Rare Cancer Types and Syndromes
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Paraganglioma
a rare type of neuroendocrine tumor that arises from clusters of cells derived from the autonomic nervous system (head, neck and spine usually)
Can be either:
Functional:
producing excess catecholamines→ HTN, sweating, rapid heartbeat
Non-functional:
not producing hormones, usually asymptomatic
Functional Paraganglioma symptoms
Excessive catecholamines (like norepinephrine)
High blood pressure: preissnt or episodic
Tachycardia/palpitations
Excessive sweating
Headaches
Anxiety
Flushing/pallor
tremors
Pheochromocytomas
paraganglioma tumor that develops in the adrenal glands
ALWAYS FUNCTIONAL
produces excessive amounts of catecholamines (adrenaline and noradrenaline) cause high blood pressure, rapid heart rate, sweating and headaches
Surgical removal of the tumor
MEN type 2B
RET
Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Marfanoid Habitus
Mucocutaneus “GNs”(?)
Pheochromocytoma/Paraganglioma
MEN type 2A
-RET
Medullary thyroid carcinoma
Parathyroid hyperplasia
Pheochromocytoma/Paraganglioma
Paraganglioma-Pheochromocytoma Syndrome
Genes: SDHA, SDHAF2, SDHB, SDHC, SDHD, MAX, THEM127
Autosomal dominant
Maternal imprinting: SDHAF2, SDHD
Tumors: Paragangliomas and Pheochromocytomas,
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs): anywhere in the GI tract
Pulmonary Chondromas:
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Other tumors:
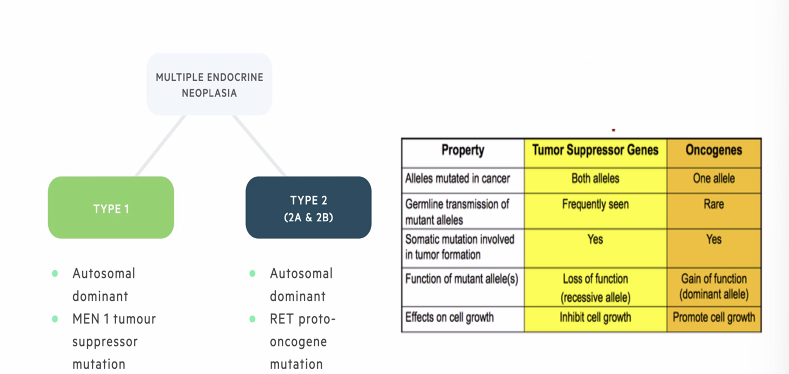
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1
Gene MEN1 (tumor suppressor)
Inheritance : autosomal dominant
Diag criteria
at least two: parathyroid, pituitary gland, gastro-intrapancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (GEP)
at least one: Endocrine tumor and first-degree rel. with MEN1
Clinical Characteristics:
Hyperparathyroidism: usually first (20-25yo) → leads to hypercalcemia by 50yo→causes the several symptoms
Symptoms
CNS: PITUATARY ADENOMA
GI:
Skeletal increased risk factor
Renal
Cardiovascular
MEN1 Clinical Characteristics
Primary hyperparathyroidism
Most common symptom
90% is the first symptom
Age of onset 20-25yo
Hypercalcemia by 50yo→ increased bone fracture risk, HTN, hypercalciuria, short QT interval
Tumors
Gastroenteropancreatic (GEP) Neuroendocrine tumors
Adrenocortical: nonfunctional
Anterior Pituitary Adenomas
growth hormone
Prolactin and Follicle stimulating hormone
Adrenotropic hormone: excess cortisol (Cushing disease)
Skin
Facial angiofibroma’s
Collaenomas
MEN1 Medical Managment
Screening starts very early—> the children of patients
Parayhtoird: imaing at 5yo
Pitoeraury: imaing 5yo
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2
Gene: RET (proto oncogene)
Autosomal dominant
MEN2A: 2 Features: medullary thyroid cancer, pheochromocytoma, parathyroid adenoma
