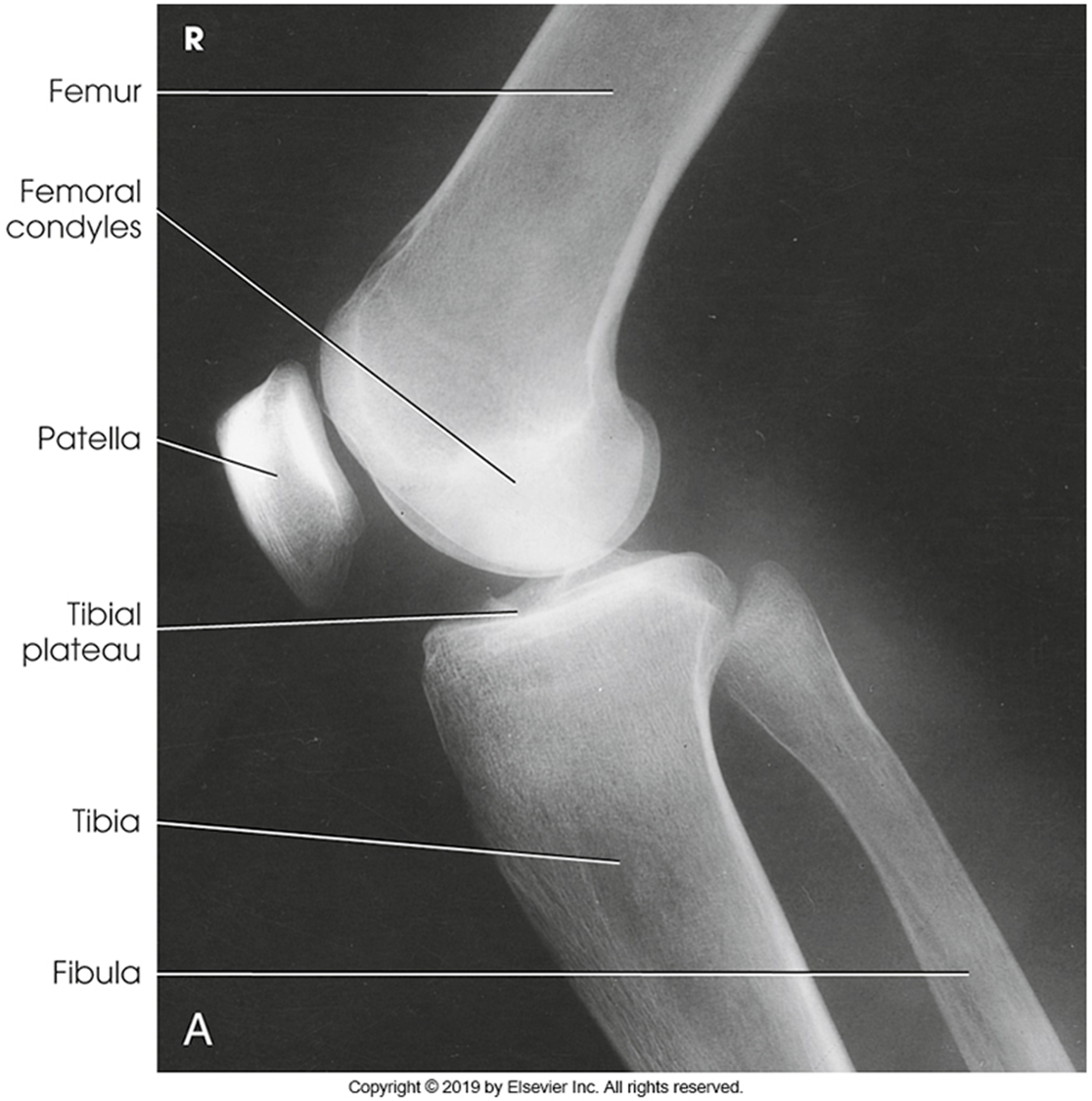
Anatomy of the knee
Lateral Rotation, the fibular head is under the tibia, if patella is towards lateral side usually means it is laterally rotated.
Joint space is not open enough
The width of the joint space is not equal
REPEAT FOR LATERAL ROTATION
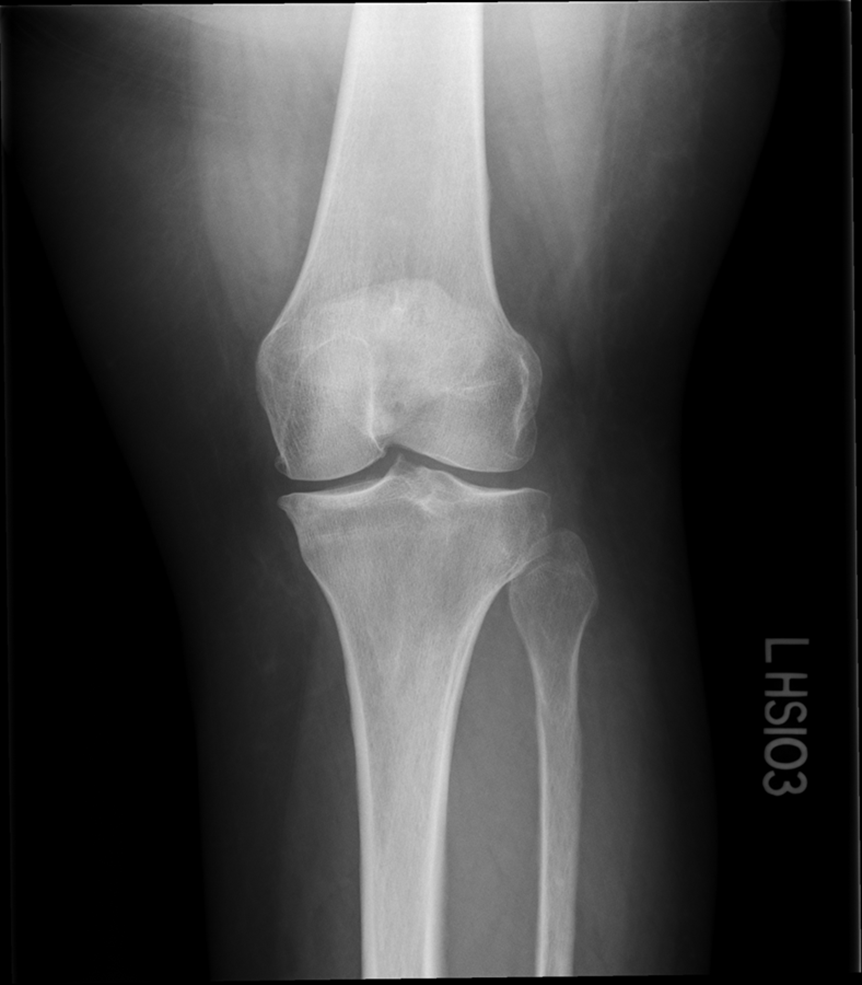
Not enough superimposition of the fibular head
Patella is in the center! good! equal distance of joint space/platoes which is good
ACCEPTABLE BECAUSE EVERYTHING ELSE IS GOOD! PATIENT COULD HAVE A MORE SEPARATED FIBULAR HEAD! THEIR ANATOMY IS DIFFERENT. CENTERING IS GOOD
Trauma Medial Oblique
•Evidence of proper collimation and the presence of a side marker placed clear of the anatomy of interest
•Tibia and fibula separated at their proximal articulation
•Posterior tibia
•Lateral condyles of the femur and tibia
•Both tibial plateaus
•Margin of the patella projecting slightly beyond the medial side of the femoral condyle
•Open knee joint
•Bony trabecular detail and surrounding soft tissues
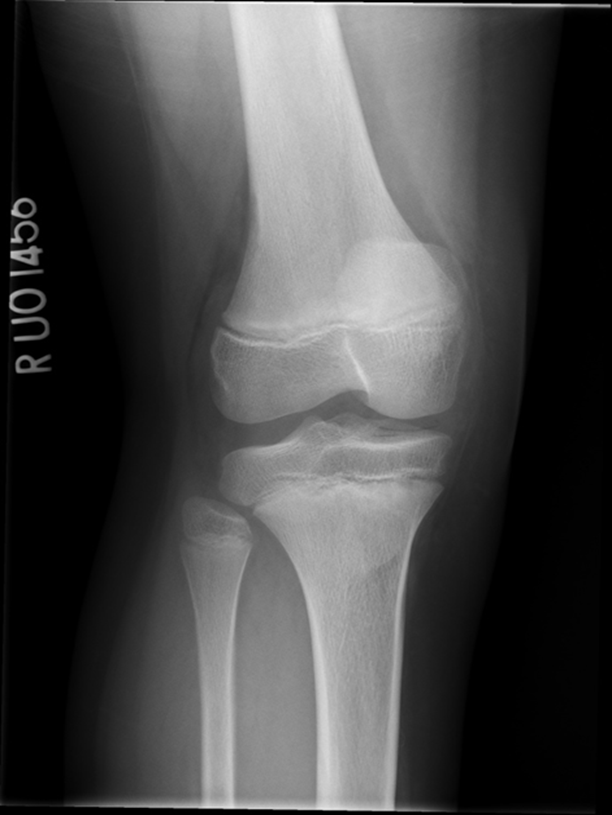
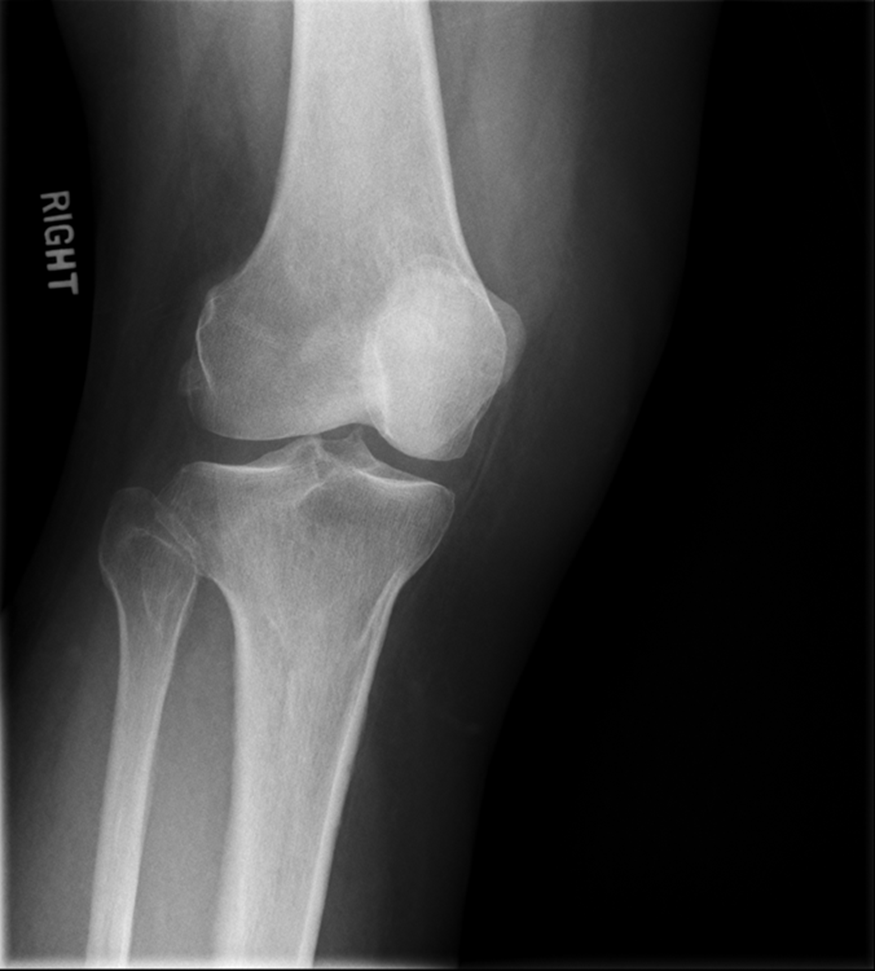
Fibular head is overlapped/under-rotated
patella looks good
central ray- towards medial aspect
center a little more and near knee joint
INCREASE MEDIAL ROTATION
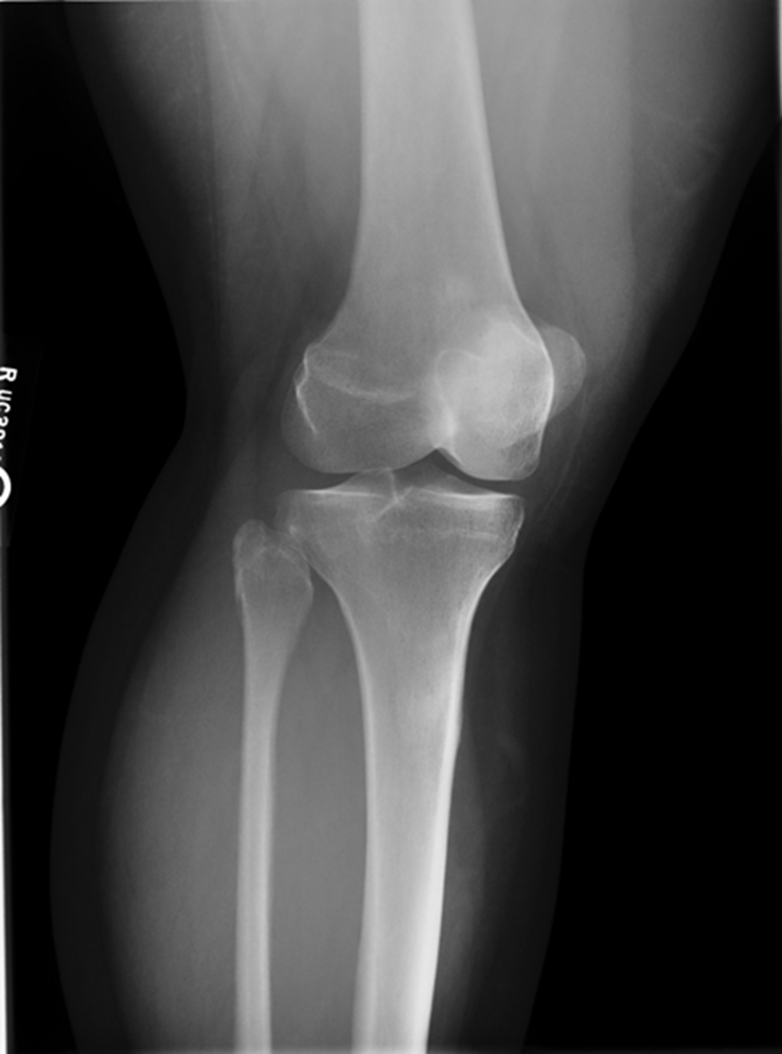
Minimal touching of fibular head
Patella coming off medial aspect
joint space is good
GOOD IMAGE
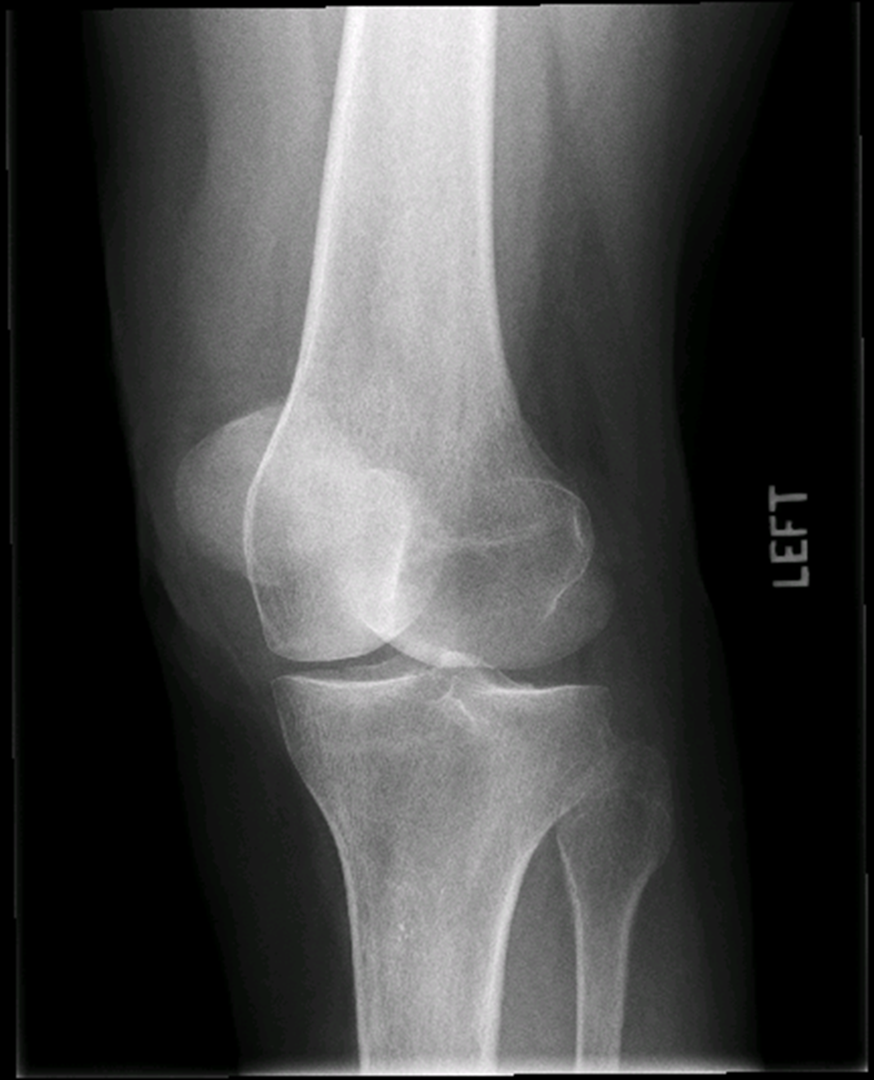
Rotated
Patella is half off femur medially
medial condyle is overlapped
OVER ROTATION
Fibular head joint space is not oepn it is covering it.
