BIOL 475 Exam 1
1/239
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
240 Terms
What are the major categories of disease?
V - vascular
I - infectious
T - traumatic/mechanical
A - autoimmune
M - metabolic/toxic/nutritional
I - idiopathic/iatrogenic
N - neoplastic
D - development/degenerative
vascular
caused by abnormalities of blood vessels
infectious
caused by the presence of a communicable pathogen
traumatic/mechanical
physical force damaging structures
autoimmune
the body’s immune system mistakenly identifies normal structures as foreign and attacks them
metabolic/toxic/nutritional
an abnormality in a biochemical pathway, presence of a toxin, or deficiency of a nutrient results in disease
idiopathic
not very satisfying, do not know exact cause of a disease
iatrogenic
disease caused by medical care or intervention
neoplastic
cancerous; caused by abnormal cell growth and division
developmental
caused by alteration or failure of a normal developmental pathway
degenerative
chronic, typically slow damage progressively interferes with a structure’s normal functioning
case studies
common method for presenting and learning elements of pathophysiology
complete H & P
asking detailed questions about a patient’s medical history and lifestyle in general
CC
chief complaint
patient’s main reason for seeking medical care, often stated in their own words
HPI
history of present illness
paragraph diving past the chief complaint, based on the history-taking experience of the practitioner
PMH
past medical history
a list of ongoing medical problems as well as major medical issues experienced in the past (major surgeries, procedures, and hospitalizations)
current meds/drug allergies
SocHx
social history
personal info ab pt including gender, age, rac/ethnicity, diet, physical activity, habits
ROS
review of systems
comprehensive run-down of common symptoms affecting the body generally and all major organs
pre-visit questionnaire
PE
physical exam
statement on patient’s overall appearance and presentation (Ex. pleasant 21 y/o female in no acute distress)
VS
vital signs
T
temperature
97.8-100.4 F
P
pulse
60-100 bpm
R
respiratory rate
10-18 bpm
BP
blood pressure
systolic: 90-120
diastolic: 60-80
HEENT
head
ears
eyes
nose
throat
CV
cardiovascular
Abd
abdomen
Ext.
extremities
progress note (SOAP)
typically written at least 1x day for inpatient
SOAP
S - subjective
O - objective
