Proteins Clinical Chemistry
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
what is the bond that forms when 2 amino acids join
peptide bond
what does a protein look like in primary structure
single chain of AA
what does a protein look like in secondary structure
alpha helixes and beta pleats
what does a protein look like in tertiary structure
structure becomes contorted and folds back upon itself
globular ball is formed
what does a protein look like in quaternary structure
several polypeptide strands join together and form a complex protein
what are some factors that could cause denaturation of proteins
heat
pH changes
mechanical forces
exposure to UV light or chemicals
what percentages are the 2 major groups of serum proteins?
albumin (~60%)
globulins (~40%)
what are the 6 individual serum proteins
albumin
alpha 1
alpha 2
beta (sometimes beta 1 and beta 2)
gamma
what are some characteristics of prealbumin
synthesized mainly in liver
migrates ahead of albumin on electrophoresis
what could decreased levels of prealbumin indicate?
hepatic damage
acute-phase inflammatory response
tissue necrosis
poor nutrition
what could increased levels of prealbumin indicate
steroid therapy
alcoholism
chronic renal failure
what are some characteristics of albumin
synthesized in liver
protein present in highest amount in plasma
buffers pH
maintains osmotic pressure
binds substances in blood
what could decreased levels of albumin indicate
malnutrition/malabsorption
liver disease
GI loss (fluids)
renal disease (if excreted excessively)
dilution by excess (IV fluids, polydipsia - extreme thirst)
what could increased levels of albumin indicate
dehydration or excessive albumin infusion
what is the equation for globulin level
globulin = total protein (g/dL) - albumin (g/dL)
what is the equation for A/G ratio
albumin (g/dL) / globulin
should always be > 1.0
what does Bence-Jones protein in urine indicate
multiple myeloma or Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia
neoplastic tumor cells