Trauma Lateral Oblique
•Evidence of proper collimation and the presence of a side marker placed clear of the anatomy of interest
•Medial femoral and tibial condyles
•Tibial plateaus
•Fibula superimposed over the lateral half of the tibia
•Margin of the patella projected slightly beyond the edge of the lateral femoral condyle
•Open knee joint
•Bony trabecular detail and surrounding soft tissues
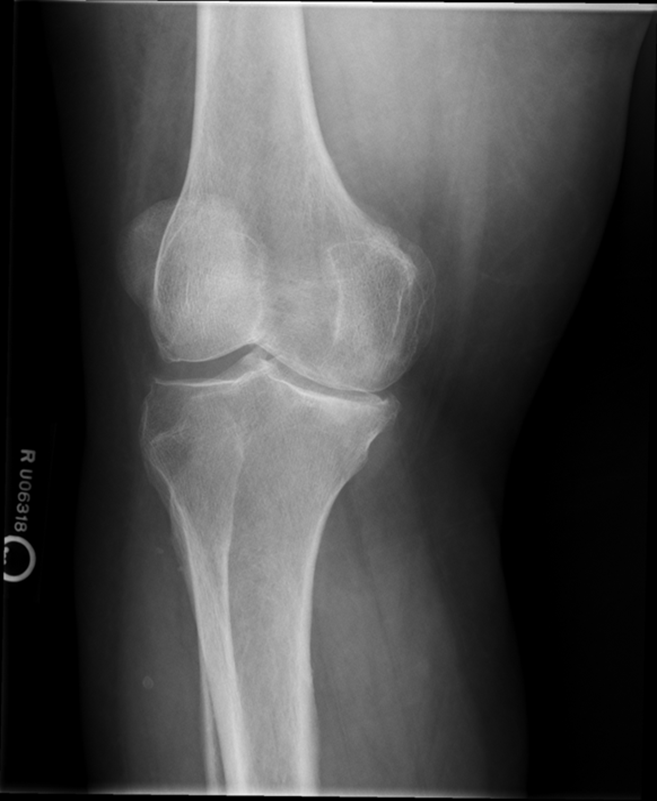
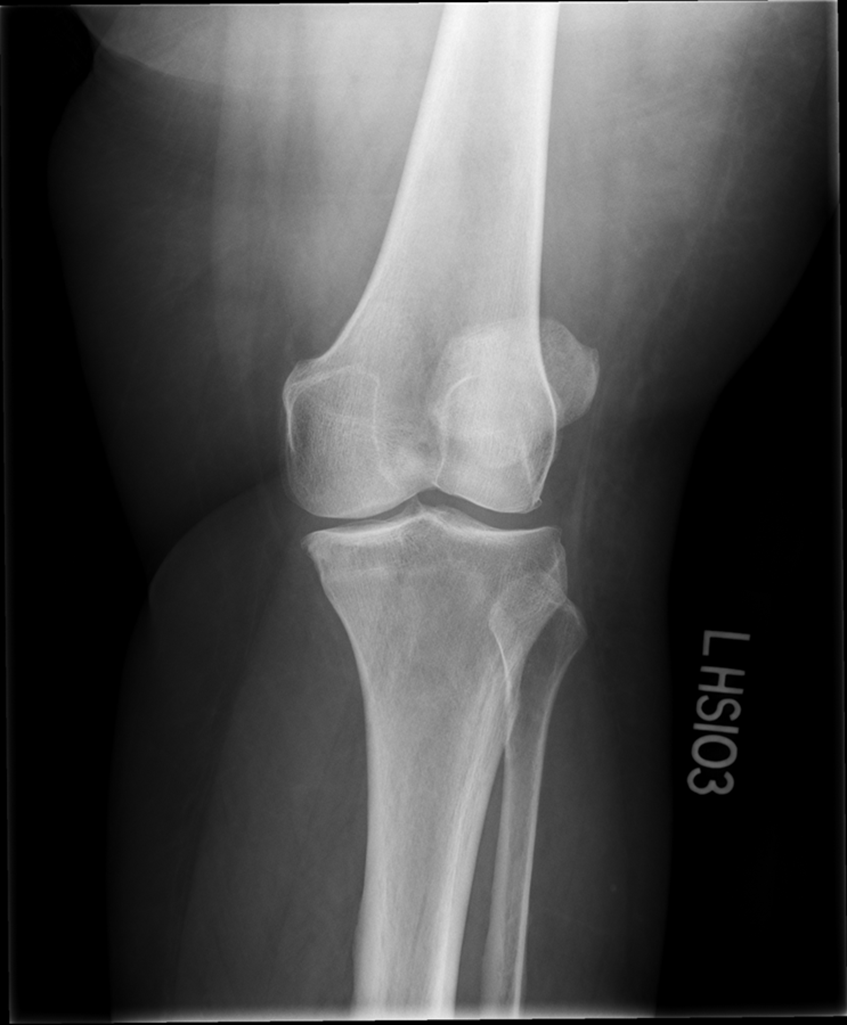
Lateral Oblique
Under rotation/ closer to AP
Patella is projected off
Increase laterality/ 45 %REPEAT
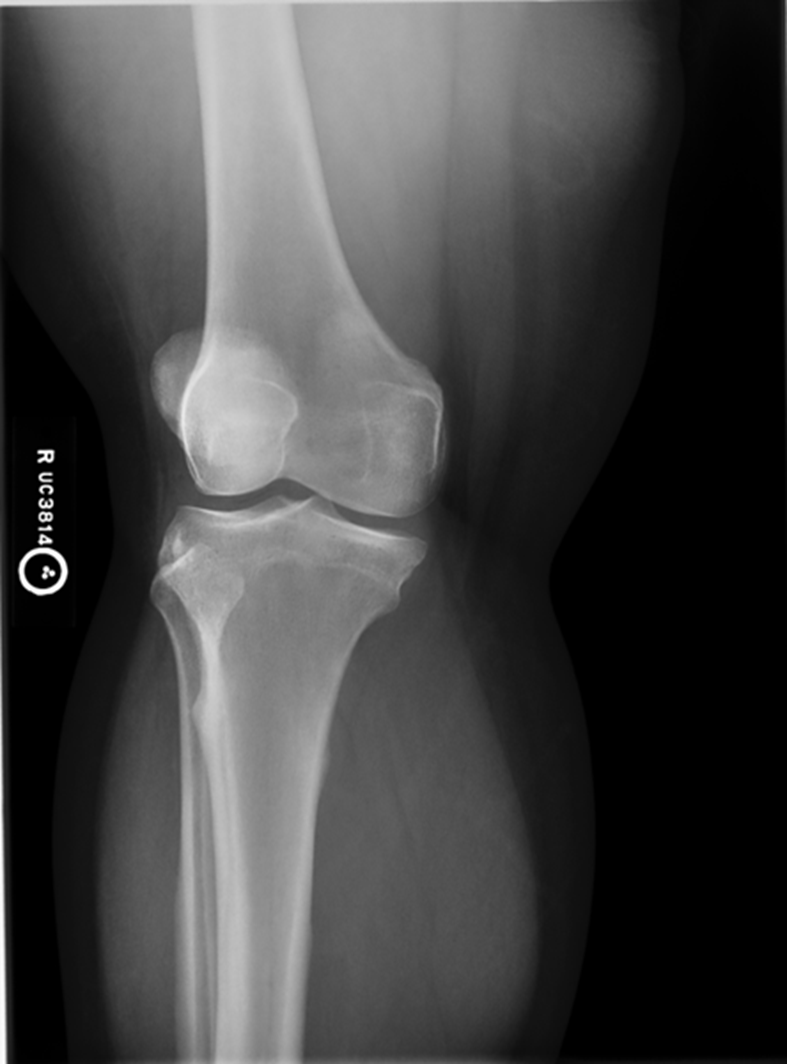
The image is good! Most is superimporsed its good, slight under rotation
Trauma and Non-Trauma Lateral Knee (Mediolateral)
•Evidence of proper collimation and the presence of a side marker placed clear of the anatomy of interest
•Knee flexed 20 to 30 degrees in true lateral position as demonstrated by femoral condyles superimposed (locate the more magnified medial condyle)
•Anterior surface of medial condyle closer to patella results from over-rotation toward the image receptor (IR).
•Anterior surface of medial condyle farther from patella results from under- rotation away from the image receptor (IR).
•Inferior surface of medial condyle caudal to lateral condyle results from insufficient cephalad central ray (CR) angle.
•Inferior surface of lateral condyle caudal to medial condyle results from too far cephalad CR angle.
•Fibular head and tibia slightly superimposed (over rotation causes less superimposition, and under rotation causes more superimposition)
•Patella in a lateral profile
•Open patellofemoral joint space
•Open joint space between femoral condyles and tibia
•Bony trabecular detail and surrounding soft tissues
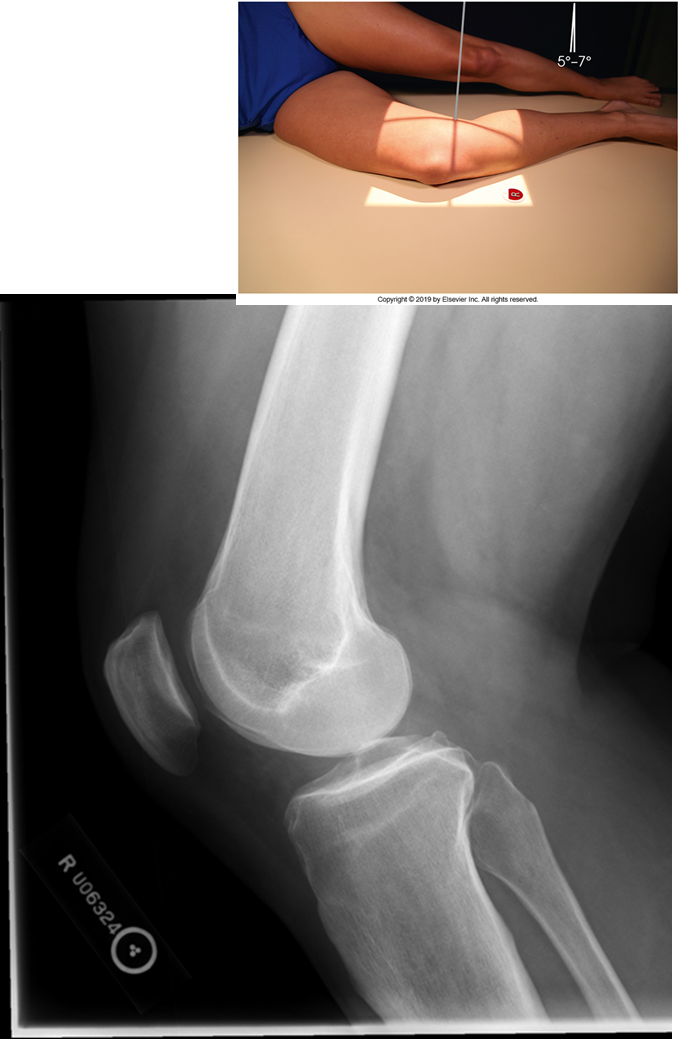
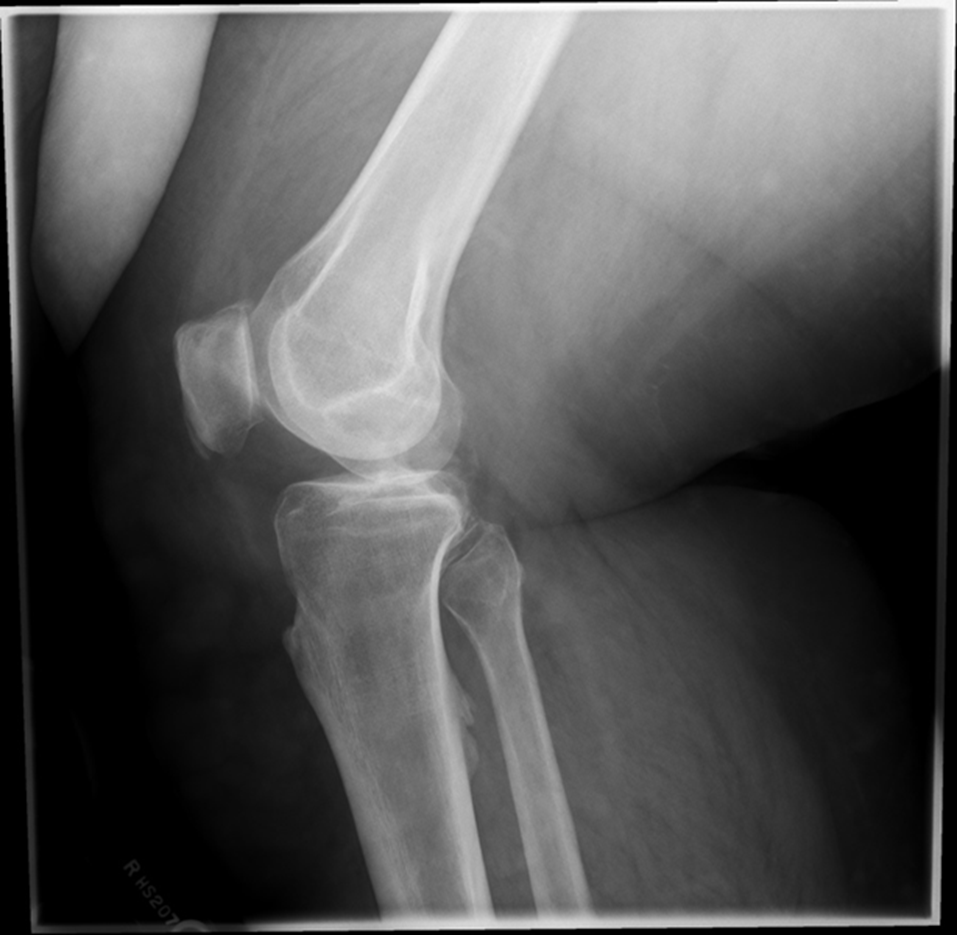