A - assessment
P - plan
S - subjective
information provided by patient and/or caregiver, including current symptoms and how they have progressed
O - objective
data that is not subject to pt’s memory or personal interpretation (VS, physical exam findings, lab results)
A - assessment
concise summary of what the provider thinks is going on
P - plan
plan of care, including changes to meds, additional tests, referral to other providers, follow-up visits
What are three reasons why lab tests are used as a first-line tool in making a diagnosis?
cost - generally inexpensive
noninvasiveness - typically venous blood sample or nasal swab
speed - hours to day turnaround time
complete blood count (5)
tests for..
RBC count
RBC size
hemoglobin and hematocrit
WBC count and differential
platelet count
chemistry panel (3)
aka Chem-7, BMP tests for…
electrolytes (Nat+, K+, Cl-)
renal function → BUN (blood urea nitrogen), creatine
blood glucose
LFT (3)
liver function tests for …
ALT/AST
bilirubin
total protein
cardiac enzymes (3)
tests for…
troponin
CK-MB
CPK
What are the benefits of medical imaging? (2)
basic chest x-ray and EKG cheap
noninvasive
What are the risks of medical imaging? (4)
MRI and CT scan are expensive
claustrophobia
exposure to radiation
IV contrast
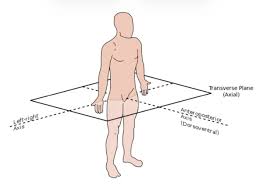
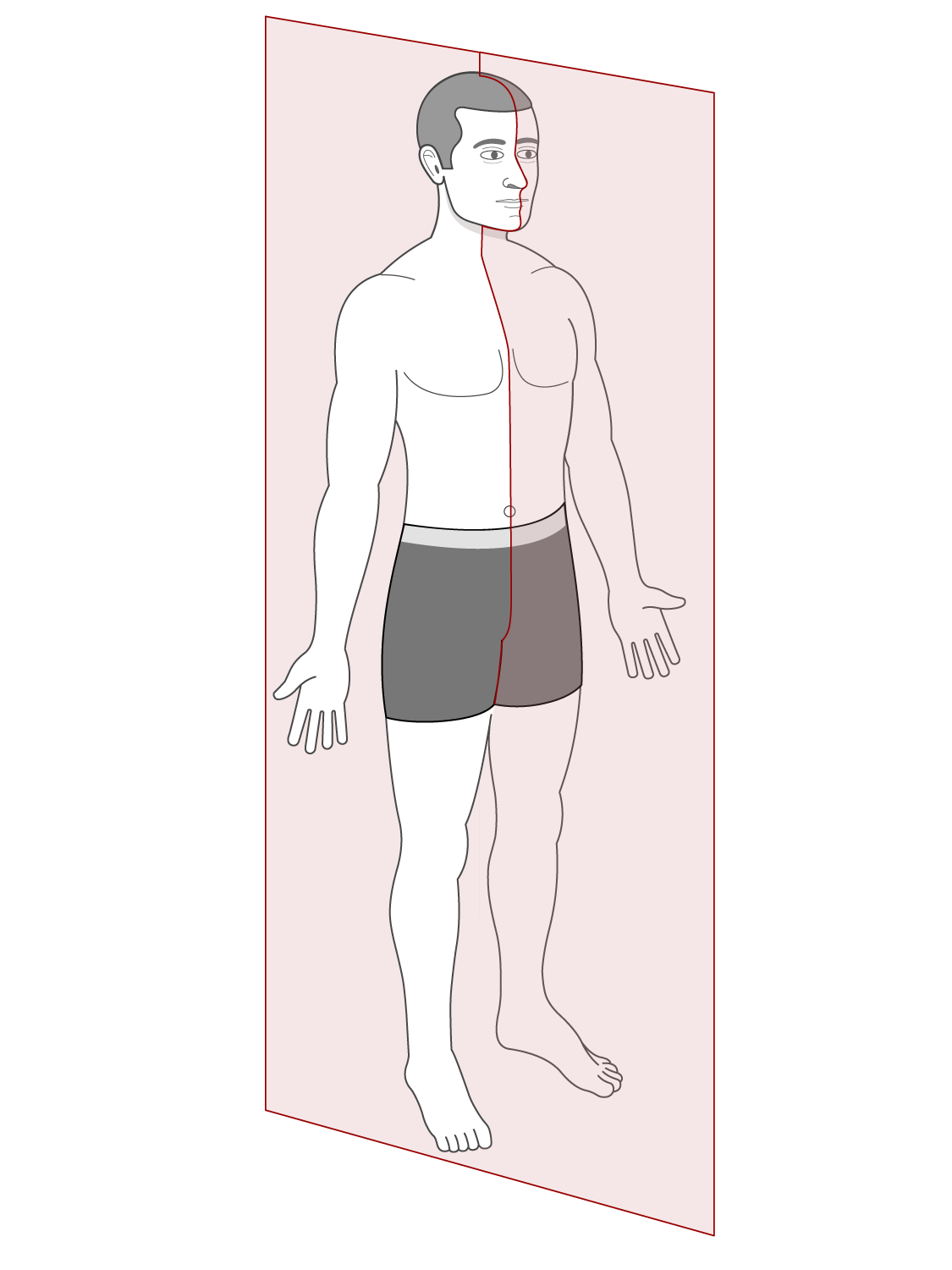
What are the 3 major planes the body is sectioned into?
transverse
sagittal
frontal
transverse
horizontally oriented plane slicing the body into superior and inferior portions
sagittal plane
vertically oriented plane slicing the front of the body into left and right halves
frontal plane
aka coronal vertically-oriented plane slicing body into anterior and posterior portions
computed tomagraphy scanning
based on x-ray tech, except x-ray and detector can rotate around the body, taking images from all angles
Advantage of x -ray
high energy allows them to pass through the body and penetrate tissues
Risk of x -ray
high-ionizing radiation capable of disrupting biological molecules, including DNA
Advantage of CT
much higher resolution images and better w/ contrast dye
Risks of CT
higher radiation dose than normal x -ray
contrast agent
material introduced into body before/during imaging to improve quality of the image by enhancing the contrast of a body fluid or tissue
What is most commonly used to enhance contrast of GI tract?
