Integrated Science Study Notes Flashcards T2
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary from Integrated Science notes on space, astronomy, the solar system, and speed.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
The Sun
A star of medium size that appears bigger and brighter because it is closer to Earth.

The Sun's Composition and Energy Production
A burning ball of gases, primarily hydrogen and helium, where hydrogen atoms react to form helium, producing vast amounts of energy.
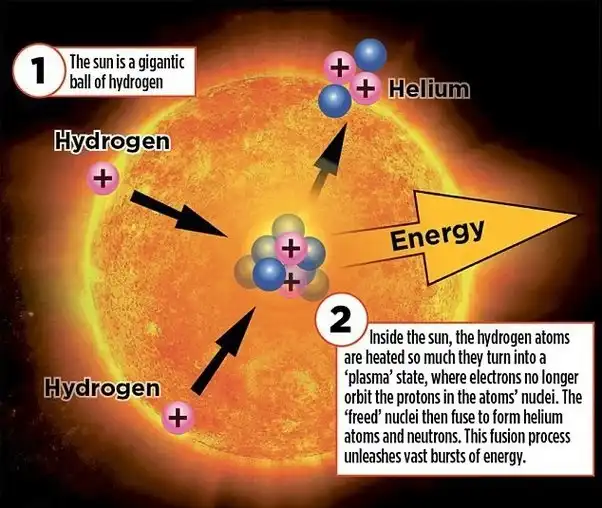
Core of the Sun
The hottest part of the sun, where hydrogen gases change into helium.
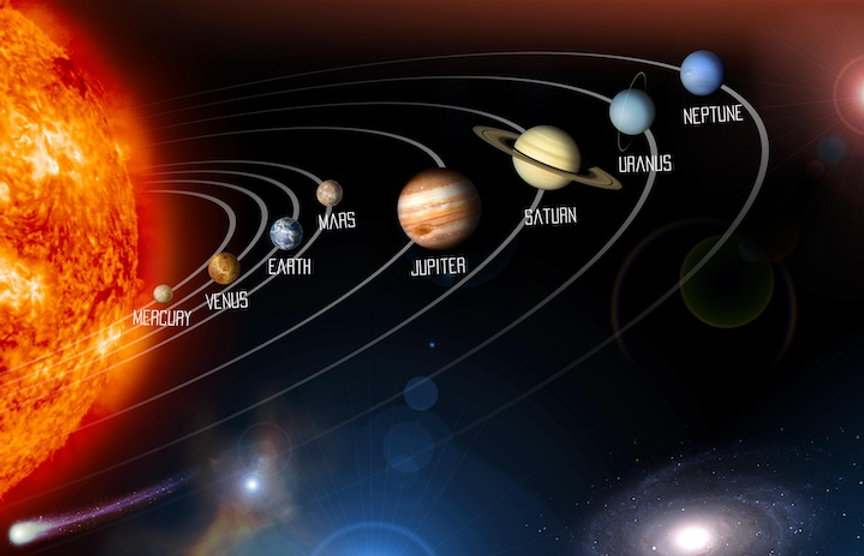
Solar System
The Sun and the objects in the region of space around it.
Objects found in the Solar System
Planets, moons, asteroids, ice, dust and dwarf planets.

Requirements for an object to be called a planet
Travel around the sun, be able to keep its orbital path clear of other objects and be almost spherical in shape.
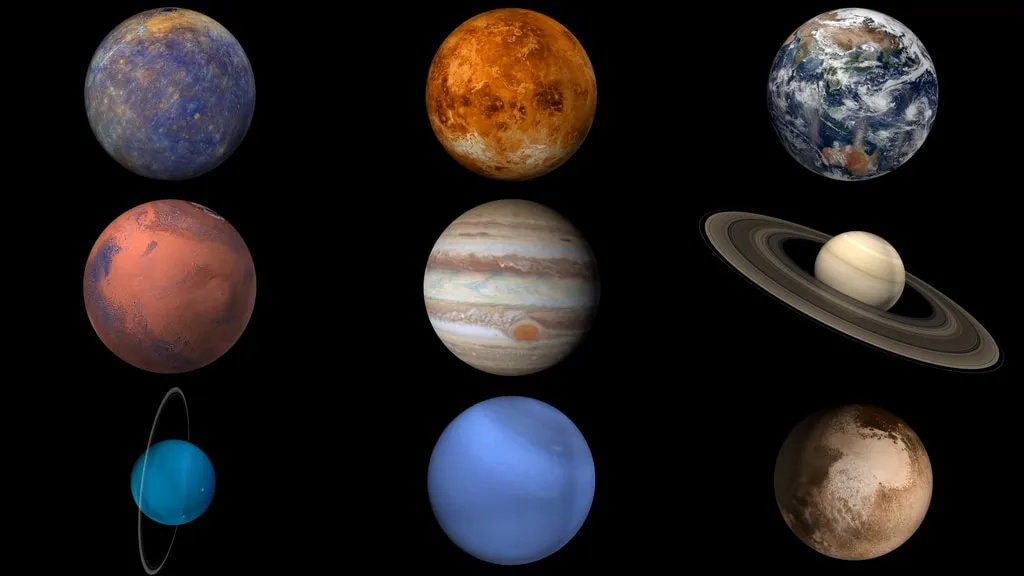