over-rotated fibular head is not touching
Patellofemoral joint space is not open (Condyle is in it)
Remove soft tissue of another leg
The medial condyle is closer to the patella it is over rotated
Lateral condyle is lower, too much tube angle
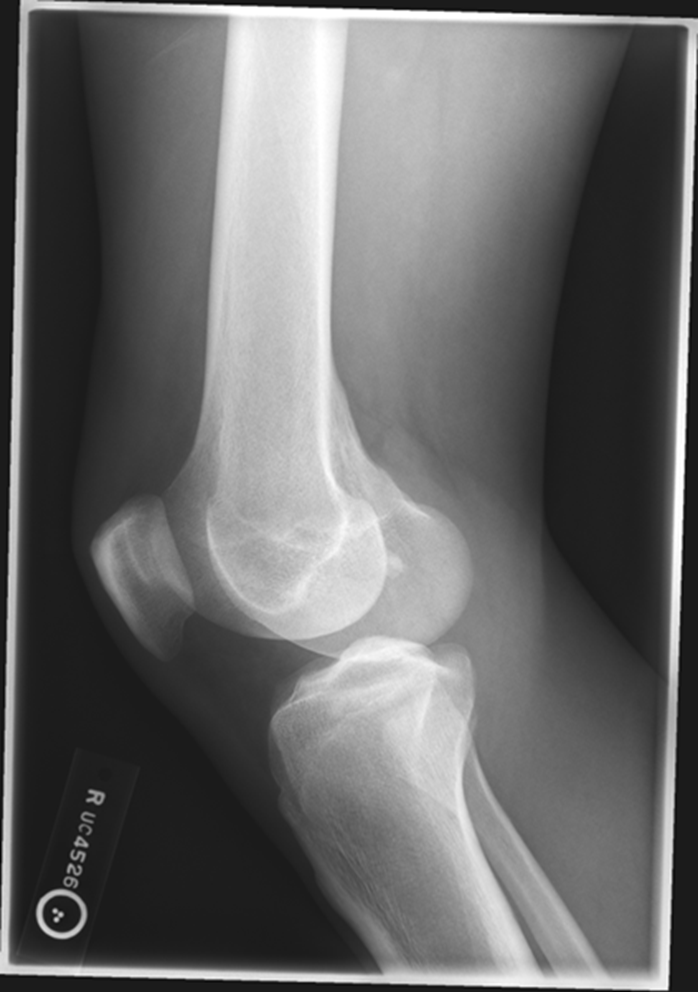
Rotation, fibula is under! Which means it is under-rotated. The condyle is in the patella femoral space, the abductor tubercle (medial condyle) , medial condyle is posterior. Central Ray is too superior. NOT ENOUGH
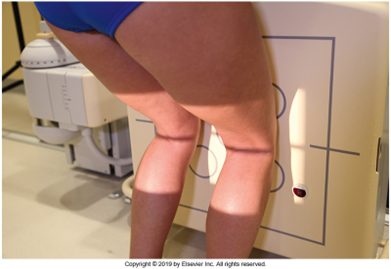
Non Trauma PA Erect (RH)
(patient age 40 and older)
•Evidence of proper collimation and the presence of a side marker placed clear of the anatomy of interest
•Both knees without rotation (RH only does the side of interest)
•Knee joint spaces centered to the exposure area (RH only does the side of interest)
Bony trabecular detail and surrounding soft tissue
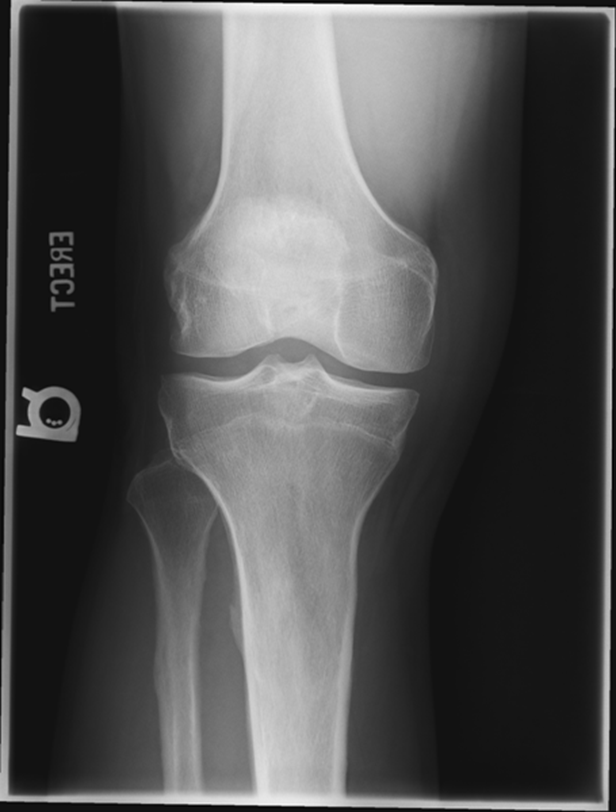
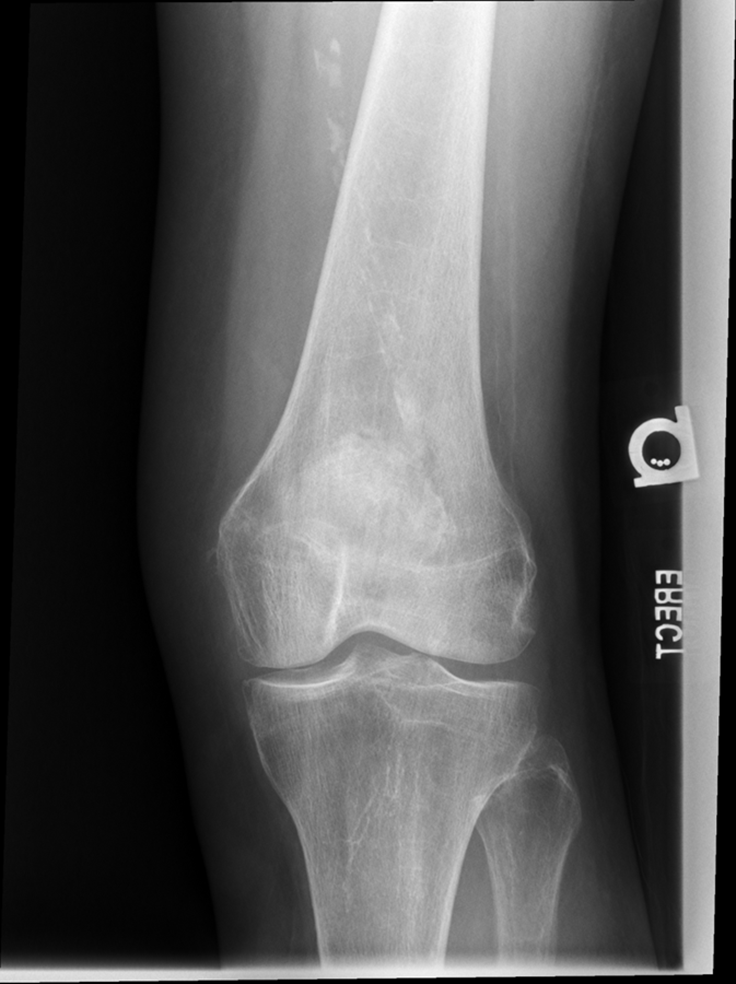
Repeat for not enough exposure -3.6
Increase Density by 2
Fix centering
joint space is narrowed off, condyles look symmetric
platues look equal
slight superimposition of tibia/fibula
GOOD IMAGE repeat for exposure index
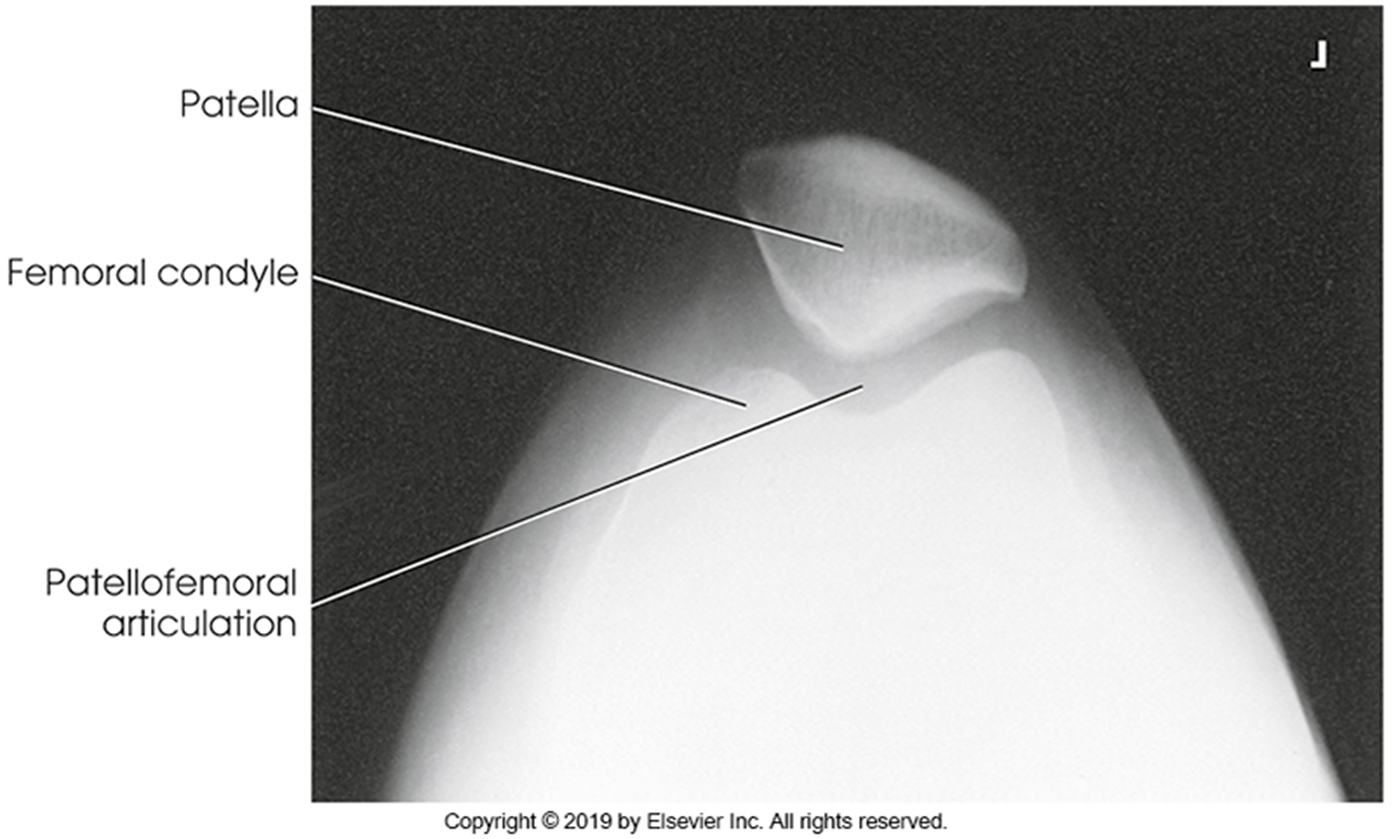
Non Trauma Patella
Erect Settegast method
(Tangential)
•Evidence of proper collimation and the presence of a side marker placed clear of the anatomy of interest
•Patella in profile
•Femoral condyles and intercondylar sulcus
•Open patellofemoral articulation
•Bony trabecular detail and surrounding soft tissues
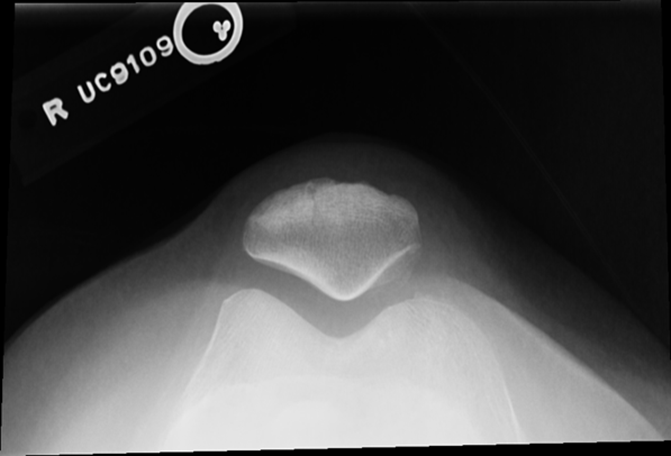
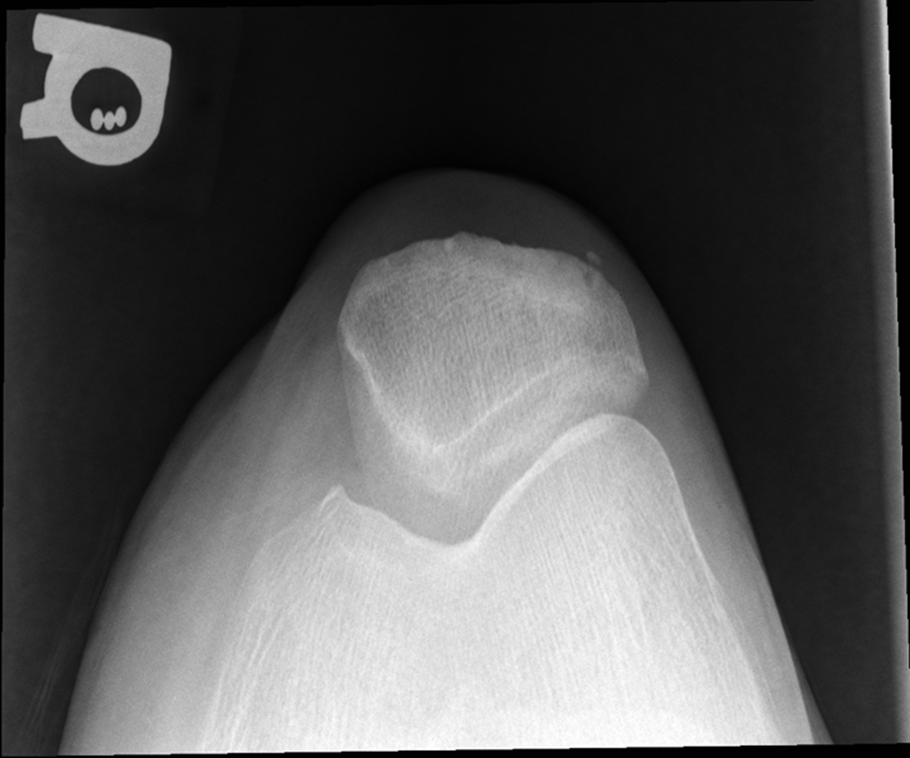
Tibia is lower under femur underorated!
TOO MUCH TUBE ANGEL OR TOO MUCH LEG FLEXTION, Medial Rotation, larger condyle
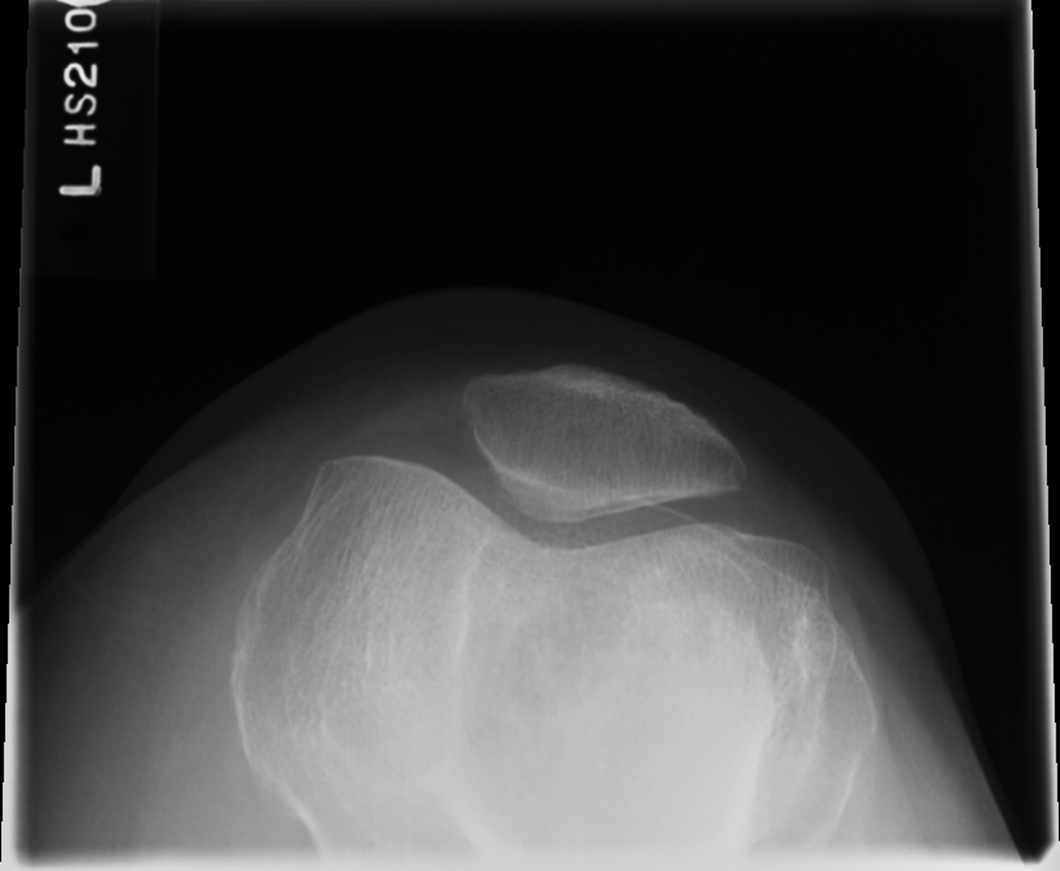
Tibia came through joint space, patella is good!!!