barium
What is used to enhance contrast between blood vessels and surrounding tissue?
iodine
ultrasound
uses sound waves to image tissue instead of electromagnetic radiation
transducer
emits high-frequency sound waves that penetrate the skin and bounce off surface based on their density
Advantages of ultrasound (5)
cheap, simple, convenient, capture motion, and no radiation
Disadvantages of ultrasound (2)
poorer resolution than CT
deeper structure difficult to image due to poor penetration of sound waves
MRI
magnetic resonance imaging
Protons within water molecules align with the magnetic field which are detected to create an image
Advantages of MRI
superior resolution of tissues without any radiation exposure
Disadvantages
higher cost and claustrophobia possible
drug
substance that alters biologic activity in a person
What are the desired effects of a drug?
therapeutic effect: action that drug takes towards treating a specific condition
indications of a drug
when a drug has multiple therapeutic effects
contraindications
a drug that cannot be used in pregnancy
What is the difference between side effects and adverse/toxic effects?
side effects - milder unwanted effects of drug that are typically anticipated and cause non permanent damage
adverse/toxic effects - severe, less common, harder to anctipate effects
effective dose
dose that is expected to produce the desired effects in an average person
toxic dose
dose that tends to cause toxicity in most people
therapeutic index
ratio of toxic dose/effective dose
Is a higher or lower value for the therapeutic index more desirable?
higher - implies large diff b/w dose we might give to treat a condition vs. dose that causes damage
synergism
combination of multiple drugs enhances therapeutic effect
anatagonism
occurs when combination of two or more drugs decrease one or all of their therapeutic effects
pharmakinetics
what the body does to a drug (administered, absorbed, distributed, metabolized, excreted)
pharmacodynamics
what the drug actually does to the body (cells/tissues effects, interactions w/ target receptors)
What are the 7 routes of administration of drugs?
oral
sublingual
subcutaneous
intramuscular
intravenous
inhalation
topical
How are drugs metabolized?
via biotransformation, and metabolites are excreted in feces and/or urine
Why is a drug’s half-life important ?
determiens drug’s dose and dosing frequency
half-life of a drug
amount of time required for clearence of 50% of a dose of a drug
What are the two types of receptors that drugs interact with?
ionotropic and metabotropic
ionotropic receptor
opens ioin channel when ligand binds (most common in neurons)
metabotropic receptor
trigger some sort of change in intracellular signaling via 2nd messengers
Brand names are typically..
capitalized
pharmacist
doctor of pharmacy degree, manage retail stores
pharmacologist
trained researchers who study drug development, mechanisms, delivery, clinical trials, and toxicity
How are controlled substances organized?
schedules - based on therapeutic value, risk, potential for abuse/addiction (schedule I highest potential)
inflammation
body’s nonspecific response to injury
What are the four cardinal signs of inflammation?
erythema → redness
heat
pain
swelling → edema
positive chemotaxis
leukocytes attract chemical released by pathogens and damaged tissues
What are the normal proportions in a differential WBC count?
Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas (most→least)
Neutrophils Lymphocytes Monocytes Esophils Basophils
lymphocytes elevated
viral infection
neutrophils elevated
bacterial infection
esonophil elevated
parasitic infection or allergy/asthma
basophil
release histamine and help in inflammation
What are the 5 steps of acute inflammation?
release of chemical mediators from injured cells
activation of pain receptors by bradykinin
mast cells and basophils release histamine
capillary dilation
bacteria enter tissue
What are the systemic effects of inflammation? (5)
fever (pyrexia)
malaise (flu)
fatigue
headache
anorexia
How does chronic inflammation differ from acute inflammation? (5)
less swelling
more lymphocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts
continued tissue destruciton
fibrous scar tissue
granuloma
What do aspirin, acetaminophen, and NSAIDs have in common?
block cyclooxygenase that decreases the synthesis of prostaglandins that mediate pain and inflammation
aspirin
irreversibly inhibits COX-1 and COX-2 reducing pain/inflammation, acts in CNS to reduce fever, and reduces blood clots
acetaminophen
acts in the CNS, decreases fever and perception of pain
NSAIDs
decrease pain and inflammation, but not as powerful of steroids
corticosteroids
most powerful inhibitors of inflammation with severe side effect