what do CSF proteins identify
increased permeability of the BBB to proteins
increased immunoglobulin production
what do increased total CSF proteins indicate
bacterial, viral, or fungal meningitis
traumatic tap
multiple sclerosis (MS)
neoplasm
what will cause edema
decrease of protein in plasma (esp. albumin <3.0 g/dL)
what are some of the a1 globulins
antitrypsin
fetoprotein
what are some of the a2 globulins
haptoglobin
ceruloplasmin (copper)
macroglobulin
what are the b-globulins
transferrin
hemopexin
lipoprotein
fibrinogen
complement
CRP (C-reactive protein)
what are the gamma globulins
IgG
IgA
IgM
IgE
IgD
which proteins are positive acute phase reactants that INCREASE during inflammation?
a1-antitrypsin, a1-glycoprotein, haptoglobin, ceruloplasmin, complement, fibrinogen, CRP
which proteins are negative acute phase reactants that DECREASE during inflammation?
prealbumin, albumin, transferrin
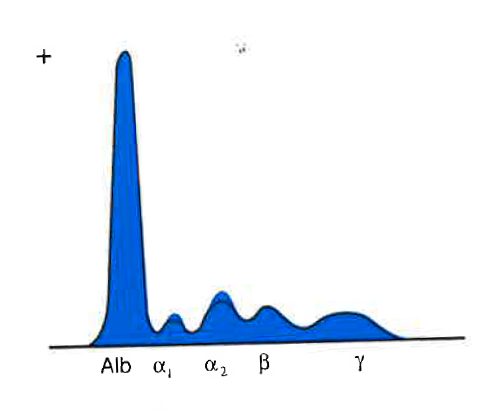
Albumin | Alpha 1 | Alpha 2 | Beta | Gamma |