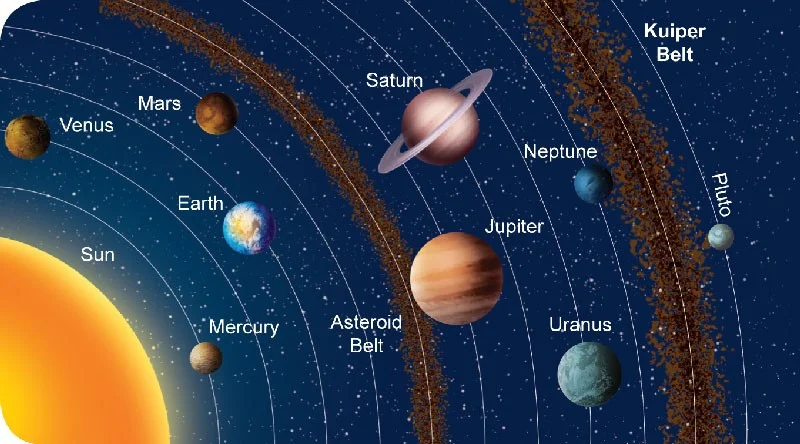
Eight Planets in the Solar System
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
Inner Rocky Planets
Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars; made up of rock.

Outer Gas Giants
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune; made up of gases and liquid.
Dwarf Planet
A planet that is not able to clear other objects in its path.

Mercury
Closest planet to the sun, with extreme temperature variations.

Venus
Has a very thick atmosphere of carbon dioxide, trapping the Sun’s heat.

Earth
Supports life due to its thick atmosphere with oxygen and abundant water.

Mars
Has a cold, desert-like surface covered with red-orange dust and rocks.

Jupiter
The biggest planet, with a thick atmosphere of hydrogen and helium and giant storms.

Saturn
Has distinctive rings made of small, solid particles and ice crystals.

Uranus
Spins on its side and has an atmosphere containing more water, methane and ammonia than other gas giants.

Neptune
Farthest planet from the sun, extremely cold and dark.

Moon
A body that revolves around a planet and reflects light from the Sun.

Asteroids
Rocks that orbit between Mars and Jupiter in the Asteroid Belt.

Meteoroid
A solid object in space, smaller than an asteroid, that can become a meteor when entering Earth’s atmosphere.

Meteor
A meteoroid that burns up in Earth’s atmosphere, creating a shooting star effect.

Meteorites
Remains of a meteor that crash into the ground before burning up completely.

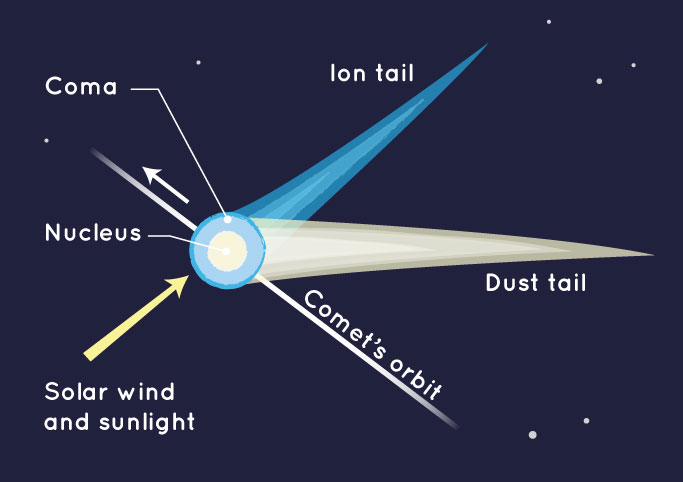
Comet
A body made of frozen gases and bits of rock, with a head, coma and tail.
Gravity
The natural force that attracts objects to each other.