Did not flex the knee enough not enough tube angle
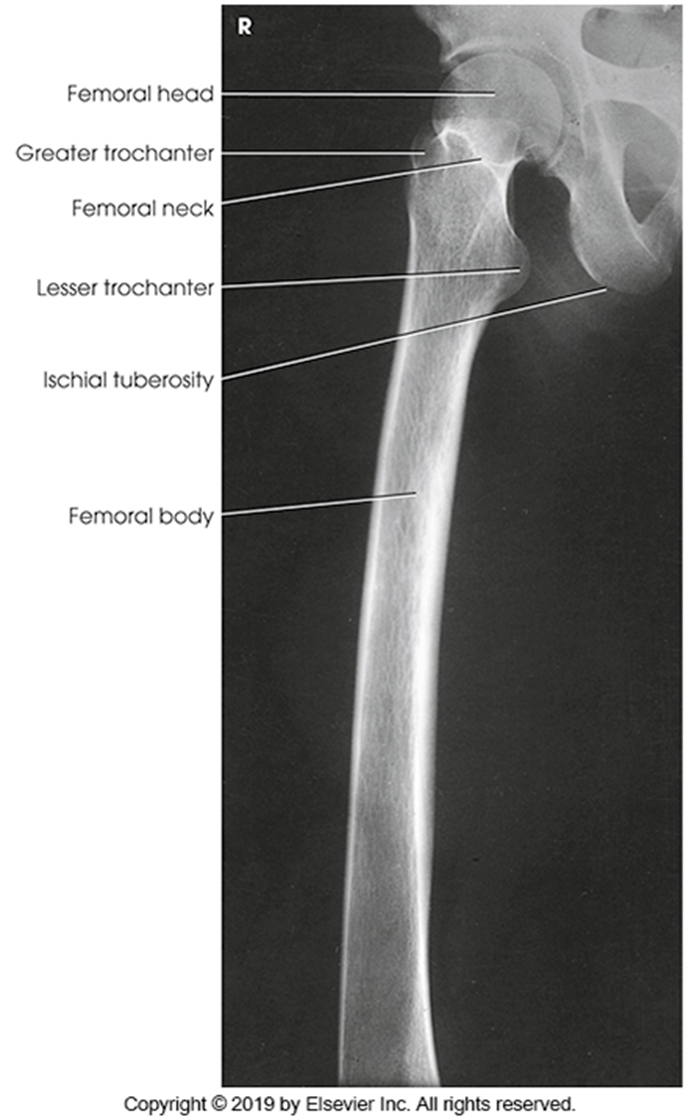
AP Femur
•Evidence of proper collimation and the presence of a side marker placed clear of the anatomy of interest
•Most of the femur and the joint nearest to the pathologic condition or site of injury (a second projection of the other joint is recommended)
•Femoral neck not foreshortened on the proximal femur
•Lesser trochanter not seen beyond the medial border of the femur or only a very small portion seen on the proximal femur
•No knee rotation on the distal femur
•Gonad shielding when indicated, but without the shield not covering proximal femur
•Any orthopedic appliance in its entirety
•Bony trabecular detail and surrounding soft tissues
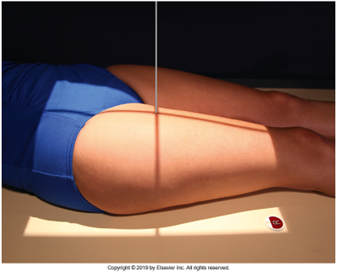
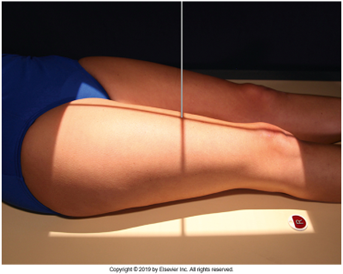
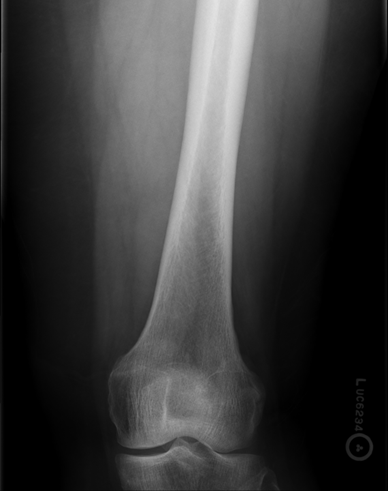
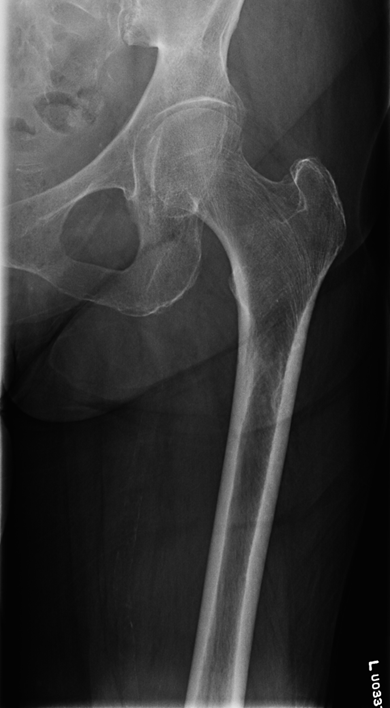
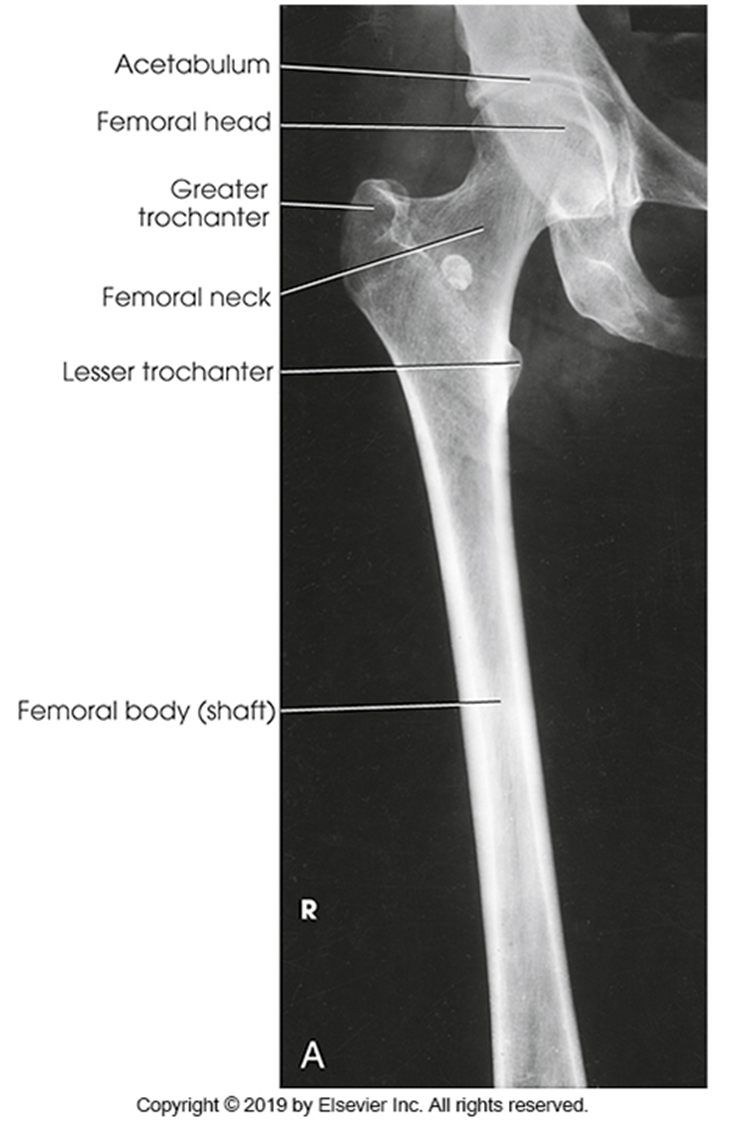
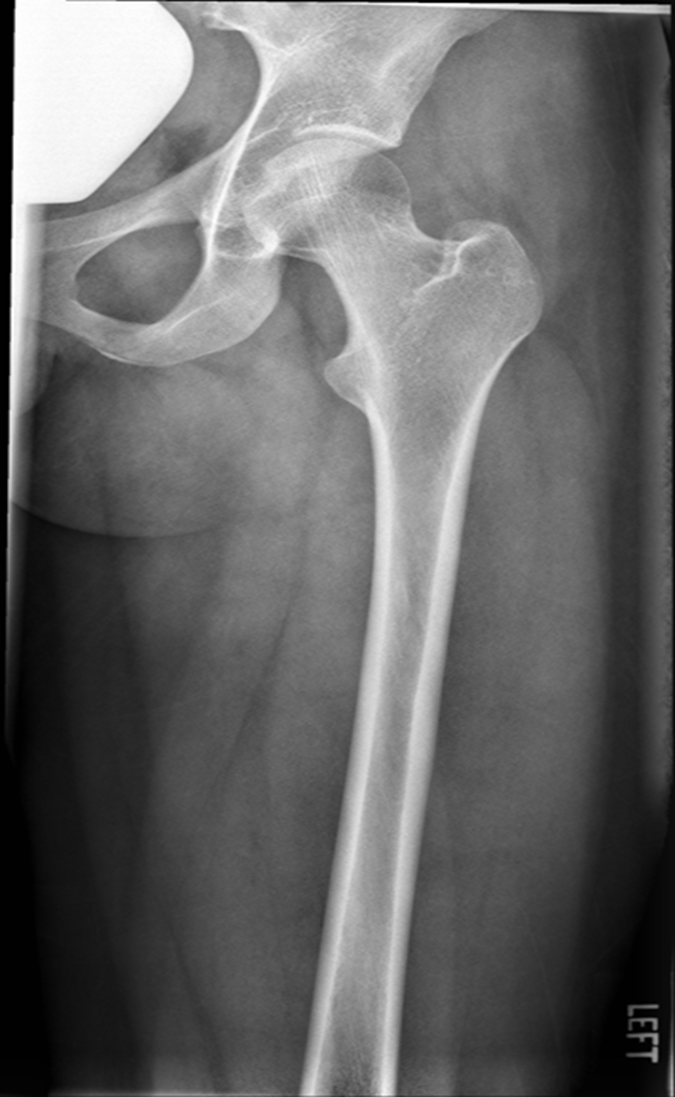
Lesser trochanter is on, leg is not rotated in, under-rotated, hanging out too laterally
Leg was not internally rotated
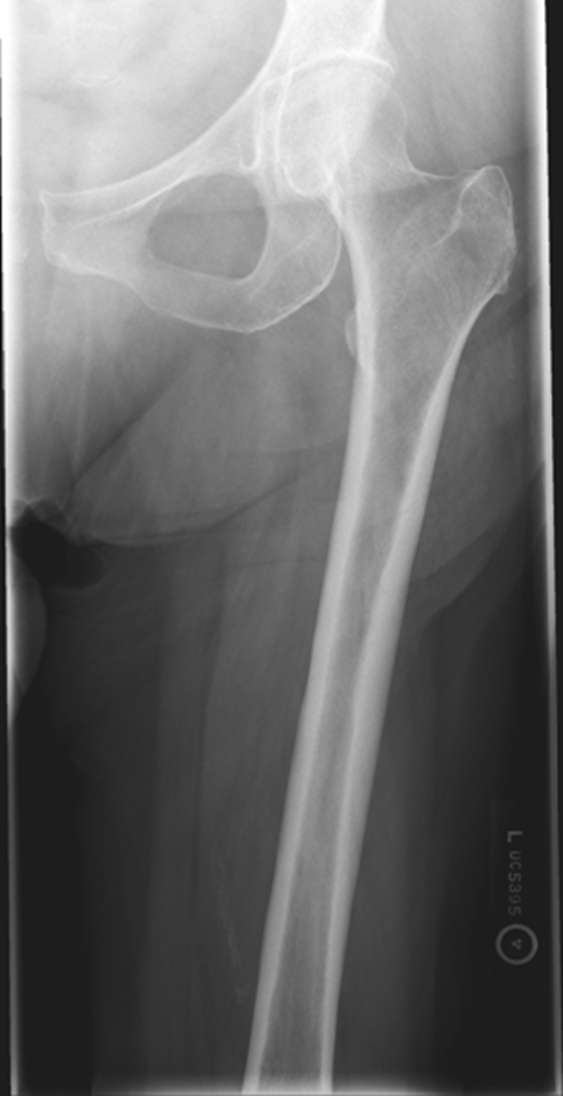
No repeat, lesser trochanter can hardly see
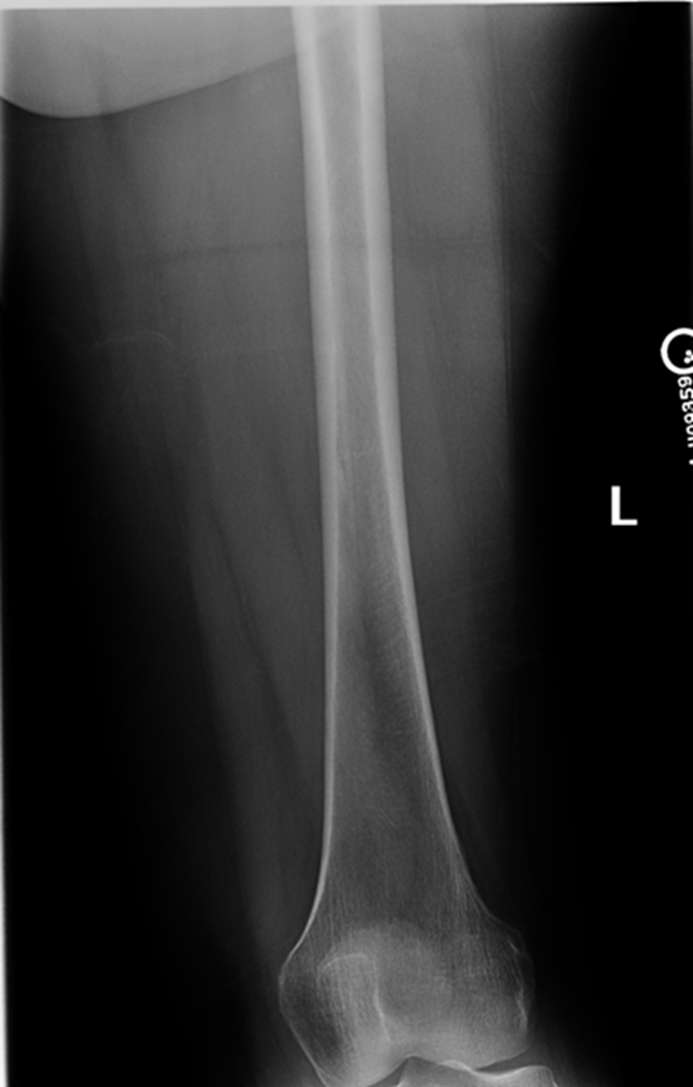
Missing anatomy
slight medial rotation
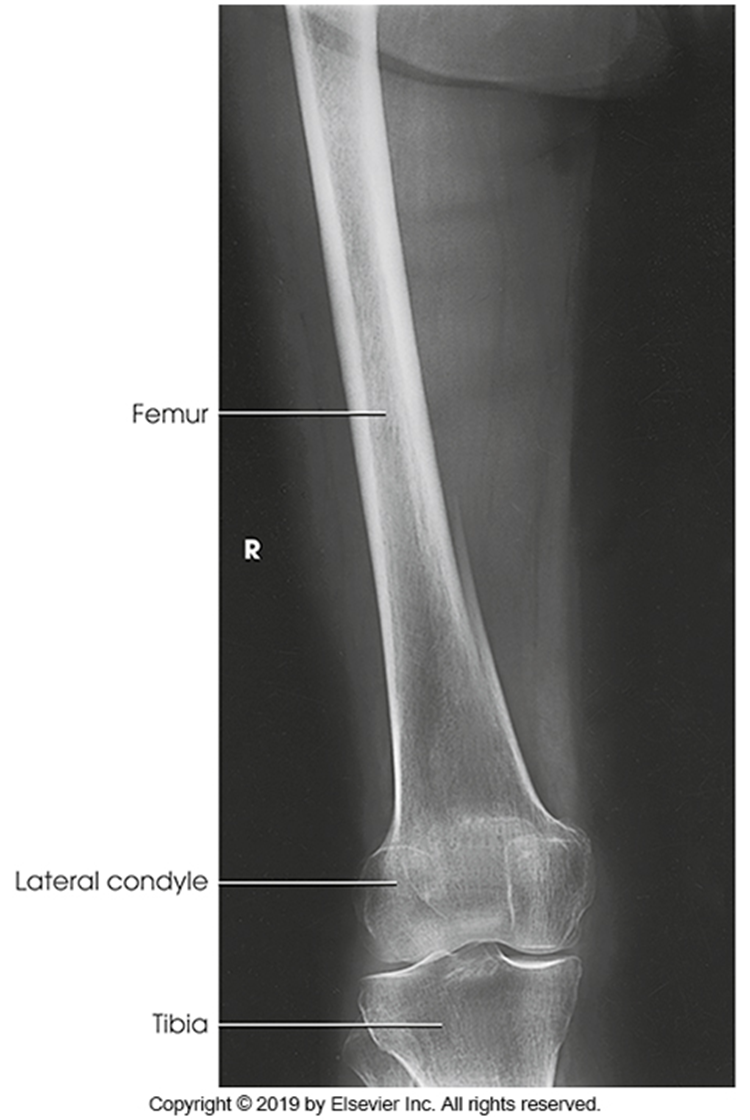
Lateral Femur
•Evidence of proper collimation and the presence of a side marker placed clear of the anatomy of interest
•Most of the femur and the joint nearest to the pathologic condition or site of injury (a second projection of the other joint is recommended)