Dec/Norm | Inc | Inc | N.C. | Dec/Norm |
what condition does this indicate
acute inflammation
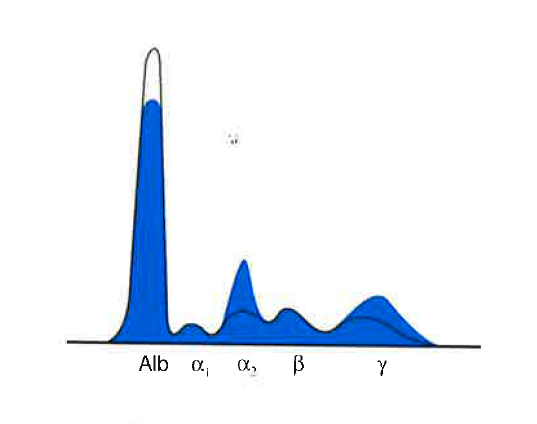
Albumin | Alpha 1 | Alpha 2 | Beta | Gamma |
Dec/Norm | Inc | Inc | Inc/Norm | Inc |
what condition does this indicate
chronic inflammation
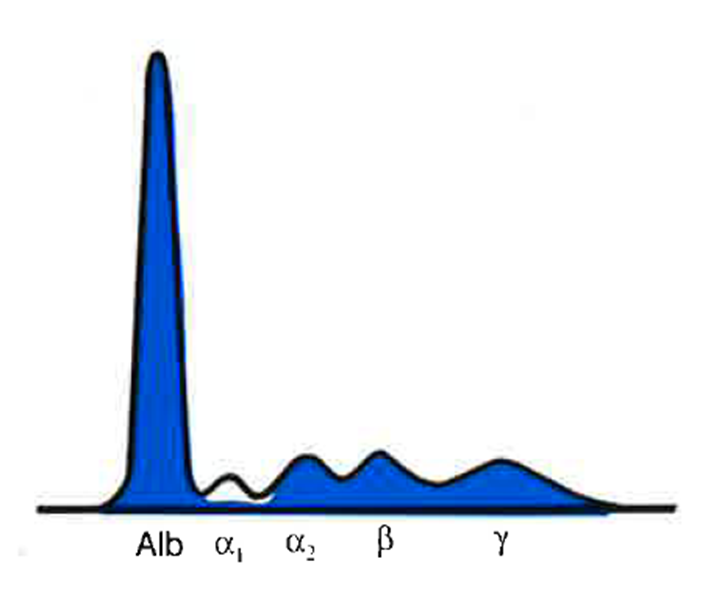
Albumin | Alpha 1 | Alpha 2 | Beta | Gamma |
Norm | Dec/Absent | Norm | Norm | Norm |
what condition does this indicate
Alpha-1-Antitrypsin (AAT) Deficiency
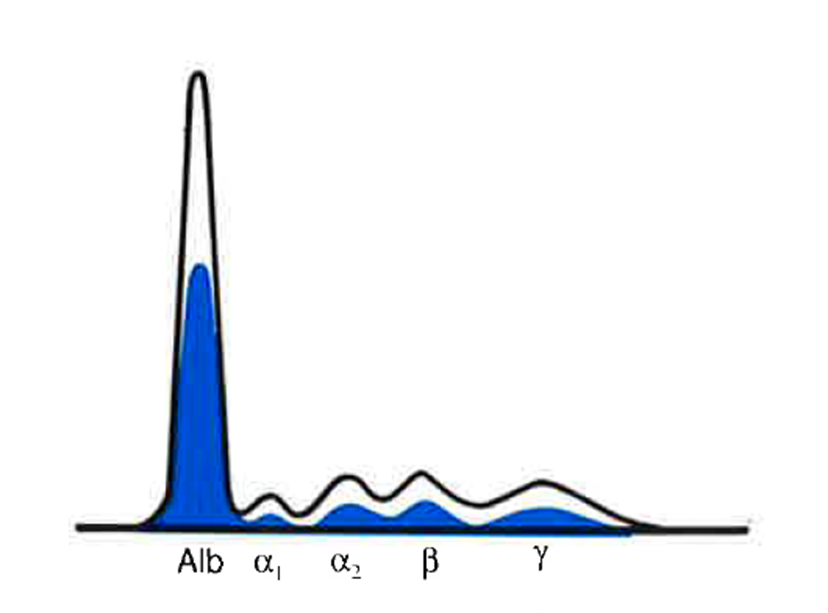
Albumin | Alpha 1 | Alpha 2 | Beta | Gamma |
Very Dec | Dec | Dec | Dec | Dec |
what condition does this indicate
Protein-Losing
Gastroenteropathies
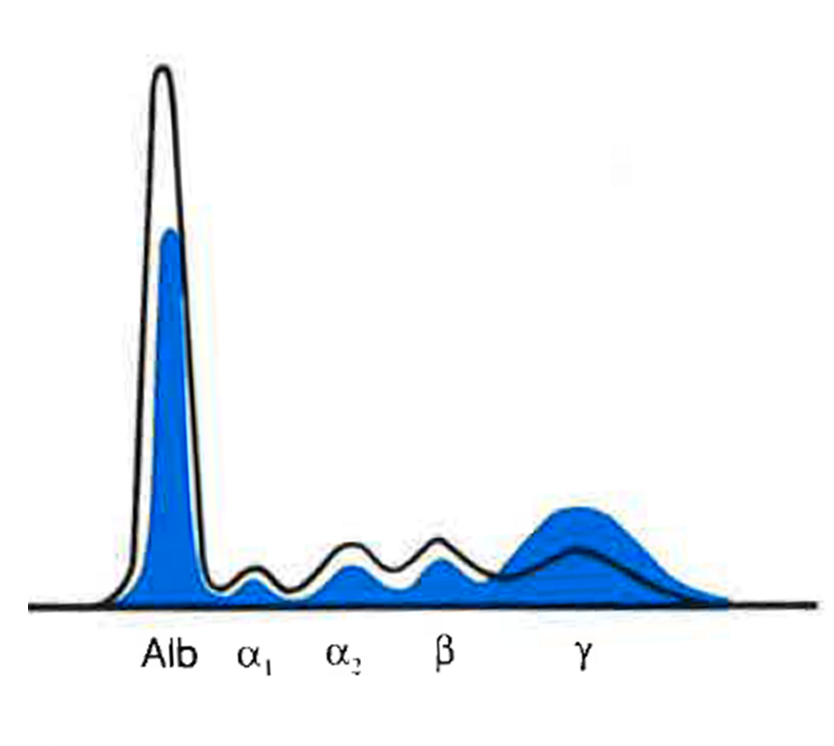
Albumin | Alpha 1 | Alpha 2 | Beta | Gamma |
Very Dec | Dec | Dec | Dec | Inc |
Severe Hepatitis
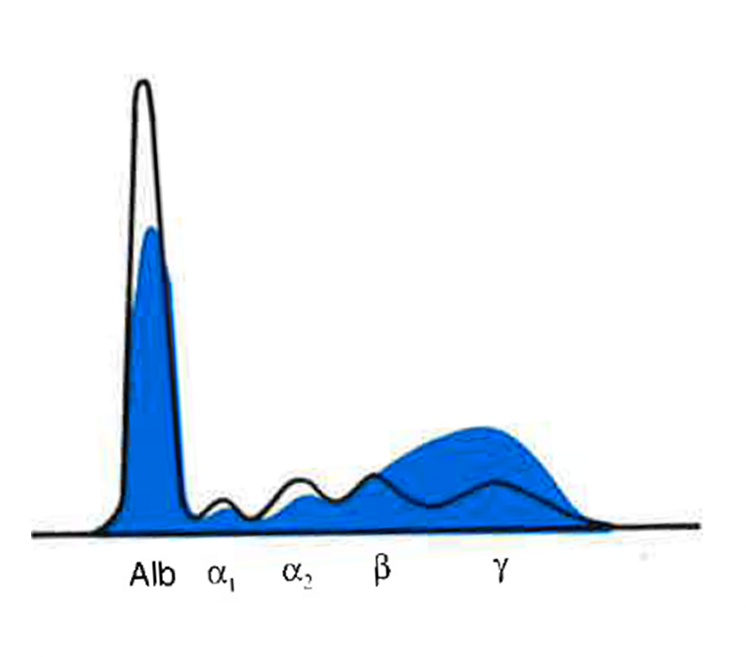
Albumin | Alpha 1 | Alpha 2 | Beta | Gamma |
Very Dec | Dec | Dec | Beta-Gamma Bridge! | |
Liver Cirrhosis
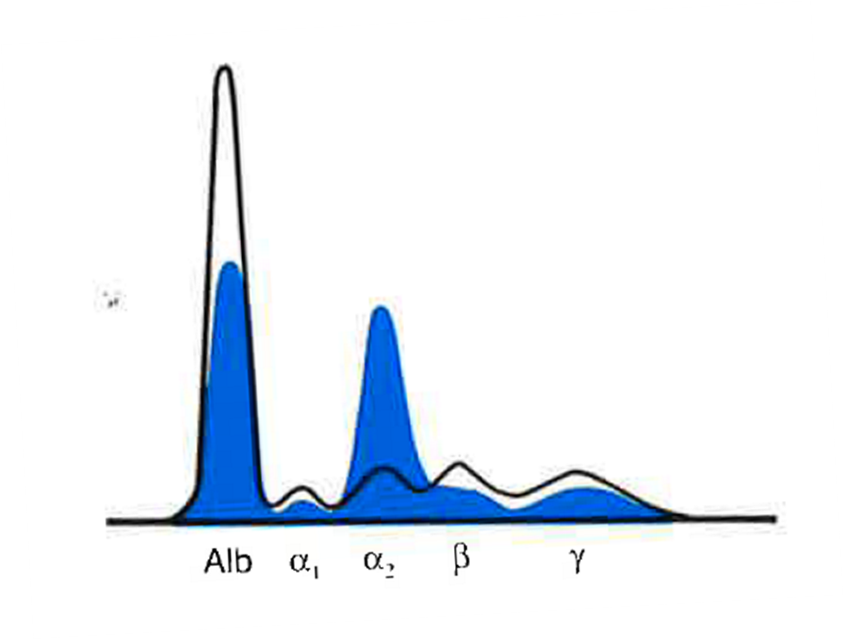