Kuiper Belt
A ring of ice and rocky objects outside the solar system, past Neptune.
Oort Cloud
A spherical cloud of dust and gases thought to surround the solar system.
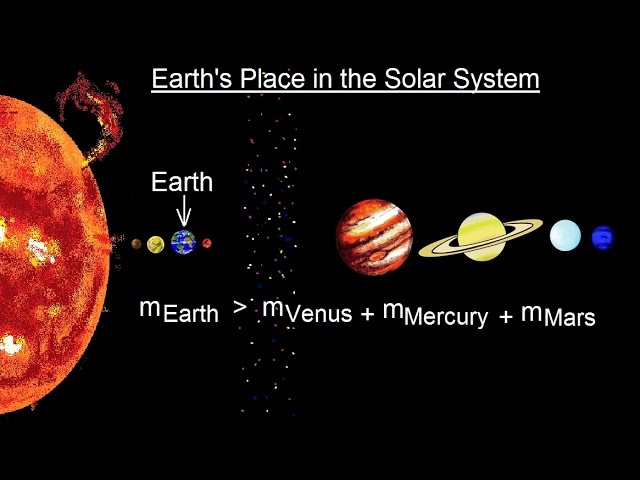
Earth's Position
The third planet from the Sun, known to support life.
Sunlight's Importance
Needed by plants to produce sugars; also heats parts of the Earth to create wind and rain.

Water on Earth
Exists in liquid, gas and solid states on Earth and constantly changes between them in the water cycle.

Oxygen
Essential for life on earth and produced by photosynthesis in green plants.

The Sun
Nearest star to Earth that produces its own energy and releases it as heat and visible light.

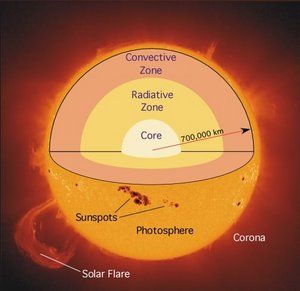
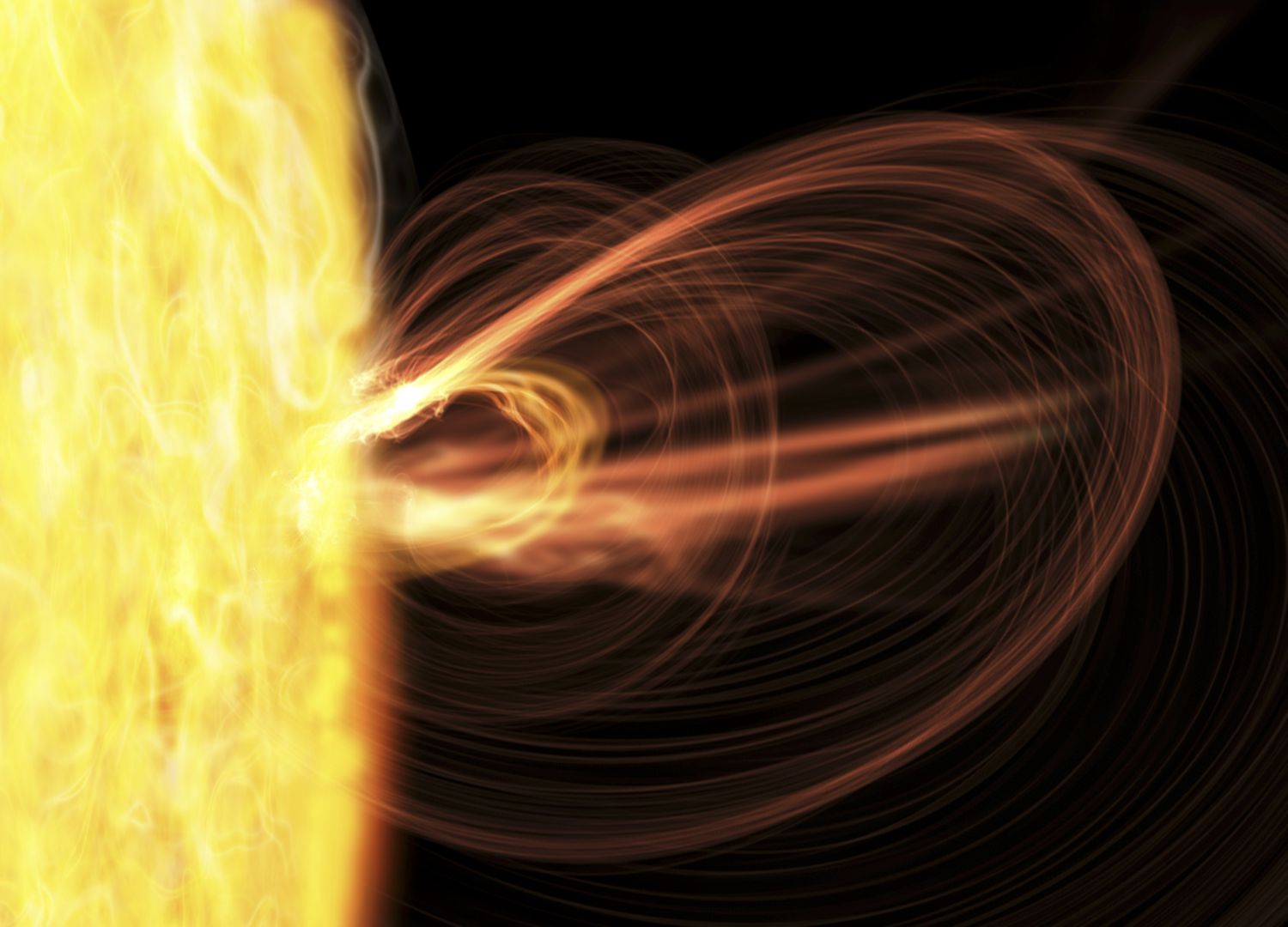
Sunspots
Magnetic storms on the Sun.
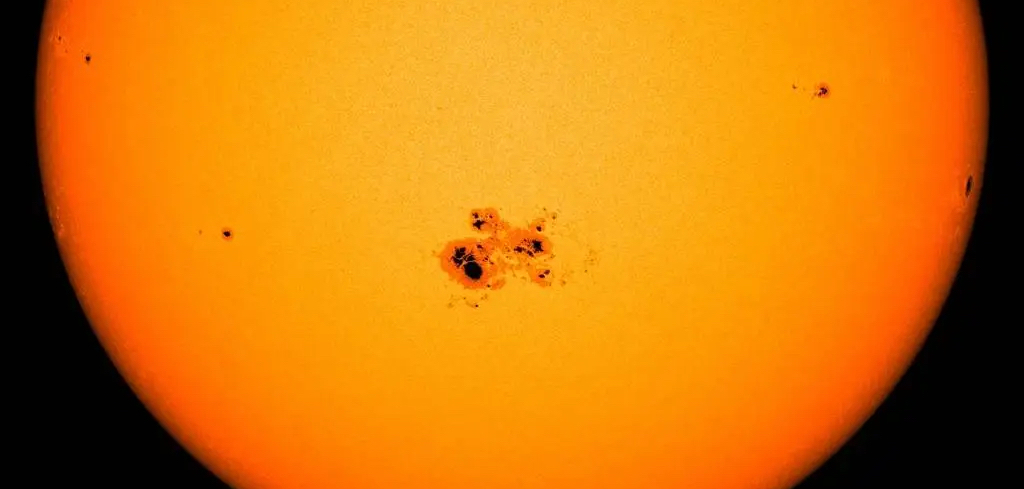