•Any orthopedic appliance in its entirety
•Bony trabecular detail and surrounding soft tissues
•
With knee included (distal)
•Superimposed anterior surface of the femoral condyles
•Patella in profile
•Open patellofemoral space
•Inferior surface of the femoral condyles not superimposed because of divergent rays
With the hip included (proximal)
•Opposite thigh not over proximal femur and hip joint
•Greater trochanter superimposed over distal femoral neck
•Lesser trochanter visible on medial aspect of proximal femur
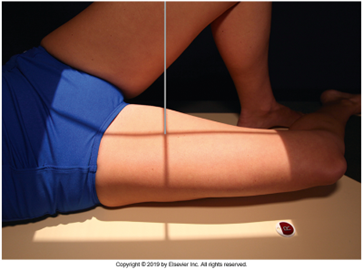
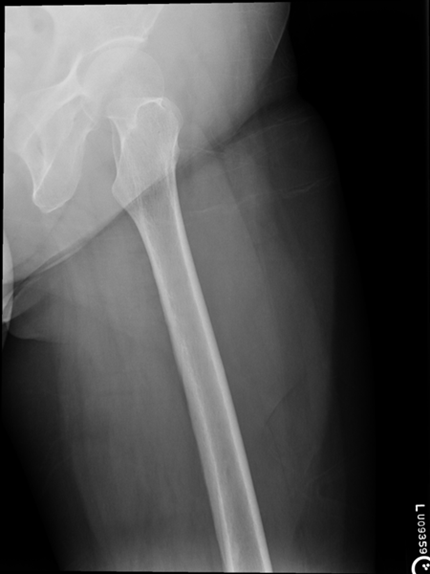
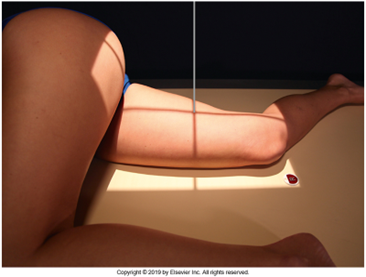
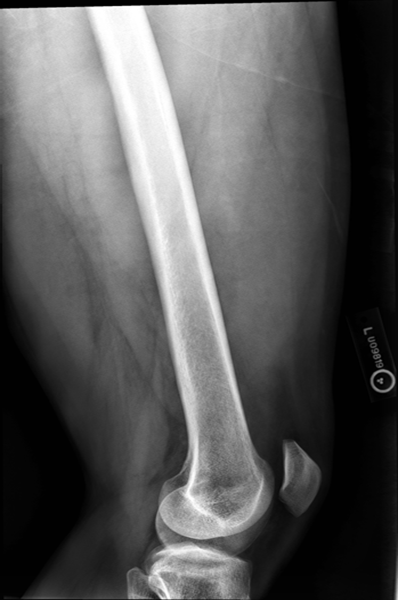
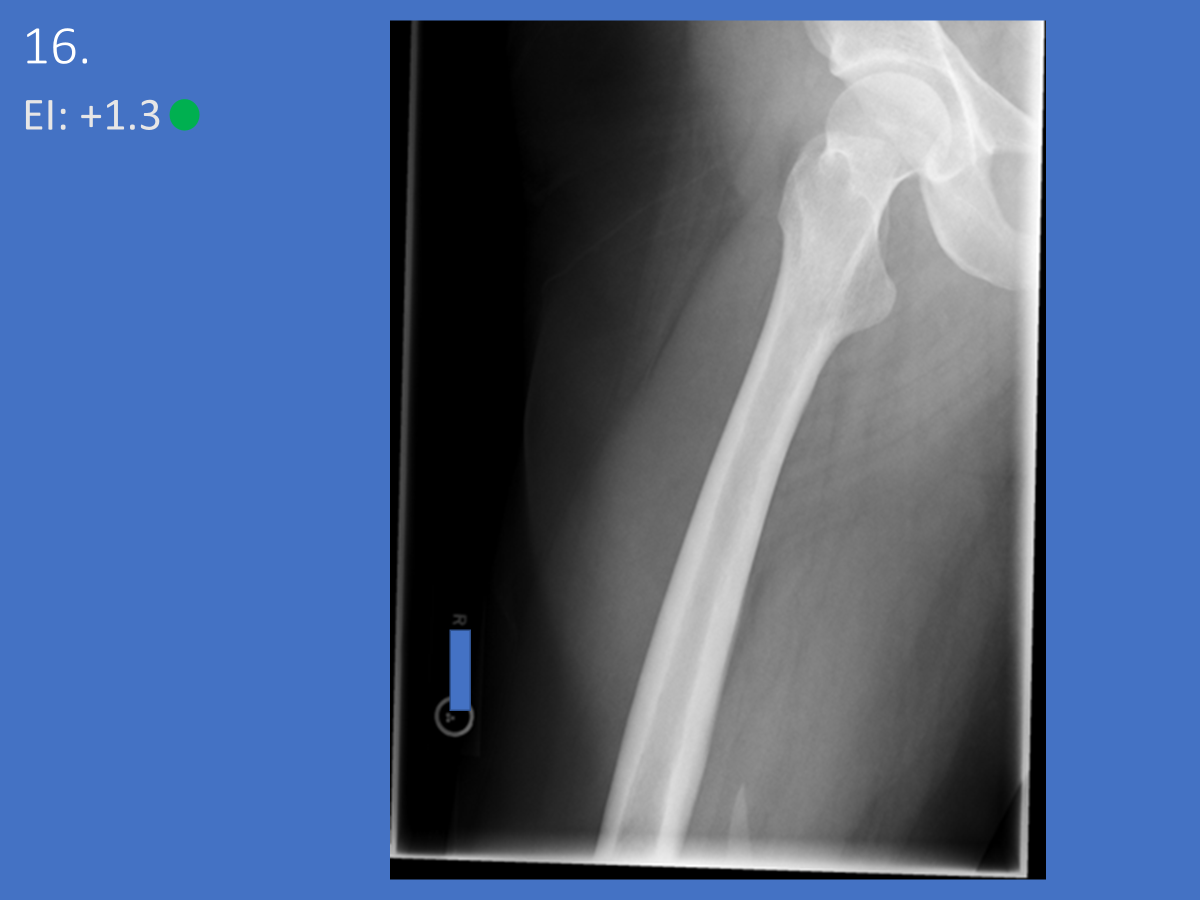
Under-rotated, sticking out laterally REPEAT, place marker bottom of light field
Can not see e lesser trochanter, can not see the greater trochanter sticking out laterally, OVER ROTATED can not see lesser
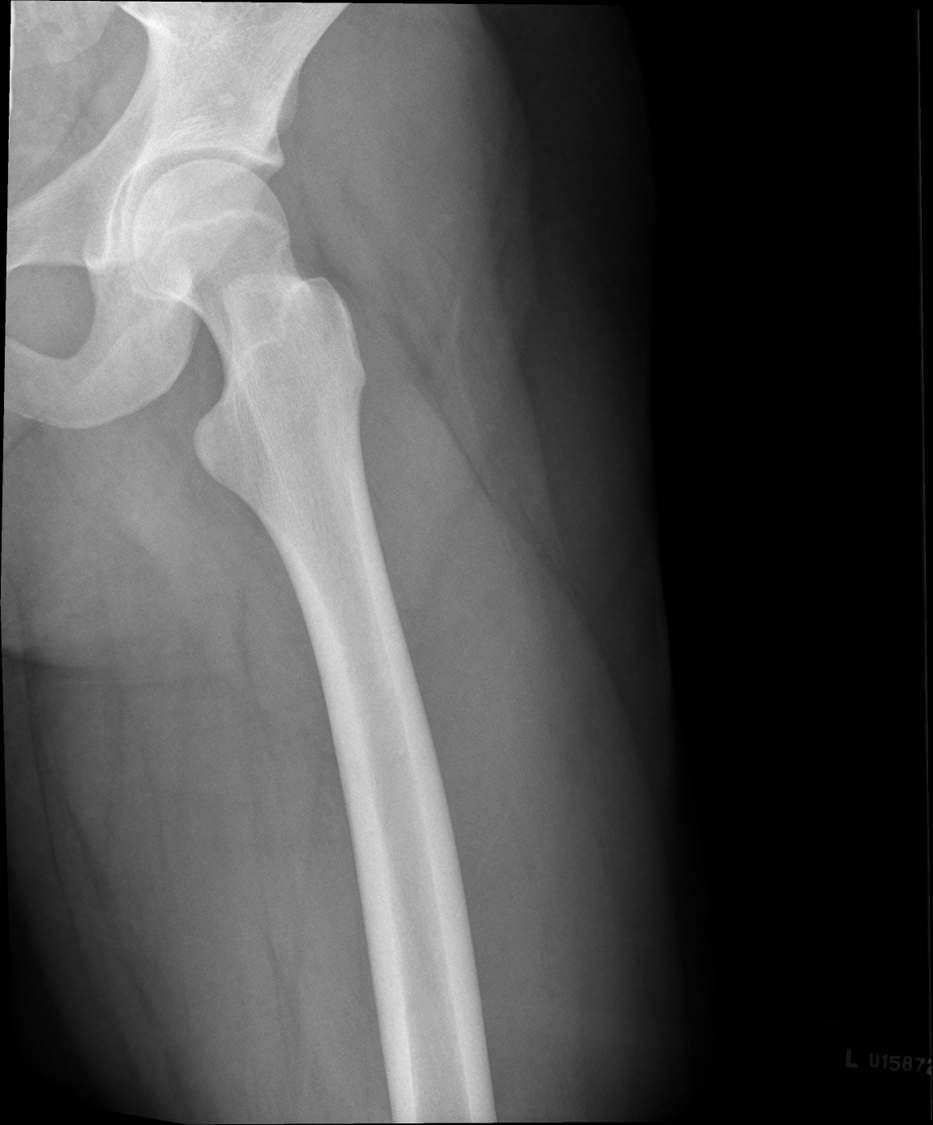
Under rotated, prominent lesser trochanter, femur is not parallel, not fully lateral, wide collimation
REPEAT under rotation
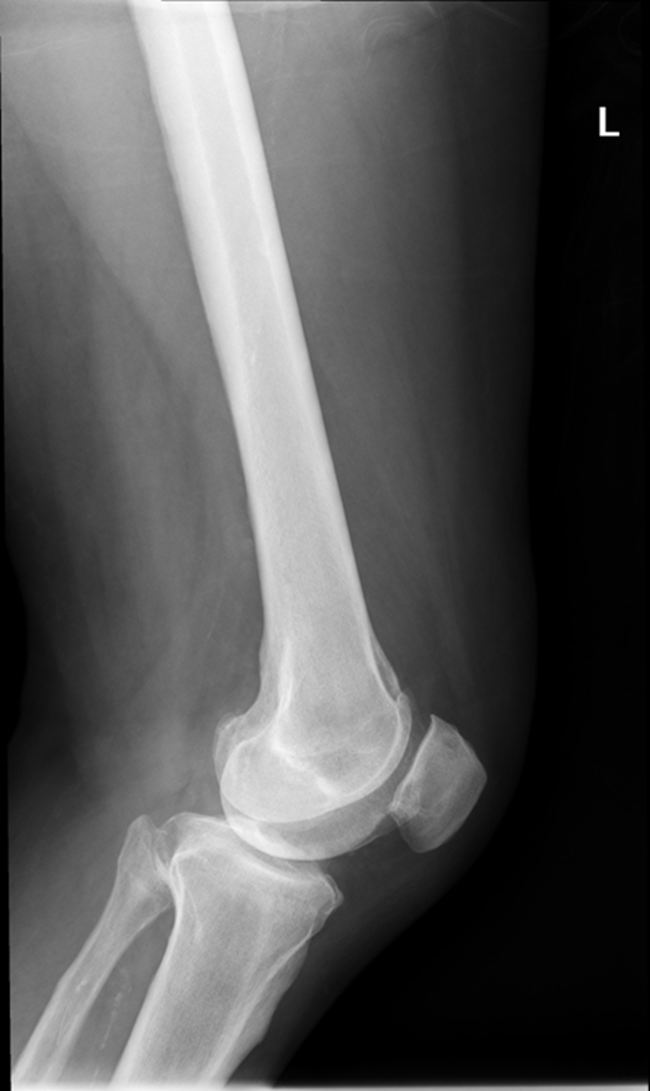
Condyle is coming into patellafemoral joint space, condyle coming down and infront, ROTATION, medial condye is inferior, medial condyle is towards patella, over-rotation
fibula is popping out back
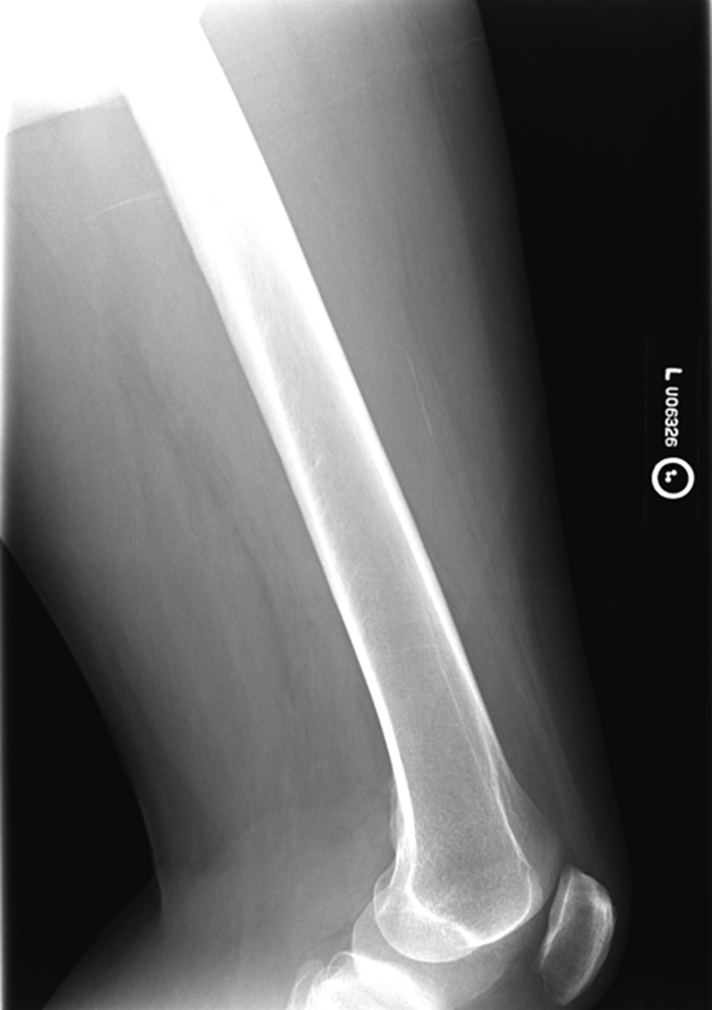
Not enough anatomy, under exposed, medial is pretty aligned, no rotation on image, increasing technique move central ray distally.