Albumin | Alpha 1 | Alpha 2 | Beta | Gamma |
Very Dec | Dec | Inc | Dec | Dec |
Nephrotic Syndrome
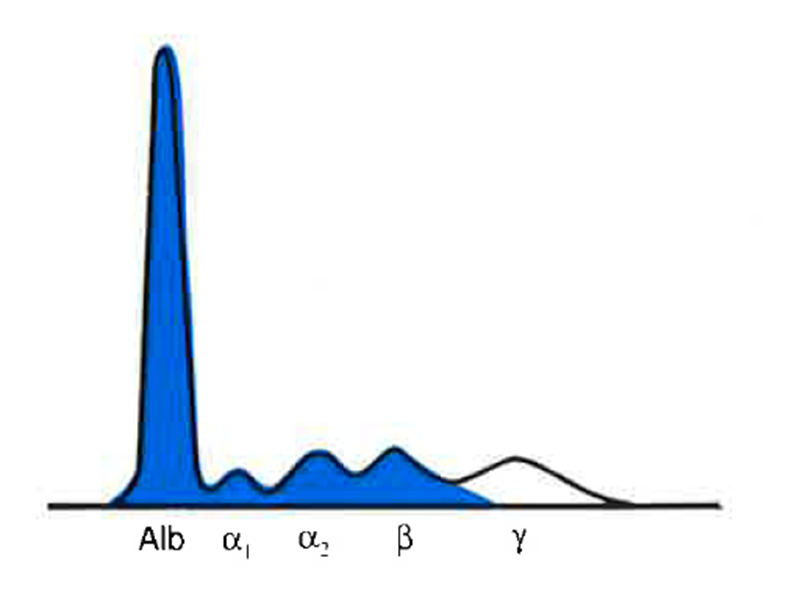
Albumin | Alpha 1 | Alpha 2 | Beta | Gamma |
Norm | Norm | Norm | Norm | Dec/Very Dec |
Hypo or agammaglobulinemia
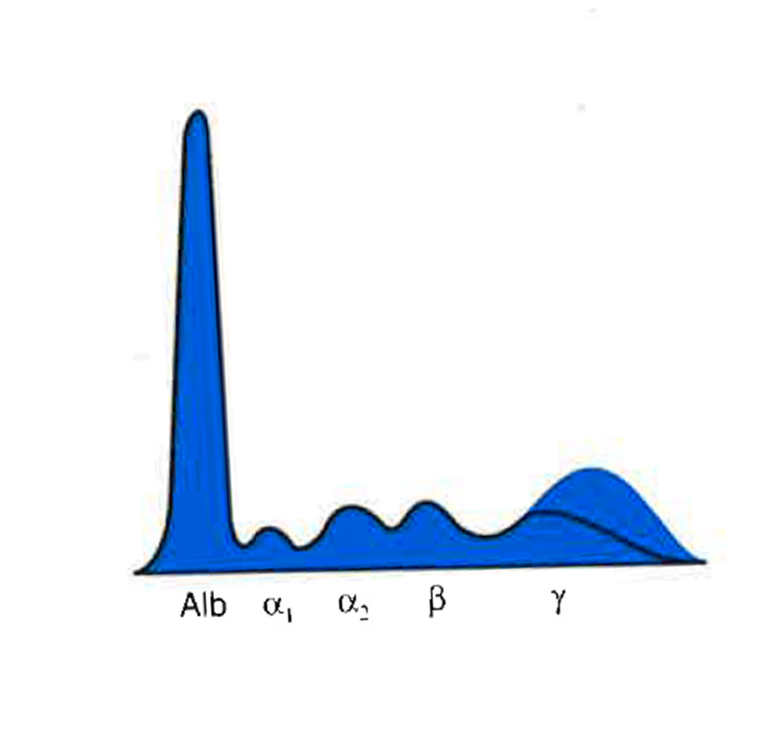
Albumin | Alpha 1 | Alpha 2 | Beta | Gamma |
Norm | Norm | Norm | Norm | Inc/Very Inc |
Polyclonal Gammopathy
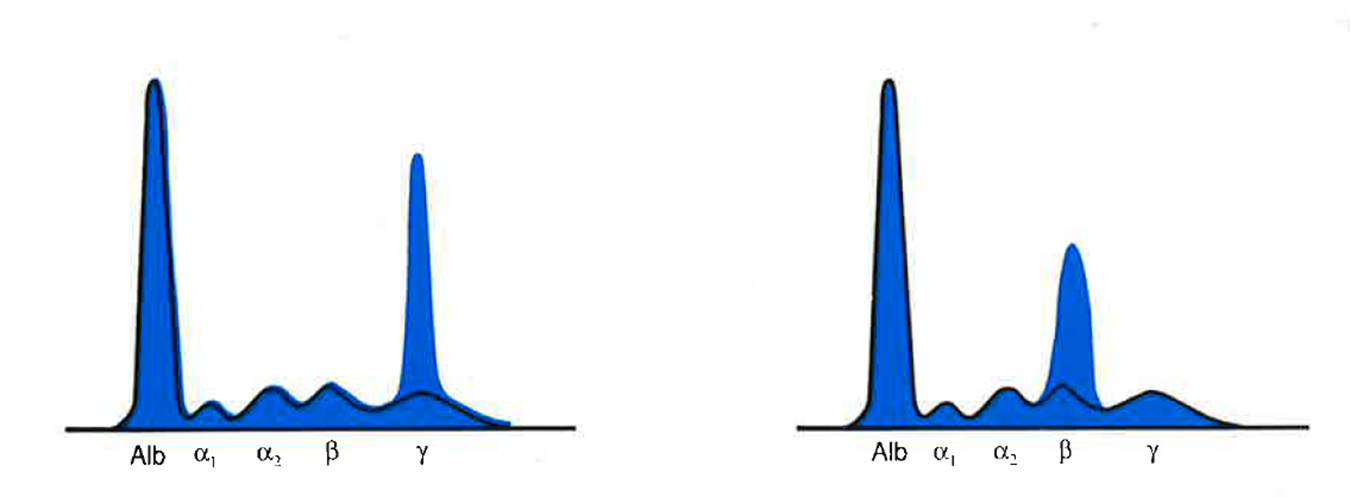
Albumin | Alpha 1 | Alpha 2 | Beta | Gamma |
Norm | Norm | Norm | Norm/M-spike | Norm/M-spike |
Monoclonal Gammopathies
Albumin and Alpha 1 decreased, Alpha 2 increased
Nephrotic Syndrome
Alpha 1, Alpha 2, Beta, Gamma all increased
Chronic inflammation
Gamma increased, Beta-Gamma Bridging present
Liver Cirrhosis
Alpha 1 and Alpha 2 increase
Acute inflammation
TP increased, Gamma increased
Monoclonal Gammopathy
M Spike present in Gamma Increase is Multiple Myeloma
TP decreased, Albumin decreased and Alpha 1, Alpha 2, Beta, Gamma all decreased
Severe Hepatic/Liver Disease