MEN2B: Marfanoid habitus, Early onset, MTC, PCC and ganglioneuromas —> bowel movement issues, renal agenesis etc (add from notes)
FMTC: Presence of 4 or more cases of MTC over more than one generation in the absence of PCC
Additional
Differntiing Multiple Endoceinre Neoplasias
MEN2 Managment Recommendations
Medullary Thyroid cancer correlates with MEN2
Prophylactic Thyroidectomy recommended: EXTREMLTY early (one variant is in 1st year, but other variants generally before 5yo)
Birt-Hogg-Dube Syndrome
Gene: FLCN
Inheritance: Autosomal Dominant
one major or two minor
Major: 5 facial or truncal papules, 1 confirmed as fibrofolliculoma
Minor:
Early onset renal cell cancer (<50yo),
Multifocal/Bilateral renal cell cancer,
renal cell cancer with mixed chromophobe/oncolytic histology,
Multiple lung cyst (ETC)
Birt-Hogg Dube Beneing SKin Findings
Fibrofollicuolmas: Hair follicle tumors present in 805 of patine >40yo
Angiofibroma: vascualr tumor
Acrochordon: skin tags
Birt Hogg Dube clincal symptoms
Benign skin findings
Pulmonary: Spontaneous pneumothorax (from LUNG CYSTS), lung nodules/cysts3
Often first symptom
age of onset: male 38yo, female 30yo
Renal Cancers: oncocytoma + chromophobe hybrid, Clear Cell + Oncocytoma, Papillary carcinoma (less common)
Birt-Hogg-Dube Surivllance and Managment
Surveillance: skin exams, annual Abdominal MRI/CT, annual thyroid ultrasound
Avoiding: cigarette smoking, high ambient pressure (scuba diving)
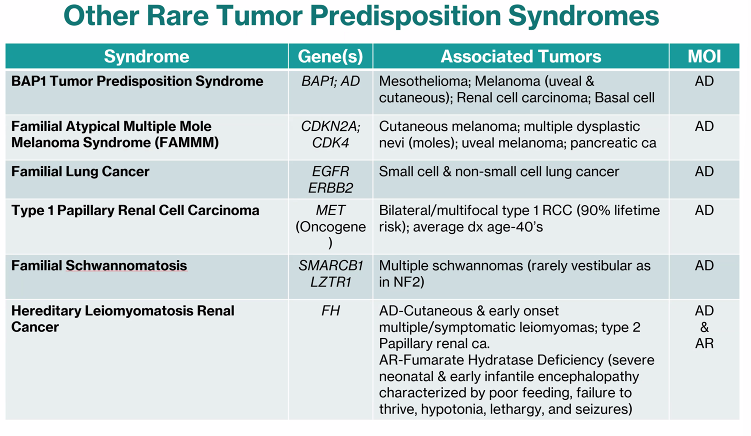
Other Rare Tumor Predispition Syndromes
When to Suspect a herdiary renal cancer sydnrome?
early onset RCC before 50
bilateral or multi focal kidney tumors
Fam hx of renal cancer or related cancers
Associated syndromic features (skin lesions, lung cysts, fibroids)
Hereditary Leiomymatosis Renal Cell Cancer (HLRCC) syndrome: Inheritiance
Fumarase (FH) gene
MONO (single) Allelic
JUST ONE PATHOGNEIC VARIANT necessary for condition
Autosomal Dominant, Highly Penetrant
Hereditary Leiomymatosis Renal Cell Cancer (HLRCC) syndrome: Clinical Findings
Cutaneous Leiomytoma: Skin Fibroids,
Uterine Leiomytoma: 100%, early diagnosis average 30yo, can cause pelvic pain and menstrual irregularity/heavy
larger, more numerous, younger age of onset that SPROADIC uterine fibroids
Aggressive Renal Cell Carcinoma: 36-44yo
usually solitary
Hereditary Leiomymatosis Renal Cell Cancer (HLRCC) syndrome: Renal Cell Carcinoma
20% lifetime risk
Aggressive forms of Renal Cell Carcinoma: Papillary Type 2
unlike other renal cancer syndromes, Papillary 2 is aggressive and metastasizes early
usually solitary, or unilateral
Hereditary Leiomymatosis Renal Cell Cancer (HLRCC) syndrome: Managmet
annual MRI of kidneys
Dermalogical exam 1-2 years
Regualr uterine
Genetics followup
Von Hippel Lindau: Gene/inheritinace
VHL gene
Tumor suppressor
Autosomal domaiant with high pentrence
20% de novo mutation
Why id denovo rate important?