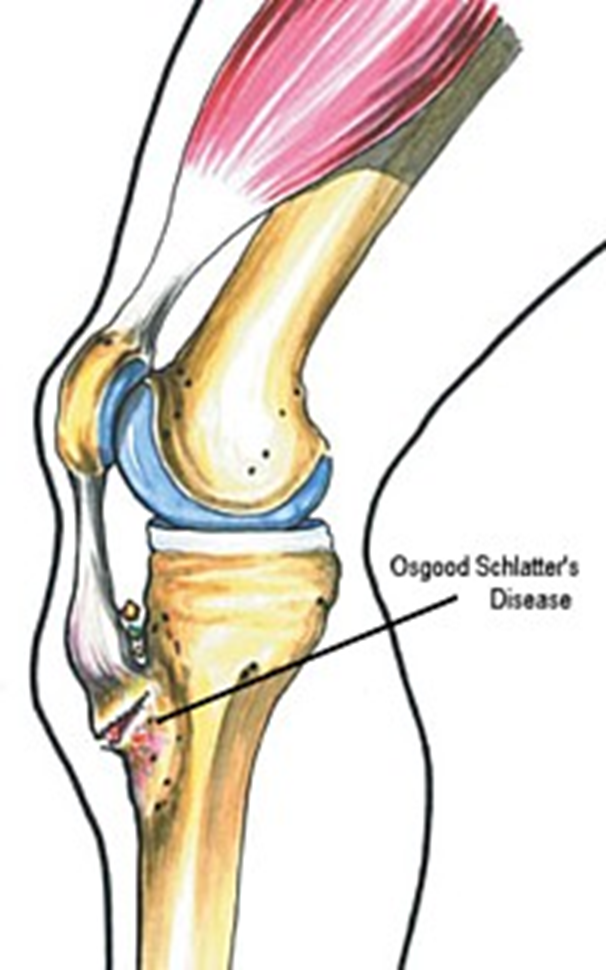
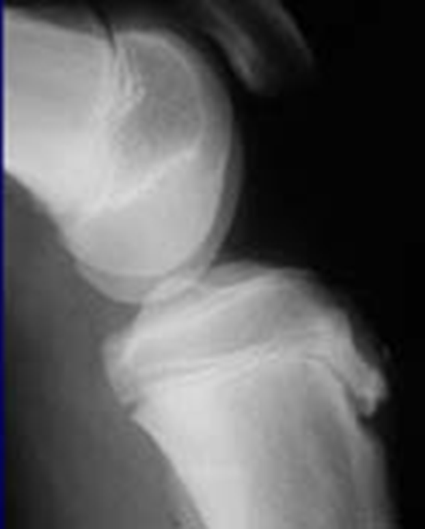
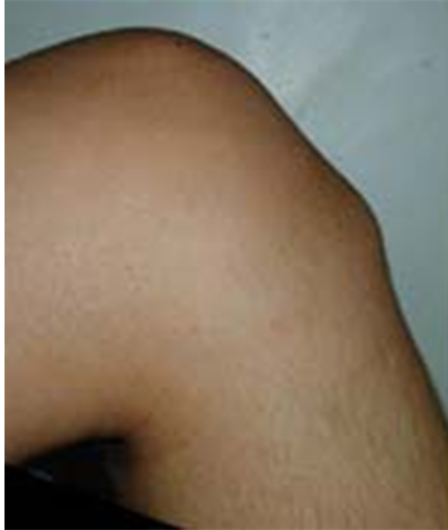
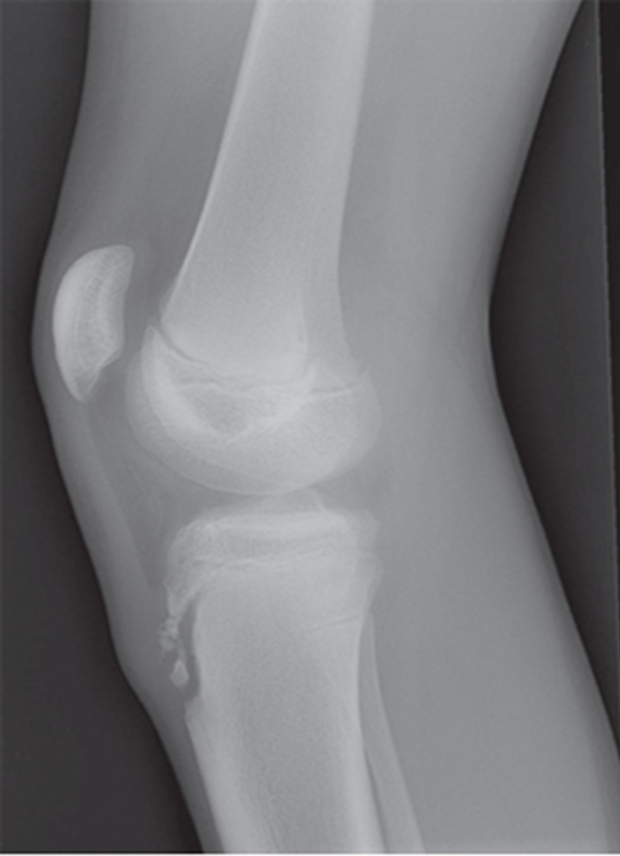
Osgood Schlatter
Incomplete separation or avulsion of the tibial tuberosity.
Cause: Repeated stress to tibial tuberosity growth plate
•stress will lead to the tendon pulling away
Complications: are uncommon, chronic pain or localized swelling,
bump in the area
Radiographic Appearance: prominent soft tissue swelling and an avulsed ossific fragment
Technical: No manual exposure factor change
Prognosis: good, resolves normally on its own once the bones
stop growing
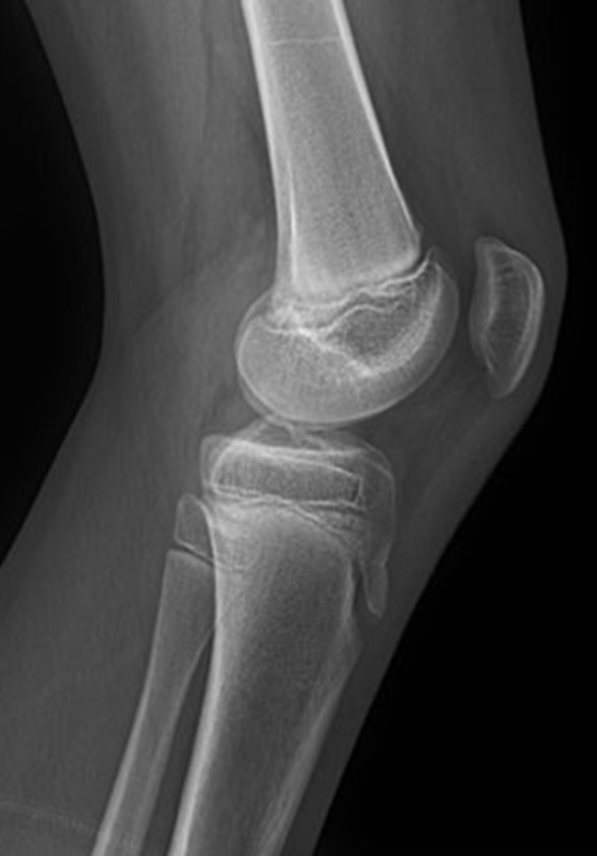
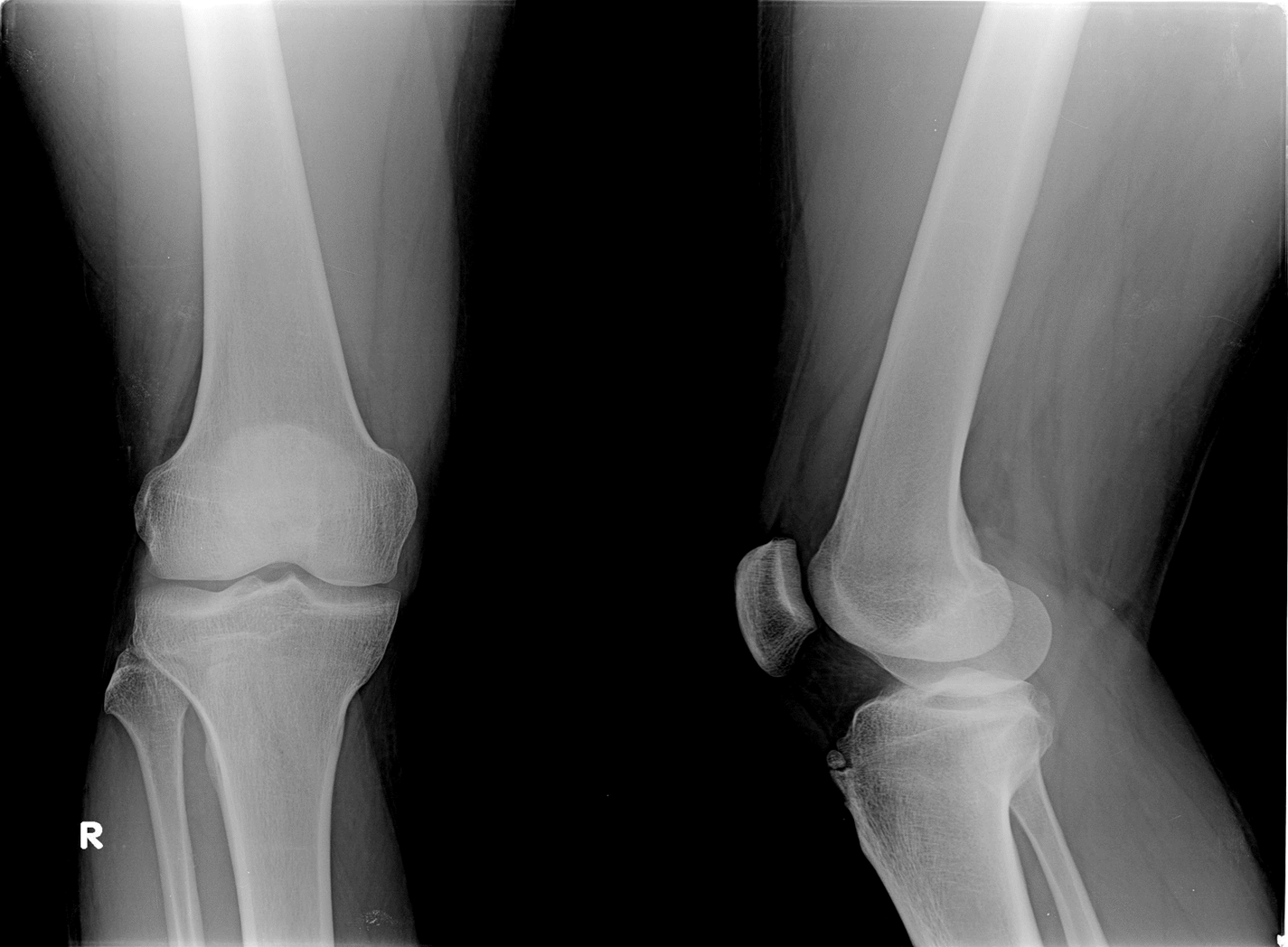
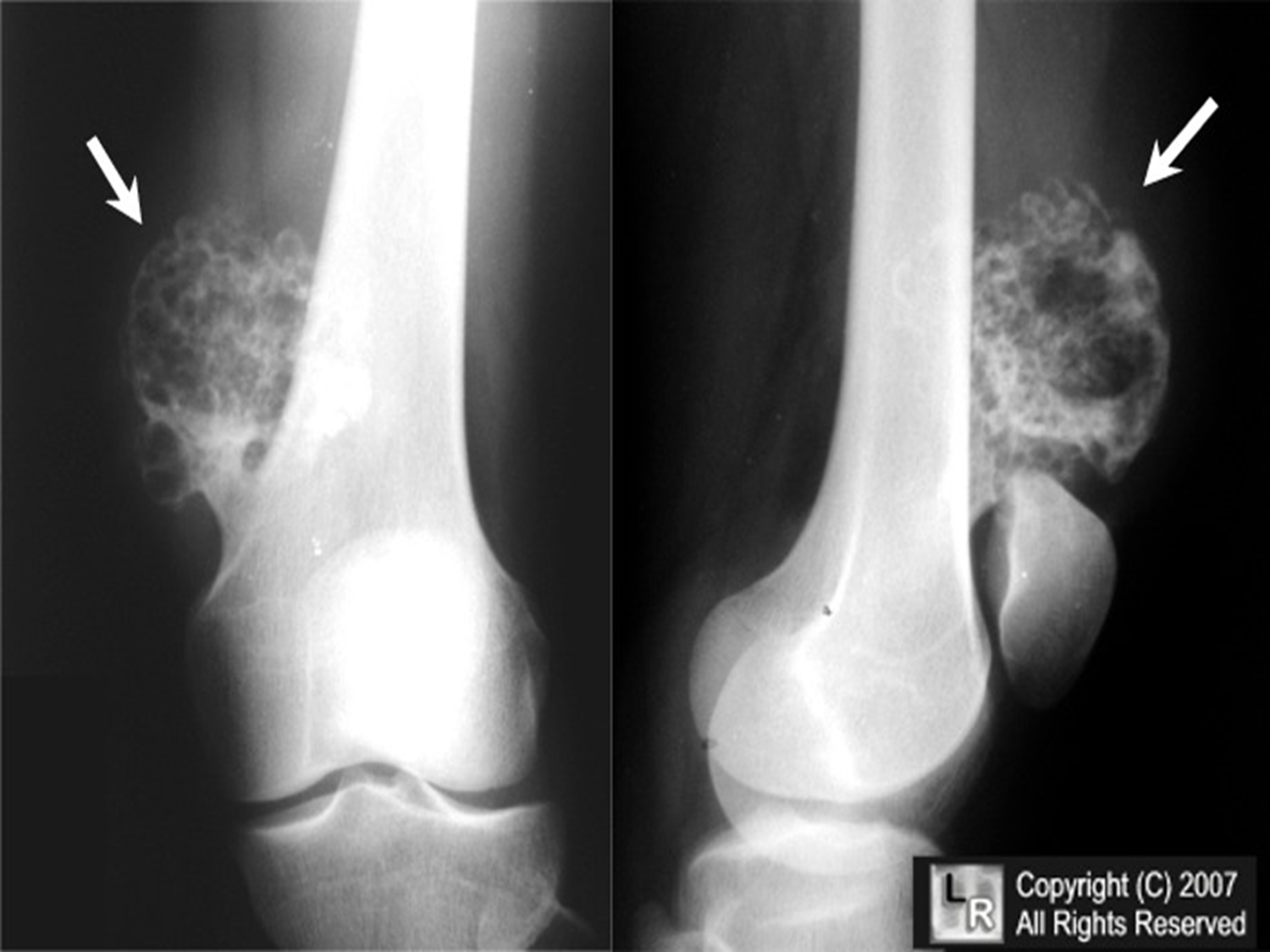
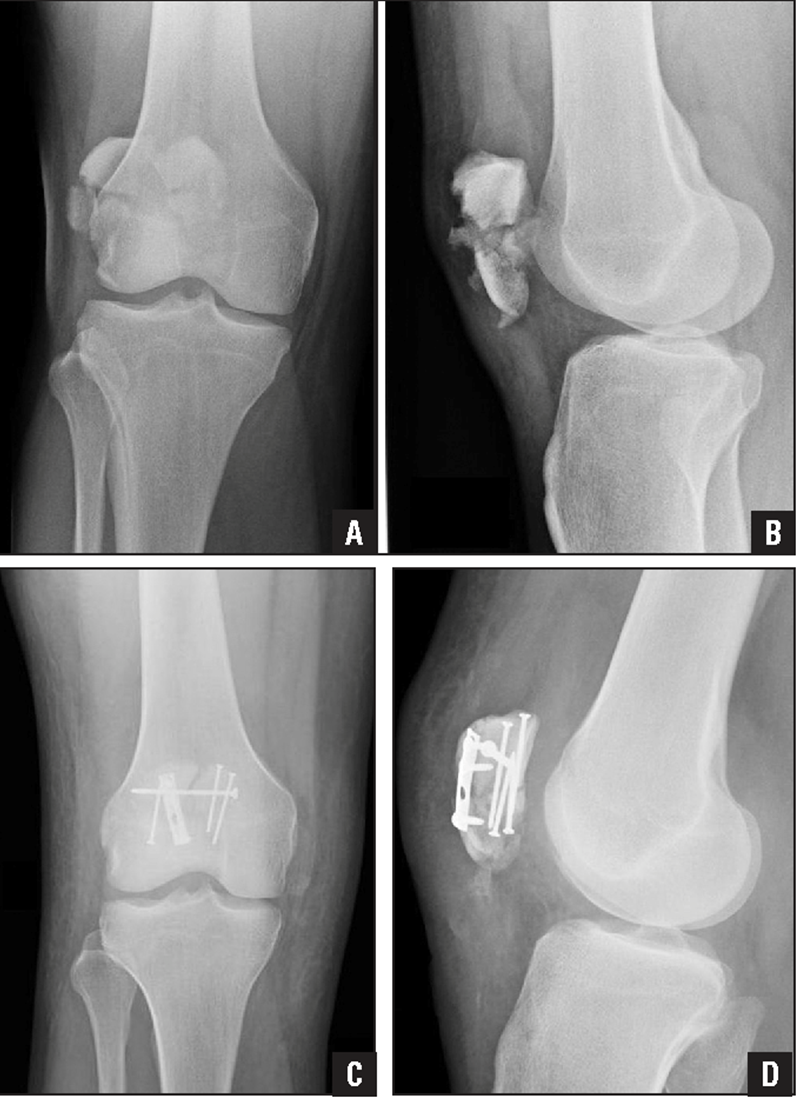
Osteochondroma
(Exostosis)
Benign projection of bone with a cartilaginous cap
Cause: idiopathic, hereditary
Complications: may turn malignant, pain, fracture of stalk
Radiographic Appearance: long axis of bone growth runs parallel to the parent bone and points away from nearest joint
Technical: No manual exposure factor change
Prognosis: Good, surgery only needed when there are mechanical