Sun flares
Large explosions triggered by the sun's magnetic fields
Alpha Centauri
Nearest neighboring star system, visible from the southern hemisphere.

Light Year
Distance that light travels in one year; used to measure great distances in space.
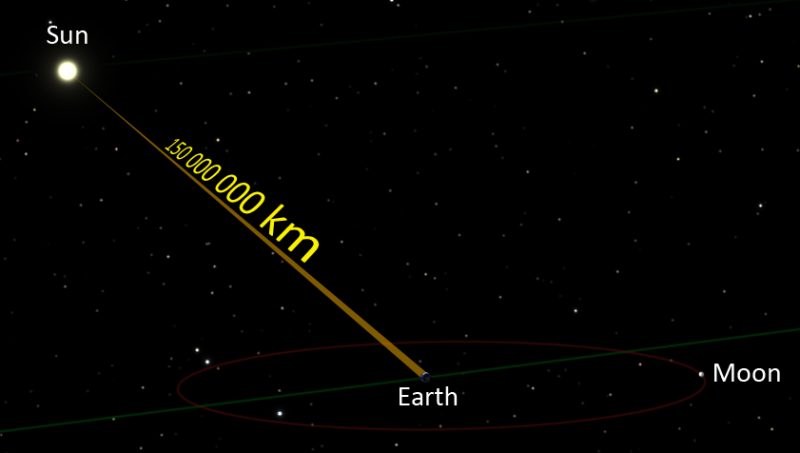
Light Hour
Distance that light travels in one hour; used to measure shorter distances in and around our solar system.
Light Minute
Distance that light travels in one minute; used to measure smaller distances between planets in our solar system.
Galaxy
A cluster of stars outside of the Milky Way

Spiral galaxies
Categorized by size, they are often colourful and shaped like a flat disc with spiral arms.
The Universe
Approximately 13.7 billion years old and is continuously expanding.