No signs or symptoms in the family hisotry, than mabye the patient has a De Novo mutation ( IF THERE IS A HIGH DENOVO RATE)
VHL Syndrome organ involvement:
Rentinal angioama (espcially young)
HALLMARK: Multiple Hemangioblastoma
Clear Cell Renal Cell caracmoa (before 40)
Renal and Pancreatic cyts
Pancreaic neuroencine tumors
Adrenal or extra-adrenal pheochromocytoma
VHL: Hemangioblastoma symptoms
Fluid buildup in brain that pushes on the brain
Dizziness,
headaches,
double vision,
vomit/swallowing difficulties
VHL: Pheochromocytoma symptoms
“Fight or Flight”
HTN
Sweating
High heartrate
Anxiety/Panic
Hereditary Papillary Renal Cancer
MET
Proto-oncogene
Autosomal dominant
Penetrance 100%
Associated cancer: RCC papillary type 1
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC)
TSC1 (hamartin) and TSC2 (tuberin)
Autosomal dominant
De Novo rate 66%
HEREDITARY RENAL CANCER SYMDOMRE
TSC Clinical features
Skin
ASH leaf spots
CNS: Tumors (leading casue of death)
Kidney
Angiomyolipomas
Cysts
Renal disease (second leading cause of early death)
Heart:
Rhabdomyomas,
Arrhytmias
Lungs: (Fill in from Lecture slides)
TSC: Skin Manifestations
Hypomelanimc macules (ASH LEAF SPOTS)
Facial angiofibroma
Shagreen patches
Ungual fibromas
TSC: CNS Clincial Findings
CNS tumors are leading cause of death in TSC
Brain lesions
Seizures
Intellcual diabltiy (AUTISM)
Developmantl Delay
Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL)
VHL
Renal cell carcinoma
Hemangioblastoma
Pancreatic endocrine neoplasm
Pheochromocytoma/Paraganglioma
Hereditary Paraganglioma 3
SDHC
GIST
Pheochromocytoma
Hereditary Paraganglioma 4
SDHB
GIST
Pheochromocytoma
SDHB/SDHAF2
“B” = Bad, “F”=Father
A high risk of malignancy and extra-adrenal sympathetic PGLs
SDHD
“D”= Dad
Parent of origin effects (Deleterious effects from Dad)
What is a rare tumor?
a tumor in organs that rarely develop malignances
a tumor with dwan unusual/uncommon pathology/histology
Risk of inherited susceptibility is often increased in rare tumors compared to common tumor types
Challenges associated with Rare Tumors
Patients may unaware of tumor’s pathology
Patient (at times, referring) may not be aware of importance of reporting certain findings
Limited information
data prone to ascertainment bias: most striking cases idented, studied and reported
Fumarase Deficiency
Bi-allelic (two pathogenic variants) of Fumarate Hydratase (FH) gene
Also called Fumaric Aciduria
Clinical symptoms
Severe neonatal and early infaitle encephalopathy
Poor feeding
Failre to thrive
hypotonia
seziures
dysmorpic facial features
SDHx genes
SDHA + SDHB (responsible for Succinate to fumarate conversion)
SDHC + SDHD (anchor enzyme to the membrane)
encode the 4 subunits of the SDH mitochondrial enzyme
Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) enzyme converts succinate to fumarate: lack of activity results in oxidative stress
ASSOCIATED WITH HEREDITARY PGL-PHEO SYNDROME
SDHD, SDHAF2 and MAX
Parent of origin pathogenic variant affects risk for Hereditary PGL-PHEO syndrome
Father: high risk of manifesting PGLs and PCCS
Mother: Low risk of manifesting (with exceptions)
SDHD→ D = DAD
Overlap of features of MEN1, 2A, 2B
Pituitary Adenoma: 1 only
Pancreatic tumors: 1 only
Parathyroid Hyperplasia: 1+2A
Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: 2A + 2B
Pheochromocytoma: 2A+ 2B
Mucosal neuromas: 2B only
Marfanoid habitus: 2B only