impingements
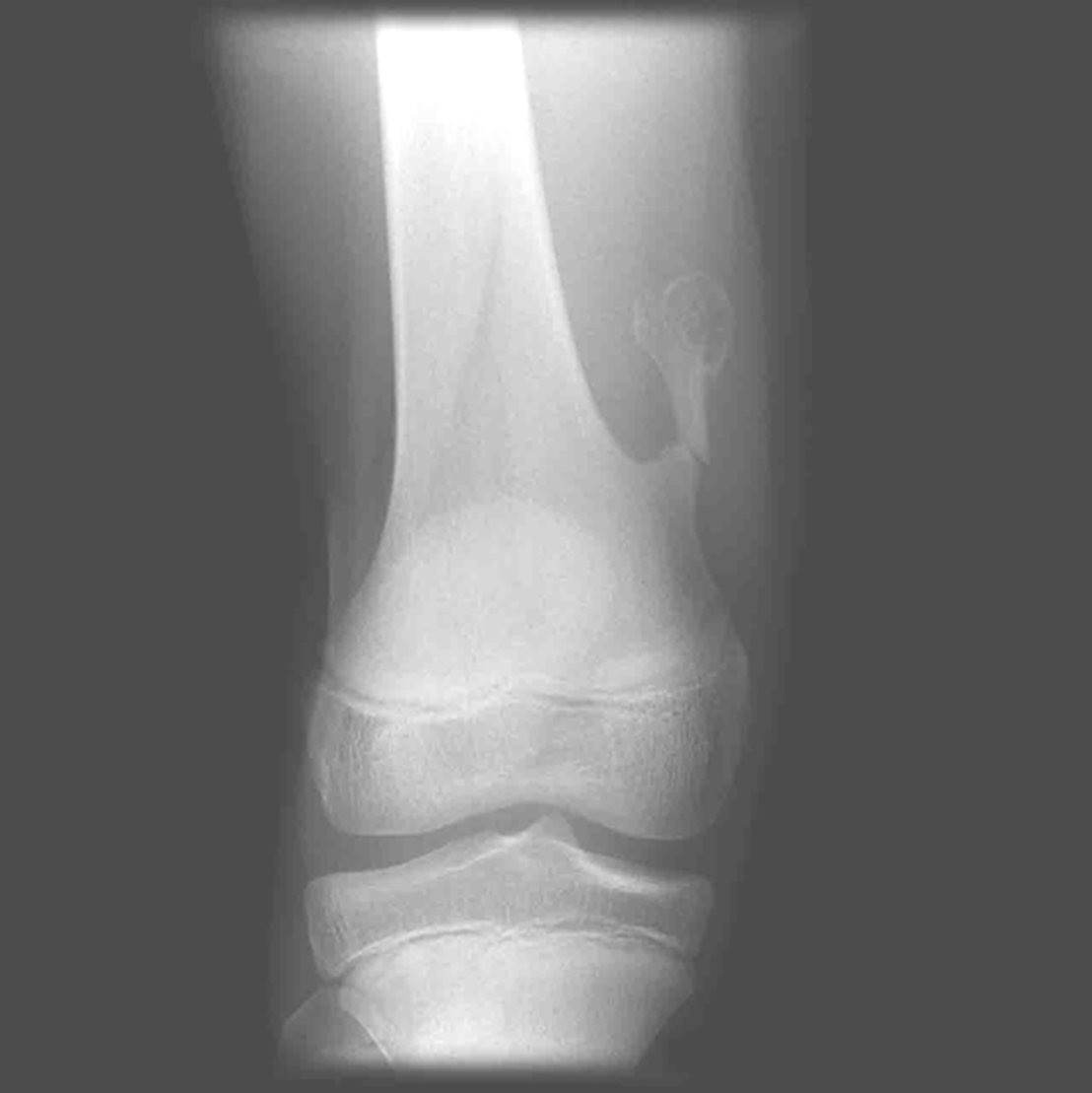
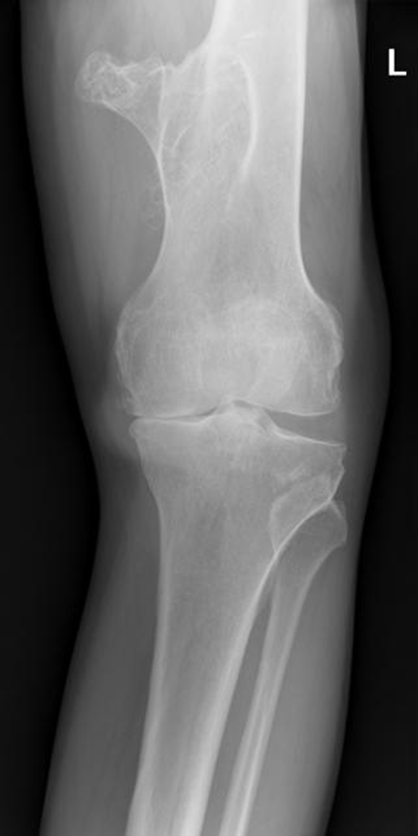
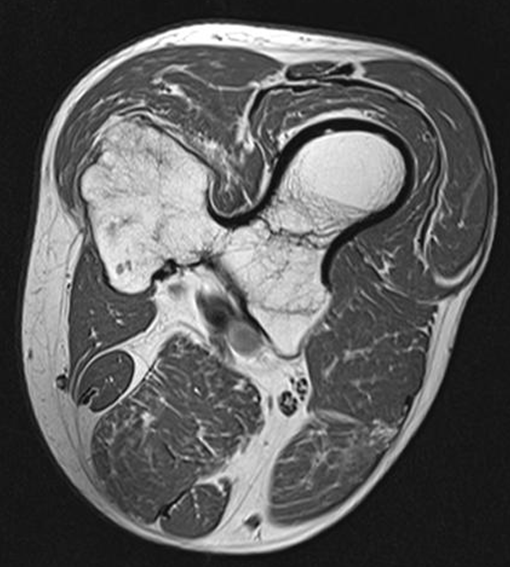
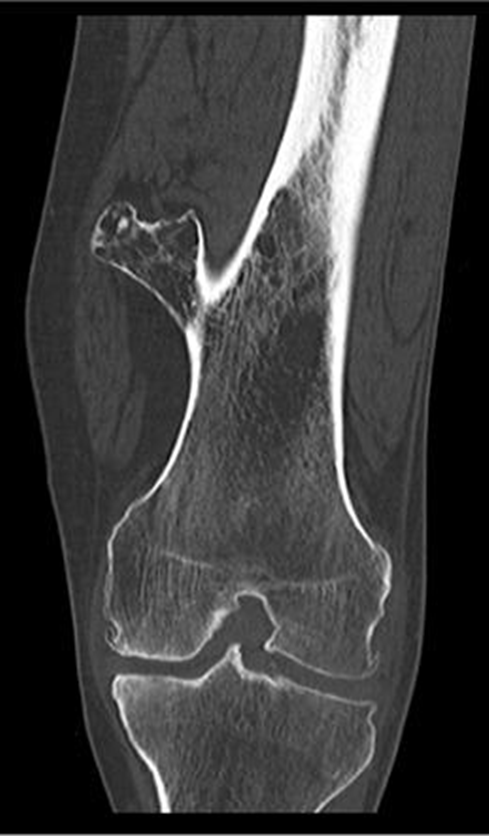
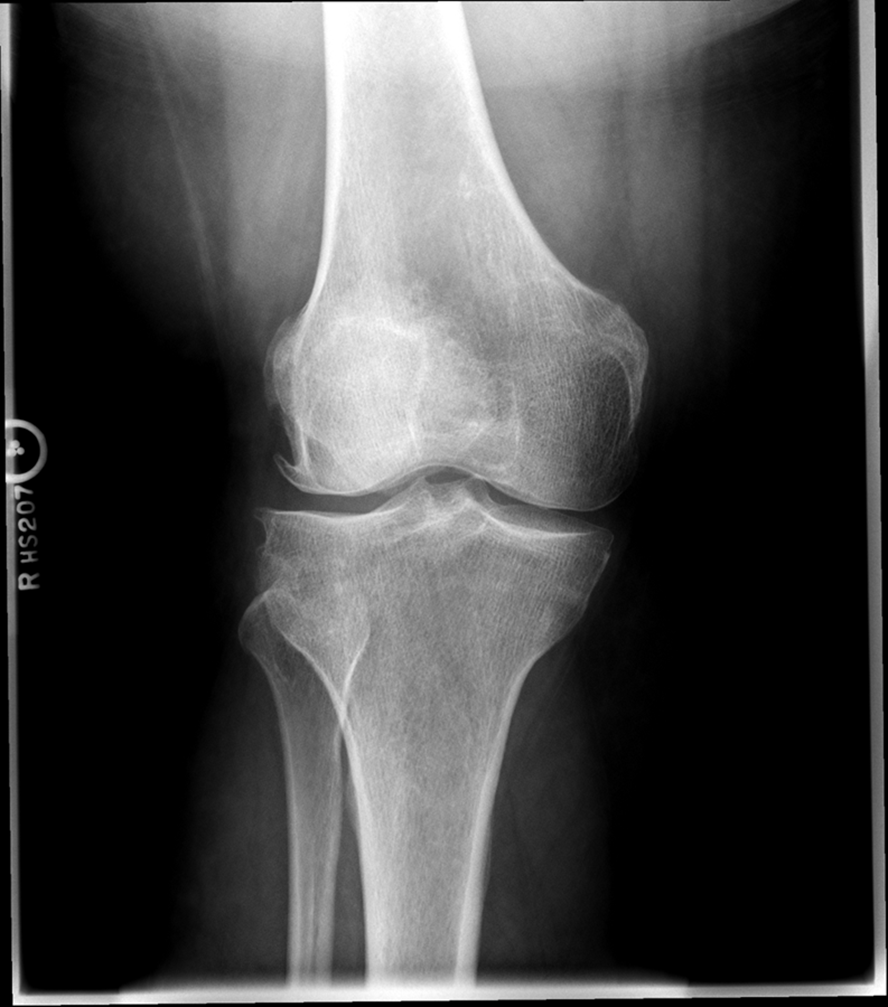
Osteoarthritis
(Degenerative Joint Disease)
Generalized disorder pathologically characterized by loss of joint cartilage and reactive new bone formation.
Cause: traumatic, stress to joints
Complications: joint pain, stiffness, trouble using joints for walking, grasping, etc
Radiographic Appearance: irregular narrowing of joint spaces and development of small bony spurs (osteophytes)
•Knee – articular ends become increasingly dense and joint narrowing is asymmetric
•Fingers – affect distal joints, marginal spurs produce well defined bony protuberances (can palpate and see knobby appearance)
•Hip – asymmetric narrowing of joint space (superiorly and laterally)
Technical: Advance Stage – Subtractive disease
•May require slight decrease
Prognosis: Some patients are unaffected by osteoarthritis while others can be severely disabled.
•Joint replacement surgery for some results in the best long-term outcome.