Constellations
Patterns that particularly bright stars appear to make.
Telescope
An instrument that uses lenses or mirrors to collect light and make distant objects appear closer.

Optical telescopes
Optical telescopes are telescopes that we look through.

Objective lens
Works by refraction, bending light to focus the image.

Reflecting telescope
Makes use of mirrors as they are much lighter than glass lenses.

Magnification
Makes the object seem closer and show more detail.

SALT (South African Large Telescope)
The single largest telescope in the Southern Hemisphere, located near Sutherland in the Karoo.

Hubble Telescope
The most famous telescope in space.

Radio telescopes
Used to find and record radio waves given off by bodies in space.
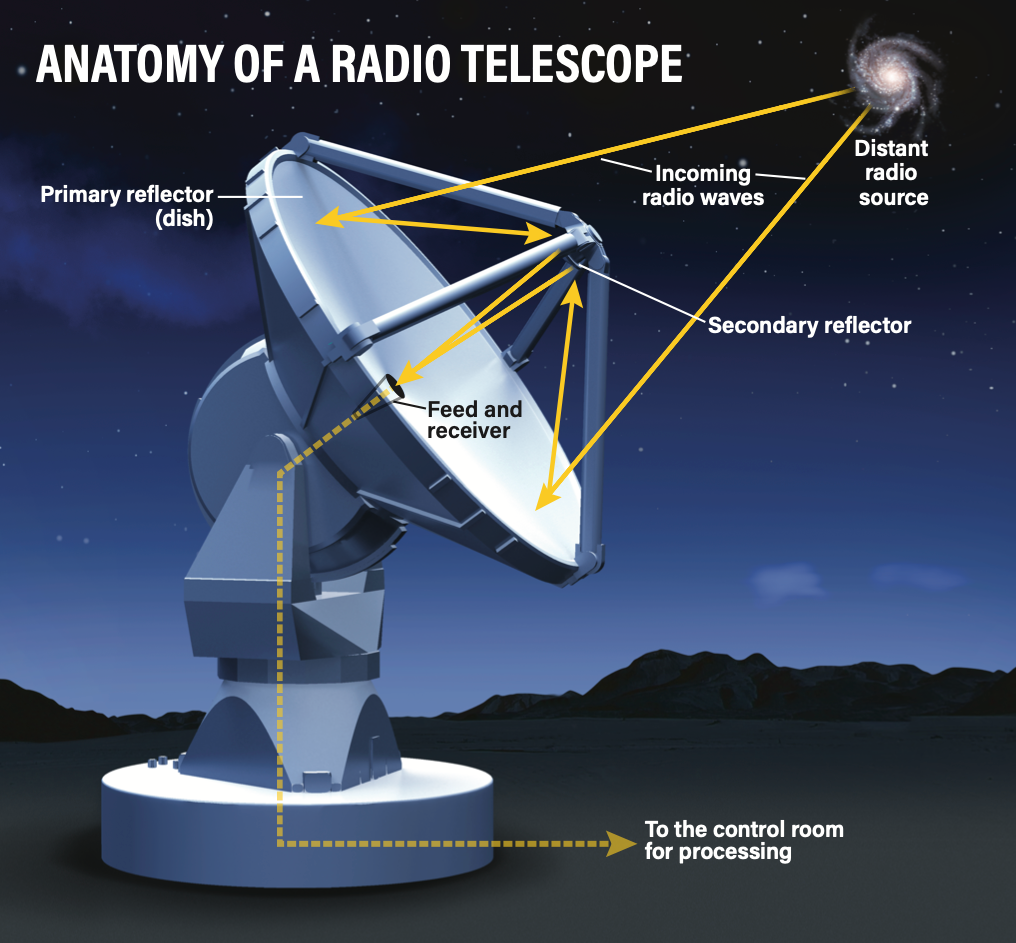
Array of telescopes
A group of radio telescopes working together to collect more information.

SKA (Square Kilometer Array)
A large radio telescope array with thousands of individual telescopes, to be the strongest telescope ever built.
Speed
Measurement of how fast something is moving.
Speed cameras
Cameras used to check speeds and make sure drivers are not travelling too fast.
Speed camera
An instrument with two detectors and a timer which calculates the speed of a car
Light gate
Emits an invisible beam of infrared light and starts/stops a timer when the beam is broken.

Spacing of Images
Equal spacing indicates steady speed; increasing spacing indicates speeding up.