Chpt 4: Cellular Metabolism
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/114
Last updated 1:25 PM on 11/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
1
New cards
Aerobic
Respiratory process that requires oxygen
2
New cards
Anaerobic Respiration
Respiratory process that doesn't require oxygen
3
New cards
Anabolism
Cellular processes in which smaller molecules are built up into larger ones
4
New cards
Catabolism
Cellular processes that break down larger molecules into smaller ones
5
New cards
Coenzyme
Substance that unites with a protein to complete the structure of an active enzyme molecule
6
New cards
Deamination
Process that removes nitrogen-containing portions of amino acid molecules
7
New cards
Mutation
Change in genetic information
8
New cards
Substrate
Substance upon which an enzyme acts
9
New cards
Enzyme
Protein that speeds up a chemical reaction without itself being consumed
10
New cards
Cellular Metabolism
The sum total of chemical reactions in the cell
11
New cards
Intermediary Metabolism
Processes that obtain, release, and use energy
12
New cards
Primary metabolites
Products of metabolism essential to survival
13
New cards
Secondary Metabolites
Are not essential to survival, but may provide an advantage/enhancement
14
New cards
Dehydration Synthesis
When smaller molecules combine to form larger ones; form of anabolism
15
New cards
Dehydration Synthesis
Stores energy in the bonds of the larger glycogen molecules
16
New cards
Anabolism
Provides all the materials a cell needs for maintenance, growth, and repair
17
New cards
Dehydration Synthesis
Molecules join and lose water molecule(s)
18
New cards
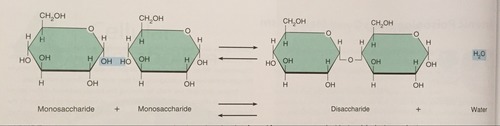
Monosaccharide + Monosaccharide ---> Disaccharide + H2O
Dehydration Synthesis of Monosaccharides into Glycogen
19
New cards
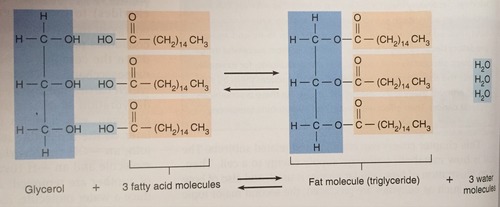
Glycerol + 3 Fatty Acids ---> Triglyceride + 3 H2O
Dehydration Synthesis of Glycerol and Fatty Acid in fat cells AKA Adipose Tissue
20
New cards
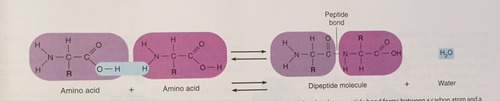
Amino Acid + Amino Acid ---> Dipeptide + H2O
Building of Protein molecules with Dehydration Synthesis
21
New cards
Dehydration Synthesis and Hydrolysis of Monosaccharide
22
New cards
Dehydration Synthesis and Hydrolysis of Glycerol and Fatty Acid
23
New cards
Dehydration Synthesis and Hydrolysis of Amino Acid
24
New cards
Peptide Bond
Holds Amino Acids together
25
New cards
Dipeptide
Two amino acids bonded together
26
New cards
Polypeptide
More than two amino acids bonded together
27
New cards
Protein
Polypeptide consisting of 100 or more amino acids
28
New cards
Hydrolysis
The break down of larger molecules into smaller ones; form of catabolism
29
New cards
Hydrolysis
The reversal of Hydration Synthesis
30
New cards
Activation Energy
The energy required for metabolic reactions
31
New cards
Active Site
Part of an enzyme that temporarily bonds with a substrate
32
New cards
Enzyme-Catalyzed Reaction
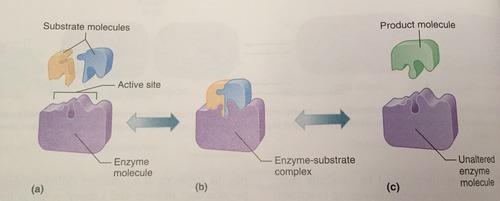
33
New cards
Metabolic Pathways
Sequences of enzyme-controlled reactions that lead to synthesis or breakdown of biochemicals
34
New cards
Lipase
Lipid splitting enzyme
35
New cards
Protease
Protein splitting enzyme
36
New cards
Amylase
Starch (amylum) splitting enzyme
37
New cards
Sucrase
Sucrose splitting enzyme
38
New cards
Maltase
Maltose (sugar) splitting enzyme
39
New cards
Lactase
Lactose (sugar) splitting enzyme
40
New cards
Rate limiting enzyme
Enzyme present in small amounts, that controls the rate of a metabolic pathway by regulating one of its steps
41
New cards
Cofactor
Non-Protein component that helps active site attain the appropriate shape
42
New cards
Cofactor
Non-Protein component that helps bind the enzyme to its substrate
43
New cards
Cofactor
May be an ion of an element (copper, zinc, iron) or a coenzyme
44
New cards
Coenzyme
Organic molecule composed of vitamin molecules or incorporate alternate forms of vitamin molecules
45
New cards
Vitamins
Essential organic molecules that human cells can't synthesize in sufficient amounts if at all
46
New cards
Energy
The capacity to change something; the ability to do work
47
New cards
Common forms of Energy
Heat
Light
Sound
Electrical
Mechanical
Chemical
Light
Sound
Electrical
Mechanical
Chemical
48
New cards
Energy
Can't be created or destroyed, but can be changed from one form to another
49
New cards
Cellular Respiration
The process that transfers energy from molecules and makes it available for cellular use
50
New cards
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
A molecule that carries energy in a form the cell can use
51
New cards
ATP
Consists of:
Adenine (1)
Ribose (1)
Phosphate (3)
Adenine (1)
Ribose (1)
Phosphate (3)
52
New cards
ATP
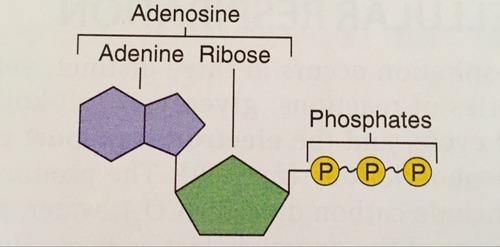
53
New cards
Skeletal Muscle Contractions
Active Transport
Secretion
Active Transport