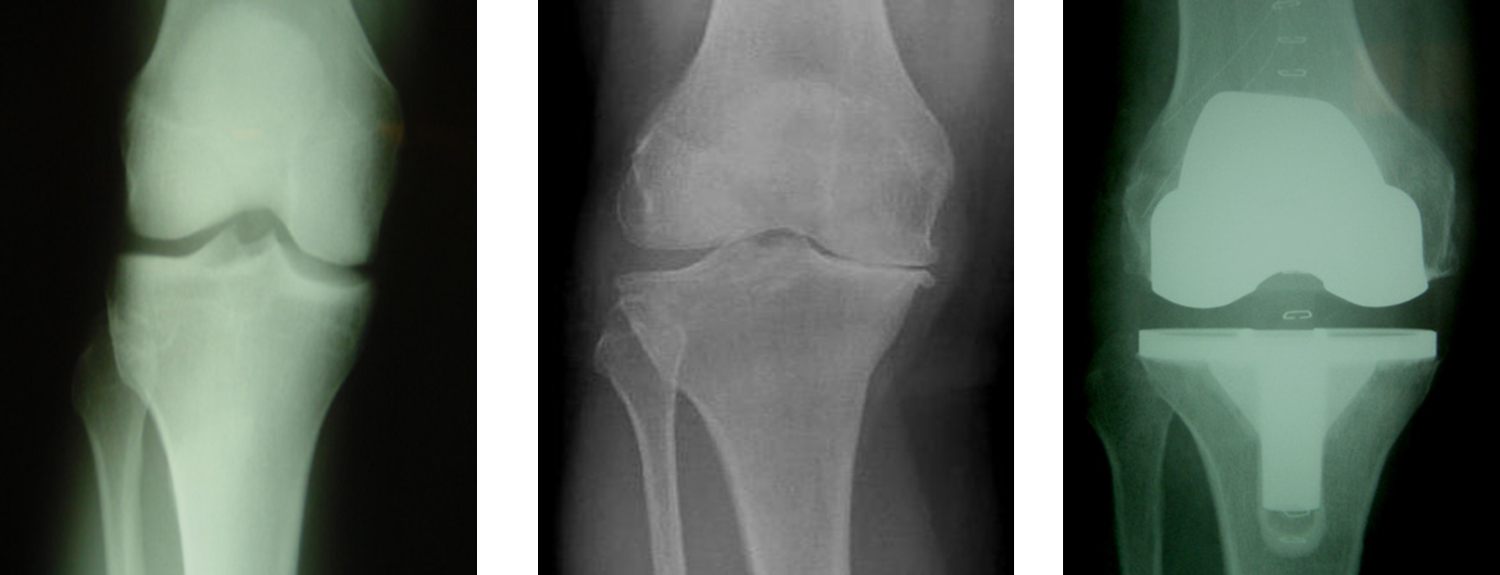
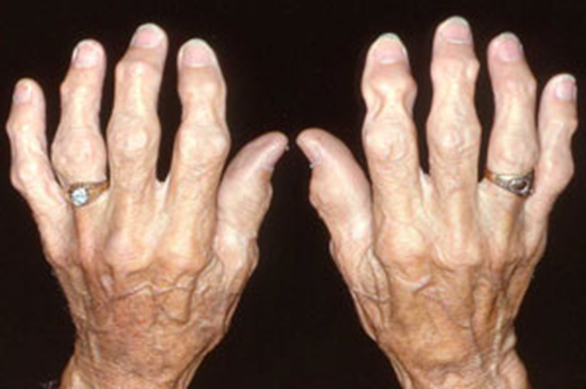
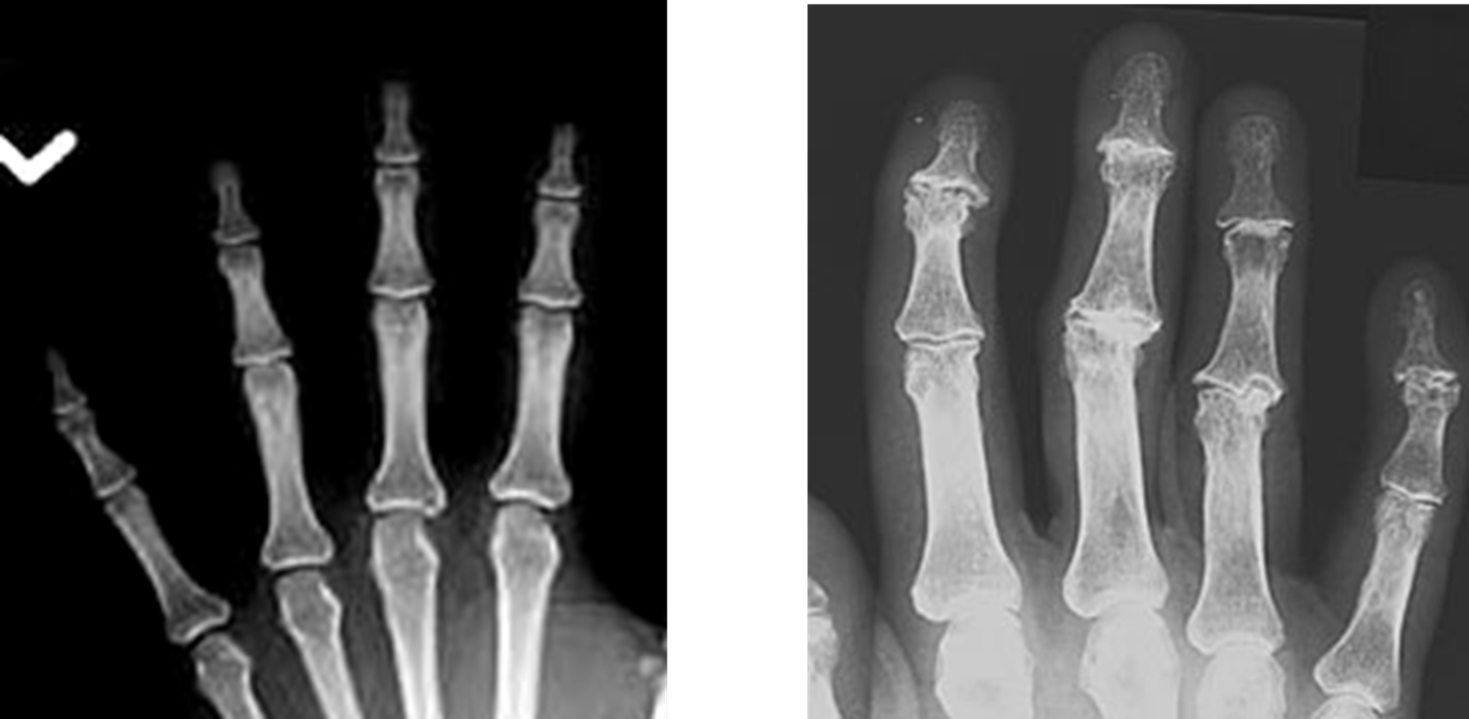
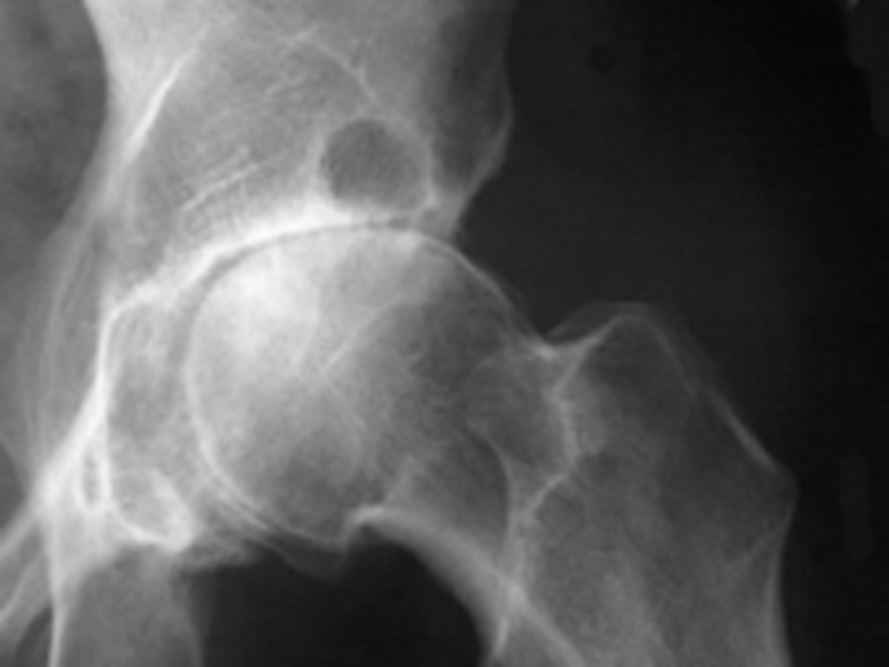
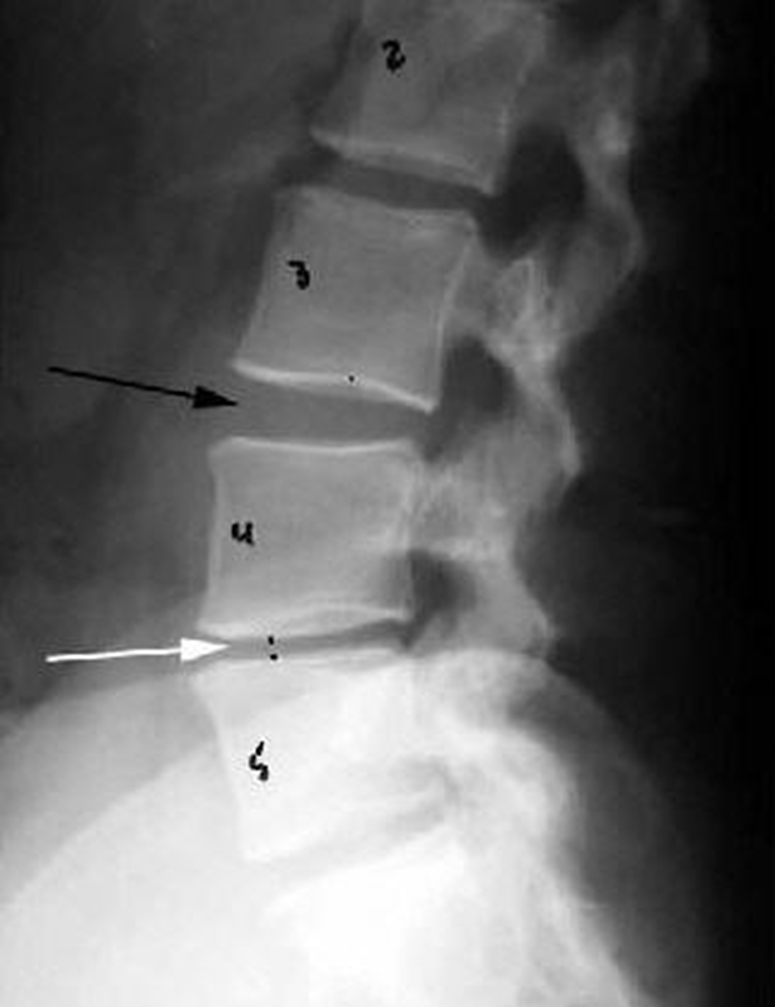
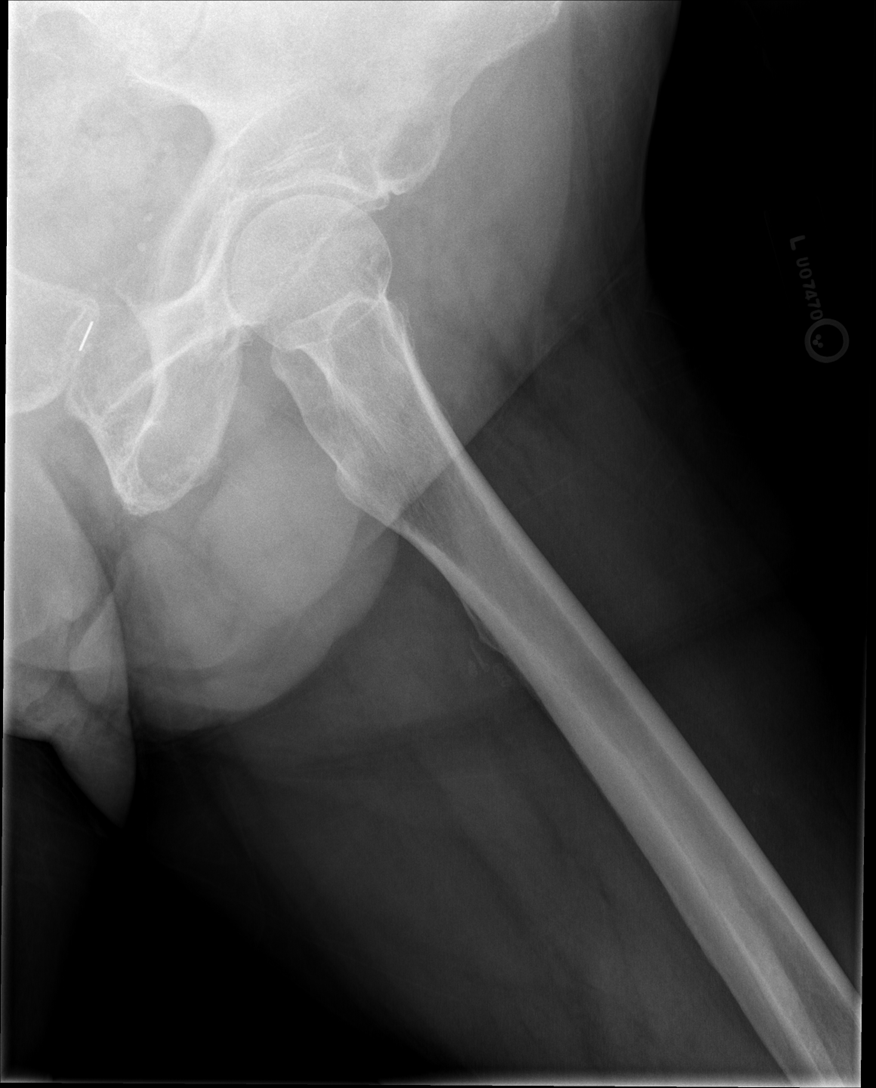
Stellate Fracture
•Fracture lines radiate form a central point of injury with a star like pattern
•Cause: Trauma - falling onto knees, knees hitting dashboard
•Complications: pain, weakness, infection, stiffness
•Radiographic appearance: comminuted fracture with a star like pattern
•No manual exposure factor change
• Prognosis/Treatment – Non operative and Operative
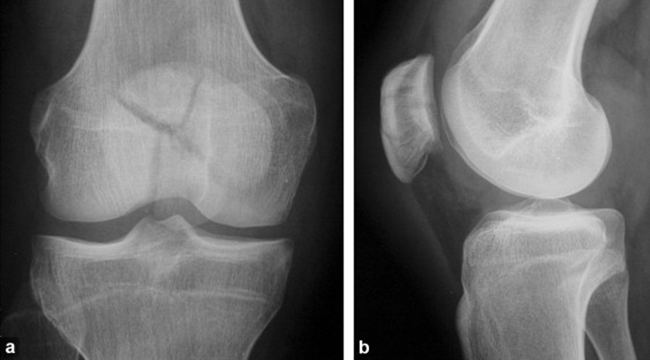
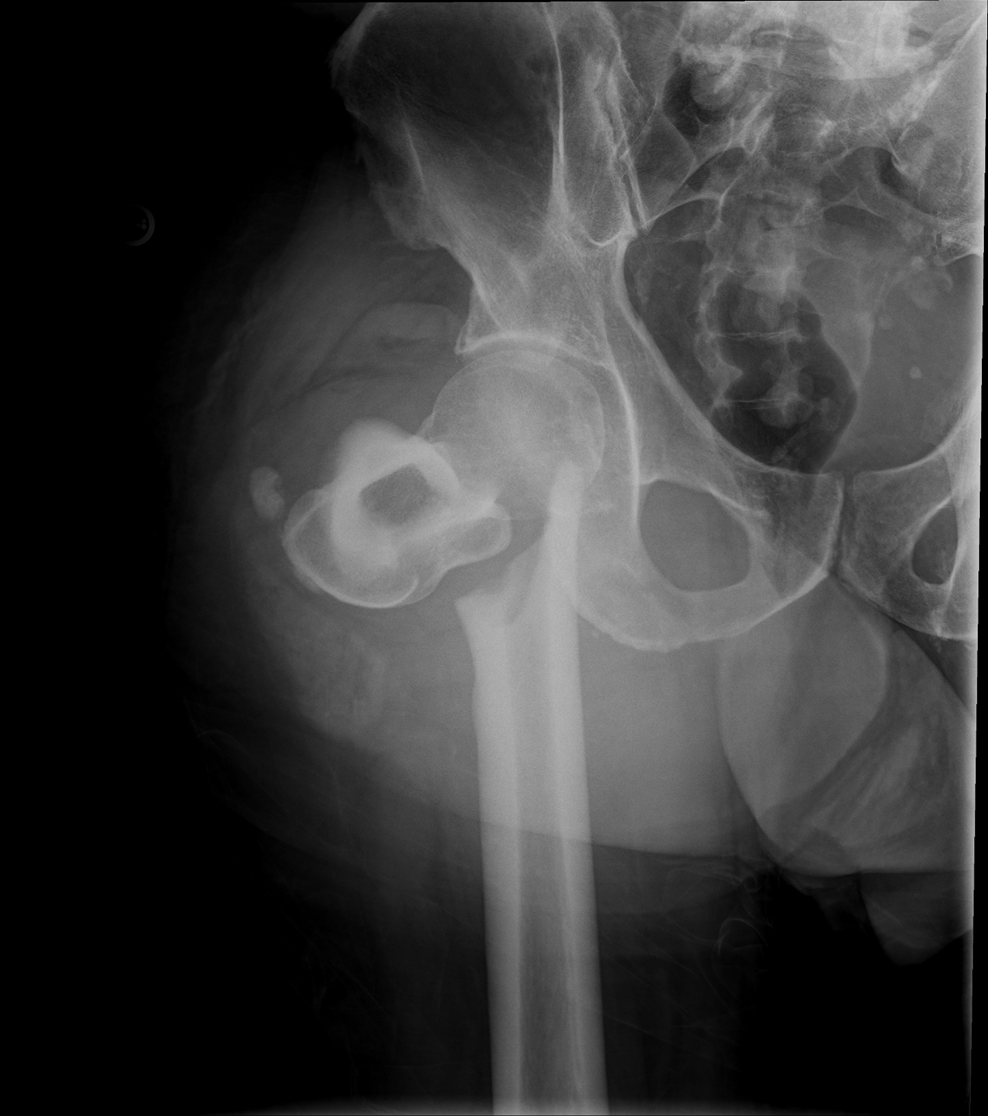
Travsverse displaced subtrochanteric fractrue proximal right femur
Trauma Knees
AP. Medial Oblique, Lateral Oblique, Lateral
Non Trauma Knee
less than 40 years old, AP, Sunrise, Lateral
40 years and older,
AP, Sunrise, Lateral, Erect PAThe