Secretion
ATP powers cellular work such as __________
54
New cards
Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP)
ATP molecule that loses its end/terminal phosphate
55
New cards
Phosphorylation
The process of ADP resynthesizing into ATP using energy released from cellular respiration
56
New cards
Oxidation
The process of oxygen combining with another chemical
57
New cards
Oxidation
Removal of hydrogen or loss of electrons
58
New cards
Oxidation
The opposite of reduction
59
New cards
The three steps of Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis
Citric Acid Cycle
Electron Transport Chain
Citric Acid Cycle
Electron Transport Chain
60
New cards
Glycolysis
Citric Acid Cycle
Electron Transport Chain
Citric Acid Cycle
Electron Transport Chain
The products of these include:
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Water
Energy
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Water
Energy
61
New cards
Glycolysis
The breaking of glucose
62
New cards
Glycolysis
Breaks glucose (a 6-carbon molecule) into two 3-carbon pyruvic acid molecules
63
New cards
Glycolysis
Anaerobic phase of cellular respiration
64
New cards
Lactic Acid
Organic compound formed from pyruvic acid during the anaerobic reactions of cellular respiration
65
New cards
Acetyl Coenzyme A
Intermediate compound produced from the oxidation of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats
66
New cards
Genetic code
The correspondence between a unit of DNA information and a particular amino acid
67
New cards
Chromosomes
Long molecules of DNA and associated proteins
68
New cards
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Genetic material
69
New cards
Gene
DNA sequence that contains the info for making a particular protein
70
New cards
Four Groups of Organic Molecules
Proteins
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Nucleic Acid
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Nucleic Acid
71
New cards
Genome
The complete set of genetic instructions in a cell. Includes the genes and other sequences.
72
New cards
Gene Expression
Genomes that control which proteins are produced in a particular cell under particular circumstances
73
New cards
Nucleotide
The building block of nucleic acid
74
New cards
Nucleotide
Consists of a 5-Carbon Sugar (ribose or dextrose), a phosphate group, and any of several nitrogenous bases
75
New cards
Antiparallel
The sugars forming the two backbones of a DNA molecule
76
New cards
DNA Base
Can be any one of:
Adenine (A)
Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C)
Guanine (G)
Adenine (A)
Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C)
Guanine (G)
77
New cards
Purines
A (adenine) and G (guanine) and they consist of two organic ring structures
78
New cards
Pyrimidines
T (thymine) and C (cytosine) and they have a single organic ring structure
79
New cards
Adenine binds to what?
Thymine
80
New cards
Guanine binds to what?
Cytocine
81
New cards
Purines always bind to ________
Pyrimidines
82
New cards
Complementary Base Pairs
A to T and G to C
83
New cards
Histones
Proteins that DNA is wound around
84
New cards
DNA Polymerase
Catalyzes the base pairing during DNA replication, hydrogen bond
85
New cards
RNA
Ribonuleic Acid, single stranded
86
New cards
Four Nitrogenous bases for RNA
Adenine
Cytosine
Guanine
Uracil (U)
Cytosine
Guanine
Uracil (U)
87
New cards
Transcription
The process of copying DNA info into an RNA sequence
88
New cards
Messenger RNA
(mRNA)
(mRNA)
RNA that carries info for a protein's amino acid sequence from the nucleus of a cell to the cytoplasm
89
New cards
RNA Polymerase
Recognizes the correct DNA strand and the right direction for RNA synthesis
90
New cards
Condons
A series of 3 bases in mRNA that aid 3 DNA bases in specifying each amino acid in a protein
91
New cards
Translation
When mRNA is translated from the language of nucleic acid to the language of amino acid
92
New cards
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Aligns amino acids in a way that enables them to bond to each other
93
New cards
Anticondon
Three contiguous nucleotides of a tRNA molecule that are complementary to a specific mRNA condon
94
New cards
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Type of RNA that forms part of the ribosome
95
New cards
Mutations
Rare distinctions in DNA sequence that affect how we look or feel
96
New cards
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)
More common genetic variants with no detectable effects
97
New cards
Copy Number Variants
The number of repeats of particular sequences in DNA
98
New cards
Mutagens
A response to exposure to certain chemicals or radiation
99
New cards
DNA Damage Response/DNA Repair
This mechanism restores the original DNA sequence
100
New cards
Anabolism
Requires energy and provides all the materials needed for a cell's maintenance, growth, and repair